When To Seek Help
Not all sores on the skin are skin cancer. But if you do develop a skincancer, the earlier it is treated, the better the outcome for you.
Most people find SCCs by checking their own skin. Check your skin regularly so you notice any changes. See a doctor if:
- you have a sore that doesnt heal in 2 months
- you notice a new and unusual looking spot
- an existing spot changes in colour, size or shape
- you have a spot that is asymmetrical
- you have a spot with an uneven border
- you have a spot with an unusual or uneven colour
- you have a spot that is larger than 7 mm
How Dangerous Is Scc
While the majority of SCCs can be easily and successfully treated, if allowed to grow, these lesions can become disfiguring, dangerous and even deadly. Untreated SCCs can become invasive, grow into deeper layers of skin and spread to other parts of the body.
Did you know?
Americans die each year from squamous cell carcinoma
Get To Know Your Skin And Check It Regularly
Look out for changes such as:
- A mole that changes shape, color, size, bleeds, or develops an irregular border
- A new spot on the skin that changes in size, shape, or color
- Sores that dont heal
- New bumps, lumps, or spots that dont go away
- Shiny, waxy, or scar type lesions
- New dark patches of skin that have appeared
- Rough, red, scaly, skin patches
If you notice any changes to your skin, seek advice from a medical professional. Basal cell carcinoma is very treatable when caught early.
Recommended Reading: Who Do You See For Skin Cancer Screening
You May Like: Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Metastasis
What Is The Outlook For People With Squamous Cell Cancer
Early detection of SCC is key to successful treatment. If SCC isnt treated in its early stages, the cancer may spread to other areas of the body, including the lymph nodes and organs. Once this occurs, the condition can be life threatening.
Those with weakened immune systems due to certain medical conditions, such as HIV, AIDS, or leukemia, have a greater risk of developing more serious forms of SCC.
What Causes Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
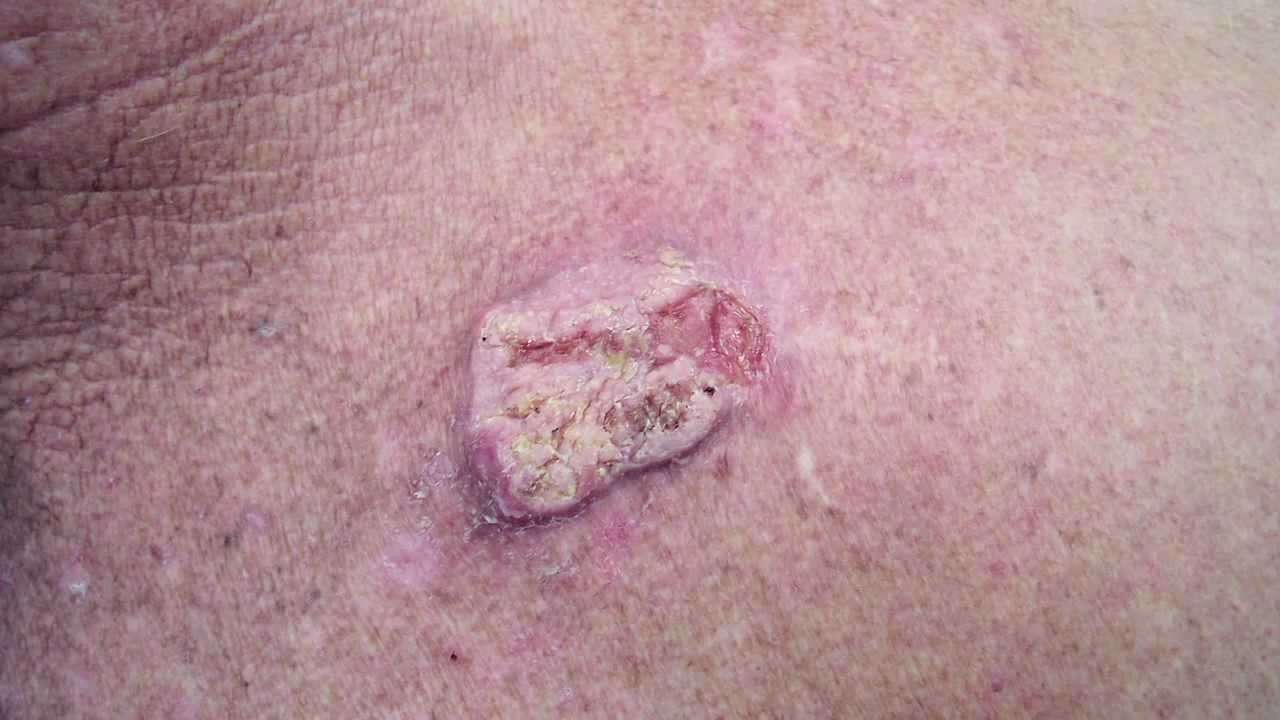
More than 90% of cases of SCC are associated with numerous DNAmutations in multiple somaticgenes. Mutations in the p53 tumour suppressor gene are caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation , especially UVB . Other signature mutations relate to cigarette smoking, ageing and immune suppression . Mutations in signalling pathways affect the epidermalgrowth factorreceptor, RAS, Fyn, and p16INK4a signalling.
