There Are Different Types Of Cancer That Start In The Skin
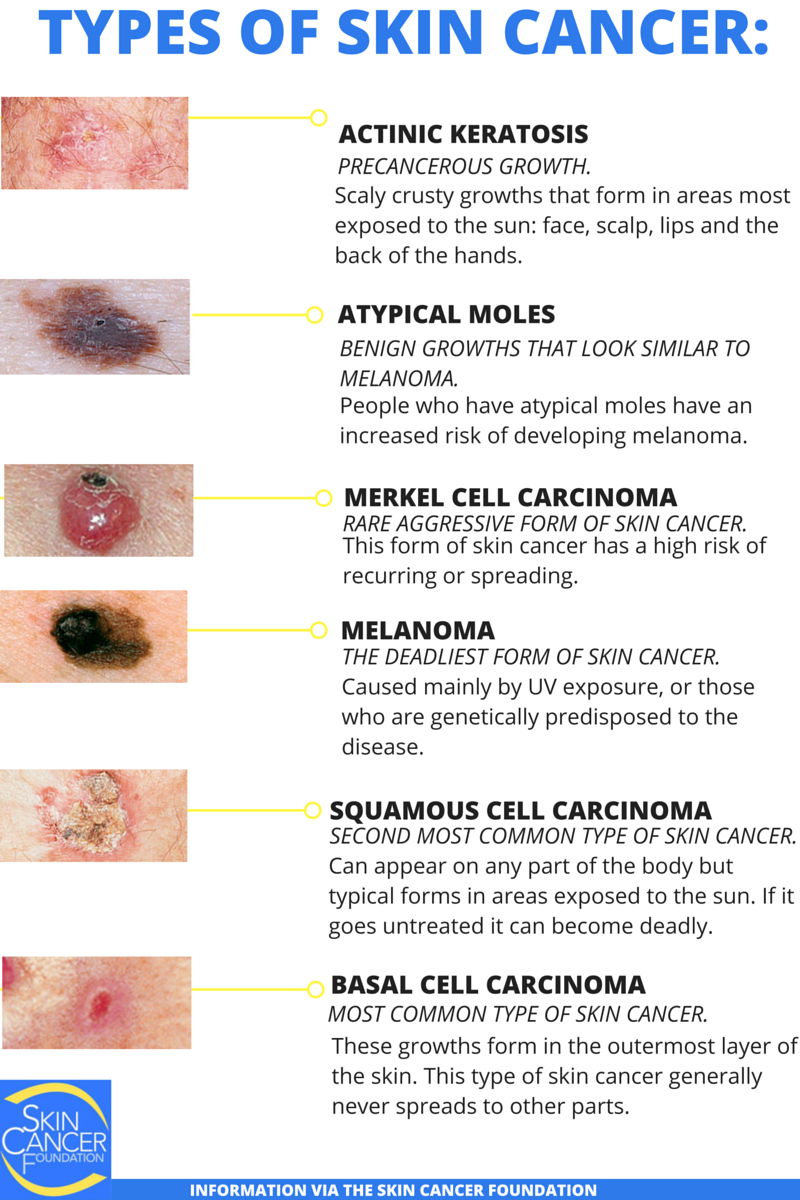
There are two main forms of skin cancer: melanoma and nonmelanoma.
Melanoma is a rare form of skin cancer. It is more likely to invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body than other types of skin cancer. When melanoma starts in the skin, it is called cutaneous melanoma. Melanoma may also occur in mucous membranes . This PDQ summary is about cutaneous melanoma and melanoma that affects the mucous membranes.
