Treatments For Advanced Melanoma
In most cases, treatment can’t cure advanced melanoma. But some can help you live longer and feel better. The goal of any therapy you get will be to shrink or remove your tumor, keep the cancer from spreading further, and ease your symptoms.
Surgery. This is the main way to remove melanoma from the skin and lymph nodes. You might also have an operation on organs where the cancer has spread. Thereâs no guarantee your surgeon will get all of it. Some melanoma is too small to see, even with high-tech scans.
Radiation. Your doctor might recommend radiation to kill any cancer cells that have been left behind after surgery or if melanoma spreads to your brain or bones. It can also relieve pain from the disease or treat melanoma that comes back over and over.
Immunotherapy or biologic therapy. These drugs help your immune system find and attack cancer cells. Depending on the ones you take, you might have to go in for treatment every 2, 3, or 4 weeks.
Your doctor might want you to take more than one drug. Some studies show that people who do have fewer side effects.
The flip side of immunotherapy is that sometimes these drugs cause your immune system to attack healthy organs. Then youâd need to stop melanoma treatment and take drugs to stop the attack.
Chemo can shrink the cancer, but chances are it will start growing again after a few months and youâll need more treatment. Immunotherapy and targeted therapy usually work better.
Other side effects include:
What Is Metastatic Melanoma
Metastatic melanoma is a cancer that starts in the cells capable of producing a colored pigment called melanin and then has spread beyond its original skin location. It may already be present at the time of the primary or initial diagnosis of the melanoma, or may show up later after surgery has been performed. Metastatic melanoma may spread through the bloodstream or the lymph system.
Early Skin Cancer Mole Pictures
Depending on the type o. Melanoma is associated with infrequent but excessive sunbathing that causes scorching sunburn. It affects people of all races, genders and ages, which is why it’s absolutely critical for americans to learn about. See pictures of skin cancer and get the facts on skin cancer symptoms, signs, treatment, prevention, causes , and types . Some types of skin cancer are more dangerous than others, but if you have a spot.
Also Check: How Long Until Melanoma Spreads
How Are Skin Cancer Survival Rates Measured
Cancer survival is measured in many different ways, including:1
- Five-year overall survival rate is the percentage of people who are still alive 5 years after diagnosis or treatment. If the 5-year overall survival rate after diagnosis is 85 percent, that means that 5 years after being diagnosed with melanoma, 85 of 100 people are still alive. Some of those people may still have cancer, others do not.
- Disease-free survival is how long a person survives after treatment without any sign of that cancer.
- Median overall survival is the average length of time from treatment that half the study population is still alive. For example, consider 100 people who are treated with a medication and 3.1 years later, 50 have died and 50 are alive. The median overall survival is 3.1 years.
When looking at a skin cancer survival rate, it is important to know what group was studied. Survival rates can differ greatly by cancer stage, age at diagnosis, gender, and race/ethnicity. The most accurate numbers about skin cancer survival are about melanoma because cases of melanoma are tracked in national cancer registries.
Factors Used For Staging Melanoma
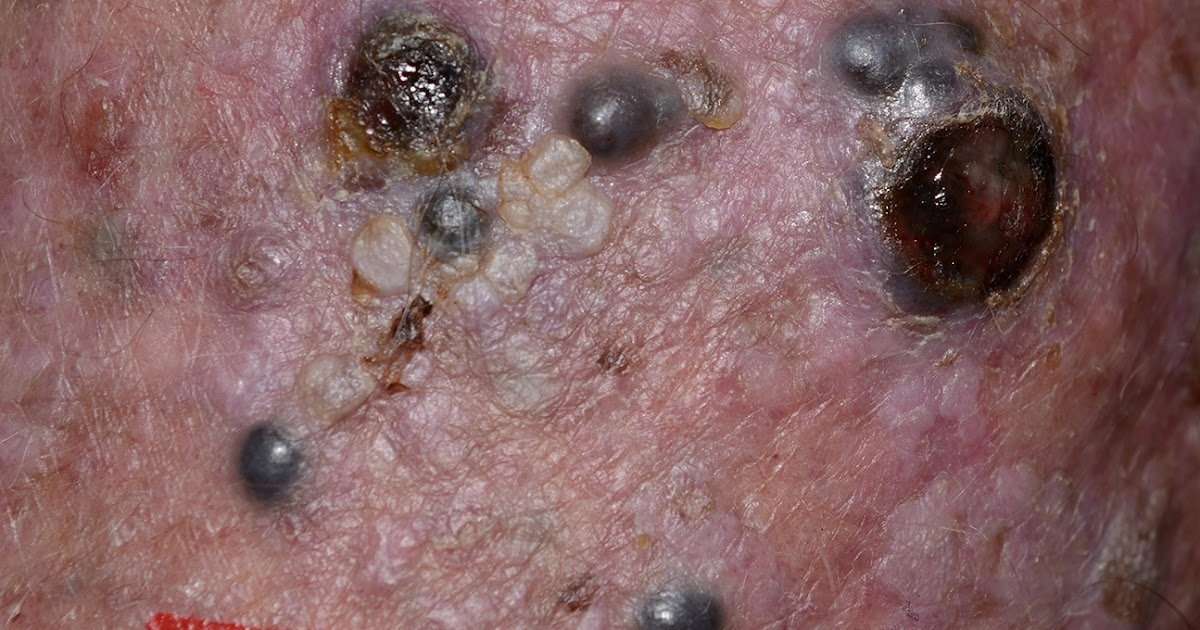
To determine the stage of a melanoma, the lesion and some surrounding healthy tissue need to be surgically removed and analyzed using a microscope. Doctors use the melanomas thickness, measured in millimeters , and the other characteristics described in Diagnosis to help determine the diseases stage.
