What Is Large Cell Lung Carcinoma
LCLC is a type of cancer that affects the lung. It can form anywhere in the lung but is more common on the outer edges.
Non-small cell carcinomas, like LCLC, are the most common form of lung cancer, making up 80 to 85 percent of all lung cancers. There are three major types of non-small cell carcinomas:
- Adenocarcinoma.Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of lung cancer and is classified as a non-small cell lung cancer. It usually begins forming in the outer sections of the lung and is the type of lung cancer most often found in nonsmokers. Adenocarcinoma makes up about 40 percent of non-small lung cancer cases.
- Large cell carcinoma. This type of lung cancer is named so because of its large, abnormal-looking cells. These cells can be found throughout the lungs. They also tend to grow more quickly and spread faster than other forms of non-small cell lung cancers. LCLC makes up 10 to 15 percent of all non-small cell lung cancers.
- Squamous cell carcinoma.Squamous cell carcinoma is another large cell carcinoma and is sometimes referred to as epidermoid carcinoma. This type of non-small cell lung cancer usually begins in the middle structures of the lung, like the bronchi. Squamous cell carcinomas make up about one-quarter of all non-small cell lung cancers.
Outside of LCLC, there are a number of other forms of lung cancer, too. These include:
How Does Tumor Grade Affect A Patients Treatment Options
Doctors use tumor grade and other factors, such as cancer stage and a patients age and general health, to develop a treatment plan and to determine a patients prognosis . Generally, a lower grade indicates a better prognosis. A higher-grade cancer may grow and spread more quickly and may require immediate or more aggressive treatment.
The importance of tumor grade in planning treatment and determining a patients prognosis is greater for certain types of cancer, such as soft tissue sarcoma, primary brain tumors, and breast and prostate cancer.;
Patients should talk with their doctor for more information about tumor grade and how it relates to their treatment and prognosis.
Selected Reference
American Joint Committee on Cancer. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th ed. New York, NY: Springer; 2010.
Related Resources
Is Stage 4 Neuroendocrine Cancer Curable
Neuroendocrine cancer/tumor starts in the neuroendocrine cells in your body. These cells have features of both the type of cells- endocrine cells and nerve cells. Most of these tumors are benign while some are malignant. These can occur anywhere in the body where neuroendocrine cells are present, but most commonly they are seen in the intestine.
Also Check: What Happens If You Have Skin Cancer
What Are Neuroendocrine Tumours
The neuroendocrine system is a network of glands and nerve cells that make hormones and release them into the bloodstream. These hormones help control normal body functions, for example digesting food.;
Neuroendocrine cells are found throughout the body, but mainly in the gastro-intestinal tract , pancreas and lungs.;;
Neuroendocrine tumours;;are an uncommon type of tumour that forms in these cells. The type is generally defined by where the abnormal cells come from and can range from low grade to high grade .;Neuroendocrine;tumours;that produce extra amounts of hormones can cause certain symptoms and are referred;to as functional tumours. However, not all;neuroendocrine tumour;produce extra hormones .;;
There are several types of;neuroendocrine tumours;including:;
- gastro-intestinal which start in the large and small bowel;
- pancreatic;which account for about 7% of;neuroendocrine;tumours;
- lung;
- merkel;cell carcinoma;which involves the Merkel cells in the top layer of the skin;