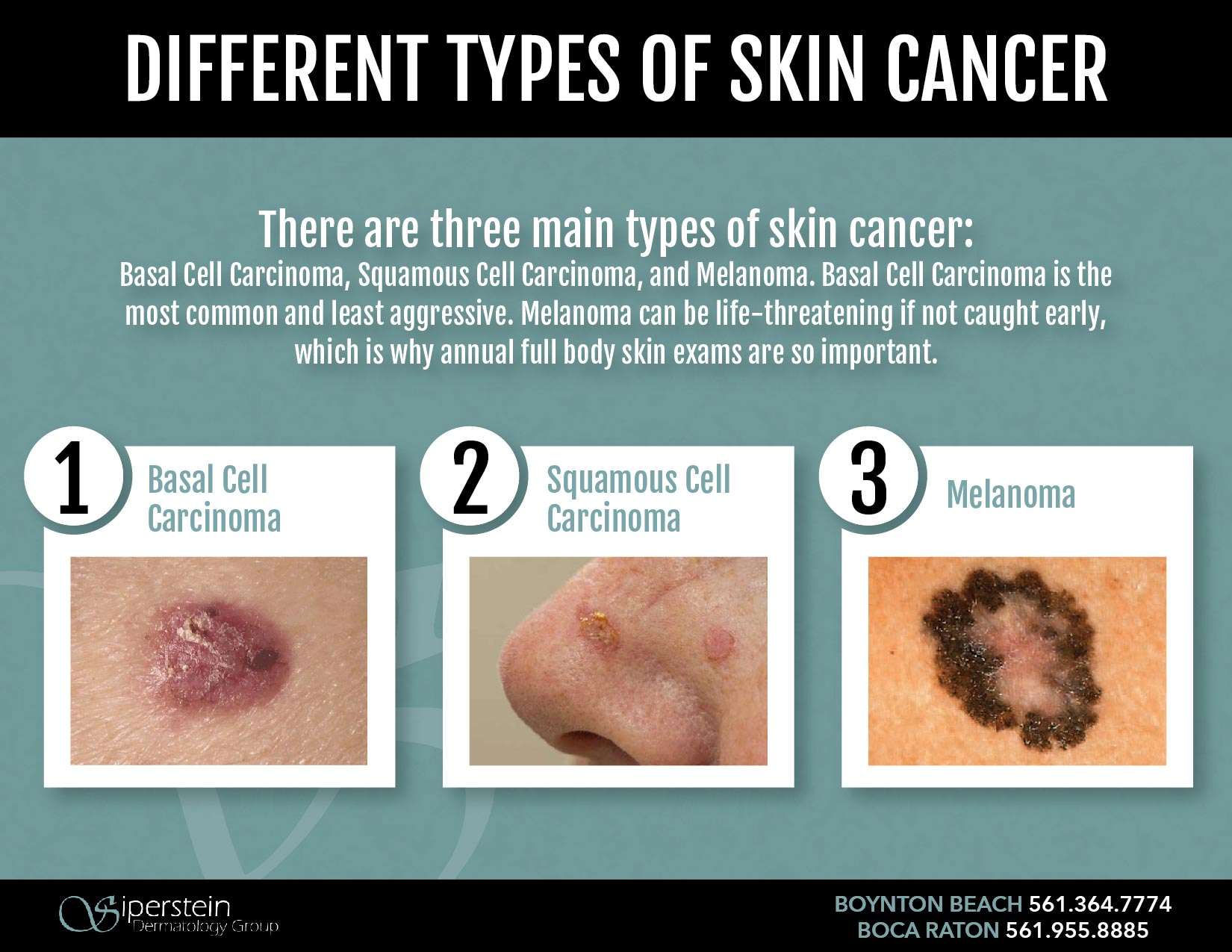
The most common types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. They are nonmelanoma skin cancers. Nonmelanoma skin cancers rarely spread to other parts of the body.
What Are The Signs Of Lentigo Maligna Melanoma
Lentigo maligna melanoma appears as a large, tan patch with an uneven border.3,4 It is initially flat and may look like a stain on the skin.3,4 This type of cancer generally takes 5 to 15 years to become invasive. Bumpiness may be a sign that it has invaded deeper layers of skin. Only 3% to 5% of these cancers become invasive.3
The large size of the lesion makes it difficult to remove these tumors. They often come back after treatment: the recurrence rate is 8-50%.3 Furthermore, removing large areas of skin can be disfiguring.3 For this reason, these lesions are sometimes removed with Mohs surgery.
Early Warning Signs Of Melanoma
The key to detecting melanoma early is to know what to look for and where to look for it. This isnt always easy, as melanoma can be a master of disguise. It may look like an age spot, a bruise, a sore, a cyst, a scar or a dark line beneath your nail. You may not feel a melanoma, but there are times that it may itch, hurt or bleed.
The ABCDE method may help you determine whether an abnormal skin growth may be melanoma:
- A is for asymmetry: Does the mark look different on each half?
