How Fast Does Melanoma Spread
Melanoma is a deadly form of skin cancer because of its ability to metastasize to local lymph nodes and other organs. It is estimated that melanoma kills, on average, over 10,000 people in the United States every year.
The first sign of flat melanoma is usually a new spot or an existing mole or freckle that changes in appearance. Some changes can include:
- A spot that has grown in size
- A spot where the edges are looking irregular versus smooth and even
- A spot that has a range of colors such as brown, black, blue, red, white or light gray.
- A spot that has become itchy or is bleeding
According to Dr. Andrew Duncanson, board-certified dermatologist at Forefront Dermatology, It is important to know that melanoma can appear on areas of the skin not normally exposed to the sun such as under the arm, chest, and buttocks. It can also appear in areas that you are not able to see easily on your own including the ears, scalp, back of legs, and bottom of feet. I always recommend to my patients to look for the ugly duckling spot the new spot that doesnt look like any others. Additionally, ask a family member to look over the hard to see areas monthly, while also getting an annual skin cancer exam by a board-certified dermatologist to detect skin cancer early.
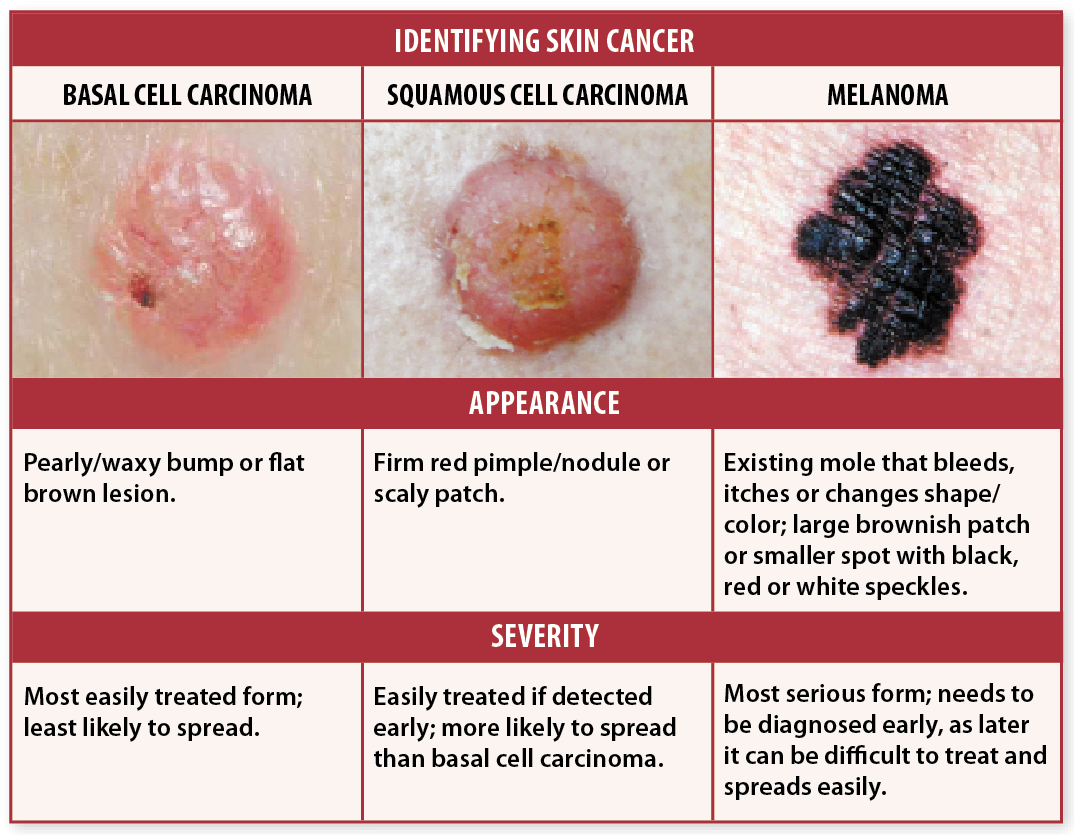
Different Types Of Cancer Start In The Skin
Skin cancer may form in basal cells or squamous cells. Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the most common types of skin cancer. They are also called nonmelanoma skin cancer. Actinic keratosis is a skin condition that sometimes becomes squamous cell carcinoma.