- neuroblastoma;which usually starts in the adrenal glands and affects immature or developing nerve cells in children.;
Neuroendocrine tumours;are not common. It is estimated that 5178 new cases will be diagnosed in Australian in 2021.;Neuroendocrine tumours;are more common in people over the age of 40. Neuroblastoma is more likely in children under the age of five.;;
Genomic Alterations In Lcnecs
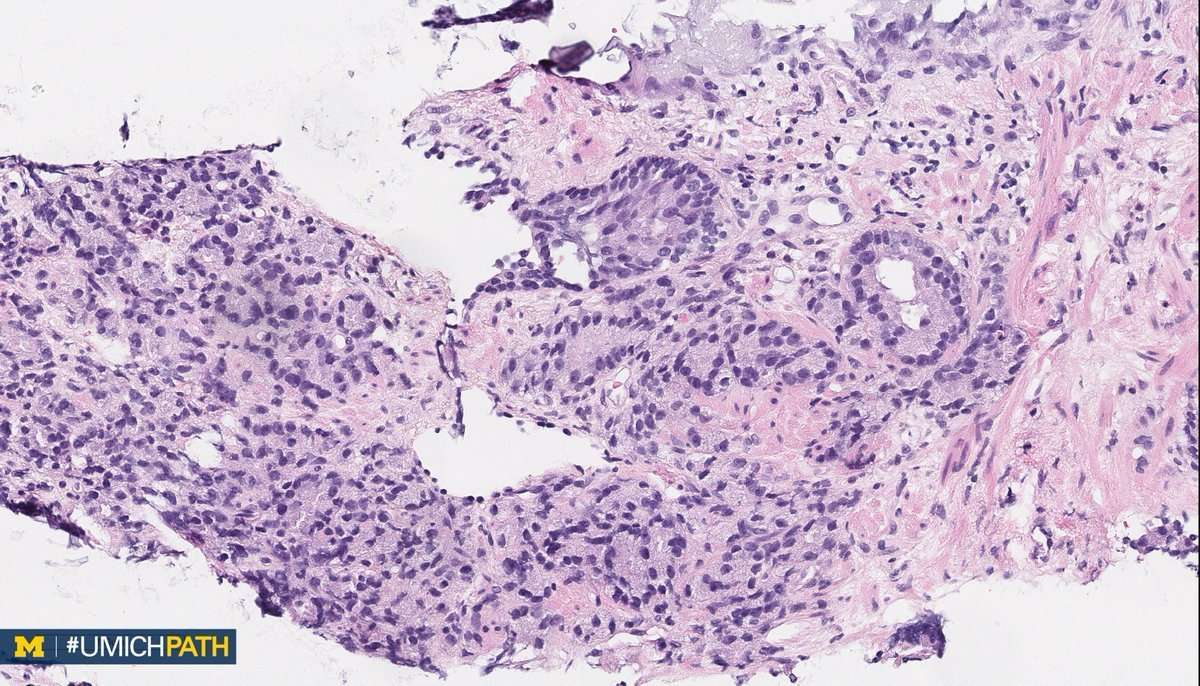
We collected 75 fresh-frozen tumor specimens from patients diagnosed with LCNEC under institutional review board approval . All tumors were thoroughly analyzed, and the histological features of pulmonary LCNECs were confirmed by expert pathologists according to the 2015 WHO classification . Most tumors were obtained from current or former heavy smokers, and enriched for stages I and II . Nineteen of 75 LCNECs included in this study showed additional histological components of lung adenocarcinoma , squamous cell carcinoma or SCLC . In subsequent analyses nucleic acids were extracted only from pure LCNEC regions .
Fig. 1
Don’t Miss: What Is Stage 2 Melanoma Skin Cancer
What Is The Standard Of Care Treatment
As with question 2, a complete answer to this question will ultimately follow on from a definitive LCNEC definition. For our day-to-day practice, the lung cancer community will remain unclear on the best choice of routine treatment unless there is an acceptable and reproducible pathological consensus on criteria for the classification of LCNEC in small diagnostic biopsy and cytology samples. If it is concluded that LCNEC is separate from other subtypes of NSCLC or SCLC, it can also be reasonably argued that no standard of care exists due to an absence of phase 3 and/or randomised clinical trials. In turn, there would be a justifiable niche for first;line clinical trial proposals given the very modest clinical benefits that have been observed in the prospective setting using chemotherapy.
Stage Iii Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The tumor cells may be of any size at the original site. A stage III SCC has begun to invade the nearby lymph nodes on the side of the body of the original cancerous growth. This new growth is still under 3 cm in size. It may also have grown into the facial bones like the bones surrounding the eye or your jaw bone.9 It has not affected any other organs.10
Also Check: What Does Merkel Cell Skin Cancer Look Like
Recommended Reading: How Serious Is Skin Cancer
Treatment For Neuroendocrine Tumours
Discussion with your doctor will help you decide on the best treatment for your tumour depending on the type of NET you have;;the symptoms you have;;where it is in your body; how far it has spread;;your age, fitness and general health;and;your preferences.;
The main treatment options for;neuroendocrine tumours;include;surgery,;chemotherapy, targeted therapy,;theranostics; peptide receptor radionuclide therapy and drug therapy . Merkel cellcarcinoma may also be treated using radiotherapy. Treatments can be given alone, in combination or one after the other. This is called multi-modality treatment. If the NET is slow-growing and not causing any symptoms you may not need immediate treatment.;
Characteristics Of Stage 4 Lung Cancers
Lung cancer is staged to classify the severity of the disease. The staging of NSCLC helps doctors choose the most appropriate course of treatment based on the likely outcome, referred to as the prognosis.
The stage of lung cancer is determined using the TNM classification system, which categorizes the severity of the disease based on three conditions:
- The size and extent of the primary tumor
- Whether nearby lymph nodes have cancer cells in them
- Whether distant metastasis has occurred
With stage 4 lung cancer, all three of these conditions will have occurred. With that said, the extent of metastasis can vary along with the prognosis.