Beta-genus human papillomaviruses are thought to play a role in SCC arising in immune-suppressed populations. -HPV and HPV subtypes 5, 8, 17, 20, 24, and 38 have also been associated with an increased risk of cutaneous SCC in immunocompetent individuals.
Also Check: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Some Squamous Cell Skin Cancers Are Deadly
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma is usually easily treated with surgery however, a subsection of patients with specific disease risk factors are more likely to develop metastases and die from the disease, according to the results of a study published in JAMA Dermatology.
Squamous cell carcinoma accounts for roughly 20% of all cases of non-melanoma skin cancer. Squamous cell carcinoma commonly involves the head or neck. The tumor may appear as a red bump or as a rough or scaly area on the skin. Squamous cell carcinoma is more likely than basal cell carcinoma to spread to lymph nodes or distant parts of the body, though this happens infrequently. Treatment of squamous cell carcinoma often involves surgery to remove the cancer.
Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin
Its important to get anything that looks suspicious checked out. Left untreated, squamous cell carcinomas can invade further into the skin and spread to other parts of the body.
They can grow extremely quickly and be very dangerous, said Dr. Amy McMichael, chair of the dermatology department at Wake Forest Baptist Health in North Carolina and a member of the American Academy of Dermatology. Sometimes if we wait a month, they are too big to remove in the office and you have to go to the operating room.
Read Also: What Are The 4 Types Of Skin Cancer
You May Like: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
What Will Happen After Treatment
Youll be glad when treatment is over. Your doctor will want you to check your skin at least once a month. It will be very important to protect yourself from getting too much sun.
For years after treatment ends, you will see your skin cancer doctor. At first, your visits may be every few months. Then, the longer youre cancer-free, the less often the visits are needed. Be sure to go to all of these follow-up visits. Your doctor will ask about symptoms and check you for signs of the cancer coming back or a new skin cancer. Other exams and tests may also be done.
Having cancer and dealing with treatment can be hard, but it can also be a time to look at your life in new ways. You might be thinking about how to improve your health. Call us at 1-800-227-2345 or talk to your cancer care team to find out what you can do to feel better.
You cant change the fact that you have cancer. What you can change is how you live the rest of your life making healthy choices and feeling as good as you can.
How Widespread Is Scc
While SCC is less common than basal cell carcinoma , the number of reported SCC cases in the U.S. has steadily increased.
- An estimated 1.8 million cases of SCC are diagnosed each year, which translates to about 205 cases diagnosed every hour.
- SCC incidence has increased up to 200 percent in the past three decades.
Reviewed by:
Read Also: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
How Does This Cancer Typically Progress
In the skin form of the disease, although spread to nearby lymph nodes or other organs is possible, it is very uncommon. With SCC of the nose, spread may occur to the lymph nodes under the chin .
Dogs with multicentric SCC often develop new lesions in other sites after surgical removal of lesions.
