Targeted Therapy Or Immunotherapy For Advanced Basal Cell Cancers
In rare cases where basal cell cancer spreads to other parts of the body or cant be cured with surgery or radiation therapy, a targeted drug such as vismodegib or sonidegib can often shrink or slow its growth.
If these drugs are no longer working , the immunotherapy drug cemiplimab can sometimes be helpful.
Infiltrative Basal Cell Carcinoma Prognosis
8 out of 10 patients who are diagnosed with non-melanoma skin cancer will have basal cell carcinoma, which can present in a wide variety of colors, shapes, and sizes. Many basal cell carcinoma lesions are red or pink sores that refuse to heal, and can also be itchy or uncomfortable. Receiving an infiltrative basal cell carcinoma prognosis is unique because unlike many other forms of basal cell carcinoma, this variant is typically white and harder to see, due to it developing in between the skins collagen fibers. This growth pattern is more unusual, as basal cell carcinoma typically forms on the top-most layer of the skin.
What Is Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma With Pictures
- Micronodular basal cell carcinoma may be more difficult to eradicate and prone to recurrence than nodular subtype. Micronodular basal cell carcinoma is thought to have a greater potential for clinically surreptitious tumor spread compared with the majority of basal cell carcinomas that are nodular
- The nodular type of basal cell carcinoma usually begins as small, shiny, firm, almost clear to pink in color, raised growth. After a few months or years, visible dilated blood vessels may appear on the surface, and the center may break open and form a scab. The border of the cancer is sometimes thickened and pearly white
- superficial basal cell skin cancer Nodular basal cell cancer. Nodular basal cell cancers can look see through and shiny. You can often also see their blood vessels. Sometimes they have a sore area and it may also have fluid filled sacs . Pigmented basal cell cancer. Pigmented basal cell cancers have dark areas.
- Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma Nodular BCC is the most common clinical subtype of BCC . 47 , 48 It occurs most commonly on the sun-exposed areas of the head and neck and appears as a translucent papule or nodule depending on duration
- Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer, with an estimated 4.3 million cases diagnosed in the United States each year .Although it rarely metastasizes, BCC can cause significant local tissue destruction, resulting in disfigurement and infiltration into vital underlying structures if left untreated
Recommended Reading: How Can You Treat Skin Cancer
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinoma
JONATHON M. FIRNHABER, MD, East Carolina University, Brody School of Medicine, Greenville, North Carolina
Am Fam Physician. 2012 Jul 15 86:161-168.
Nonmelanoma skin cancer, which includes basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, is the most common cancer in the United States. Approximately 80 percent of nonmelanoma skin cancers are basal cell carcinoma and 20 percent are squamous cell carcinoma. Although the National Cancer Institute does not formally track the incidence and prevalence of nonmelanoma skin cancers, multiple longitudinal studies indicate that the incidence has risen sharply over the past two decades.1
Recommended Reading: Does Basal Cell Carcinoma Need To Be Removed
Possible Side Effects Of Radiation
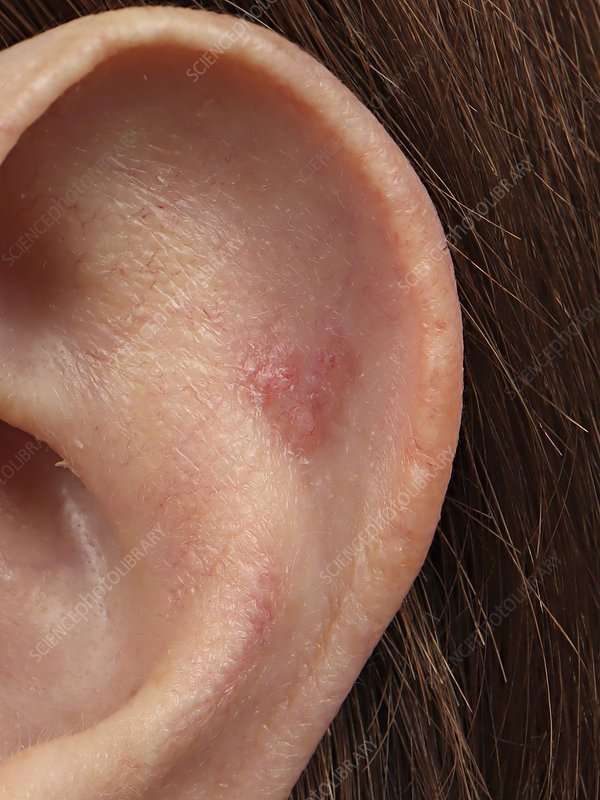
Side effects of radiation are usually limited to the area getting radiation, and can include:
- Skin irritation, ranging from redness to blistering and peeling
- Changes in skin color
- Hair loss in the area being treated
- Damage to saliva-making glands and teeth when treating cancers near these structures
With longer treatment, these side effects may get worse.
