What Are The Symptoms Of Melanoma Of The Head And Neck
Melanomas usually present as an abnormal mole or growth on the skin. Many people have normal moles that are small, even, tan or brown in color, round or oval, and either flat or raised. Melanoma arises from abnormal melanocytes, or pigment cells, that become cancerous. These are usually brown or black in color because of melanin production by melanocytes. Any change in size of a mole, or the appearance of a new mole, should be evaluated for the ABCDE rule:
- A=Asymmetry: The appearance or shape of one half of the mole does not match the other side.
- B=Border irregularity: The mole has irregular or uneven borders, particularly if they are ragged or notched.
- C=Color variation: Variation in color throughout the lesion, with patches of different shades of brown or tan in a mole, is concerning.
- D=Diameter: Lesions that are larger than ¼ inch, or the size of a pencil eraser, may represent melanoma; however, melanomas can be smaller than this.
- E=Evolving: A lesion that changes in size, color, shape or texture is suspicious for melanoma.
Melanomas may also have the appearance of a wart, crusty spot, ulcer, mole or sore. It may or may not bleed or be painful. If you have a preexisting mole, any change in the characteristics of this spot such as a raised or irregular border, irregular shape, change in color, increase in size, itching or bleeding is a warning sign of melanoma. Sometimes the first sign of head and neck melanoma is an enlarged lymph node in the neck.
How Do People Find Signs Of Melanoma On Their Own Skin
Performing a skin self-exam as often as recommended by your dermatologist is the best way. While examining your skin, you want to look for the following:
-
Mole that is changing in any way
-
Spot that looks different from the rest of the spots on your skin
-
Growth or spot on your skin that itches, bleeds, or is painful
-
Band of color beneath or around a nail
-
Sore that doesnt heal or heals and returns
The ABCDEs of melanoma can help you find changes to a mole, freckle, or other spot on your skin.
How Can You Manage Stage 3 Melanoma
Managing stage 3 melanoma can be challenging. With technological and medical advances, this diagnosis may not be as severe as it once was.
After your surgery or if youre unable to undergo surgery, you may need adjuvant treatment to prevent the cancer from coming back. There is adjuvant radiation therapy and adjuvant immunotherapy. These therapies help reduce the risk of melanoma returning, but they dont increase your survival rate.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Best Treatment For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
How Often Should You Follow Up With Your Doctor
After your treatment, your doctor will recommend a regular follow-up schedule to monitor your cancer. Theyll be checking to make sure the cancer hasnt come back or new cancerous lesions havent appeared. The types of follow-up include:
A yearly skin check: Skin checks are an important aspect of detecting melanoma in its earliest, most treatable stages. You should also conduct a skin check on yourself once per month. Look everywhere from the bottoms of your feet to behind your neck.
Imaging tests every three months to a year: Imaging studies, such as an X-ray, CT scan, or brain MRI, look for cancer recurrence.
Physical exam as needed: A physical exam to assess your overall health is important when you have had melanoma. For the first two years, youll want to get an exam every three to six months. Then for the next three years, the appointments can be every three months to a year. After the fifth year, the exams can be as needed. Do a monthly self-examination of your lymph nodes to check your progress.
Your doctor may recommend a different schedule based on your overall health.