The digit form of SCC is far more aggressive. It can spread to the local lymph nodes and beyond. For this reason, your veterinarian may recommend staging . Staging may include bloodwork, urinalysis, X-rays of the lungs, and possibly an abdominal ultrasound. If any lymph nodes appear to be affected , samples may be taken via FNA to determine if the tumor has spread into them.
What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin
Squamous cells are found throughout the human body. These cells line organs, such as the lungs, throat, and thyroid. We also have squamous cells in our skin.
The job of squamous cells is to protect what lies beneath. In our skin, these cells sit near the surface, protecting the tissue beneath.
Anywhere we have squamous cells, we can develop a type of cancer called squamous cell carcinoma .
In the skin, this cancer is usually not life-threatening. It tends to grow slowly, but it can grow deep. When the cancer grows deep, it can injure nerves, blood vessels, and anything else in its path. As the cancer cells pile up, a large tumor can form.
Most people who develop this skin cancer have fair skin that they seldom protected with sunscreen or sun-protective clothing. Before developing this skin cancer, they tend to notice signs of sun damage on their skin, such as age spots, patches of discolored skin, and deep wrinkles.
Anyone can develop squamous cell carcinoma
While anyone can develop this skin cancer, you have a greater risk if you live with a transplanted organ, use tanning beds, or have fair skin that you seldom protected from the sun.
Another sign of sun-damaged skin is having one or more pre-cancerous growths on your skin called actinic keratoses . Some AKs progress, turning into squamous cell carcinoma of the skin.
To find out what this skin cancer can look like and see pictures of it, go to: Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: Signs and symptoms.
ImageGetty Images
Also Check: Ductal Breast Cancer Survival Rates
Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Deadly
Skin cancer is by far the most common type of cancer and each year there are more new cases of skin cancer than the combined cases of breast, prostate, lung and colon cancer. This translates to one in five Americans developing skin cancer over their lifetime. Following basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common type of skin cancer. According to the American Cancer Society, about 5.4 million basal and squamous cell skin cancers are diagnosed each year in America. Squamous cell carcinoma accounts for ~20% of these cases.
Who is at risk for squamous cell carcinoma?Skin cancer occurs at every age in persons of every ethnicity and gender. Risk for squamous cell carcinoma increases with the following factors:
- Ultraviolet light exposure from the sun and indoor tanning