After many years, new skin cancers sometimes develop in areas previously treated by radiation. For this reason, radiation usually is not used to treat skin cancer in young people. Radiation is also not recommended for people with certain inherited conditions , who may be at higher risk for new cancers, or for people with connective tissue diseases , which radiation might make worse.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Symptoms Of Melanoma
Types Of Basal Cell Cancer: Nodular Superficial And
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common skin cancer and the least dangerousbut it’s far from a trivial matter, reports the May issue of the Harvard Women’s Health Watch.The good news is that basal cell carcinoma rarely spreads , and it can easily be treated and cured when discovered early Basal cell carcinomas can be thin or thick and their appearance varies. They are most common on areas that have long-term exposure to the sun, such as the face and arms, although they are also common on the back and chest. Nodular basal cell carcinoma. Nodular basal cell carcinoma often appears as a pink lump with a pearly consistency The characteristics and location of basal cell carcinoma vary somewhat with the type, although many are a mixture of types. The most common form, nodular, usually shows up as a shiny bump, generally on the face, scalp, ears, or neck. It may bleed easily. And it often ulcerates and crusts over, which may create the illusion that it’s healing Basal cell carcinoma is the most common cancer in humans and the most common cancer of the skin. It is a neoplasm of basal keratinocytes that is found more frequently in men than women and is typically seen on the face. Rates of BCC have been increasing over the last several decades, particularly in young women Abstract. Basal cell carcinoma is a slow-growing malignant skin tumor and its often found in elderly patients on sun exposed areas that confirming chronic UV radiation. Demographic, clinical and.
Basal Cell Carcinoma: High Risk And Low Risk
Mohs surgeon Erica Lee researches ways to improve quality of life in people with skin cancer.
When any type of cancer is diagnosed, its classified according to certain characteristics. Basal cell carcinomas are classified based on the risk of recurrence , which depends mostly on where the tumor is located.
Basal cell carcinomas are considered to be high risk if:
- they are located in the middle or central part of the face, such as the eyelids, nose, ears, and lips
- they have come back after first treatment
- they are wider than 2 centimeters
Basal cell carcinomas are considered to be a low risk for coming back if:
- they are small and superficial
- they have a clear, defined edge
- they havent been treated before
You May Like: How Do You No If You Have Skin Cancer
Prevention Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Because basal cell carcinoma is often caused by sun exposure, people can help prevent this cancer by doing the following:
-
Avoiding the sun: For example, seeking shade, minimizing outdoor activities between 10 AM and 4 PM , and avoiding sunbathing and the use of tanning beds
-
Wearing protective clothing: For example, long-sleeved shirts, pants, and broad-brimmed hats
-
Using sunscreen: At least sun protection factor 30 with UVA and UVB protection used as directed and reapplied every 2 hours and after swimming or sweating but not used to prolong sun exposure
In addition, any skin change that lasts for more than a few weeks should be evaluated by a doctor.
Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
There are several types of basal cell carcinomas.
The nodular type of basal cell carcinoma usually begins as small, shiny, firm, almost clear to pink in color, raised growth. After a few months or years, visible dilated blood vessels may appear on the surface, and the center may break open and form a scab. The border of the cancer is sometimes thickened and pearly white. The cancer may alternately bleed and form a scab and heal, leading a person to falsely think that it is a sore rather than a cancer.
Other types of basal cell carcinomas vary greatly in appearance. For example, the superficial type appears as flat thin red or pink patches, and the morpheaform type appears as thicker flesh-colored or light red patches that look somewhat like scars.
Also Check: How Do You Die From Melanoma
How Is Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin Treated
In general, the treatment of Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin depends upon a variety of factors including:
- The subtype of BCC
- The location of the tumor
- The number of tumors
- The size of the tumor
- Whether the tumor has metastasized
A combination of treatment methods may be used to treat Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin. The type of surgery may include:
- Shave biopsy of skin: This procedure is used for small tumors. There is no requirement of sutures after the surgery
- Excision of tumor: In this procedure, the tumor and surrounding tissue are removed with clear margins. Depending upon the amount of skin removed, surgical sutures may be necessary
- Mohs surgery: In this procedure, the tumor is removed layer by layer precisely, until clear margins are achieved. Each layer removed is examined under a microscope through a âfrozen sectionâ procedure, for the presence of residual tumor
In most cases, a surgical removal of the entire tumor is the preferred treatment option. This can result in a cure.
