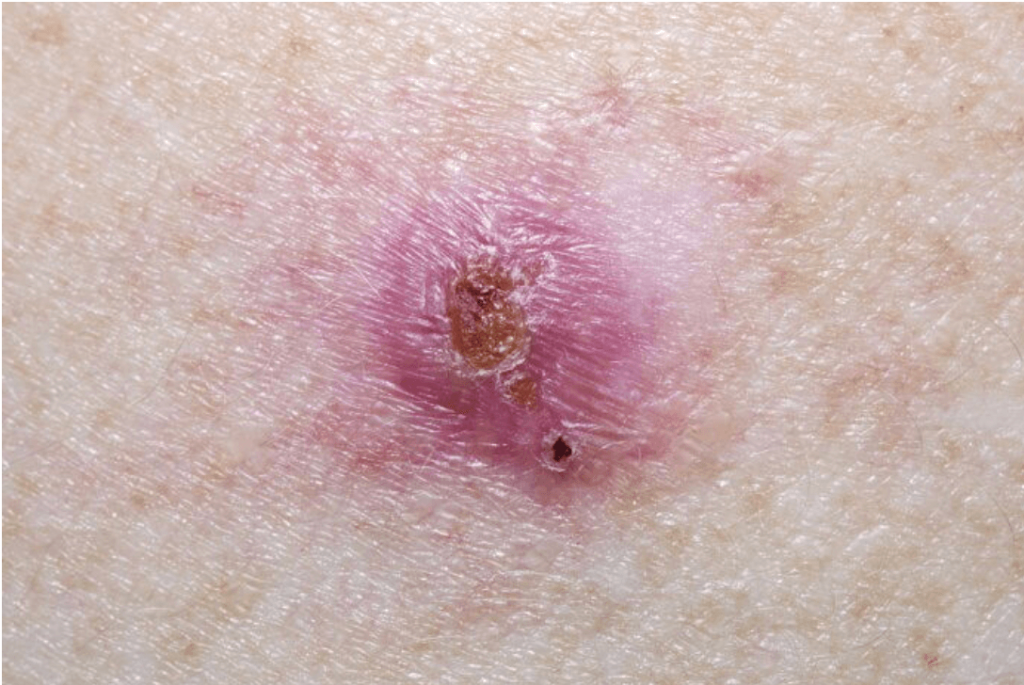
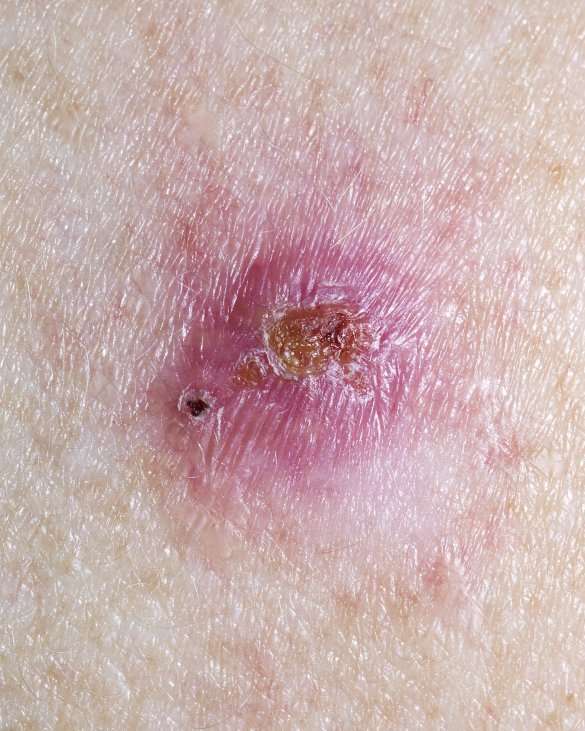
What Are The Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The first sign of an SCC is usually a thickened, red, scaly spot thatdoesnt heal. You are most likely to find an SCC on the back of your hands,forearms, legs, scalp, ears or lips. If its on your lips, it can look like asmall ulcer or patch of scaly skin that doesnt go away.
An SCC may also look like:
- a crusted sore
- a sore or rough patch inside your mouth
- a red, raised sore around your anus or genitals
An SCC will probably grow quickly over several weeks or months.
How Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated
It is usually possible to completely remove an SCC. The best type oftreatment for you will depend on the size of the SCC and where it is.
Usually, the doctor will remove an SCC using simple skin surgery. Theywill then look at the area under a microscope to check all the cancer has beenremoved. If it has spread, you might need radiotherapy afterwards.
