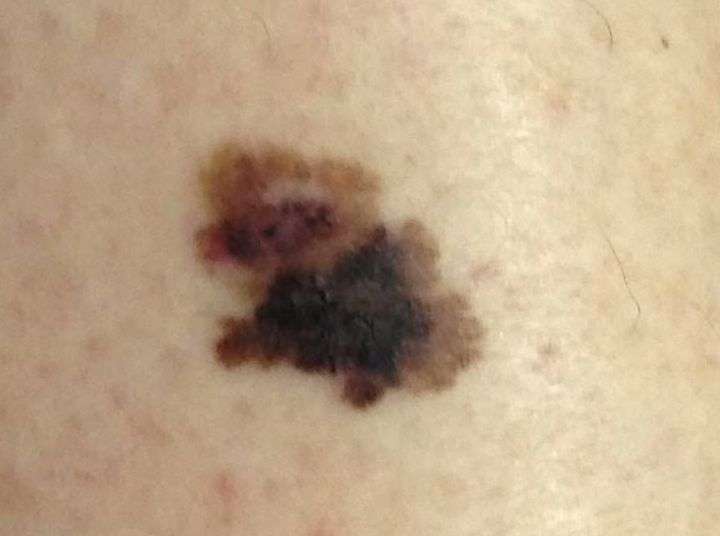
What Is Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is the abnormal and uncontrolled growth of cells in the skin. Skin cancer usually arises on skin exposed to the sun, such as the face, lips, ears, scalp, neck, chest, arms and hands and on the legs especially in women. Though more common in lighter skin tones, skin cancer affects people of all skin tones.
There are three major types of skin cancer:
Each type of skin cancer has a different pathology and presentation.
What Is Melanoma Skin Cancer
Melanoma is a form of skin cancer, arising from cells within the skin called melanocytes.
These melanocytes are normally responsible for producing melanin, a dark coloured pigment which is responsible for giving our skin its colour and the formation of moles on the skin.
As with other forms of skin cancer, melanomas are linked to exposure to UV light. It is thought that your genetics may also have a role in whether you develop melanoma and there does appear to be a higher risk of skin cancers if other family members have also had skin cancer.
Some studies also suggest that those with many moles or pale skin that burns easily in the sun are also at an increased risk of melanoma.
In its initial stages, a melanoma begins by a concentrated overgrowth of melanocytes which start to accumulate. After this process has started, the melanocytes begin to spread to other layers of skin, and if undetected or ignored, can spread to other parts of the body . After being diagnosed, the melanoma will be staged depending on the extent of its growth.
Minimising your exposure to UV light is one simple way to reduce your risk of skin cancer. This can be by reducing your amount of time out in the sun as well as using a high SPF sunscreen.
What Is An Ugly Duckling Mole
Everyone has moles and lesions. Your harmless moles and lesions probably look alike.7 Melanomas stick out from the crowd. Therefore, dermatologists look for the so-called ugly ducklings. This is another way of deciding if a mole or lesion is suspicious, even if it does not meet the ABCDE criteria above.
Also Check: Melanoma On Nose Prognosis
Signs And Symptoms Of Melanoma
The most common sign of melanoma is the appearance of a new mole or a change in an existing mole.
This can happen anywhere on the body, but the most commonly affected areas are the back in men and the legs in women.
Melanomas are uncommon in areas that are protected from sun exposure, such as the buttocks and the scalp.
In most cases, melanomas have an irregular shape and are more than 1 colour.
The mole may also be larger than normal and can sometimes be itchy or bleed.
Look out for a mole that gradually changes shape, size or colour.
Superficial spreading melanoma are the most common type of melanoma in the UK.
They’re more common in people with pale skin and freckles, and much less common in people with darker skin.
They initially tend to grow outwards rather than downwards, so they do not pose a problem.
But if they grow downwards into the deeper layers of skin, they can spread to other parts of the body.
You should see a GP if you have a mole that’s getting bigger, particularly if it has an irregular edge.
Is My Cat At Risk For Skin Cancer
Technically, any cat is at risk to develop skin cancer. While many people know that exposure to the sun increases the chance of developing skin cancer, some skin cancers appear for no discernable reason. There are certain factors, though, that can increase the likelihood that your cat will develop cancer.
