How Is Melanoma Diagnosed
If you have a mole or other spot that looks suspicious, your doctor may remove it and look at it under the microscope to see if it contains cancer cells. This is called a biopsy.
After your doctor receives the skin biopsy results showing evidence of melanoma cells, the next step is to determine if the melanoma has spread. This is called staging. Once diagnosed, melanoma will be categorized based on several factors, such as how deeply it has spread and its appearance under the microscope. Tumor thickness is the most important characteristic in predicting outcomes.
Melanomas are grouped into the following stages:
- Stage 0 : The melanoma is only in the top layer of skin .
- Stage I: Low-risk primary melanoma with no evidence of spread. This stage is generally curable with surgery.
- Stage II: Features are present that indicate higher risk of recurrence, but there is no evidence of spread.
- Stage III: The melanoma has spread to nearby lymph nodes or nearby skin.
- Stage IV: The melanoma has spread to more distant lymph nodes or skin or has spread to internal organs.
How Serious Is My Cancer
If you have melanoma, the doctor will want to find out how far it has spread. This is called staging. Your doctor will want to find out the stage of your cancer to help decide what type of treatment is best for you.
The stage describes the growth or spread of the melanoma through the skin. It also tells if it has spread to other parts of your body.
Your cancer can be stage 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4. The lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. A higher number, like stage 4, means a more serious cancer that has spread beyond the skin. Be sure to ask the doctor about the cancer stage and what it means for you.
Metastatic Behavior In Melanoma: Timing Pattern Survival And Influencing Factors
Faruk Tas
1Institute of Oncology, Istanbul University, 34390 Istanbul, Turkey
Abstract
Metastatic melanoma is a fatal disease with a rapid systemic dissemination. This study was conducted to investigate the metastatic behavior, timing, patterns, survival, and influencing factors in MM. 214 patients with MM were evaluated retrospectively. Distant metastases were the most frequent for patients initially metastatic. The median and 1-year survival rates of initially MM patients were 10 months and 41%, respectively. The median time to metastasis for patients with localized disease was 28 months. The timing of appearance of metastases varied minimally however, times to metastases for distant organs varied greatly. For the first metastatic pathway, more than half of the primary metastases were M1A . These findings were in contrast to the results compared with those with metastatic in diagnosis . The median and 1-year survival rates of all patients were 12 months and 49%, respectively. Outcome was higher in M1A than visceral metastases . In conclusion, the fact that over half of all recurrences/metastases occurred within 3 years urges us to concentrate follow-up in the early time periods following diagnosis. Because the clinical behavior of MM is variable, the factors for survival consisting of site and number of metastases should be emphasized.
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
3.1. Metastases at Presentation
3.2. Metastases during Follow-Up
| From |
4. Discussion
Also Check: Is Melanoma Caused By Sun Exposure
Risk Factors For Metastatic Melanomas
You cannot get metastatic melanoma without first having melanoma, though the primary melanoma may be so small its undetectable. Major risk factors for melanomas include:
- Light skin, light-colored hair or light-colored eyes
- Skin prone to burning easily
- Multiple blistering sunburns as a child
- Family history of melanoma
- Frequent exposure to sun or ultraviolet radiation
- Certain genetic mutations
- Exposure to environmental factors, such as radiation or vinyl chloride
Other factors have been connected with increased metastasis. In a 2018 study in the Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia and a 2019 study in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, the following factors were associated with higher levels of metastasis:
- Male gender
- Primary tumor thickness of more than 4 mm
- Nodular melanoma, which is a specific subtype that a care team would identify
- Ulceration of the primary tumor
Complementary And Alternative Treatments
It’s common for people with cancer to seek out complementary or alternative treatments. When used alongside your conventional cancer treatment, some of these therapies can make you feel better and improve your quality of life. Others may not be so helpful and in some cases may be harmful. It is important to tell all your healthcare professionals about any complementary medicines you are taking. Never stop taking your conventional treatment without consulting your doctor first.All treatments can have side effects. These days, new treatments are available that can help to make many side effects much less severe than they were in the past.