- B is for border: Are the edges jagged or irregular?
- C is for color: Is your lesion uneven in color with specks of black, brown and tan?
- D is for diameter: Is your lesion getting larger?
- E is for evolving or elevation: Has your lesion changed in size, shape or texture over the past few weeks or months?
If the answer to any of these questions is yes, or even maybe, see a dermatologist for a proper evaluation. The only way to be sure whether a mole is melanoma is to visit a doctor.
Other melanoma warning signs may include:
- Sores that dont heal
- Pigment, redness or swelling that spreads outside the border of a spot to the surrounding skin
- Itchiness, tenderness or pain
Read Also: How Can You Tell If You Have Skin Cancer
What Are The Types Of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer, the abnormal growth of skin cells that mostly develops on the skin caused by sun exposure. But this cancer may also occur on areas of your skin not ordinarily exposed to sunlight. Skin cancer is common cancer in the United States, affecting more than 3.5 million individuals every year. According to the Cancer Treatment Centers of America ,physicians treat cancer every day, giving them the knowledge and experience to help a person make informed decisions about care.
There are two categories of Skin cancer and are Non-melanoma and Melanoma skin cancers. Non-melanoma skin cancer such as basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, do not spread and may require little more than minor surgery or treatment. Whereas melanoma skin cancer, which accounts for about 2 percent of all skin cancers but is responsible for most skin cancer deaths, will spread through the lymphatic system or bloodstream to other organs.
In this article, we will cover related topics such as skin cancer symptoms, its stages, causes, types, treatments, who can easily get skin cancer, and its prevention.
Surgery For Skin Cancer
Small skin cancer lesions may be removed through a variety of techniques, including simple excision , electrodesiccation and curettage , and cryosurgery .
Larger tumors, lesions in high-risk locations, recurrent tumors, and lesions in cosmetically sensitive areas are removed by a technique called Mohs micrographic surgery. For this technique, the surgeon carefully removes tissue, layer by layer, until cancer-free tissue is reached.
Malignant melanoma is treated more aggressively than just surgical removal. To ensure the complete removal of this dangerous malignancy, 1-2 cm of normal-appearing skin surrounding the tumor is also removed. Depending on the thickness of the melanoma, neighboring lymph nodes may also be removed and tested for cancer. The sentinel lymph node biopsy method uses a mildly radioactive substance to identify which lymph nodes are most likely to be affected.
Continued
Also Check: How Can Skin Cancer Kill You
Who Is At Risk
Much like with BCC, the more time you spend in the sun, the more at risk you are for developing SCC. About 90% of nonmelanoma skin cancers are caused by sun exposure, and people who have tanned indoors have a 67% higher risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma.
Your risk for SCC is higher if you:
- Have a history of skin cancer
- Have a history of unprotected exposure to the sun or tanning beds
- Have a weakened immune system due to a chronic condition or medication
- Are over age 50
- Have a history of chronic skin infections, precancerous skin growths or human papillomavirus
Keeping Cancer In Check
Chronic exposure to the sun or intermittent sunburns can lead to skin cancer. Skin cancer risk doubles with five or more sunburns in a lifetime, but just one bad sunburn can double the risk of melanoma. While skin cancer is uncommon in African Americans, Latinos and Asians, it can also be more deadly because they are often diagnosed later in the course of the disease.
Its important to examine your skin regularly. You should report any changes in an existing mole or any new moles to your physician. People with fair complexions have the highest risk of developing skin cancer, but everyone should avoid the sun and practice safety measures to protect their skin.
The American Cancer Society recommends the Slip, Slop, Slap and Wrap policy. When you go out in the sun, slip on a shirt, slop on sunscreen, slap on a hat and wrap on sunglasses to protect your eyes and the sensitive skin around them.
Exposure to the UV rays of tanning lamps is not safe. Tanning lamps give out UV rays, which can cause long-term skin damage and can contribute to skin cancer. Tanning bed use has been linked with an increased risk of melanoma, especially for people under 30. Most doctors and health organizations recommend not using tanning beds and sun lamps.
Also Check: What Is The Best Treatment For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Recommended Reading: Can Children Get Skin Cancer
Four Main Types Of Skin Melanoma
There are four main types of skin melanoma.
