Recurrent Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinomas are the most common type of skin cancer, according to the American Cancer Society. These cancers develop within the basal cell layer of the skin, in the lowest part of the epidermis.
Patients who have had basal cell carcinoma once have an increased risk of developing a recurrent basal cell cancer. Basal cell cancers may recur in the same location that the original cancer was found or elsewhere in the body. As many as 50 percent of cancer patients are estimated to experience basal cell carcinoma recurrence within five years of the first diagnosis.
Basal cell carcinomas typically grow slowly, and it is rare for them to metastasize or spread to nearby lymph nodes or other parts of the body. But early detection and treatment are important.
After completing treatment for basal cell carcinoma, it is important to perform regular self-examinations of the skin to look for new symptoms, such as unusual growths or changes in the size, shape or color of an existing spot. Skin cancers typically develop in areas of the body that are exposed to the sun, but they may also develop in areas with no sun exposure. Tell your oncologist or dermatologist about any new symptoms or suspicious changes you may have noticed.
- Have a history of eczema or dry skin
- Have been exposed to high doses of UV light
- Had original carcinomas several layers deep in the skin
- Had original carcinomas larger than 2 centimeters
Skin Cancer Support Groups And Counseling
Living with skin cancer presents many new challenges for you and for your family and friends. You will probably have many worries about how the cancer will affect you and your ability to “live a normal life,” that is, to care for your family and home, to hold your job, and to continue the friendships and activities you enjoy.
Many people with a skin cancer diagnosis feel anxious and depressed. Some people feel angry and resentful others feel helpless and defeated. For most people with skin cancer, talking about their feelings and concerns helps. Your friends and family members can be very supportive. They may be hesitant to offer support until they see how you are coping. Don’t wait for them to bring it up. If you want to talk about your concerns, let them know.
Continued
Some people don’t want to “burden” their loved ones, or prefer talking about their concerns with a more neutral professional. A social worker, counselor, or member of the clergy can be helpful. Your dermatologist or oncologist should be able to recommend someone.
Many people with cancer are profoundly helped by talking to other people who have cancer. Sharing your concerns with others who have been through the same thing can be remarkably reassuring. Support groups for people with cancer may be available through the medical center where you are receiving your treatment. The American Cancer Society also has information about support groups throughout the U.S.
The Katie Couric Curve
Survival is way up in colon cancer because it is caught earlier due to routine colonoscopy , says Vijay Trisal, MD, an assistant professor of oncological surgery at the City of Hope National Cancer Center in Duarte, Calif. After her husband died of colon cancer, NBC newswoman Katie Couric had a colonoscopy live on national television. In the following weeks and months, the numbers of people across the country having colonoscopies increased more than 20%, according to researchers at the University of Michigan Health System and the University of Iowa.
“We are picking up earlier cancers and that’s making a difference, and part of the difference is also very good chemotherapy for colon cancer,” he says. For example, it used to be that if colon cancer had spread to the liver, “survival was nine to 11 months, but now we can resect the liver and chemotherapy kills the microscopic disease, so we seeing survival in the range of 50%,” he tells WebMD.
Overall, “advances in cancer have been in treating the microscopic disease,” he says. “Chemotherapy for breast cancer and colon cancer has significantly improved because we can kill the small disease that is not visible and regrows either in the vicinity of the cancer or spreads throughout the body.” Chemotherapy can knock out errant cancer cells along with the main tumor.
Recommended Reading: Melanoma On Face Prognosis
Determining If The Cancer Has Spread
As part of your diagnosis, your doctor will also determine what stage the cancer is in. The different stages refer to whether and how far the cancer has spread in your body, on a Roman numeral scale of I to IV. A stage I cancer is small and contained to the body part where it originated, whereas a stage IV cancer has spread aggressively to other parts of the body.
Depending on the type of skin cancer that a person has, it may be more or less likely that it has spread through the body. For instance, basal cell skin cancer rarely spreads beyond the skin where it starts. However, melanomas and large squamous cell carcinomas are more likely to spread into other regions of the body. Cases of melanoma, in particular, may call for further tests to determine the specific stage theyre in.