Doctors also use results from diagnostic tests to answer these questions about the stage of melanoma:
-
How thick or deep is the original melanoma, often called the primary melanoma or primary tumor?
-
Where is the melanoma located?
-
Has the melanoma spread to the lymph nodes? If so, where and how many?
-
Has the melanoma metastasized to other parts of the body? If so, where and how much?
The results are combined to determine the stage of melanoma for each person. The stages of melanoma include: stage 0 and stages I through IV . The stage provides a common way of describing the cancer, so doctors can work together to create the best treatment plan and understand a patient’s prognosis.
Recommended Reading: What Does Well Differentiated Mean
What Are The Prognosis And Survival Rates For Metastatic Melanoma
The prognosis for thin melanomas completely removed by surgery remains quite good although patients require long-term monitoring to watch for both new melanomas as well as evidence of late recurrence and previously undiagnosed metastasis of the original one. Survival rates for melanoma, especially for metastatic melanoma, vary widely according to many factors, including the patient’s age, overall health, location of the tumor, particular findings on the examination of the biopsy, and the depth and stage. Survival statistics are generally based on five-year survival. Much of the success reported for the targeted therapies focus on “disease free” time because, in many cases, the actual five-year survival is not affected. It is hoped that combination therapy with two or more agents targeting different stages of the melanoma cell cycle will change that.
- For stage 1 , five-year survival is near 100%.
- For stage 2 , five-year survival is 80%-90%.
- For stage 3 , five-year survival is around 50%.
- For stage 4 , five-year survival is 10%-25% depending upon sex and other demographic factors.
Staging And Grading For Stage 4 Cancer
Most cancers are staged using some form of the TNM system. Doctors may also use the TNM system to help determine the extent of certain cancers in each stage. The TNM system stands for:
- T , or the size of the original tumor
- N , or whether the cancer is present in the lymph nodes
- M , or whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body
Not all cancers are staged using the TNM system, though. Some cancers, especially liquid cancers, are staged through different established protocols. The Binet and Rai systems, for example, are used to stage certain types of leukemia. Female reproductive system cancers, such as cervical cancer, are staged with a separate staging system created by the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics .
As your care team gathers information about your cancer for the purposes of staging, they may need to order several tests, including:
Your care team may likely also need to perform a biopsy, a procedure that involves removing a sample of cells and analyzing it for signs of cancer. Imaging scans may be able to tell your care team where your cancer is, but looking at the cancer cells specifically tell them how fast they are likely to growor what grade they are.
Grading is different from staging and is done for most, but not all, cancers.
The grade of your cancer is part of how your cancer care team stages your cancer and determines your prognosis, or outlook.
Read Also: Stage 2 Cancer Symptoms
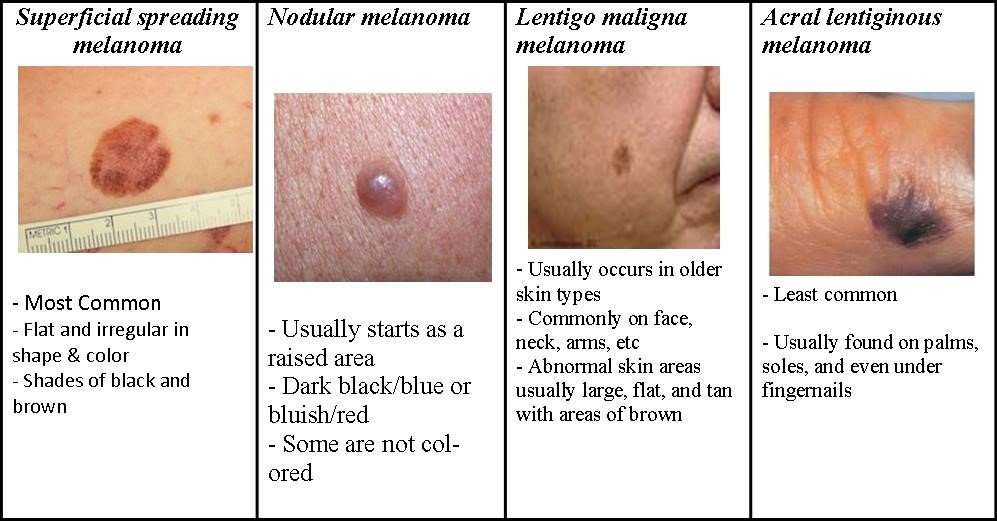
What Are The 4 Types Of Melanoma
There are four main types of skin melanoma:
- Superficial spreading melanoma is the most common type. It is more commonly found on the arms, legs, chest and back.