Melanoma is less common than basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma. It is more likely to invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body.
This summary is about basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, and actinic keratosis. See the following PDQ summaries for information on melanoma and other kinds of cancer that affect the skin:
What Are The Stages Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is classified into the following stages, which are partly based on how far the cancer has spread throughout the body:
- Stage 0 Squamous cell carcinoma develops in the squamous cells, which are located in the epidermis . During Stage 0, the cancer hasnt spread beyond the epidermis.
- Stage 1 When squamous cell carcinoma progresses to Stage 1, it means that the cancer has spread deeper into the skin, but not into any lymph nodes or healthy tissues.
- Stage 2 A Stage 2 classification means that, in addition to progressing deeper into the skin, the cancer also displays at least one high-risk feature. This might include metastasizing to the lower skin layers or the nerves. However, at this stage, the cancer still hasnt spread to lymph nodes or healthy tissues.
- Stage 3 Once squamous cell carcinoma reaches Stage 3, the cancer has spread into lymph nodes but not any other tissues or organs.
- Stage 4 This is the final stage of squamous cell carcinoma, where the cancer has spread to at least one distant organ, whether that be the brain, the lungs or a separate area of skin.
If you think you might have squamous cell carcinoma, its important to seek prompt medical attention to minimize the risk of cancer spread. The specialists in Moffitt Cancer Centers Cutaneous Oncology Program can provide you with the comprehensive diagnostic and treatment services you need. Call or complete our new patient registration form online to request an appointment.
- BROWSE
Recommended Reading: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
What Affects How Fast Melanoma Spreads
The type of melanoma makes a difference. When the cancer cells invade the deeper skin layers, known as invasive melanoma, it spreads faster, grows faster and is the most dangerous. Superficial melanomas and Lentigo maligna melanomas grow more slowly, are often easier to treat, and have a higher cure rate than invasive melanoma, when diagnosed in an early stage.
Certain genetic changes can affect how quickly this cancer spreads. Certain gene abnormalities encourage this cancer to invade surrounding tissue. People who have two copies of the cyclin variant were at an 80 percent higher risk of developing melanoma.
The composition of abnormal cells, or the grade of cancer, can result in melanoma spreading faster. When high grade cancer is present and very abnormal cells make up the tumor, this cancer most often spreads and grows very fast. Low grade cancer in which the tumor is made of cells that only slightly differ from normal cells, most often grow slowly, and in some cases, do not spread at all.
Spread Through The Bloodstream
Cancer cells can go into small blood vessels and then get into the bloodstream. They are called circulating tumour cells .
Researchers are looking at using circulating tumour cells to diagnose cancer instead of a tissue sample . And at whether they can test circulating cancer cells to predict which treatments will work better. They are also looking to detect circulating tumour DNA to help diagnose cancer and monitor treatment.
The circulating blood sweeps the cancer cells along until they get stuck somewhere. Often they get stuck in a very small blood vessel such as a capillary.
Then the cancer cell must move through the wall of the capillary and into the tissue of the organ close by. The cell can multiply to form a new tumour if:
- the conditions are right for it to grow
- it has the nutrients that it needs.
This is quite a complicated process and most cancer cells don’t survive it. Of the many thousands of cancer cells that reach the bloodstream, only a few survive to form a secondary cancer.
The white blood cells in our immune system find and kill some cancer cells. Others cancer cells might die because they get battered around by the fast flowing blood.
Cancer cells in the circulation may try to stick to platelets to form clumps to give themselves some protection. Platelets are blood cells that help the blood to clot. This could also help the cancer cells to move into the surrounding tissues.