Your doctor may evaluate multiple factors in order to stage the cancer. Using biopsies and imaging tests, your doctor may take a look at:
-
The size and thickness of the tumor, and whether it has grown into surrounding tissues
-
Nearby lymph nodes, to check for signs of cancer spread
Cancer: The Good The Bad And The Ugly
We’ve made great progress since President Nixon declared war on cancer 30 years ago, but can the war be won?
With cancer survivor Lance Armstrong winning his seventh Tour de France, and walks, runs and other highly visible fund-raising opportunities — often overflowing with survivors and their families — taking place almost ubiquitously across the map, it certainly seems that doctors are finally winning, or at least making some significant strides — in the war against cancer.
But are they?
The word “cancer” still strikes a chord of fear in most people, but the truth is that today many cancers including breast, colon and prostate may no longer be the death sentences that they once were. Others like melanoma and pancreatic cancer, however, are still proving somewhat vexing and insurmountable. But ultimately, we are turning a corner: survival statistics are up for many cancers, smoking is down, and some of the best minds in the world are trying to crack the cancer codes. Advances Against Colon Cancer
Judah Folkman, MD, the Andrus Professor of Pediatric Surgery and professor of cell biology at Harvard Medical School and director of the vascular biology program at Children’s Hospital, both in Boston, agrees: “Lance Armstrong is really amazing, and the fact that we can do it once means you can maybe do it again,” he says.
Here’s how we are doing so far.
You May Like: Well Differentiated
Knowledge Is Your Best Defense
What Is Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer is the out-of-control growth of abnormal cells in the epidermis, the outermost skin layer, caused by unrepaired DNA damage that triggers mutations. These mutations lead the skin cells to multiply rapidly and form malignant tumors. The main types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma , squamous cell carcinoma , melanoma and Merkel cell carcinoma .
The two main causes of skin cancer are the suns harmful ultraviolet rays and the use of UV tanning beds. The good news is that if skin cancer is caught early, your dermatologist can treat it with little or no scarring and high odds of eliminating it entirely. Often, the doctor may even detect the growth at a precancerous stage, before it has become a full-blown skin cancer or penetrated below the surface of the skin.
Americans will develop skin cancer by age 70.
The Four Major Types Of Melanoma
Melanoma can be divided into different subtypes. A few of the most common subtypes are:
- Superficial spreading melanoma.Superficial spreading melanoma is the most common type of melanoma. Lesions are usually flat, irregular in shape, and contain varying shades of black and brown. It can occur at any age.
- Lentigo maligna melanoma. Lentigo maligna melanoma usually affects adults over 65 and involves large, flat, brownish lesions.
- Nodular melanoma.Nodular melanoma can be dark blue, black, or reddish-blue, but may have no color at all. It usually starts as a raised patch.
- Acral lentiginous melanoma.Acral lentiginous melanoma is the least common type. Typically it affects the palms, soles of the feet, or under finger and toenails.
Don’t Miss: Merkel Cancer Prognosis
Biological Therapies And Melanoma
Biological therapies are treatments using substances made naturally by the body. Some of these treatments are called immunotherapy because they help the immune system fight the cancer, or they occur naturally as part of the immune system.
There are many biological therapies being researched and trialled, which in the future may help treat people with melanoma. They include monoclonal antibodies and vaccine therapy.
Treatment For Skin Cancer
The primary goal of skin cancer treatment is to remove all of the cancerous cells. We use a few different types of removal methods depending on multiple factors including the type, extent, and location of your skin cancer. The main types of treatment include:
- Surgical Excision
- Electrodesiccation and Curettage
For skin cancers that are in sensitive areas of the body, such as the face and ears or for particularly large skin cancers, we recommend a specialized surgery called MOHS surgery. With this, the surgeon looks at the removed areas under the microscope during the surgery and removes any additional abnormal tissue necessary, until the entire cancer is assured to be completely removed. This is performed at specially-trained surgeons offices.