- History of sunburns, especially during childhood
- Lighter skin color equating to increased sensitivity to ultraviolet light. Although less common overall in darker skin types, squamous cell carcinoma accounts for a larger proportion of skin cancers in this population.
- Incidence increases with age
- Male gender men are especially at risk after age 60, whereas women account for more skin cancers in those under age 40
- Personal or family history of skin cancer
- Human Papillomavirus Virus infection
- Immunosuppression
- Within scars from burns or other injuries as well as non-healing wounds of any type
Tests That May Be Done
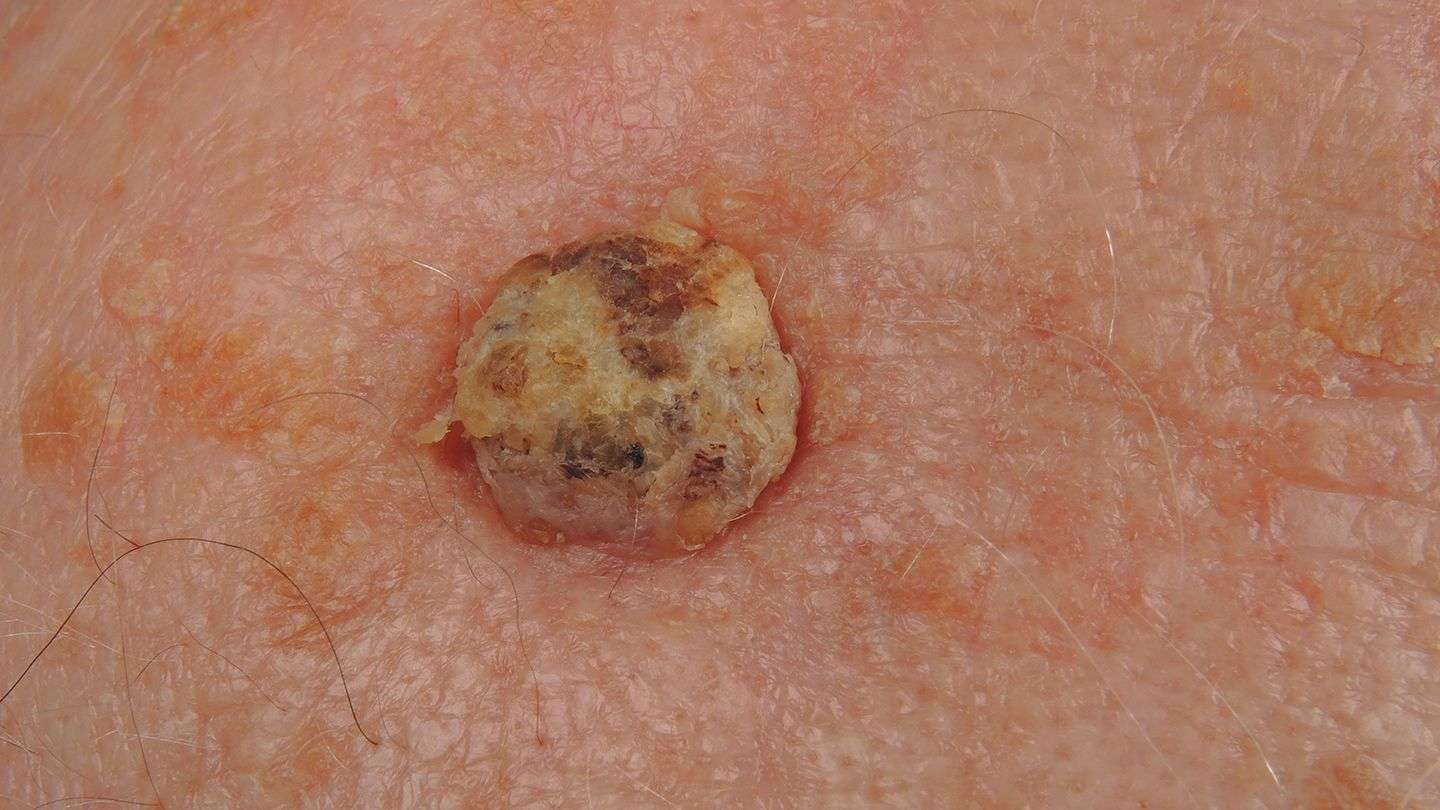
The doctor will ask you questions about when the spot on your skin first showed up and if it has changed in size or the way it looks or feels. The rest of your skin will be checked. During the exam your doctor will check the size, shape, color and texture of any skin changes. If signs are pointing to skin cancer, more tests will be done.
Skin biopsy
In a biopsy, the doctor takes out a small piece of tissue to check it for cancer cells. A biopsy is the only way to tell for sure if you have skin cancer and what kind it is.
There are many types of skin biopsies. Ask your doctor what kind you will need. Each type has pros and cons. The choice of which type to use depends on your own case.
In rare cases basal and squamous cell skin cancer can spread to the nearby lymph nodes Ask your doctor if your lymph nodes will be tested.
Basal and squamous cell cancers don’t often spread to other parts of the body. But if your doctor thinks your skin cancer might spread, you might need imaging tests, such as MRI or CT scans.
Don’t Miss: What Does Stage 3b Melanoma Mean
Who Gets Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Risk factors for cutaneous SCC include:
- Age and sex: SCCs are particularly prevalent in elderly males. However, they also affect females and younger adults.
- Previous SCC or another form of skin cancer are a strong predictor for further skin cancers.
- Previous cutaneous injury, thermal burn, disease
- Inherited syndromes: SCC is a particular problem with xeroderma pigmentosum, albinism, and epidermodysplasia verruciformis
- Other risk factors include ionising radiation, exposure to arsenic, and immune suppression due to disease or medicines. Organ transplant recipients have an increased risk of developing SCC.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Causes
Exposure to ultraviolet rays, like the ones from the sun or a tanning bed, affects the cells in the middle and outer layers of your skin and can cause them to make too many cells and not die off as they should. This can lead to out-of-control growth of these cells, which can lead to squamous cell carcinoma.