What Does Scalp Melanoma Look Like
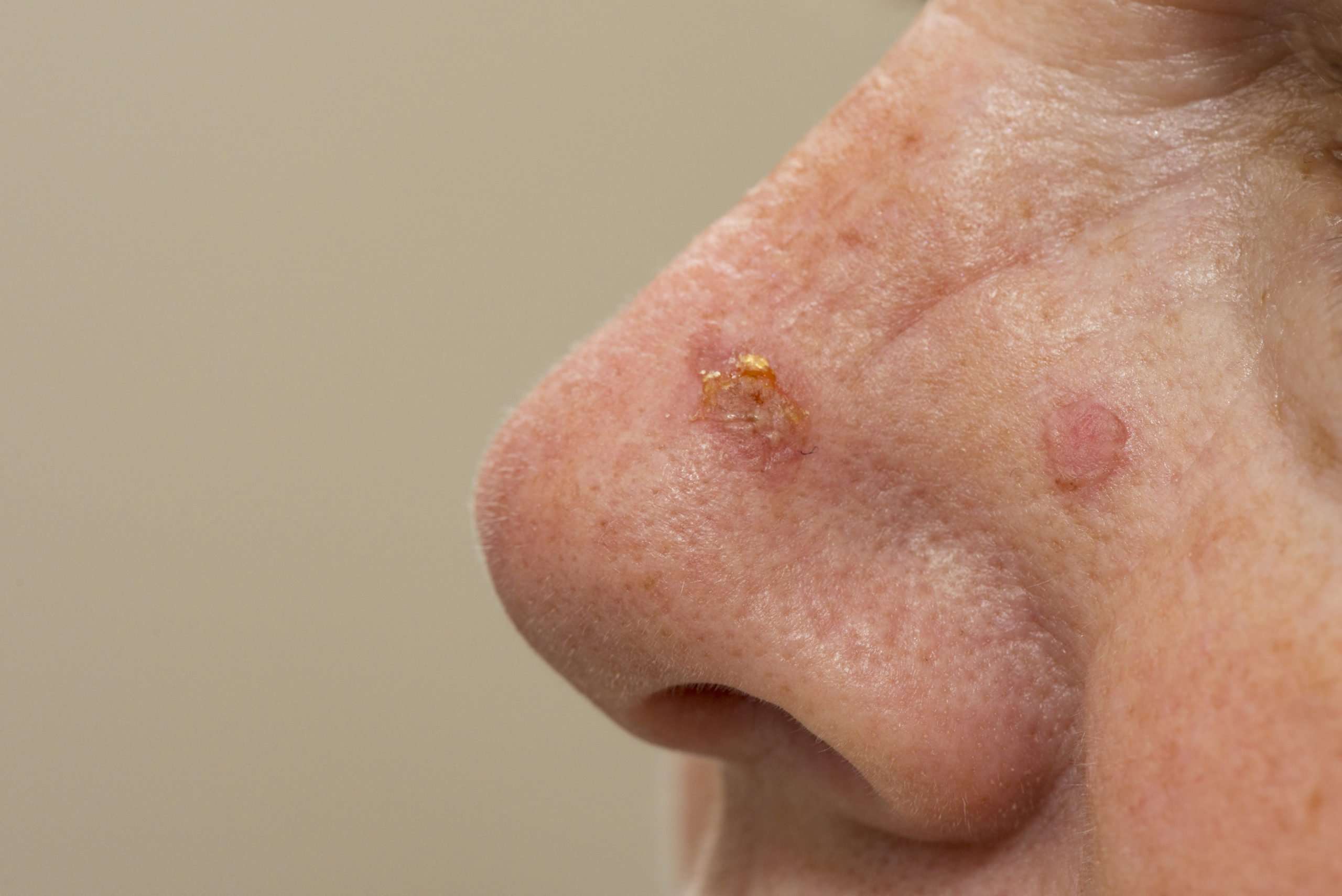
Melanoma is one of the most serious forms of cancer, and because its appearance can closely mimic natural moles, freckles, and age spots, it can be easy to overlook. Its important to know what to look for and perform regular skin cancer screenings to ensure you receive treatment for this condition in the earliest stages. According to Dr. Gregory Walker of U.S. Dermatology Partners in Waco, Texas, Melanoma can be easily overlooked in obvious places on the body, but many people dont know that the scalp, fingernails and toenails, and other harder to see areas often hide this condition until it has progressed to more advanced stages. Patients who know what to look for and regularly screen their skin for cancers, are much more likely to receive a diagnosis in early, more treatable stages. Keep reading to hear more from Dr. Walker about what scalp melanoma looks like and how to check for this condition and prevent serious health concerns.
Also Check: How To Protect Your Self From Skin Cancer
Treating Stage I Melanoma
Stage I melanoma is typically treated by wide excision . The width of the margin depends on the thickness and location of the melanoma. Most often, no other treatment is needed.
Some doctors may recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy to look for cancer in nearby lymph nodes, especially if the melanoma is stage IB or has other characteristics that make it more likely to have spread. You and your doctor should discuss this option.
If the SLNB does not find cancer cells in the lymph nodes, then no further treatment is needed, although close follow-up is still important.
If cancer cells are found on the SLNB, a lymph node dissection might be recommended. Another option might be to watch the lymph nodes closely by getting an ultrasound of the nodes every few months.
If the SLNB found cancer, adjuvant treatment with an immune checkpoint inhibitor or targeted therapy drugs might be recommended to try to lower the chance the melanoma will come back. Other drugs or perhaps vaccines might also be options as part of a clinical trial.