In some cases, we can use a topical chemotherapy cream to treat the cancer instead of performing a procedure, although this is not common and not considered first-line treatment.
Another, less common treatment treatment method is a procedure that uses a specialized radiation device. There are only a few centers in the area that have this device, and patients have expressed mixed reviews due to the number of treatments required. Additionally, the results are not better than other treatment methods.
You May Like: Stage Iii Melanoma
Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Be Cured
In the vast majority of cases, basal cell skin cancer can be cured. The survival rates are excellent however, the exact statistics remain unknown. Unlike other cancers, basal and squamous cell skin cancers are not tracked by cancer registries, so the statistics are not available.
In some cases, basal skin cancer can recur. The risk of recurrence appears to be linked to the type of treatment used to treat the cancer.
Research has indicated that the recurrence risk is:
- Just above 10% after surgical excision
- Slightly less than 8% after electrodesiccation and curettage
- Approximately 7.5% after cryotherapy
- Less than 1% after Mohs micrographic surgery
Treatment options vary depending on the subtype, staging, and location of the basal skin cancer.
What Is Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is the most common form of cancer in the United States. Almost all skin cancers are the result of too much exposure to ultraviolet light. This is found in sunlight, tanning booths, and sunlamps. Skin cancer is usually one of the most curable types of cancer.
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are two of the most common forms of skin cancer. They are very curable. These cancers occur in the basal and squamous cell layers at the top of the skin. They are almost always slow-growing. If found early, they are easy to treat and do not spread.
Melanoma is a less common but aggressive form of skin cancer. It occurs in skin cells that make a skin color pigment called melanin. If it is not found early, it will likely spread to other tissues. It can spread through the whole body and may cause death. Only 2% of skin cancer cases are melanoma. But it causes the most deaths from skin cancer.
You May Like: Stage 3b Melanoma Survival Rate
Skin Cancer Symptoms And Signs
Basal Cell Carcinoma
BCC is the most common type of skin cancer and has a predilection for sun-exposed skin. Tumors may appear as a pearly or waxy bumps usually with visible blood vessels , or as a flat scaly reddish patch with a brown border, or as a hard or scar-like lesion . Frequently BCCs can be itchy, often bleed, or in more advanced cases, ulcerate.
How Is Actinic Keratosis Treated
Treatment for an actinic keratosis may include:
-
Cryotherapy. This treatment freezes the lesion.
-
Topical chemotherapy. This is medicine applied to the skin.
-
Laser surgery. This can remove lesions from the face and scalp, and actinic cheilitis from the lips.
-
Other treatments. These are done to remove or destroy the lesion.
Most actinic keratoses can be treated and cured. In rare cases they may come back. Its important to have regular skin exams after treatment. This will help check for new actinic keratoses and skin cancer.
You May Like: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
What Are The Risks Or Complications Of Skin Graft Surgery
Most skin grafts are successful. But sometimes the transplanted skin doesnt take to the new area. If the transplanted skin doesnt take, you may need another skin graft. An unsuccessful skin graft usually results from:
- Blood or pus pooling underneath the transplanted skin.
- Infection.
- Injury or damage to the graft site .
- Problems with blood circulation that cause the wound to heal too slowly .
Other complications of skin graft surgery include:
- Bleeding.
- Contracture, when the grafted skin shrinks and pulls in at the edges.
- Discolored, patchy or uneven skin.
- Loss of skin sensation or increased sensitivity to pain.
- Pain that lasts after the area has healed .
- Scar tissue building up around the graft site.
New Warriors Join Battle
New “smart” drugs are also promising weapons in this war. “This year, there has been enormous progress in the angiogenesis inhibitors, and it is the first year that there has been a significant increase in survival of the three top cancers – colon, breast, and lung — due to antiangiogenic therapies being introduced,” Folkman tells WebMD. Antiangiogenic drugs, also called angiogenesis inhibitors, starve tumors to death by cutting off their blood supply.
For example, Avastin targets a protein called vascular endothelial growth factor , which plays a role in making new blood vessels for tumors . This drug was approved in the U.S. for colon cancer in February 2004, and by January 2005 it had been approved in 27 other countries, he says.