Cats who spend most their time outside and therefore have extended exposure to the sun are more at risk. Cats with light fur especially those with white fur are more at risk due to the furs inability to block harmful solar rays.
You May Like: Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rates
What Is Scalp Melanoma
Melanoma is a serious and potentially deadly form of skin cancer. It is more likely to spread locally as well as metastasize , and it accounts for more skin cancer-related deaths than basal and squamous cell carcinomas combined. Melanoma takes its name from melanocytes, the skins pigment-producing cells, where this condition originates. All types of melanoma are more likely to spread to lymph nodes and other tissues, but on the scalp, there are numerous blood vessels and other tissues that can quickly be impacted by melanoma cells.
According to Dr. Walker, The good news is that scalp melanoma is one of the rarest forms of this cancer, accounting for less than 5% of melanoma cases. The bad news is that scalp melanoma tends to be a more severe prognosis than other forms of melanoma. However, research indicates that this is largely because of how late in development its typically diagnosed. Simply put, people are more likely to overlook this condition until its very advanced, making it more difficult to treat.
The Warning Signs Of Skin Cancer
Skin cancers — including melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma — often start as changes to your skin. They can be new growths or precancerous lesions — changes that are not cancer but could become cancer over time. An estimated 40% to 50% of fair-skinned people who live to be 65 will develop at least one skin cancer. Learn to spot the early warning signs. Skin cancer can be cured if it’s found and treated early.
Don’t Miss: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
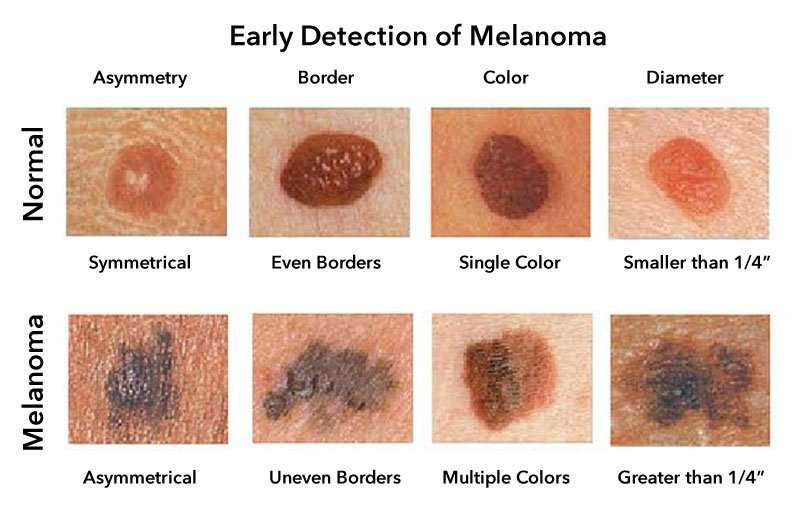
The Abcdes Of Melanoma
The first five letters of the alphabet are a guide to help you recognize the warning signs of melanoma.
A is for Asymmetry. Most melanomas are asymmetrical. If you draw a line through the middle of the lesion, the two halves dont match, so it looks different from a round to oval and symmetrical common mole.
B is for Border. Melanoma borders tend to be uneven and may have scalloped or notched edges, while common moles tend to have smoother, more even borders.
C is for Color. Multiple colors are a warning sign. While benign moles are usually a single shade of brown, a melanoma may have different shades of brown, tan or black. As it grows, the colors red, white or blue may also appear.
D is for Diameter or Dark. While its ideal to detect a melanoma when it is small, its a warning sign if a lesion is the size of a pencil eraser or larger. Some experts say it is also important to look for any lesion, no matter what size, that is darker than others. Rare, amelanotic melanomas are colorless.
E is for Evolving. Any change in size, shape, color or elevation of a spot on your skin, or any new symptom in it, such as bleeding, itching or crusting, may be a warning sign of melanoma.
If you notice these warning signs, or anything NEW, CHANGING or UNUSUAL on your skin see a dermatologist promptly.
A is for Asymmetry
D is for Diameter or Dark
E is for Evolving
E is for Evolving
Types Of Skin Malignancies:
- Melanoma the least common form of skin cancer, but responsible for more deaths per year than squamous cell and basal cell skin cancers combined. Melanoma is also more likely to spread and may be harder to control.