Don’t Miss: Basal Skin Cancer Survival Rates
Different Kinds Of Skin Cancer
There are many types of skin cancer. Some are very rare. Your doctor can tell you more about the type you have.
The two most common kinds of skin cancers are:
- Basal cell cancer, which starts in the lowest layer of the skin
- Squamous cell cancer, which starts in the top layer of the skin
Another kind of skin cancer is called melanoma. These cancers start from the color-making cells of the skin . You can read about melanoma in If You Have Melanoma Skin Cancer.
What Makes Yale Medicines Approach To Squamous Cell Carcinoma Unique
Simple, small cancers can often be treated very well by a local dermatologist, according to Dr. Leffell. We rarely see the small cancers. We get referred to the cases that need special attention.
Dr. Leffell emphasizes that at Yale Medicine, the patient always comes first. We like to have a discussion with the patient about what happens after the skin cancer is removed, he says. We talk about what’s involved with plastic surgery and what’s involved with letting the area heal naturally. We prefer to take a minimalist approach and let the patient decide what they want us to do and how they want to let their skin heal.
If the decision is made to repair the wound using plastic surgery, we do that immediately in the office setting, Dr. Leffell says. Alternatively, allowing the wound to heal naturally is often a great option, and does not rule out doing plastic surgery down the road if needed, though that is very rarely the case.
Don’t Miss: Does Skin Cancer Burn And Itch
Prevention Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Because basal cell carcinoma is often caused by sun exposure, people can help prevent this cancer by doing the following:
-
Avoiding the sun: For example, seeking shade, minimizing outdoor activities between 10 AM and 4 PM , and avoiding sunbathing and the use of tanning beds
-
Wearing protective clothing: For example, long-sleeved shirts, pants, and broad-brimmed hats
-
Using sunscreen: At least sun protection factor 30 with UVA and UVB protection used as directed and reapplied every 2 hours and after swimming or sweating but not used to prolong sun exposure
In addition, any skin change that lasts for more than a few weeks should be evaluated by a doctor.
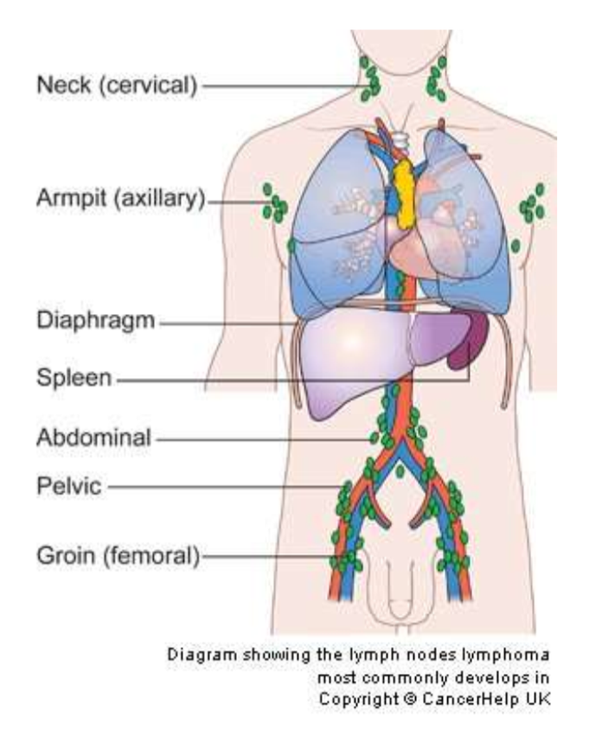
Spread Through The Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system is a network of tubes and glands in the body that filters body fluid and fights infection. It also traps damaged or harmful cells such as cancer cells.
Cancer cells can go into the small lymph vessels close to the primary tumour and travel into nearby lymph glands . In the lymph glands, the cancer cells might die. But some may survive and grow to form tumours in one or more lymph nodes. This is called lymph node spread.