Read Also: How Can You Detect Skin Cancer
Where Does Melanoma Spread To
Unfortunately, melanoma can potentially to many places in the body. One of the reasons melanoma is so serious is that it can get into the lymph nodes and the bloodstream, and spread from there to the vital organs. Consequently, cancer that develops in a mole on your back, for example, can migrate to your brain, lungs, bones, liver, or other organs and areas.
As to the question of, Where does melanoma spread to first? that depends on a variety of factors including where it develops initially.
Many Melanomas Dont Require Immediate Treatment
Many people have this concept that all melanomas are extremely rapidly growing cancers, says Dr. Marghoob. They think that waiting even one day after the diagnosis of melanoma can be fatal.
While some subtypes of melanoma do grow extremely fast, says Dr. Marghoob, most early melanomas dont require immediate treatment, allowing ample time to detect, treat, and cure them. Dr. Marghoob advises checking your skin on a monthly basis. If you notice a changing spot on your skin, dont delay in getting it checked out by a dermatologist, he says. And if your doctor does think you may have a melanoma, know that for most people its not necessary to rush to treatment. Most people can take the time they need to meet with doctors and understand their options.
Don’t Miss: How Dangerous Is Melanoma Skin Cancer
How Dangerous Is Melanoma Its All A Matter Of Timing
Skin cancer holds the unfortunate distinction of being the worlds most common cancer. Though its prevalence around the globe is disturbing, there is some good news: When caught early, skin cancers are almost always curable.
You might already know that catching a cancer early means a more favorable prognosis. But it can be difficult to comprehend just how big a difference early detection makes with melanoma, the most dangerous form of skin cancer. Melanoma should never be underestimated, but treating a tumor early rather than after it is allowed to progress could be lifesaving.
Leland Fay, 46, understands better than most the seriousness of this distinction. When the Monument, Colorado native was diagnosed with melanoma in 2012, he was given a bleak prognosis due to the advanced stage of the tumor it had already reached stage IV.
Leland hadnt thought much of the little black mole on his head a few months earlier, when a dermatologist froze it off during a routine exam. But the mole resurfaced, bigger than it had been originally. After a biopsy and imaging tests, doctors told Leland it was melanoma, and that it had already spread. He could have as few as six weeks to live.
To fully comprehend the significance of timing, it can be helpful to understand exactly what happens to a melanoma when it advances to a later stage, and what it means when a melanoma spreads beyond the original tumor site.
How Is Melanoma Treated When It Spreads To The Brain
Scientists have learned that attacking this cancer with different types of treatment can improve how well each individual treatment works.
According to the Emory Medical Center, doctors used this approach to treat Mr. Carter. His treatment began with surgery. This was followed by radiation therapy and immunotherapy .
Keep all of your follow-up appointments
Research shows that the earlier melanoma is found in the brain, the more effective treatment can be.
When melanoma spreads to the brain, the treatment plan may include:
Surgery: Doctors may recommend surgery to:
-
Remove the tumor.
-
Reduce the size of a tumor. This can make other treatments more effective.
-
Take out some of the tumor so that it can be examined. This allows your doctors to choose the medication most likely to help.
-
Relieve symptoms, such as headaches.
While surgery can remove existing tumors, other treatment often follows. This approach helps to kill cancer cells that surgery cannot remove.
Following surgery, you may be treated with radiation, medication, or both.
Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy helps to kill cancer cells that are too small to be seen. It may also be a treatment option when several tumors have formed in the brain or surgery is too risky.
Two types of radiation therapy are used to treat melanoma in the brain:
The type of radiation used depends on many considerations, including the number of tumors and where they appear in the brain.