For this reason, stage 4 NSCLC was broken down into two substages with the release of the new TNM classification system in 2018:
- Stage 4a lung cancer, in which cancer has spread within the chest to the opposite lung; or to the lining around the lungs or the heart; or to the fluid around the lungs or heart
- Stage 4b lung cancer, in which cancer has spread to one area outside of the chest, including a single non-regional lymph node
- Stage 4c lung cancer, in which cancer has spread to one or multiple places in one or more distant organs, such as the brain, adrenal gland, bone, liver, or distant lymph nodes.
Stage 4 lung cancer is incurable. Treatments, therefore, are focused on slowing the progression of the disease, minimizing symptoms, and maintaining an optimal quality of life.
Recommended Reading: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
Also Check: Is Renal Cell Carcinoma Hereditary
Data Processing And Analyses Of Dna Sequencing Data
The sequencing reads were aligned to the human reference genome NCBI build 37 with BWA . Possible PCR-duplicates were masked and not included for subsequent studies. We applied our in-house analysis pipeline,, to analyze the data for somatic mutations, copy number alterations and genomic rearrangements. In brief, the mutation calling algorithm considers local sequencing depth, forward-reverse bias, and global sequencing error, to thus determine the presence of a mutated allele. We determined the somatic status of these mutations by assessing the absence of these variants in the sequencing data of the matched normal.
We determined genomic rearrangements from WGS data of 11 human LCNECs following the procedure as previously described,. In brief, the sequencing data were analyzed for discordant read-pairs, which were not within the expected mapping distance or which revealed an incorrect orientation. Discordant read-pairs were analyzed for breakpoint-spanning reads, in which one read-pair shows partial alignments to two distinct genomic loci. Rearranged genomic loci were then reported at instances where at least one breakpoint-spanning read was identified. The genomic rearrangements called from each tumor sample were further filtered against the sequencing data of a matched normal and additionally against a library of normal genomes to thus minimize the detection of false-positive rearrangements.
Ischemic Therapy Embolization Chemoembolization
As the liver has a dual vascular supply and liver metastases derive the majority of blood from the hepatic artery selective metastasis ischemia may be induced by occlusion of tumor vessels. With surgical hepatic artery ligation and hepatic dearterialization significant palliation with relief of symptoms has been reported but only for a limited period. However, morbidity is high and mortality may occur. Temporary hepatic dearterialization provide the same relief of humoral symptoms and reduction of tumor growth but with significantly less morbidity. To make repeat tumor ischemia possible an implantable occluder allowing external repeated blockage of the hepatic artery flow can be put in place at a laparotomy. Ischemia is produced through the occluder for 16 hours every second month. The treatment can be continued for several years and often on an ambulatory basis. This technique caused a 50% decrease of 5-HIAA, symptom relief and reduced tumor bulk in a series of carcinoid patients. However, there is today general agreement that embolization with microspheres is preferable to ligation or occlusion of the hepatic artery. Embolization can be done selectively depending on tumor bulk and can be repeated. The response rate is 45% to 60% for tumor reduction and amelioration of clinical symptoms in parallel with reduced hormone or amine levels.
Thus, it remains to be shown if chemoembolization has any advantages to the effects obtained after embolization alone.
Read Also: Does Melanoma Skin Cancer Itch
What You Need To Know
- The most common types of lung cancer include lung nodules, non-small cell lung cancer, small cell lung cancer and mesothelioma.
- Rare lung cancers often dont originate in the lung.
- Rare lung cancers vary according to size, recommended treatment options and rate of metastasis.
The most common types of lung cancer are those found right in the lungs. Other rarer types of cancer may also occur in the lungs and chest wall.
You May Like: What Is Renal Carcinoma Cancer
Once You Know The Grade And Stage
After your doctor has figured out these things, you’ll discuss ideas for treatment. Which one you get depends on whether your disease has spread, and what organs it affects.
Ask questions so you can understand your diagnosis. And make sure you know all the treatment options for your cancer stage and grade, so you can feel good about the choice you and your doctor make. It’s OK to ask for a second opinion from another doctor.
Also Check: Can Someone Die From Skin Cancer
Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization Assay
Genomic rearrangements of PTK6 on chromosome 20 were assessed through a dual-color break-apart fluorescence in situ hybridization assay following previous protocols. In brief, the BAC clone RP11-939M14 labeled centromeres with biotin and CTD-3228E10 labeled telomeric sites with digoxigenin . The samples were analyzed with a 63× oil immersion objective at a fluorescence microscope equipped with appropriate filters, a charge-coupled device camera and the FISH imaging and capturing software Metafer 4 . Two independent scientists analyzed the experiment . Translocations were derived from a split of a signal pair, resulting in a single red and green signal, single red or green signals resulting from signal loss, were referred to as a rearrangement through deletion. In cases where cells were wild type and displayed no rearrangements, a juxtaposed red and green signal was observed.