How Are Moles Evaluated
If you find a mole or spot that has any ABCDE’s of melanoma — or one that’s tender, itching, oozing, scaly, doesn’t heal or has redness or swelling beyond the mole — see a doctor. Your doctor may want to remove a tissue sample from the mole and biopsy it. If found to be cancerous, the entire mole and a rim of normal skin around it will be removed and the wound stitched closed. Additional treatment may be needed.
Don’t Miss: Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Malignant
Skin Cancer Diagnosis & Treatment
On skin cancer diagnosis, Dr. Truong says, To the untrained eye, skin cancer can mimic the appearance of natural irregularities or other common skin conditions. The deadliest form of skin cancer, melanoma, may look like a mole, therefore, it is very important to note new growths or changing lesions, and to bring them to the attention of your dermatologist. A skin biopsy may be needed for a definitive diagnosis.
Once a patient receives a definitive skin cancer diagnosis, treatment planning begins. The treatment depends on the type of skin cancer, the size, location, and level of aggressiveness. The main methods of treatment include surgery, radiation, and light-based treatments.
Surgery is the most common and effective treatment for most skin cancers. Depending on the size, aggressiveness, and location of the skin cancer, a wide local excision or Mohs micrographic surgery may be recommended. Both surgeries are minimally invasive and usually done under local anesthesia. Mohs Micrographic Surgery is a specialized skin cancer surgery designed to remove skin cancers on sensitive areas such as the head and neck. The surgery removes skin cancer completely while preserving as much healthy skin as possible. The cancerous lesion is removed layer by layer, and the margins of each specimen are examined by your Mohs surgeon while you wait. Due to the on-site 100% margin evaluation, cure rates are superior and more healthy skin can be preserved, minimizing the scar.
Treating Stage Iv Melanoma
Stage IV melanomas have already spread to distant lymph nodes or other areas of the body. Skin tumors or enlarged lymph nodes causing symptoms can often be removed by surgery or treated with radiation therapy.
Metastases in internal organs are sometimes removed, depending on how many there are, where they are, and how likely they are to cause symptoms. Metastases that cause symptoms but cannot be removed may be treated with radiation, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or chemotherapy.
The treatment of widespread melanomas has changed in recent years as newer forms of immunotherapy and targeted drugs have been shown to be more effective than chemotherapy.
Immunotherapy drugs called checkpoint inhibitors such as pembrolizumab or nivolumab are typically the first drugs tried, especially in people whose cancer cells do not have BRAF gene changes. These drugs can shrink tumors for long periods of time in some people. Ipilimumab , a different type of checkpoint inhibitor, is not typically used by itself as the first treatment, although it might be combined with nivolumab or pembrolizumab. This slightly increase the chances that the tumor will shrink, although itâs also more likely to result in serious side effects, which needs to be considered carefully. People who get any of these drugs need to be watched closely for serious side effects..
Itâs important to carefully consider the possible benefits and side effects of any recommended treatment before starting it.
Read Also: What Types Of Melanoma Are There
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Skin Cancers
Basal cell and squamous cell cancers are by far the most common skin cancers, and actually are more common than any other form of cancer. Because they rarely spread to other parts of the body, basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers are usually less concerning and are treated differently from melanoma. These cancers are discussed in Basal and Squamous Cell;Skin Cancer.
How Common Is Melanoma
Melanoma accounts for only about 1% of all skin cancers, but causes the great majority of skin cancer-related deaths. Its one of the most common cancers in young people under 30, especially in young women.
Melanoma incidence has dramatically increased over the past 30 years. Its widely accepted that increasing levels of ultraviolet exposure are one of the main reasons for this rapid rise in the number of melanoma cases.
Also Check: How Quickly Can Melanoma Appear
Looking For Signs Of Skin Cancer
Non melanoma skin cancers;tend to develop most often on skin that’s exposed to the sun.
To spot skin cancers early it helps to know how your skin normally looks. That way, you’ll notice any changes more easily.