Other things can contribute to this kind of overgrowth, too, like conditions that affect your immune system.
Also Check: Malignant Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Request An Appointment At Moffitt Cancer Center
Please call for support from a Moffitt representative. New Patients and Healthcare Professionals can submit an online form by selecting the appropriate buttonbelow. Existing patients can call . for a current list of insurances accepted at Moffitt.
NEW PATIENTS To request a new patient appointment, please fill out the online form or call 1-888-663-3488.
REFERRING PHYSICIANS Providers and medical staff can refer patients by submitting our online referral form.
Moffit now offers Virtual Visits for patients. If you are eligible for a virtual appointment, our scheduling team will discuss this option further with you.
Moffitt Cancer Center is committed to the health and safety of our patients and their families. For more information on how were protecting our new and existing patients, visit our COVID-19 Info Hub
How Serious Is My Cancer
If you have skin cancer, the doctor will want to find out how far it has spread. This is called staging.
Basal and squamous cell skin cancers don’t spread as often as some other types of cancer, so the exact stage might not be too important. Still, your doctor might want to find out the stage of your cancer to help decide what type of treatment is best for you.
The stage describes the growth or spread of the cancer through the skin. It also tells if the cancer has spread to other parts of your body that are close by or farther away.
Your cancer can be stage 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4. The lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. A higher number, like stage 4, means a more serious cancer that has spread beyond the skin. Be sure to ask the doctor about the cancer stage and what it means for you.
Other things can also help you and your doctor decide how to treat your cancer, such as:
- Where the cancer is on your body
- How fast the cancer has been growing
- If the cancer is causing symptoms, such as being painful or itchy
- If the cancer is in a place that was already treated with radiation
- If you have a weakened immune system
Don’t Miss: What Happens If You Pick At A Basal Cell Carcinoma
What Happens If Merkel Cell Carcinoma Is Left Untreated
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare but aggressive and potentially fatal form of skin cancer. It typically affects people above the age of 50 and those who have weakened immune systems. In most cases, Merkel cell carcinoma begins as a skin-toned growth that may bleed easily. The bumps or nodules may also have blue, purple, or red coloring. Because the Merkle cells are near nerve endings, this form of cancer has numerous health risks, and if left untreated, Merkle cell cancer may spread to the brain, lungs, or bones, becoming fatal.
What Are The Clinical Features Of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Cutaneous SCCs present as enlarging scaly or crusted lumps. They usually arise within pre-existing actinic keratosis or intraepidermal carcinoma.
- They grow over weeks to months
- They may ulcerate
- They are often tender or painful
- Located on sun-exposed sites, particularly the face, lips, ears, hands, forearms and lower legs
- Size varies from a few millimetres to several centimetres in diameter.
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
Read Also: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Basal Cell Carcinoma Stages
There are certain features that are considered to make the cancer at higher risk for spreading or recurrence, and these may also be used to stage basal cell carcinomas. These include:
- Greater than 2 mm in thickness
- Invasion into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin
- Invasion into the tiny nerves in the skin
- Location on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip
After the TNM components and risk factors have been established, the cancer is given a stage. For basal cell carcinoma staging, the factors are grouped and labeled 0 to 4. The characteristics and stages of basal cell carcinoma are:
Stage 0: Also called carcinoma in situ, cancer discovered in this stage is only present in the epidermis and has not spread deeper to the dermis.
Stage 1 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer is less than 2 centimeters, about 4/5 of an inch across, has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs, and has one or fewer high-risk features.
Stage 2 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer is larger than 2 centimeters across, and has not spread to nearby organs or lymph nodes, or a tumor of any size with 2 or more high-risk features.
Stage 3 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer has spread into facial bones or 1 nearby lymph node, but not to other organs.
Stage 4 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer can be any size and has spread to 1 or more lymph nodes which are larger than 3 cm and may have spread to bones or other organs in the body.