NTRK1 break-apart FISH were performed with the ZytoLight SPEC NTRK1 Dual Color Break Apart Probe . According to previous protocols, 4m sections of FFPE tissue were treated with the Paraffin pretreatment reagent kit , and then stained with the probes following the instructions of the manufacturer. An NTRK1 rearrangement was diagnosed when >15% of the nuclei showed either a split pattern with 3 and 5 signals separated by a distance superior to the diameter of the largest signal, or isolated 3 signals.
Analysis Of Rna Sequencing Data
In order to detect chimeric transcripts, RNA-seq data were processed using TRUP,. In brief, paired-end RNA-seq reads were aligned to the human reference genome . We used TRUP to identify potential chimeric transcripts. Gene expression levels were determined with Cufflinks v2.0.2 referring only to paired-end reads that uniquely mapped within the expected mapping distance. The expression was quantified as FPKM and the expression values served as a filter for identifying significantly mutated genes .
Read Also: What Does Stage 3b Melanoma Mean
Gene Expression Profiling And Clustering Studies
For clustering purposes a set of genes that were both highly expressed and had highly variable expression patterns was identified in all lung cancer subtypes. Quality control procedures performed prior to any clustering analysis did not detect any evidence of batch effects.
After median centering the log2 values by gene, unsupervised consensus clustering was applied using the ConsensusClusterPlus R package, with partitioning around medioids and a Spearman correlation-based distance. Additional hierarchical clustering of the consensus clustering classes was performed, applying average linkage and a Pearson correlation-based distance.
The statistical significance of the differences in gene expression patterns present in the subtype was assessed with the SigClust R package by referring to the clustering gene sets and by using 1000 permutations and the default covariance estimation method. ClaNC was used to identify genes whose expression patterns characterize the subtypes. R 3.0.2 was used to perform all statistical analyses and create all figures.
We furthermore performed consensus clustering of LCNECs alone. The transcriptional data on LCNECs was analyzed and hierarchical clustering referred to 475 very highly expressed and very highly variable genes. The consensus clustering approach yielded a k=4 clustering solution: class 1 , class 2 , class 3 , and class 4 . ClaNC was then applied to the clustering solution, which further identified 540 classifier genes .
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia /small Lymphocytic Lymphoma
CLL and SLL are closely related diseases. In fact, many doctors consider them different versions of the same disease. The same type of cancer cell is seen in both CLL and SLL. The only difference is where the cancer cells are found. In CLL, most of the cancer cells are in the blood and bone marrow. In SLL, the cancer cells are mainly in the lymph nodes and spleen.
Both CLL and SLL are usually slow-growing diseases, although CLL, which is much more common, tends to grow more slowly. Treatment is the same for CLL and SLL. They are usually not curable with standard treatments, but many people can live a long time with them. Sometimes, these can turn into a more aggressive type of lymphoma over time.
You May Like: How Do You Get Basal Cell Carcinoma
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know You Have Skin Cancer
Update On Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma
Kenzo Hiroshima1, Mari Mino-Kenudson2
1Department of Pathology, Tokyo Womens Medical University, Yachiyo Medical Center, Yachiyo, Japan 2Department of Pathology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School , USA
Correspondence to:
Keywords: Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma ; small cell carcinoma; morphology; molecular alterations; treatment
Submitted May 29, 2017. Accepted for publication Jun 21, 2017.
doi: 10.21037/tlcr.2017.06.12
Rare Cancer Stories: Neuroendocrine Tumor Stage 4
Cancer details: Unknown site of origin, metastasis1st Symptoms: Pain in upper backTreatment: Chemotherapy, immunotherapy
Going from a point four years ago where I felt I had very little hope at recovering, I am now very happy and healthy. I still get the immunotherapy treatment and get regular scans but Im living a normal life.
Im just so grateful that theres so much research and advancements being made in cancer, and just so much cause for hope.
Jennifer P.
Before Diagnosis
What were your first symptoms?
I was in India traveling, going trekking in the Himalayas. I had noticed that my upper back was starting to hurt and I dismissed it during the trip. Thought it was yoga-related or workout-related. Didnt really think too much of it. The pain was just like above my right shoulder and initially it did not feel different than pain I felt before. It just felt like tight, sore muscle, something like that, and thats what it felt like for a while.
But then couple months later then it started to feel like it was just intensifying. It felt like maybe a deeper type of pain at that point. It definitely got worse, and then the pain that I felt in my neck that felt like I slept the wrong way, but in a really bad way, got worse. It never got better, so its that type of feeling.;
Describe the tests/scans you underwent
Don’t Miss: How To Detect Melanoma Early