Other techniques to treat this skin cancer may include:
- Cryotherapy: Here the tumor tissue is destroyed through a freezing technique. Typically liquid nitrogen is used to freeze the tumor
- Topical creams, such as 5-fluorouracil cream and imiquimod cream, are two examples that can be used for topical treatment. These creams may be applied for several weeks, which slowly destroys the tumor
Dont Miss: What Is The Main Cause Of Skin Cancer
General Principles In Outer Nose Repair
Most of nasal skin is of the sebaceous type. Whenever possible, scar lines should be placed along relaxed skin tension lines. Aesthetic units of the nose need consideration although tumours do not respect their borders. Aging affects the nose anatomy. Characteristic symptoms are frown lines , transverse crease on the nasal root, drooping of tip of nose, and deepened nasolabial folds. Skin diseases of elderly, like rosacea and rhinophyma can interfere with surgical techniques.
The skin covering the bony parts is highly movable, while the skin over cartilage parts is thicker, tighter and bound to the cartilage. Healing by second ary intention of convex surfaces like the nose tip should be avoided since healing often is delayed and may lead to uneven scars.
Recommended Reading: How Fast Does Melanoma Metastasis
Nodular Ulcerative Basal Cell Carcinoma Answers From
- Nodular basal cell cancer is the most common subtype. It’s very rare for basal cell skin cancer to spread to another part of the body to form a secondary cancer. It’s possible to have more than one basal cell cancer at any one time and having had one does increase your risk of getting another
- Nodular basal cell carcinomas are more common on the head and neck, while other types often appear on the trunk, arms or legs. Evolution. Basal cell carcinomas often grow without causing any discomfort. They are the least dangerous form of skin cancer, but if left untreated, they can grow and destroy nearby or underlying tissues
- Basal cell carcinoma is the most common but least dangerous type of skin cancer. BCCs usually appear on the head, neck or upper body. See your doctor if you think you have a BCC, because it is easier to treat if diagnosed early on
- For basal cell carcinoma staging, the factors are grouped and labeled 0 to 4. The characteristics and stages of basal cell carcinoma are: Stage 0: Also called carcinoma in situ, cancer discovered in this stage is only present in the epidermis and has not spread deeper to the dermis
Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma
Nodular basal cell carcinoma comprises about 60-80% of the cases and occurs most often on the skin of the head. Clinically it is presented by elevated, exophytic pearl-shaped nodules with telangiectasie on the surface and periphery . Subsequently, nodular BCC can extend into ulcerative or cystic pattern. The endophytic nodules are presented clinically as flat enduring plaques. The hemorrhagic lesions can resemble hemangioma or melanoma, especially if are pigmented. The lesions with big sizes and the central necrosis are defined as ulcus rodens. Histology revel nest-like infiltration from basaloid cells. . Differential diagnosis can be made by traumatically changed dermal nevus and amelanotic melanoma.
Nodular basal cell carcinoma. Peripheral palisading and retraction from surrounding stroma are clearly seen this case also shows keratinization
Also Check: What Is Good For Skin Cancer
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
An evidence-based approach to basal cell cancer
Basal cell cancer is relatively common. Patients often first present to the primary care provider with complaints of an abnormal skin lesion. When diagnosed early, it has an excellent prognosis, but if there is a delay in diagnosis, the tumor can advance and lead to significant morbidity. Basal cell cancer is best managed by an interprofessional team that includes a dermatologist, mohs surgeon, plastic surgeon, nurse practitioner, primary care provider, and a dermatopathologist. Basal cell carcinomas typically have a slow growth rate and tend to be locally invasive. Tumors around the nose and eye can lead to vision loss. In most cases, surgical excision is curative. However, because recurrences can occur, these patients need long-term follow up.
Infiltrative Basal Cell Carcinoma Treatment
Due to the visually challenging element of this kind of skin cancer, the most recommended infiltrative basal cell carcinoma treatment method is Mohs surgery. This surgical procedure aims to remove unhealthy cells from the skin by cutting them out with a scalpel, allowing the healthy tissue to heal around the area. Depending on the patients circumstances, other non-melanoma skin cancer treatments include topical creams, chemotherapy, and IG-SRT, a radiotherapy treatment that helps avoid surgery but with similar results.
You May Like: Is Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma Curable
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin signs and symptoms may include:
- Infiltrating BCC of Skin is a slow-growing malignant tumor. The tumor is a typical skin lesion, with thickened skin, presenting as a poorly-demarcated plaque
- The surface of the plaque may be red, if intact. Else, it may appear as an ulcer, if the surface is eroded
- It is typically observed on sun-exposed areas of the body common sites include the head and neck region, arms and legs, etc.