To look at areas you cant see easily, you could try using a hand held mirror and reflect your skin onto another mirror. Or you could get your partner or a;friend to look. This is very important if you’re regularly outside in the sun for work or leisure.;
You can;take;a photo;of anything that doesn’t look quite right. If you can it’s a good idea to put a ruler or tape measure next to the abnormal area;when you take the photo. This;gives you a more accurate idea about its size and can help you tell if it’s changing. You can then show these pictures to your doctor.;
Epidermis The Epidermis Is The Top Or Outer Layer Of The Skin That You Can See It Is A Thin Tough Layer Of Skin That Protects The Body Gives Skin Its Colour And Makes New Skin The Epidermis Is Made Of Several Different Types Of Cells
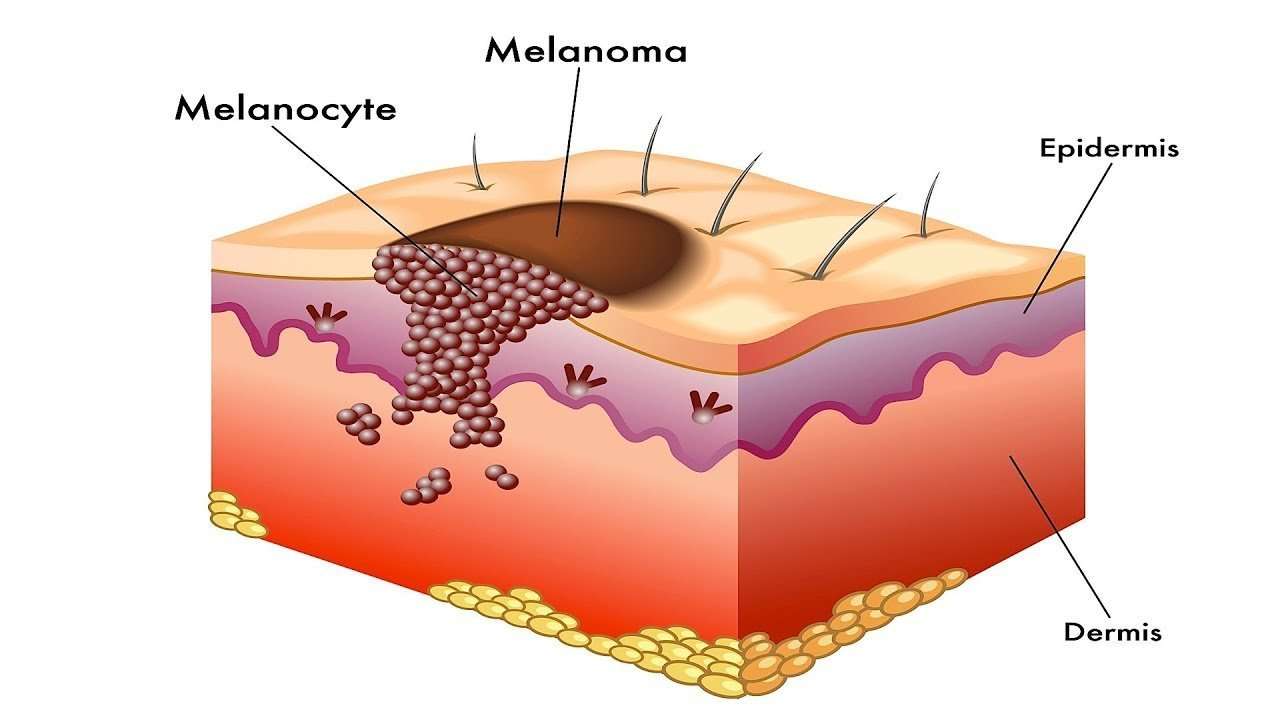
Squamous cells
Squamous cells are flat cells that make up the outer part of the epidermis . Squamous cells start from keratinocytes, which are cells that contain a tough, protective protein called keratin. As keratinocytes move toward the surface of the skin, they go through changes. The keratinocytes get bigger and flatter and stick together , then eventually die. The dead squamous cells on the surface of the skin are constantly shed from the skin and replaced by new cells.
Basal cells
Basal cells are round cells in the deepest part of the epidermis . Basal cells continually divide, make new cells and push the older cells toward the surface of the skin. The older cells eventually become mature keratinocytes and squamous cells.
Don’t Miss: Can Skin Cancer Cause Pain
Basal Cell Carcinoma: The Most Common Skin Cancer
Basal cell carcinoma, which is also called basal cell skin cancer, is the most common form of skin cancer, accounting for about 80 percent of all cases.
Rates of basal cell carcinoma have been increasing. Experts believe this is due to more sun exposure, longer lives, and better skin cancer detection methods.
This type of cancer begins in the skins basal cells, which are found in the outermost layer, the epidermis. They usually develop on areas that are exposed to the sun, like the face, head, and neck.