Supportive care can:
Also Check: What Is Malignant Skin Cancer
Symptoms Of Metastatic Cancer
Metastatic cancer does not always cause symptoms. When symptoms do occur, what they are like and how often you have them will depend on the size and location of the metastatic tumors. Some common signs of metastatic cancer include:
- pain and fractures, when cancer has spread to the bone
- headache, seizures, or dizziness, when cancer has spread to the brain
- shortness of breath, when cancer has spread to the lung
- jaundice or swelling in the belly, when cancer has spread to the liver
How Fast Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
Squamous cell carcinoma rarely metastasizes , and when spreading does occur, it typically happens slowly. Indeed, most squamous cell carcinoma cases are diagnosed before the cancer has progressed beyond the upper layer of skin. There are various types of squamous cell carcinoma and some tend to spread more quickly than others.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does It Take To Get Melanoma Biopsy Results
Biological Therapies And Melanoma
Biological therapies are treatments using substances made naturally by the body. Some of these treatments are called immunotherapy because they help the immune system fight the cancer, or they occur naturally as part of the immune system. There are many biological therapies being researched and trialled, which in the future may help treat people with melanoma. They include monoclonal antibodies and vaccine therapy.
Clinical Staging Of Melanoma
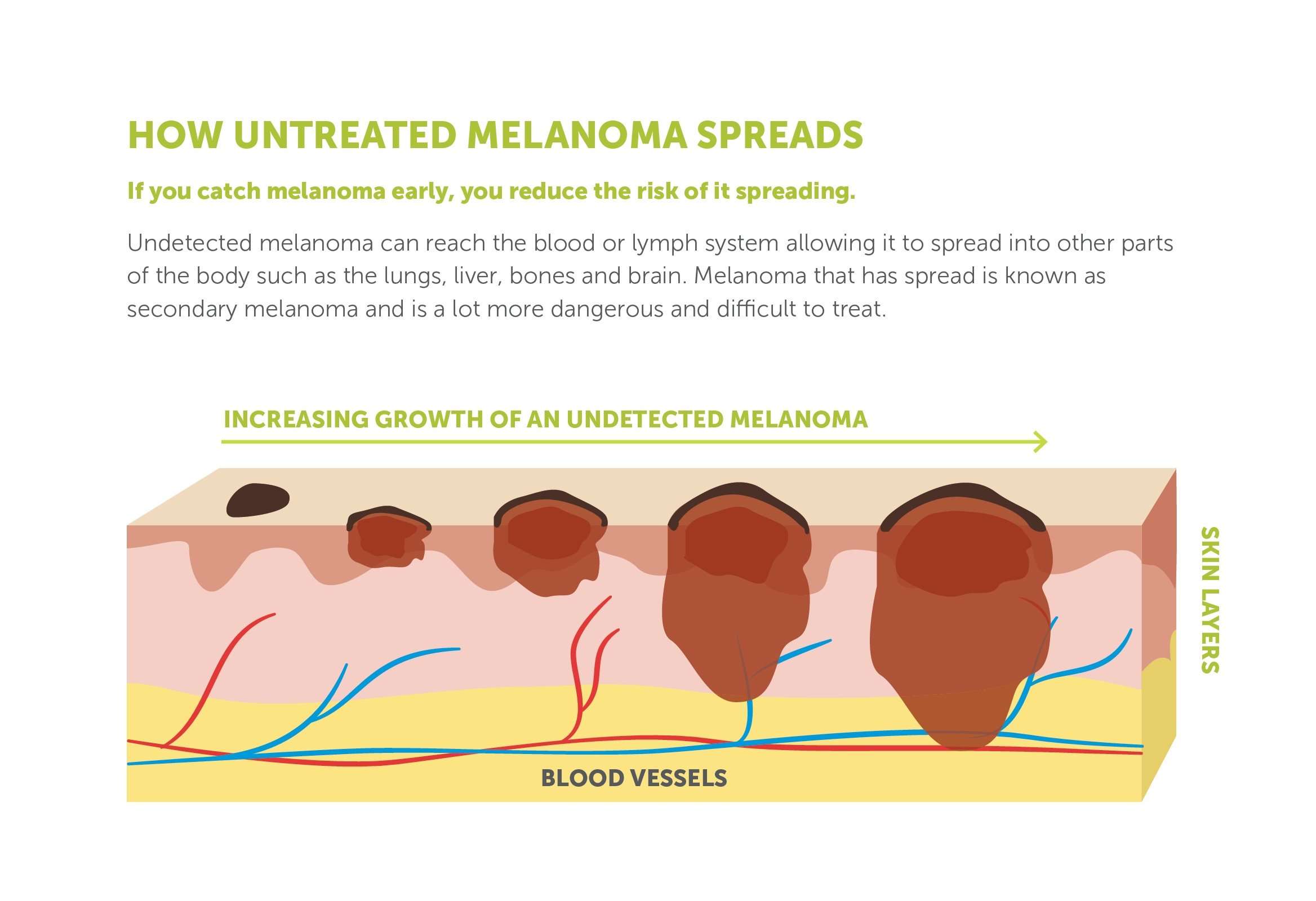
Clinical staging is assessed by your doctor after examining your lymph nodes.
| Melanoma stage | ||
|---|---|---|
| Melanoma only found in the top layer of skin. | No further investigation or treatment is needed. | |
| Stage I | A thin melanoma that has invaded less than 2 mm into the skin. There is no sign of spread to lymph nodes or other parts of the body. | No further investigation or treatment is needed. |
| Stage II | Melanoma has grown thicker and is more than 2 mm in thickness. There is no sign of spread to lymph nodes or other parts of the body. | No further investigation or treatment is needed. |
| Stage III | Melanoma can be any thickness but it has spread to involve nearby lymph nodes or melanoma has been found on nearby skin . | Further surgery is undertaken to cut out the lymph nodes and any melanoma in the nearby skin. |