This 2 minute video is about the lymphatic system.
Also Check: Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch
Mohs Microscopically Controlled Surgery
|
Because skin cancer cells often have spread beyond the edges of the visible patch on the skin, doctors sometimes use a special surgical technique to make sure they remove all of the cancer. In this technique, called Mohs microscopically controlled surgery or Mohs micrographic surgery, doctors first remove the visible tumor and then begin cutting away the edges of the wound bit by bit. During surgery, doctors examine pieces of tissue to look for cancer cells. Tissue removal from the area continues until the samples no longer contain cancer cells. This procedure enables doctors to limit the amount of tissue removed and thus is especially useful for cancers near such important sites as the eye. After removing all of the cancer, doctors decide how best to replace the skin that has been cut away. They may bring the edges of the remaining skin together with sutures or use a skin graft or skin flap. Or they may place dressings on top of the wound and let the skin heal on its own. Mohs surgery reduces recurrence rates for skin cancers. This surgery is useful for basal cell and squamous cell cancers but is less often used for melanoma. |
How Cancer Can Spread To Other Areas Of The Body
Cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system . There they can start to grow into new tumours.
Cancers are named according to where they first started developing. For example, bowel cancer that has spread to the liver is called bowel cancer with liver metastases or secondaries. It is not called liver cancer. This is because the cancerous cells in the liver are cancerous bowel cells. They are not liver cells that have become cancerous.
Don’t Miss: Metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
Determine Your Skin Cancer Risk
The guidelines above apply to everyone, but certain individuals are at a higher risk for developing skin cancer and should be especially cautious with sun exposure.
If any of the descriptions below apply to you, see a dermatologist for a full-body examination once a year. Skin cancer risk is cumulative. The more risk factors you have and the more sun damage over a lifetime the higher your risk.
Skin cancer risk factors include:
- Personal history of skin cancer or precancerous skin lesions
- Tendency to freckle or burn easily
- Lots of sun exposure throughout your life
- Many sunburns as a child or adolescent
- Family history of skin cancer or conditions that are more likely to develop into skin cancer, such as dysplastic nevus syndrome or numerous atypical moles
- Chronic, non-healing wounds or burn injuries
- Radiation therapy
- Exposure to toxic materials, such as arsenic
- Exposure to certain subtypes of human papilloma virus . HPV 6,11,16 and 18 have been linked to the development of squamous cell carcinoma, especially in patients with compromised immune systems.
- Organ transplant patients on immunosuppressant drugs have an increased risk of skin cancer
How Is Metastasis Detected
If your doctor suspects that your melanoma may have spread, there are several tools available to verify the diagnosis. These include a blood test for lactate dehydrogenase , which increases when melanoma metastasizes, and imaging studies, such as chest X-ray, computed tomography , magnetic resonance imaging , positron emission tomography and ultrasound.
The doctor may also need to take a sample of your lymph nodes, using a procedure called “sentinel lymph node mapping.” If confirmed, there are many treatments available, including chemotherapy, immunotherapy, radiation therapy and surgery.
You May Like: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
Surgery For Basal And Squamous Cell Skin Cancers
Surgery is a common treatment for basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers. Different surgical techniques can be used. The options depend on the type of skin cancer, how large the cancer is, where it is on the body, and other factors. Most often the surgery can be done in a doctors office or hospital clinic using a local anesthetic . For skin cancers with a high risk of spreading, surgery sometimes will be followed by other treatments, such as radiation or chemotherapy.
Melanoma Skin Cancer Growth Rate
Melanoma skin cancer is the most dangerous and aggressive type of skin cancer, but it is significantly less common than other, non-melanoma types of skin cancer like Squamous cell carcinoma and Basal cell carcinoma. Melanoma skin cancer has a rapid growth rate, which is what makes it so dangerous it can turn life-threatening in just six weeks and poses a high risk of spreading to other parts of the body if left untreated. The early form of squamous cell carcinoma is known as Bowens disease.