Other ways of removing the SCC are:
- scraping it off then sealing the base of the wound with an electric needle or liquid nitrogen
- using a laser to burn the SCC away
- freezing it off
- Applying creams, liquids or lotions directly onto the SCC. Sometimes the doctor will shine a light on the area to make the medicine work
After treatment, you will need follow-up appointments with your doctor. You will be at greater risk of developing another skin cancer, so its more important than ever to protect your skin from the sun.
What Is The Treatment For Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Cutaneous SCC is nearly always treated surgically. Most cases are excised with a 310 mm margin of normal tissue around a visible tumour. A flap or skin graft may be needed to repair the defect.
Other methods of removal include:
- Shave, curettage, and electrocautery for low-risk tumours on trunk and limbs
- Aggressive cryotherapy for very small, thin, low-risk tumours
- Mohs micrographic surgery for large facial lesions with indistinct margins or recurrent tumours
- Radiotherapy for an inoperable tumour, patients unsuitable for surgery, or as adjuvant
Read Also: Does Skin Cancer Burn And Itch
How Dangerous Is Scc
While the majority of SCCs can be easily and successfully treated, if allowed to grow, these lesions can become disfiguring, dangerous and even deadly. Untreated SCCs can become invasive, grow into deeper layers of skin and spread to other parts of the body.
Did you know?
Americans die each year from squamous cell carcinoma
What About Other Treatments That I Hear About
When you have cancer you might hear about other ways to treat the cancer or treat your symptoms. These may not always be standard medical treatments. These treatments may be vitamins, herbs, special diets, and other things. You may wonder about these treatments.
Some of these are known to help, but many have not been tested. Some have been shown not to help. A few have even been found to be harmful. Talk to your doctor about anything youre thinking about using, whether its a vitamin, a diet, or anything else.
Read Also: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
How Serious Is A Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Id had a few skin cancers removed before, all basal cell carcinomas , the most common type. But when I was diagnosed with a squamous cell carcinoma on my scalp, it seemed different, and a little more scary. I asked C. William Hanke, MD, a Mohs surgeon at the Laser and Skin Surgery Center of Indiana and a senior vice president of The Skin Cancer Foundation, what we need to know about this second most common form of skin cancer.
Q: When people talk about nonmelanoma skin cancers, they tend to lump basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas together as the ones that are far less dangerous than melanoma. Should we take SCCs more seriously?
Dr. Hanke: Yes and no. BCCs hardly ever metastasize. Ive seen two cases in my entire career. But when SCCs that havent been treated early get big, then the chance of metastasis becomes real. Its uncommon, but its much more common than in BCC. We see it in our practice. But we dont want to scare people into thinking that just because they have squamous cell, Oh wow, Ive got a chance of metastasis. Remember, the rate is very low. Its just those big ones.
Q: OK, so its rare. But what happens when an SCC does spread?
Q: Whats the usual treatment for SCCs?
Q: How can we detect SCCs as early as possible?
What Is The Outlook For Someone Who Has Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin
When found early, this cancer is highly treatable. Left untreated, however, SCC can spread deep into the skin and travel to other parts of the body, making treatment difficult.
While treatment can remove the cancer, its important to know that this cancer can return. You also have a greater risk of developing another skin cancer.
Thats why self-care becomes so important after treatment for SCC of the skin. Youll find the self-care that dermatologists recommend at, Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: Self-care.
ImagesGetty Images
ReferencesAlam M, Armstrong A, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J Am Acad Dermatol 2018 78:560-78.
Anadolu-Brasie R, Patel AR, et al., Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. In: Nouri K, et al. Skin Cancer. McGraw Hill Medical, China, 2008: 86-114.
Marrazzo G, Zitelli JA, et al. Clinical outcomes in high-risk squamous cell carcinoma patients treated with Mohs micrographic surgery alone. J Am Acad Dermatol 2019 80:633-8.
Que SKT, Zwald FO, et al. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: Management of advanced and high-stage tumors. J Am Acad Dermatol 2018 78:249-61.
Ribero S, Stucci LS, et al. Drug therapy of advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: Is there any evidence? Curr Opin Oncol. 2017 29:129-35.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves cemiplimab-rwlc for metastatic or locally advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. New release issued 9/28/2018. Last accessed 1/13/2020.
Also Check: Stage Iii Melanoma Prognosis
What Do Cancer Survival Rates Mean
When learning about cancer survival rates, its important to keep in mind that these statistics are based on a very large and diverse group of people. Because no two people with squamous cell carcinoma are alike, the general survival rate cannot be used to predict a specific patients outcome. Additionally, survival rates are broad benchmarks. While useful as a baseline point of reference for physicians, this information is not detailed enough to reflect the different treatments people have had, nor is it recent enough to include the results of the latest breakthrough treatments now available to patients through clinical trials .