Amelanotic Melanoma Risk Factors
Though these risk factors dont mean someone will develop melanoma, they are linked with increased risk of all forms of the cancer, including amelanotic melanoma.
Exposure to UV rays: Damage to DNA in your skin cells, from exposure to UV rays , is the No. 1 risk factor for all types of melanoma. Both natural sunlight and artificial tanning lamps increase the risk of developing this type of skin cancer. Getting many sunburns during childhood also has been associated with the development of melanoma on the chest, back and legs.
Moles: If you have a lot of moles or have atypical moles, youre at greater risk of developing melanoma. Additionally, patients with the inherited condition dysplastic nevus syndrome are at a high risk of developing melanoma during their lifetime.
Fair skin: People who have light-colored, freckled skin and blond or red hair with blue or green eyes are at a greater risk of developing melanoma. This is especially true if your skin tends to burn as opposed to tanning when exposed to UV rays.
Race: Melanoma is 20 times more likely for white people than it is for black people, according to the American Society of Clinical Oncology .
Family and personal history: If your close relatives have a history of melanoma, youre at increased risk. If youve previously had melanoma or another type of skin cancer, the chance of developing it again is also greater.
Read Also: Can You Survive Stage 4 Melanoma Cancer
Can Changing My Diet Help Prevent Melanoma
The American Cancer Society advocates eating a plant-based diet over an animal-based diet as part of a healthy plan to avoid all cancers. Growing evidence suggests that plants pack a powerful punch in any fight against cancer because they’re nutritious, cholesterol-free and fiber-rich.
Theres no doubt that a healthy diet can protect your immune system. Having a strong immune system is important to help your body fight disease. Some research has shown that a Mediterranean diet is a healthy choice that may help prevent the development of cancer. Talk to your healthcare provider about the role food plays in lowering your cancer risks.
Some skin and immune-system healthy foods to consider include:
- Daily tea drinking: The polyphenols in tea help strengthen your immune system. Green tea contains more polyphenols than black tea.
- High vegetable consumption: Eating carrots, cruciferous and leafy vegetables is linked to the prevention of cutaneous melanoma.
- Weekly fish intake: Study participants who ate fish weekly seemed to avoid developing the disease when compared to those who did not eat fish weekly.
What Happens If Basal Cell Carcinoma Is Left Untreated
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer, and it is considered very low risk for metastasizing and spreading to other parts of the body. It is typically very slow-progressing and is usually diagnosed and treated in very early stages. If left untreated, basal cell carcinomas can be locally destructive to the tissues where it grows, and it can invade deeper structures such as nerves, cartilage, and even bone. In most cases, basal cell carcinoma develops on the face, ears, neck, head, shoulders, hands, and other areas that receive frequent sun exposure. The tumors may look like raised bumps on the skin that are usually smooth and pearly/shiny in appearance. Blood vessels can sometimes be seen within the lesions, and in some cases, a wound may form and bleed easily.
Also Check: What Are The Different Types Of Melanoma Skin Cancer
There Are Three Ways That Cancer Spreads In The Body
Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood:
- Tissue. The cancer spreads from where it began by growing into nearby areas.
- Lymph system. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the lymph system. The cancer travels through the lymph vessels to other parts of the body.
- Blood. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through the blood vessels to other parts of the body.
Patients Can Enter Clinical Trials Before During Or After Starting Their Cancer Treatment
Some clinical trials only include patients who have not yet received treatment. Other trials test treatments for patients whose cancer has not gotten better. There are also clinical trials that test new ways to stop cancer from recurring or reduce the side effects of cancer treatment.
Clinical trials are taking place in many parts of the country. Information about clinical trials supported by NCI can be found on NCIs clinical trials search webpage. Clinical trials supported by other organizations can be found on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
You May Like: What Is Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma
What Is A Melanocyte
Melanocytes are skin cells found in the upper layer of skin. They produce a pigment known as melanin, which gives skin its color. There are two types of melanin: eumelanin and pheomelanin. When skin is exposed to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or tanning beds, it causes skin damage that triggers the melanocytes to produce more melanin, but only the eumelanin pigment attempts to protect the skin by causing the skin to darken or tan. Melanoma occurs when DNA damage from burning or tanning due to UV radiation triggers changes in the melanocytes, resulting in uncontrolled cellular growth.