Basal cell carcinomas may look like:
- A flesh-colored, round growth
- A pinkish patch of skin
- A bleeding or scabbing sore that heals and then comes back
They typically grow slowly and dont spread to other areas of the body. But, if these cancers arent treated, they can expand deeper and penetrate into nerves and bones.
Though its rare, basal cell carcinoma can be life-threatening. Experts believe that about 2,000 people in the United States die each year from basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma.
Some risk factors that increase your chances of having a basal cell carcinoma include:
- Being exposed to the sun or indoor tanning
- Having a history of skin cancer
- Being over age 50
- Having chronic infections, skin inflammation, or a weakened immune system
- Being exposed to industrial compounds, radiation, coal tar, or arsenic
- Having an inherited disorder, such as nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome or xeroderma pigmentosum
Less Common Skin Cancers
Uncommon types of skin cancer include Kaposi’s sarcoma, mainly seen in people with weakened immune systems; sebaceous gland carcinoma, an aggressive cancer originating in the oil glands in the skin; and Merkel cell carcinoma, which is usually found on sun-exposed areas on the head, neck, arms, and legs but often spreads to other parts of the body.
Also Check: What Happens If I Have Melanoma
New Types Of Treatment Are Being Tested In Clinical Trials
This summary section describes treatments that are being studied in clinical trials. It may not mention every new treatment being studied. Information about clinical trials is available from the NCI website.
Vaccine therapy
Vaccine therapy is a cancer treatment that uses a substance or group of substances to stimulate the immune system to find the tumor and kill it. Vaccine therapy is being studied in the treatment of stage III melanoma that can be removed by surgery.
Possible Signs And Symptoms Of Melanoma
The most important warning sign of melanoma is a new spot on the skin or a spot that is changing in size, shape, or color.
Another important sign is a spot that looks different from all of the other spots on your skin .
If you have one of these warning signs, have your skin checked by a doctor.
The ABCDE rule is another guide to the usual signs of melanoma. Be on the lookout and tell your doctor about spots that have any of the following features:
- A is for Asymmetry: One half of a mole or birthmark does not match the other.
- B is for Border:The edges are irregular, ragged, notched, or blurred.
- C is for Color:The color is not the same all over and may include different shades of brown or black, or sometimes with patches of pink, red, white, or blue.
- D is for Diameter:The spot is larger than 6 millimeters across , although melanomas can sometimes be smaller than this.
- E is for Evolving: The mole is changing in size, shape, or color.
Some melanomas dont fit these rules. Its important to tell your doctor about any changes or new spots on the skin, or growths that look different from the rest of your moles.
Other warning signs are:
- A sore that doesnt heal
- Spread of pigment from the border of a spot into surrounding skin
- Redness or a new swelling beyond the border of the mole
- Change in sensation, such as itchiness, tenderness, or pain
- Change in the surface of a mole scaliness, oozing, bleeding, or the appearance of a lump or bump
You May Like: How Many People Survive Skin Cancer
Is Mucosal Melanoma Skin Cancer
All melanomas are a form of skin cancer. It affects cells called melanocytes, which give skin its pigment. Typically, melanomas form on the surface of the skin. This is known as cutaneous melanoma. The most common locations for melanoma are the chest, back, legs, neck, and face.â
Mucosal melanomas also affect the melanocytes, but they don’t form on the skin you can see. Instead, they develop on the mucous membranes inside your body. You can have mucosal melanoma of the mouth, nose, anus, vagina, or, very rarely, in the gastrointestinal tract.â
ââMucosal melanoma is far less common than cutaneous melanoma. Fewer than 1% of melanoma diagnoses are mucosal melanomas.
Tests To Check Your Lymph Nodes
If you are diagnosed with melanoma, your doctor may suggest some tests to check the lymph nodes. Not everyone needs these test. Whether you have them depends on the size of the melanoma and if the lymph nodes look or feel swollen. These tests include:
- A sentinel lymph node biopsy
A sentinel lymph node biopsy is a way of checking the lymph nodes closest to the melanoma
- Ultrasound
An ultrasound scan;uses sound waves to make up a picture of an area of the body.
- Fine needle aspiration
If the ultrasound scan of the lymph nodes is abnormal, the doctor will do a fine needle aspiration.
Read Also: Can Laser Hair Removal Cause Skin Cancer