Also Check: What Does Negative For High Grade Urothelial Carcinoma Mean
Understanding Non Melanoma Skin Cancers
The prognosis for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma is usually good, but some patients have poor outcomes. To identify factors associated with poor outcomes, researchers conducted a 10-year retrospective cohort study that included 985 patients and 1,832 tumors. The majority of patients had one tumor, 21.2 percent of patients had two to four tumors, and a small percentage of patients had more than four tumors. Most were treated with standard excision and 20.2 percent were treated with Mohs surgery.
The data revealed that 4.6 percent of patients experienced local recurrence, 3.7 percent developed metastases, and 2.1 percent died from the disease. Upon analysis, one consistent predictor of poor outcome was tumor size of 2 cm or more. Multivariate risk analysis revealed that several specific disease factors were associated with metastasis and disease-specific death:
Also Check: Tumor Calcification
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- Do you know the stage of the cancer?
- If not, how and when will you find out the stage of the cancer?
- Would you explain to me what the stage means in my case?
- What will happen next?
There are many ways to treat skin cancer. The main types of treatment are:
- Surgery
- Immunotherapy
- Chemotherapy
Most basal cell and squamous cell cancers can be cured with surgery or other types of treatments that affect only the spot on the skin.
The treatment plan thats best for you will depend on:
- The stage and grade of the cancer
- The chance that a type of treatment will cure the cancer or help in some way
- Your age and overall health
- Your feelings about the treatment and the side effects that come with it
What Are The Most Common Skin Cancers
According to the Skin Cancer Foundation , squamous cell carcinoma is diagnosed in more than 1 million people in the U.S. every year, and is responsible for the deaths of more than 15,000 people. The SCF recommends an annual skin exam by a dermatologist, and you may need more frequent screening if you are at higher risk.
Read Also: Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
What Survival Rates Mean
The survival rate is the percentage of people who live for a certain period of time with this cancer. The number is based on research done on large groups of people with the same stage of cancer.
Experts dont know the exact survival numbers for late-stage SCC, because cancer registries dont track statistics for this cancer. However, your doctor may be able to give you an estimate of your prognosis.
When it comes to surviving cancer, everyone is different. Your outcome will depend on the specific treatments you have and how well you respond to them. Talk to your doctor about your outlook and what it means.
Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Be Prevented
The best way to prevent SCC is to avoid sunburn. Avoid going outin the sun when the UV Index is higher than 3, such as in the middle of theday. Seek shade, wear a hat, sunglasses and clothing that protects you from thesun, and always use an SPF30+ sunscreen. Do not go to tanningsalons.
If you are at very high risk of developing another skin cancer, yourdoctor may prescribe you specific vitamins.
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 3 Life Expectancy
Treating Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Most of squamous cell carcinomas can be cured if they are treated early. Once squamous cell carcinoma has spread beyond the skin, though, less than half of people live five years, even with aggressive treatment.
There are many ways to treat squamous cell carcinoma that has not spread. These include:
- cutting away the cancer and a small amount of healthy tissue around it. If a large area of skin is removed, a skin graft may be necessary.
- scraping away the cancer with a surgical tool. An electric probe is used to kill any cancerous cells left behind.
- freezing cancer cells with liquid nitrogen. This treatment is usually used only for very small tumors or for a patch of skin that looks abnormal but isn’t yet cancerous.
- destroying the tumor with radiation.
- shaving away the cancer, one thin layer at a time. Each layer is examined under the microscope as it is removed. This technique helps the doctor preserve as much healthy skin as possible.
- applying drugs directly to the skin or injecting them into the tumor
- using a narrow laser beam to destroy the cancer.
The treatment that is best for you depends on the size and location of the cancer, whether it has returned after previous treatment, your age, and your general health.
Once your treatment is finished, it’s important to have regular follow-up skin exams. Your doctor may want to see you every three months for the first year, for example, and then less often after that.