- Nodular melanoma is the second most common type.
- Lentigo maligna melanoma is less common.
- Acral lentiginous melanoma is the rarest type.
- Changes in texture, or scales, oozing or bleeding from an existing mole.
How Is The Stage Determined
The system most often used to stage basal and squamous cell skin cancers is the American Joint Commission on Cancer TNM system. The most recent version, effective as of 2018, applies only to squamous and basal cell skin cancers of the head and neck area . The stage is based on 3 key pieces of information:
- The size of the tumor and if it has grown deeper into nearby structures or tissues, such as a bone
- If the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes
- If the cancer has spread to distant parts of the body
Numbers or letters after T, N, and M provide more details about each of these factors. Higher numbers mean the cancer is more advanced.
Once a persons T, N, and M categories have been determined, this information is combined in a process called stage grouping to assign an overall stage. The earliest stage of skin cancer is stage 0 . The other stages range from I through IV . As a rule, the lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. A higher number, such as stage IV, means cancer has spread more.
If your skin cancer is in the head and neck area, talk to your doctor about your specific stage. Cancer staging can be complex, so ask your doctor to explain it to you in a way you understand. For more information, seeCancer Staging.
Don’t Miss: Is Carcinoma Curable
Recurrence In Nearby Lymph Nodes
If nearby lymph nodes werenât all removed during the initial treatment, the melanoma might come back in these lymph nodes. Lymph node recurrence is treated by lymph node dissection if it can be done, sometimes followed by adjuvant treatments such as radiation therapy and/or immunotherapy or targeted therapy . If surgery is not an option, radiation therapy or systemic treatment can be used.
See A Picture Of And Learn About Moles A Common Skin Condition In The Emedicinehealth Image Collection Gallery
Whatever the cause, if you’re looking to regain a more eve. Two new studies find an association between breast cancer and moles. According to the american cancer society, just over 100,000 new cases of skin cancer are diagnosed in the united states each year. However, the researchers can only hypothesize on the mechanisms driving this association. Some types of skin cancer are more dangerous than others, but if you have a spot. Skin keratosis, also known as seborrheic keratosis, are harmless, noncancerous growths that appear on the face, neck, shoulders. Melanoma is associated with infrequent but excessive sunbathing that causes scorching sunburn. See before and after photos of patients who have undergone reconstructive plastic surgery after skin cancer removal . See a picture of and learn about moles, a common skin condition, in the emedicinehealth image collection gallery. Home image collection gallery list moles are pigmented skin growths that are may be brown, black, or bluish. Common causes range from illness to injury to inflammation. Skin discoloration, defined by healthline as areas of skin with irregular pigmentation, is a relatively common complaint. See pictures of skin cancer and get the facts on skin cancer symptoms, signs, treatment, prevention, causes , and types .
Two new studies find an association between breast cancer and moles. Depending on the type o. However, the researchers can only hypothesize on the mechanisms driving this association.
You May Like: Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Stage I And Stage Ii Melanoma
Stage I and stage II melanoma describe invasive cancer that has grown below the epidermis to the next layer of skin, the dermis. It has not reached the lymph nodes.
Two major factors help determine the seriousness of stage I melanoma and stage II melanoma: Breslow depth and ulceration.
Breslow depth is a measurement that doctors use to describe the depth of an invasive melanoma in millimeters. It measures how far melanoma cells have reached below the surface of the skin. The thinner the melanoma, the better the chances for a cure.
Ulceration means that there is broken skin covering the melanoma. This breakage can be so small that it can only be seen under a microscope. Ulceration is an important factor in staging. A melanoma with ulceration may require more aggressive treatment than a melanoma of the same size without ulceration.