| Stage IV | Melanoma has spread to other parts of the body such as the lungs, brain or skin far away from the original site. These are melanoma metastases | Further surgery is undertaken if possible to cut out melanoma metastases. Additional treatment with radiotherapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy or targeted therapy drugs may be offered to fight or kill the cancer cells. |
When melanoma is removed at its earliest stage , the cure rate is almost 100%. If melanoma is successfully removed in stage I or II, over 90% of people make a full recovery.
Stage III and IV melanoma are called advanced melanoma.
Don’t Miss: What Is Stage 2 Melanoma Skin Cancer
Melanoma Can Be Colorless
While its true that many melanomas are dark brown to black in color, some melanomas have no color and appear as pink spots or bumps. Beware of isolated pink spots, especially if the spot looks different than the other marks on the skin, says Dr. Marghoob. Pay attention to any spot or mark that has an uneven texture, shape, border, or distribution of colors. In addition, any spot that has changed in some way should prompt a visit to your local doctor.
Signs And Symptoms Of Melanoma
The most common sign of melanoma is the appearance of a new mole or a change in an existing mole.
This can happen anywhere on the body, but the most commonly affected areas are the back in men and the legs in women.
Melanomas are uncommon in areas that are protected from sun exposure, such as the buttocks and the scalp.
In most cases, melanomas have an irregular shape and are more than 1 colour.
The mole may also be larger than normal and can sometimes be itchy or bleed.
Look out for a mole that gradually changes shape, size or colour.
Superficial spreading melanoma are the most common type of melanoma in the UK.
They’re more common in people with pale skin and freckles, and much less common in people with darker skin.
They initially tend to grow outwards rather than downwards, so they do not pose a problem.
But if they grow downwards into the deeper layers of skin, they can spread to other parts of the body.
You should see a GP if you have a mole that’s getting bigger, particularly if it has an irregular edge.