What Are The Risk Factors For Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Skin is the advanced form of SCC of skin. The chief contributing factors for squamous cell carcinoma of skin include:
- Exposure to intense sun for long periods during the course of work or due to regular participation in outdoor sports activities
- Frequent use of tanning beds, tanning parlors
- People living in geographical regions where hot-dry, desert-like climatic conditions prevail
- Radiation therapy
- Coal tar exposure
- Smoking, tobacco chewing
- Individuals with weak immune system, which could be due to cancer treatment, AIDS, or those on immunosuppressant drugs after receiving an organ transplant
- Those with sensitive skin, who get easily sunburned
- Caucasians are more vulnerable compared to other darker-toned individuals
SCC of skin in certain locations has higher chances of metastasis and they include:
- On the lips
- In the region of radiation scar
- In the region of scar due to burns
- Vulvar skin
- Perianal skin
The following subtypes are the more aggressive forms of SCC of skin, and hence, there is a greater possibility of metastasis:
- Acantholytic squamous cell carcinoma of skin
- Spindle cell squamous cell carcinoma of skin
- Pseudovascular squamous cell carcinoma of skin
- Adenosquamous carcinoma of skin
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
Dont Miss: How Does Skin Cancer Occur
Read Also: Carcinoma Cancer Symptoms
Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Be Cured
The majority of SCC tumors are found early and treated while they are still small. Treatment at an early stage can usually remove SCC.2
SCC is more likely than BCC to invade deeper layers of skin and spread to other parts of the body.2 This is uncommon. However, about 5% to 10% of SCC tumors are considered aggressive.2,4 It is more difficult to treat aggressive SCC. By one estimate, between 3,900 and 8,800 white individuals died from SCC in 2012.1 In the Midwest and southern United States, SCC may cause as many deaths as melanoma.1
Your dermatologist may recommend regular follow up for several years after treating any SCC. Most of the cases that return do so with 2 years of initial treatment.5
Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
| Other names | Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma , epidermoid carcinoma, squamous cell epithelioma |
|---|---|
| SCC of the skin tends to arise from pre-malignant lesions, actinic keratoses surface is usually scaly and often ulcerates . | |
| 51,900 |
Squamous-cell skin cancer, also known as cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma , is one of the main types of skin cancer along with basal cell cancer and melanoma. It usually presents as a hard lump with a scaly top but can also form an ulcer. Onset is often over months. Squamous-cell skin cancer is more likely to spread to distant areas than basal cell cancer. When confined to the outermost layer of the skin, a precancerous or in situ form of cSCC is known as Bowen’s disease.
The greatest risk factor is high total exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the Sun. Other risks include prior scars, chronic wounds, actinic keratosis, lighter skin, Bowen’s disease, arsenic exposure, radiation therapy, tobacco smoking, poor immune system function, previous basal cell carcinoma, and HPV infection. Risk from UV radiation is related to total exposure, rather than early exposure.Tanning beds are becoming another common source of ultraviolet radiation. Risk is also elevated in certain genetic skin disorders, such as xeroderma pigmentosum and certain forms of epidermolysis bullosa. It begins from squamous cells found within the skin. Diagnosis is often based on skin examination and confirmed by tissue biopsy.
Read Also: Stage 2 Cancer Symptoms
After Skin Cancer Treatment
Most skin cancer is cured surgically in the dermatologistâs office. Of skin cancers that do recur, most do so within three years. Therefore, follow up with your dermatologist as recommended. Make an appointment immediately if you suspect a problem.
If you have advanced malignant melanoma, your oncologist may want to see you every few months. These visits may include total body skin exams, regional lymph node checks, and periodic chest X-rays and body scans. Over time, the intervals between follow-up appointments will increase. Eventually these checks may be done only once a year.
Recommended Reading: When Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spreads
What Is The Prognosis Of Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
- The prognosis of Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Skin is generally guarded or unpredictable
- The prognosis may further depends upon the following set of factors:
- Stage of tumor: In higher-stage tumors, such as tumors with metastasis, the prognosis is typically poor
- The subtype of squamous cell carcinoma of skin
- The site of metastasis: Metastasis to the local lymph nodes do better than the spread of cancer to distant sites
- The surgical resectability of the tumor
- Overall health of the individual: Individuals with overall excellent health have better prognosis compared to those with poor health
- Age of the individual: Older individuals generally have poorer prognosis than younger individuals
- Whether the tumor is occurring for the first time, or is a recurrent tumor. Recurring tumors have a poorer prognosis compared to tumors that do not recur
- Response to treatment: Tumors that respond to treatment have better prognosis compared to tumors that do not respond so well to treatment
If Metastatic SCC of Skin occurs in the following group of individuals, the prognosis is worse to poor:
- Individuals who have undergone an organ transplant
- Individuals who are chronically alcoholic
- Those with genetic disorders such as xeroderma pigmentosa
Don’t Miss: Basaloid Tumor
What Dermatologists Want You To Know About Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, or cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, is a type of skin cancer that develops when the squamous cells in the top layer of your skin grow out of control. Youll often find squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma lumped together. Thats because they both affect cells in the top layer of the skin.
But there are a couple of key differences between the two types of cancer. Both are often found in areas of your body exposed to sunlight. But squamous cell carcinoma can also develop in areas that dont get much sun exposure, like the inside of the mouth, palms, soles of the feet and genitals. And with early detection, squamous cell carcinoma is highly treatable. But this cancer can be dangerous in its advanced stages.