About Melanin
Naturally darker-skinned people have more eumelanin and naturally fair-skinned people have more pheomelanin. While eumelanin has the ability to protect the skin from sun damage, pheomelanin does not. Thats why people with darker skin are at lower risk for developing melanoma than fair-skinned people who, due to lack of eumelanin, are more susceptible to sun damage, burning and skin cancer.
Treatment Of Stage Ii Melanoma
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage II melanoma may include the following:
- Surgery to remove the tumor and some of the normal tissue around it. Sometimes lymph node mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy are done to check for cancer in the lymph nodes at the same time as the surgery to remove the tumor. If cancer is found in the sentinel lymph node, more lymph nodes may be removed.
- A clinical trial of new types of treatment to be used after surgery.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Read Also: Will Basal Cell Carcinoma Kill You
Melanoma Is A Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In Melanocytes
The skin is the bodys largest organ. It protects against heat, sunlight, injury, and infection. Skin also helps control body temperature and stores water, fat, and vitamin D. The skin has several layers, but the two main layers are the epidermis and the dermis . Skin cancer begins in the epidermis, which is made up of three kinds of cells:
- Squamous cells: Thin, flat cells that form the top layer of the epidermis.
- Basal cells: Round cells under the squamous cells.
- Melanocytes: Cells that make melanin and are found in the lower part of the epidermis. Melanin is the pigment that gives skin its natural color. When skin is exposed to the sun or artificial light, melanocytes make more pigment and cause the skin to darken.
The number of new cases of melanoma has been increasing over the last 30 years. Melanoma is most common in adults, but it is sometimes found in children and adolescents.
For More Information About Skin Cancer
National Cancer Institute, Cancer Information Service Toll-free: 4-CANCER 422-6237TTY : 332-8615
Skin Cancer Foundation
Media file 1: Skin cancer. Malignant melanoma.
Media file 2: Skin cancer. Basal cell carcinoma.
Media file 3: Skin cancer. Superficial spreading melanoma, left breast. Photo courtesy of Susan M. Swetter, MD, Director of Pigmented Lesion and Cutaneous Melanoma Clinic, Assistant Professor, Department of Dermatology, Stanford University Medical Center, Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System.
Media file 4: Skin cancer. Melanoma on the sole of the foot. Diagnostic punch biopsy site located at the top. Photo courtesy of Susan M. Swetter, MD, Director of Pigmented Lesion and Cutaneous Melanoma Clinic, Assistant Professor, Department of Dermatology, Stanford University Medical Center, Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System.
Media file 5: Skin cancer. Melanoma, right lower cheek. Photo courtesy of Susan M. Swetter, MD, Director of Pigmented Lesion and Cutaneous Melanoma Clinic, Assistant Professor, Department of Dermatology, Stanford University Medical Center, Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System.
Continued
Media file 6: Skin cancer. Large sun-induced squamous cell carcinoma on the forehead and temple. Image courtesy of Dr. Glenn Goldman.
Also Check: How To Know Skin Cancer Symptoms
Treatments For Amelanotic Melanoma
Treatment for all melanomas depends on the staging and is tailored to your symptoms. Your doctor works with you in a process called shared decision-making to determine the best course of treatment depending on your situation and goals.
One, or a combination, of the following treatments may be recommended:
Surgery is the most common treatment for melanoma and typically removes the cancerous tumor as well as a small amount of healthy surrounding tissue, called a margin. Wide excision involves removal of the primary melanoma and may include a skin graft. Lymph node dissection to remove the affected lymph nodes may be done if cancer is found during SLNB testing.
Radiation therapy, which uses high-dose energy rays to kill cancer cells, may be used as treatment to prevent your melanoma from recurring, to manage symptoms if its spread to your bones, and when the cancer has spread to a large area of lymph nodes or skin that cannot be treated surgically.
Immunotherapy augments the bodys immune system, boosting your ability to fight the cancer. Treatments include: PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors, CTLA-4 inhibitors, Interleukin-2, Interferon and virus therapy.
Targeted therapy targets the genes, proteins or tissue environment that is causing your cancer to flourish. It helps prevent the growth of cancer cells by blocking the pathways necessary for melanomas to grow. Targeted therapy includes: BRAF inhibitors, MEK inhibitors, KIT inhibitors and tumor-agnostic treatment.
Expert