- The tumor may be solitary or many in number. In children, if it is associated with basal cell nevus syndrome, then multiple lesions may be observed
- Some Infiltrating BCC of Skin may have pigmented appearance and may resemble a melanoma
- Most lesions are less than 1-2 cm, but some may grow to larger sizes of even 10 cm
- The carcinoma has a tendency to penetrate deep into the subcutaneous tissue
- The lesion may grow and there may be itching sensation, ulceration, and bleeding
Benign And Malignant Tumors
Several benign and malignant tumors can have a clinical appearance similar to that of SGC. These include BCC, SCC, melanoma, Merkel cell carcinoma, lymphoma, sweat gland neoplasm, junctional squamous papilloma, hereditary benign intraepithelial dyskeratosis, metastatic carcinoma, and other rare tumors.1
Basal cell carcinoma
The nodular BCC is more common on the lower lid and is white rather than yellow. BCC is also more likely to become ulcerated than SGC. Although diffuse sclerosing BCC may closely simulate SGC, it very rarely exhibits diffuse invasion of the conjunctiva. Histologically, BCC typically shows peripheral palisading of nuclei and retraction artifact that are not seen in SGC.
Squamous cell carcinoma
SCC is more superficial and lacks a yellow color. Conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia can be very similar to diffuse epithelial invasion by SGC, except for eyelid involvement, which is less likely to be present in SGC. Histopathologically, SCC is the lesion most often confused with SGC.6,14,15 Unlike SGC, SCC cells have more abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, lack lipid vacuoles, and demonstrate eddy formation and keratin cysts.
Melanoma
Nodular or diffuse cutaneous melanoma in the eyelid or conjunctiva can usually be distinguished from SGC by its black or brown pigmentation, but amelanotic melanoma can resemble SGC.
Other tumors
You May Like: Can Laser Hair Removal Cause Skin Cancer
You May Like: What Is Stage 4 Melanoma Cancer
Types Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
There are several types of basal cell carcinoma, including:
- Nodular basal cell carcinoma: Approximately 60-80% of all basal cell carcinomas that present on the face or head are nodular. It is the most common subtype, and it is also known as nodulocystic carcinoma. It presents as a shiny, smooth nodule. It may have a dip in the center, with rolled edges, and blood vessels are often seen to cross its surface.
- Superficial spreading basal cell carcinoma: Most commonly seen on the upper body, back, and shoulders, this type is more common in younger adults. It presents as shallow, scaly, irregular plaques that are pink or a similar color to the skin itself. Almost all superficial spreading basal cell carcinomas are secondary to sun damage.
- Sclerosing basal cell carcinoma : This type can be challenging to diagnose. Most commonly seen on the face, it can look like a small, waxy, white scar that expands over time. It can be more dangerous or disfiguring because it is often not recognized as skin cancer until it has grown.
- Pigmented basal cell carcinoma: Most commonly occurs in people with a darker skin tone, particularly Asians. The pigmentation can be found in the different basal cell carcinoma subtypes and it can appear dark blue, dark brown, or black.
It is possible that you can get more than one type of basal cell carcinoma simultaneously. If you have one type, it increases your risk of getting another. Basal cell carcinoma rarely spreads to other parts of the body.
Physical And Emotional Support
Jen says, After the actual cancer was removed at Suburban Hospital, Dr. Desai performed two reconstructions at Johns Hopkins Hospital, starting with a forehead flap procedure, which was really an uncomfortable process.
Dr. Desai says, The forehead flap is a time-honored method for rebuilding the tissues of the nose when there is a large defect due to cancer surgery or trauma. A piece of skin from the forehead is cut away and sewn over the nose. When the flap forms its own blood supply, in two or three weeks, its cut free from the forehead and gives the plastic surgeon tissue to work with in reforming the nose.
Jen says that while the flap of skin from her forehead was healing around her nose, she wanted to hide her appearance from her children. For a week she closed herself off in her bedroom, and she and her children passed loving notes under the door. Jens husband, Greg, was right by her side, changing her bandages and cleaning her wounds every day. Jen says that the support from her family, along with her religious faith, were essential in helping her face the long recovery.
She got additional support at Johns Hopkins. I can’t even say how phenomenal Dr. Desai was. He was so down-to-earth and helped me understand everything that was happening to me. Every time I went, he encouraged me and was honest, but positive.
Jen is getting back to her busy life, supported by her family, her faith, and her care team at Johns Hopkins.
Read Also: How To Tell If Skin Cancer Is Melanoma