- Nonmelanoma malignancies:
- Squamous cell cancer the second-most common skin cancer. It’s more aggressive and may require extensive surgery, depending on location and nerve involvement.
- Basal cell cancer the most common form of skin cancer. It is rarely fatal but can be locally aggressive.
These skin malignancies are typically caused by ultraviolet radiation from exposure to the sun and tanning beds.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Die From Melanoma
Skin Cancer In Cats: Recognizing The Signs
When most people think about skin cancer, they normally picture fair-skinned people who spend a lot of time in the sun. They remind themselves to lather up in sunblock before going to the beach, the golf course, or even out for a walk.
Skin cancer is responsible for 40% of cancer cases worldwide in humans. We rarely, though, think about our pets being susceptible to skin cancer but they are. The sun is incredibly powerful. Cats, like humans, can fall victim to skin cancer from extended exposure to the suns rays. In fact, skin cancer is the second most common cancer in cats.
Looking For Signs Of Skin Cancer
Non melanoma skin cancers tend to develop most often on skin that’s exposed to the sun.
To spot skin cancers early it helps to know how your skin normally looks. That way, you’ll notice any changes more easily.
To look at areas you cant see easily, you could try using a hand held mirror and reflect your skin onto another mirror. Or you could get your partner or a friend to look. This is very important if you’re regularly outside in the sun for work or leisure.
You can take a photo of anything that doesn’t look quite right. If you can it’s a good idea to put a ruler or tape measure next to the abnormal area when you take the photo. This gives you a more accurate idea about its size and can help you tell if it’s changing. You can then show these pictures to your doctor.
Recommended Reading: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
Squamous Cell Skin Cancers
Squamous cell skin cancers can vary in how they look. They usually occur on areas of skin exposed to the sun like the scalp or ear.
Thanks to Dr Charlotte Proby for her permission and the photography.
You should see your doctor if you have:
- a spot or sore that doesn’t heal within 4 weeks
- a spot or sore that hurts, is itchy, crusty, scabs over, or bleeds for more than 4 weeks
- areas where the skin has broken down and doesn’t heal within 4 weeks, and you can’t think of a reason for this change
Your doctor can decide whether you need any tests.
-
Cancer and its management J Tobias and D HochhauserBlackwell, 2015
-
Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology VT De Vita, TS Lawrence and SA RosenbergWolters Kluwer, 2018
How Can You Make A Difference In The Fight Against Melanoma
Jackie was diagnosed with melanoma at the age of 22.
Also Check: Malignant Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Risk Of Further Melanomas
Most people treated for early melanoma do not have further trouble with the disease. However, when there is a chance that the melanoma may have spread to other parts of your body, you will need regular check-ups. Your doctor will decide how often you will need check-ups everyone is different. They will become less frequent if you have no further problems. After treatment for melanoma it is important to limit exposure to the sun’s UV radiation. As biological family members usually share similar traits, your family members may also have an increased risk of developing melanoma and other skin cancers. They can reduce their risk by spending less time in the sun and using a combination of sun protection measures during sun protection times. It is important to monitor your skin regularly and if you notice any changes in your skin, or enlarged lymph glands near to where you had the cancer, see your specialist as soon as possible.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
DermNet NZ
Squamous cell carcinoma in situ, also known as Bowens disease, is a precancerous condition that appears as a red or brownish patch or plaque on the skin that grows slowly over time. The patches are often found on the legs and lower parts of the body, as well as the head and neck. In rare cases, it has been found on the hands and feet, in the genital area, and in the area around the anus.
Bowens disease is uncommon: only 15 out of every 100,000 people will develop this condition every year. The condition typically affects the Caucasian population, but women are more likely to develop Bowens disease than men. The majority of cases are in adults over 60. As with other skin cancers, Bowens disease can develop after long-term exposure to the sun. It can also develop following radiotherapy treatment. Other causes include immune suppression, skin injury, inflammatory skin conditions, and a human papillomavirus infection.
Bowens disease is generally treatable and doesnt develop into squamous cell carcinoma. Up to 16% of cases develop into cancer.
You May Like: What Does Stage 3b Melanoma Mean
Melanomas That Could Be Mistaken For A Common Skin Problem
Melanoma that looks like a bruise
Melanoma can develop anywhere on the skin, including the bottom of the foot, where it can look like a bruise as shown here.