Other antiangiogensis drugs being used include thalidomide and Tarceva. Tarceva blocks tumor cell growth by targeting a protein called HER1/EGFR that is important for cell growth in advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer. Tarceva “blocks three angiogenic proteins and really is an angiogenic inhibitor,” Folkman says. Thalidomide became notorious in the 1960s when it was prescribed to pregnant women to ease morning sickness, but was found to cause severe birth defects by limiting the blood flow to developing limbs. As a result, many children were born limbless or with severely shortened limbs. Now scientists are capitalizing on these same blood-limiting properties to help block the blood supply to tumors.
Read Also: Life Expectancy Metastatic Melanoma
Victories In The Fight Against Cancer
In 2005, there will be 1,372,910 new cancer cases in the U.S. and 570,280 cancer deaths , according to statistics from the ACS.
Overall, “if you look across the board, there are very few cancers in which we are not seeing declines in mortality,” Glynn says. “We are seeing reductions in prostate, colorectal, and breast cancers, and stomach cancer has basically fallen off of the edge of the earth in the U.S.,” he says. “In lung cancer among men, we are seeing a drop, and we will be seeing a drop among women by 2010,” he predicts. Still, lung cancer remains the top cancer killer in both sexes, according to the ACS. It is responsible for nearly one in three cancer deaths in men and about one in four among women.
According to the latest ACS statistics, death rates for all cancer sites combined decreased 1.5% per year from 1993 to 2001 in men and 0.8% per year from 1992 to 2001 in women.