Melanoma is considered stage 1A when:
- the tumor is less than or equal to 1 millimeter thick in Breslow depth
Melanoma is considered stage IB when:
- the tumor is 1.1 to 2 millimeters thick in Breslow depth without ulceration
Melanoma is considered stage IIA when:
- the tumor is 1.1 to 2 millimeters thick in Breslow depth with ulceration
- the tumor is 2.1 to 4 millimeters thick in Breslow depth without ulceration
Melanoma is considered stage IIB when:
- the tumor is 2.1 to 4 millimeters thick in Breslow depth with ulceration
- the tumor is more than 4 millimeters in Breslow depth without ulceration
Melanoma is considered stage IIC when:
Other Factors That Can Affect Outlook And Treatment Options
The stage of a skin cancer can help give an idea of how serious the cancer is likely to be, including how likely it might be to return after treatment. But other factors are also important to consider. Some of these include:
- The location of the tumor
- How fast the tumor has been growing
- How well-defined the borders of the tumor are
- If the tumor has been causing symptoms, such as pain or itchiness
- How the cancer cells look under a microscope
- If the cancer cells have invaded small nerves or blood vessels in and around the tumor
- If the cancer is in a place that was previously treated with radiation
- If the person has a weakened immune system
Your doctor can explain if any of these factors might affect your treatment or outlook.
Also Check: How Fast Does Cancer Kill
Treating Stage 4 Melanoma
If melanoma comes back or spreads to other organs it’s called stage 4 melanoma.
In the past, cure from stage 4 melanoma was very rare but new treatments, such as immunotherapy and targeted treatments, show encouraging results.
Treatment for stage 4 melanoma is given in the hope that it can slow the cancer’s growth, reduce symptoms, and extend life expectancy.
You may be offered surgery to remove other melanomas that have grown away from the original site. You may also be able to have other treatments to help with your symptoms, such as radiotherapy and medicine.
If you have advanced melanoma, you may decide not to have treatment if it’s unlikely to significantly extend your life expectancy, or if you do not have symptoms that cause pain or discomfort.
It’s entirely your decision and your treatment team will respect it. If you decide not to receive treatment, pain relief and nursing care will be made available when you need it. This is called palliative care.
What Are The Survival Rates For Bcc
Cancer registries do not collect information about basal cell carcinoma because the majority of BCCs are diagnosed and treated easily in a doctors office.
Advanced BCC is so rare that there is very little information about survival rates. One study of 100 cases of metastatic BCC between 1981 and 2011 showed that median overall survival is 4.5 years. How far the cancer spread made a big difference in survival. For regional metastasis, survival was 7.2 years. For distant metastasis, it was 2 years. These estimates are based on a time when chemotherapy or radiation therapy were the only treatment options.9
Survival time with advanced BCC might be improving with newer treatments. In trials for a targeted therapy called Erivedge® , median overall survival was 2.8 years. The 1-year survival rate was 84.4 percent and the 2-year survival rate was 68 percent. Odomzo® , another targeted therapy, has similar survival outcomes. Trials of sonidegib show that 2-year survival is 93 percent for people with locally advanced BCC and 69 percent for people with metastatic BCC.10,11
Don’t Miss: Lobular Breast Cancer Stage 1
What Do Stage 4 Tumors Look Like
A change to an existing mole or normal skin can be the first sign that the cancer has spread. But the physical symptoms of stage 4 melanoma arent the same for everyone. A doctor will diagnose stage 4 melanoma by looking at the primary tumor, the spread to nearby lymph nodes, and whether the tumor has spread to different organs. While your doctor wont base their diagnosis only on what your tumor looks like, part of their diagnosis involves looking at the primary tumor.
How Do You Treat Stage 4 Melanoma
The good news is that even stage 4 melanoma can be treated. The sooner the cancer is found, the sooner it can be removed and the higher your chances are for recovery. Stage 4 melanoma also has the most treatment options, but these options depend on:
- where the cancer is
- how advanced the cancer has become
- your age and overall health
How you respond to treatment also affects your treatment options. The five standard treatments for melanoma are:
- surgery: to remove the primary tumor and affected lymph nodes
- chemotherapy: a drug treatment to stop growth of cancer cells
- radiation therapy: the application of high-energy X-rays to inhibit growth and cancer cells
- immunotherapy: treatment to boost your immune system
- targeted therapy: the use of drugs or other substances to attack cancer drugs
Other treatments may also depend on where the cancer has spread to. Your doctor will discuss your options with you to help map out a treatment plan.
You May Like: Invasive Lobular Carcinoma Grade 2 Survival Rates
The Braf Gene Mutation And Melanoma
Roughly half of all documented melanoma cases present with mutations in the BRAF gene. The melanoma cells that have these changes create a BRAF protein, which aids them in their growth. If a person with the BRAF gene mutation has melanoma, knowing about the mutation is of great benefit for treatment because healthcare providers can use targeted therapy to inhibit the BRAF gene mutation from aiding in the growth of the cancer.
If a diagnosis of melanoma is already established, the healthcare provider will look at two factors to determine how advanced a stage 4 melanoma has become: the location of the distant tumors and an elevated level of serum lactate dehydrogenase , which is an enzyme responsible for turning sugar into energy. The higher the LDH level in body fluids, the more damage the cancer has done.