Melanoma that looks like a cyst
This reddish nodule looks a lot like a cyst, but testing proved that it was a melanoma.
Dark spot
In people of African descent, melanoma tends to develop on the palm, bottom of the foot, or under or around a nail.
Did you spot the asymmetry, uneven border, varied color, and diameter larger than that of a pencil eraser?
Dark line beneath a nail
Melanoma can develop under a fingernail or toenail, looking like a brown line as shown here.
While this line is thin, some are much thicker. The lines can also be much darker.
What Are The Symptoms Of Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck
Skin cancers usually present as an abnormal growth on the skin. The growth may have the appearance of a wart, crusty spot, ulcer, mole or sore. It may or may not bleed and can be painful. If you have a preexisting mole, any change in the characteristics of this spot such as a raised or an irregular border, irregular shape, change in color, increase in size, itching or bleeding are warning signs of melanoma. Sometimes the first sign of melanoma or squamous cell cancer is an enlarged lymph node.
Johns Hopkins Head and Neck Cancer Surgery Specialists
Our head and neck surgeons and speech language pathologists take a proactive approach to cancer treatment. Meet the Johns Hopkins specialists who will work closely with you during your journey.
Read Also: Does Insurance Cover Skin Cancer Screening
Don’t Miss: Small Blue Cell Tumor Prognosis
How Your Skin Works
Your skin works as a barrier to protect your body against things like water loss, bacteria, and other harmful contaminants. The skin has two basic layers: a deeper, thicker layer and an outer layer . The epidermis contains three main types of cells. The outermost layer is composed of squamous cells, which are constantly shedding and turning over. The deeper layer is called the basal layer and is made of basal cells. Lastly, melanocytes are cells that make melanin, or the pigment that determines your skin color. These cells produce more melanin when you have more sun exposure, causing a tan. This is a protective mechanism by your body, and its actually a signal that you are getting sun damage.
The epidermis is in constant contact with the environment. While it sheds skin cells regularly, it can still sustain damage from the sun, infection, or cuts and scrapes. The skin cells that remain are constantly multiplying to replace the sloughed skin, and they can sometimes begin to replicate or multiply excessively, creating a skin tumor that may either be benign or skin cancer.
Here are some common types of skin masses:
Dont Miss: How Deadly Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Biological Therapies And Melanoma
Biological therapies are treatments using substances made naturally by the body. Some of these treatments are called immunotherapy because they help the immune system fight the cancer, or they occur naturally as part of the immune system. There are many biological therapies being researched and trialled, which in the future may help treat people with melanoma. They include monoclonal antibodies and vaccine therapy.
Read Also: Squamous Cell Stage 4
Medical Treatment For Skin Cancer
Surgical removal is the mainstay of therapy for both basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas. For more information, see Surgery.
People who cannot undergo surgery may be treated by external radiation therapy. Radiation therapy is the use of a small beam of radiation targeted at the skin lesion. The radiation kills the abnormal cells and destroys the lesion. Radiation therapy can cause irritation or burning of the surrounding normal skin. It can also cause fatigue. These side effects are temporary. In addition, a topical cream has recently been approved for the treatment of certain low-risk nonmelanoma skin cancers.
In advanced cases, immune therapies, vaccines, or chemotherapy may be used. These treatments are typically offered as clinical trials. Clinical trials are studies of new therapies to see if they can be tolerated and work better than existing therapies.
What Does Scalp Melanoma Look Like
Melanoma is one of the most serious forms of cancer, and because its appearance can closely mimic natural moles, freckles, and age spots, it can be easy to overlook. Its important to know what to look for and perform regular skin cancer screenings to ensure you receive treatment for this condition in the earliest stages. According to Dr. Gregory Walker of U.S. Dermatology Partners in Waco, Texas, Melanoma can be easily overlooked in obvious places on the body, but many people dont know that the scalp, fingernails and toenails, and other harder to see areas often hide this condition until it has progressed to more advanced stages. Patients who know what to look for and regularly screen their skin for cancers, are much more likely to receive a diagnosis in early, more treatable stages. Keep reading to hear more from Dr. Walker about what scalp melanoma looks like and how to check for this condition and prevent serious health concerns.
You May Like: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Metastasize