“Five-year survival for all cancers combined used to be about 50% and now it’s 75%,” Glynn says. “We have made a lot of progress in early detection,” he says. “Fewer than 1/2 of all women were receiving mammograms several years ago and now it’s close to 80%, we have mapped the human genome, which will eventually lead to individual treatment and prevention, and smoking is down in women to under 20%,” he says.
Five-year survival describes the percentage of people still alive within a five-year period after diagnosis or treatment of cancer.
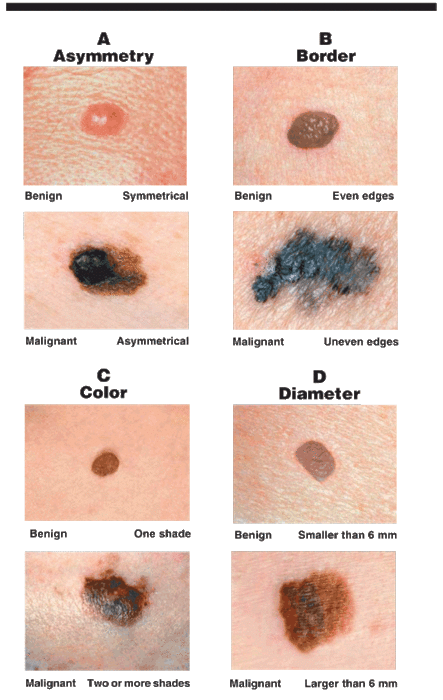
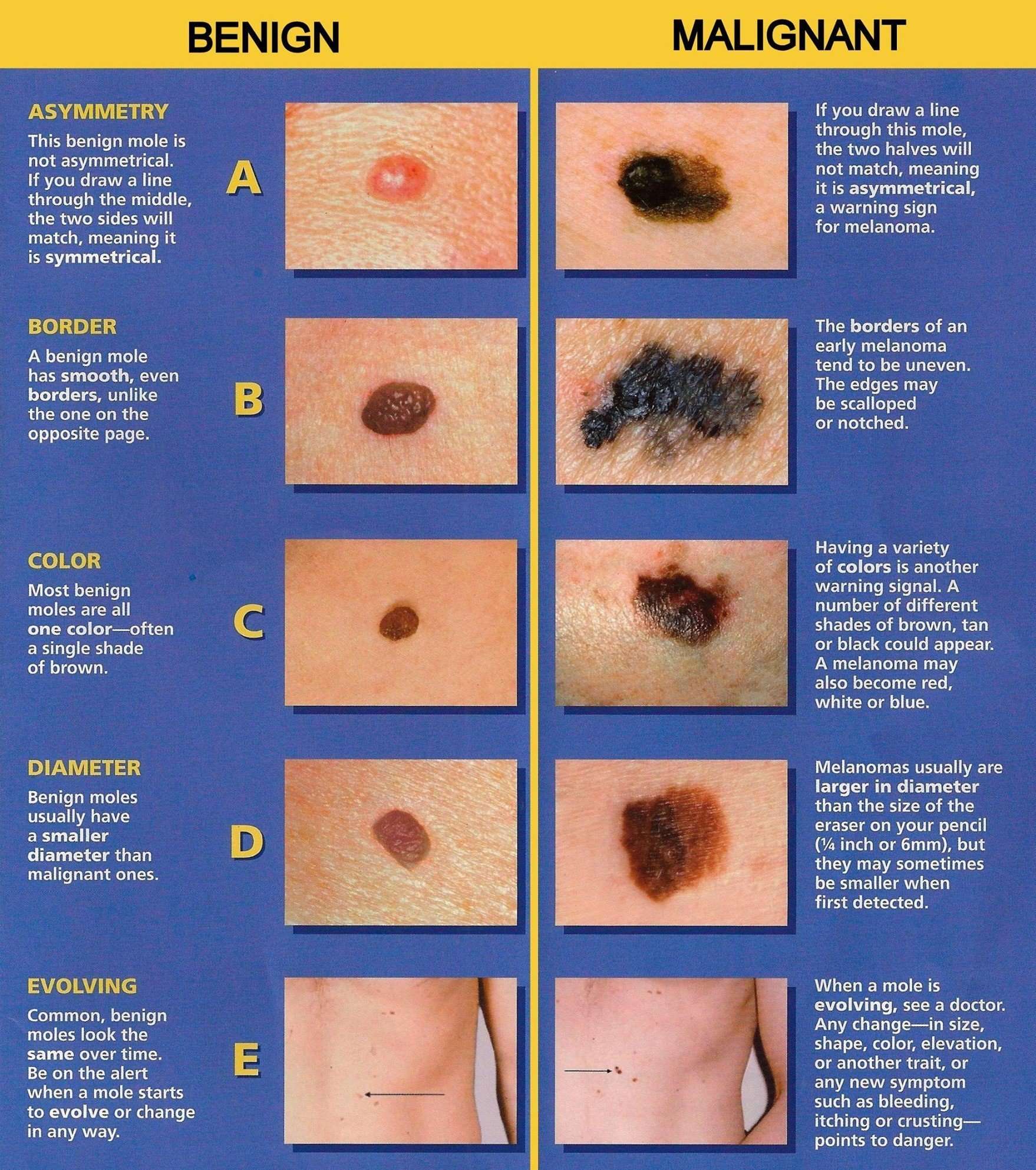
Get To Know Your Skin And Check It Regularly
Look out for changes such as:
- A mole that changes shape, color, size, bleeds, or develops an irregular border
- A new spot on the skin that changes in size, shape, or color
- Sores that don’t heal
- New bumps, lumps, or spots that don’t go away
- Shiny, waxy, or scar type lesions
- New dark patches of skin that have appeared
- Rough, red, scaly, skin patches
If you notice any changes to your skin, seek advice from a medical professional. Basal cell carcinoma is very treatable when caught early.
Read Also: Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer Survival Rate
What Is The Staging For Skin Cancer
There is no specific staging system for basal cell carcinoma. If the tumor is wider than 2 cm , it is probably a more serious tumor. Basal cell carcinomas of the ears, nose, and eyelid may also be of more concern, regardless of the size.
There is a staging system for squamous cell carcinoma. Large tumors that are thicker than 2 mm, invade the nerve structures of the skin, occur on the ear, and have certain worrisome characteristics under the microscope are of more concern. If the tumor metastasizes to a site at some distance from the primary tumor, the cancer is likely to be a dangerous tumor.