Don’t Miss: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
Treatment Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
-
Removal of the tumor
Doctors may remove the cancer in the office by scraping and burning it with an electric needle or by cutting it out. Doctors may destroy the cancer by using extreme cold .
Certain chemotherapy drugs may be applied to the skin. Photodynamic therapy , in which chemicals and a laser are applied to the skin, also may be used. Occasionally, radiation therapy is used.
A technique called Mohs microscopically controlled surgery may be required for some basal cell carcinomas that are large or regrow or occur in certain areas, such as around the nose and eyes.
People whose cancer has spread to nearby tissues or spread to other parts of the body and who are not candidates for surgery or radiation therapy may be given the drug vismodegib or sonidegib taken by mouth.
Leaving Basal Cell Carcinoma Untreated
Basal cell carcinoma is a slow growing cancer, but this doesnt mean it can be ignored. This is the least dangerous form of skin cancer and rarely spreads to other internal parts of the body. While death is a rare consequence there is the potential for disfigurement. Over time basal cell carcinoma can expand and cause ulcers and damage the skin and tissues.
Any damage could be permanent and have an impact on the way you look. Depending on how long the basal cell carcinoma has been present, radiotherapy may be required. This is the most common form of skin cancer and is often found on the face. You may notice a small lump which is shiny or pearl like and this is a sign you should get checked. This type of cancer generally does not cause any pain.
Read Also: Osteomyoma
How Long Does It Take For A Squamous Cell Skin Cancer To Spread
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Treating Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Most of squamous cell carcinomas can be cured if they are treated early. Once squamous cell carcinoma has spread beyond the skin, though, less than half of people live five years, even with aggressive treatment.
There are many ways to treat squamous cell carcinoma that has not spread. These include:
- cutting away the cancer and a small amount of healthy tissue around it. If a large area of skin is removed, a skin graft may be necessary.
- scraping away the cancer with a surgical tool. An electric probe is used to kill any cancerous cells left behind.
- freezing cancer cells with liquid nitrogen. This treatment is usually used only for very small tumors or for a patch of skin that looks abnormal but isn’t yet cancerous.
- destroying the tumor with radiation.
- shaving away the cancer, one thin layer at a time. Each layer is examined under the microscope as it is removed. This technique helps the doctor preserve as much healthy skin as possible.
- applying drugs directly to the skin or injecting them into the tumor
- using a narrow laser beam to destroy the cancer.
The treatment that is best for you depends on the size and location of the cancer, whether it has returned after previous treatment, your age, and your general health.
Once your treatment is finished, it’s important to have regular follow-up skin exams. Your doctor may want to see you every three months for the first year, for example, and then less often after that.
Recommended Reading: Squamous Cell Carcinoma Skin Metastasis
How Dangerous Is Melanoma Its All A Matter Of Timing
Skin cancer holds the unfortunate distinction of being the worlds most common cancer. Though its prevalence around the globe is disturbing, there is some good news: When caught early, skin cancers are almost always curable.
You might already know that catching a cancer early means a more favorable prognosis. But it can be difficult to comprehend just how big a difference early detection makes with melanoma, the most dangerous form of skin cancer. Melanoma should never be underestimated, but treating a tumor early rather than after it is allowed to progress could be lifesaving.
Leland Fay, 46, understands better than most the seriousness of this distinction. When the Monument, Colorado native was diagnosed with melanoma in 2012, he was given a bleak prognosis due to the advanced stage of the tumor it had already reached stage IV.
Leland hadnt thought much of the little black mole on his head a few months earlier, when a dermatologist froze it off during a routine exam. But the mole resurfaced, bigger than it had been originally. After a biopsy and imaging tests, doctors told Leland it was melanoma, and that it had already spread. He could have as few as six weeks to live.
To fully comprehend the significance of timing, it can be helpful to understand exactly what happens to a melanoma when it advances to a later stage, and what it means when a melanoma spreads beyond the original tumor site.