Read Also: Does Skin Cancer Make You Tired
Comparing Metastatic Melanoma Cells In Lymph Versus Blood
Most studies of cancer cell metastasis in people have focused on cells circulating in the blood. Thats because its much easier to collect patient blood samples than it is to collect samples of lymph, the clear fluid that carries immune cells through vessels of the lymphatic system, Dr. Morrison said.
Dr. Morrisons team found that human melanoma cells injected into lymph nodes in the mice were more likely to form distant tumors than melanoma cells injected into blood.
To study the role of lymph in metastasis, lead investigator Jessalyn Ubellacker, Ph.D., a postdoctoral researcher in Dr. Morrisons lab, figured out how to collect melanoma cells from lymph in mice. This allowed the team to do the first side-by-side comparison of melanoma cells spreading through lymph and through blood in the same animal, Dr. Morrison said.
Next the team found that melanoma cells in lymph experienced less oxidative stress than melanoma cells in blood. That offered a potential explanation for why melanoma cells from lymph nodes were surviving better and better able to form a tumor, Dr. Morrison said.
Further experiments showed that melanoma cells in blood are vulnerable to ferroptosisa form of cell death that occurs when lipids damaged by oxidative stress build up in the outer membrane of a cell. By contrast, melanoma cells from lymph nodes were protected from ferroptosis.
The 4 Stages Of Melanoma
Two main things determine the stage of melanoma: The thickness or depth of the tumor and how far it has spread when its diagnosed, explains David Polsky, M.D., dermatologist at NYU Langone Medical Center in New York City. In stages 0, 1, and 2, the melanoma is limited to the skin. In stage 3, its spread to the lymph nodes, small structures throughout your body that help filter fluids and fight infection. In the most advanced stage, stage 4, melanoma cells have broken away from the original tumor, traveled through the body and formed a new tumor somewhere else.
Read Also: Can You Get Skin Cancer From Radiation Treatments
What About Other Treatments That I Hear About
When you have cancer you might hear about other ways to treat the cancer or treat your symptoms. These may not always be standard medical treatments. These treatments may be vitamins, herbs, special diets, and other things. You may wonder about these treatments.
Some of these are known to help, but many have not been tested. Some have been shown not to help. A few have even been found to be harmful. Talk to your doctor about anything youre thinking about using, whether its a vitamin, a diet, or anything else.
Has My Melanoma Spread
Author: Vanessa Ngan, Staff Writer Copy Editor: Clare Morrison Chief Editor: Dr Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand, October 2013. About Melanoma is sponsored by the New Zealand Dermatological Society Incorporated.
open
App to facilitate skin self-examination and early detection. Read more.
So youve been to your doctor and your pathology report has come back positive for melanoma. Looking on the bright side, youve now got a diagnosis and can move forward and plan your road to recovery.
What happens next depends very much on how deeply your melanoma has grown into the skin and whether or not melanoma cancer cells have spread to other parts of your body. Your pathology report refers to this as the pathological stage of melanoma and it helps in planning the next steps.
Your doctor will examine your lymph nodes. If they are enlarged, a sample may be taken using a fine needle .
If they are not enlarged, sentinel node biopsy may be recommended to find out if melanoma cells have spread to the lymph nodes.
Also Check: How Do You Know If You Have Melanoma
When Should I Call My Doctor
You should have a skin examination by a doctor if you have any of the following:
- A personal history of skin cancer or atypical moles .
- A family history of skin cancer.
- A history of intense sun exposure as a young person and painful or blistering sunburns.
- New or numerous large moles.
- A mole that changes in size, color or shape.
- Any mole that itches, bleeds or is tender.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Receiving a diagnosis of melanoma can be scary. Watch your skin and moles for any changes and seeing your doctor regularly for skin examinations, especially if youre fair-skinned, will give you the best chances for catching melanoma early when its most treatable.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 06/21/2021.
References