Dont Miss: What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Head And Neck
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Symptoms
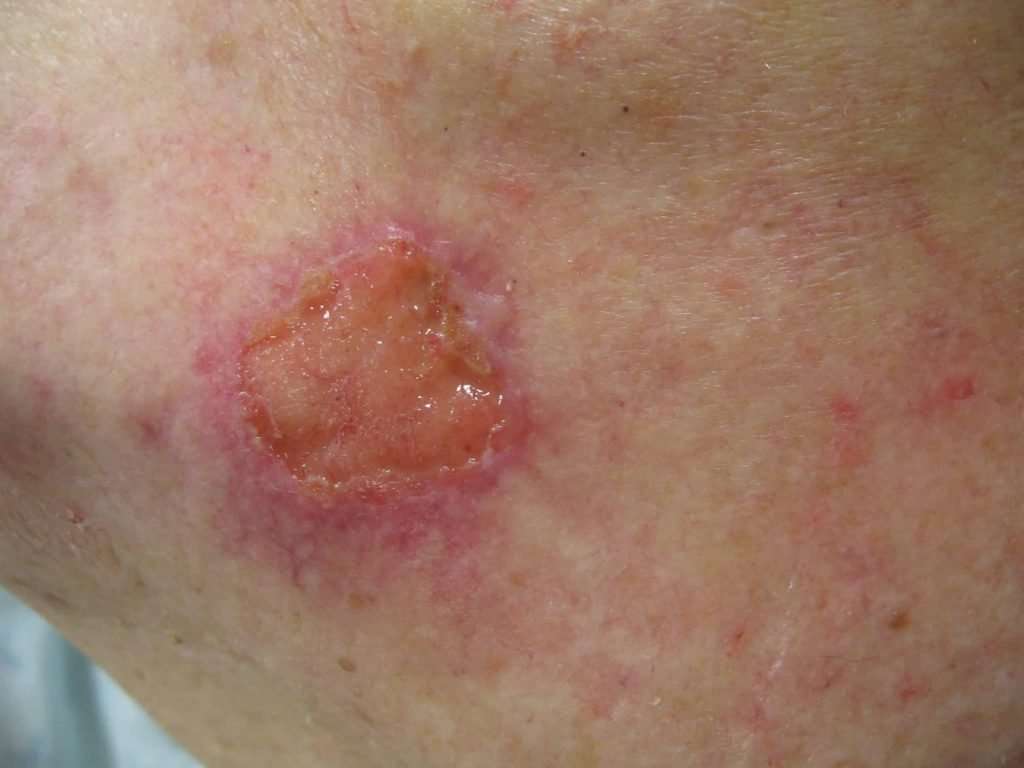
Squamous cell cancer can keratinize and blacken.
Squamous cell carcinoma is most likely to be found on an area that is exposed to the sun such as your scalp, arms, back of the hands, ears or lips. However, it can also occur in areas such as inside your mouth, on your anus and on your genitals.
Distinguishing marks of squamous cell carcinoma could include:
- A firm, red nodule
- A flat sore with a scaly crust
- A new sore or raised area on an old scar or ulcer
- A rough, scaly patch on your lip that may grow into an open sore
- A red sore or rough patch inside your mouth
- A red, raised patch or wart-like sore on or in the anus or on your genitals
Also Check: Basal Cell Carcinoma Etiology
Scc Is Mainly Caused By Cumulative Uv Exposure Over The Course Of A Lifetime
If youve had a basal cell carcinoma you may be more likely to develop a squamous cell skin carcinoma, as is anyone with an inherited, highly UV-sensitive condition such as xeroderma pigmentosum.
Chronic infections, skin inflammation, HIV and other immune deficiency diseases, chemotherapy, anti-rejection drugs used in organ transplantation, and excessive sun exposure can all lead to a risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
Occasionally, squamous cell carcinomas arise spontaneously on what appears to be normal, healthy skin. Some researchers believe the tendency to develop these cancers can be inherited.
SCCs may occur on all areas of the body including the mucous membranes and genitals, but are most common in areas frequently exposed to the sun:
- Ears
- Previous BCC or SCC
- Chronic inflammatory skin conditions or chronic infections
But anyone with a history of substantial sun exposure is at increased risk. Those whose occupations require long hours outside or who spend their leisure time in the sun are also at risk.