What Is Choroidal Melanoma
Choroidal melanoma is a cancer that affects part of the eye. It develops in the choroid, the sponge-like membrane at the back of the eye between the sclera and the retina. The choroid is rich in blood vessels and supplies nutrients to the retina.
Over time, many choroidal melanomas enlarge and cause the retina to detach. This can lead to vision loss. The tumors also can spread to other parts of the body. The liver is the most common site for metastasis. If it spreads, this cancer can be fatal.
Although choroidal melanoma is rare, it is the most common eye cancer in adults. It usually occurs in people who are middle-aged or older.
Melanomas usually occur in the skin. But they can also develop in places where certain cells contain the pigment melanin. The choroid is one such example.
Lifestyle Changes For Melanoma Of The Eyelid
Below are some of the lifestyle changes for melanoma of the eyelid:
- Avoiding direct sun during the noon is a good lifestyle change for melanoma of the eyelid.
- Using protections like medicated sun skin lotions or using covers to avoid sun burns if you are very light skinned.
- Taking good care of your skin.
- If you are growing any mole on your eyelid, get it checked.
Who Is At Risk For Intraocular Melanoma
A risk factor is anything that may increase your chance of having a disease. The exact cause of someones cancer may not be known. But certain risk factors can make it more likely for a person to develop cancer. Some risk factors may not be in your control. But others may be things you can change.
Anyone can develop intraocular melanoma. But certain factors may make you more likely to get it. They include:
- Having fair skin and light-colored eyes
- Being older
- Exposure to UV light sources from the sun or tanning beds
- Certain inherited skin problems, such as dysplastic nevus syndrome
Talk with your healthcare provider about your risk factors for intraocular melanoma and what you can do about them.
Also Check: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
Collaborative Ocular Melanoma Study
The COMS was designed and conducted to evaluate radiotherapy for treatment of choroidal melanoma, either in comparison to enucleation or in combination with enucleation . Both US and Canadian centers participated in the COMS. In addition, a nonrandomized observational study of small choroidal melanoma was conducted at a subset of COMS centers. A parallel prospective study of quality of life among patients in the brachytherapy trial was conducted as well. The COMS was sponsored by the National Eye Institute and the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, US Department of Health and Human Services. The COMS design and findings are discussed in detail in Chapter 150 , which cites most publications from the COMS only primary outcome publications are cited here.
Barbara S. Hawkins, Andrew P. Schachat, in, 2013
What Are The Symptoms Of Intraocular Melanoma
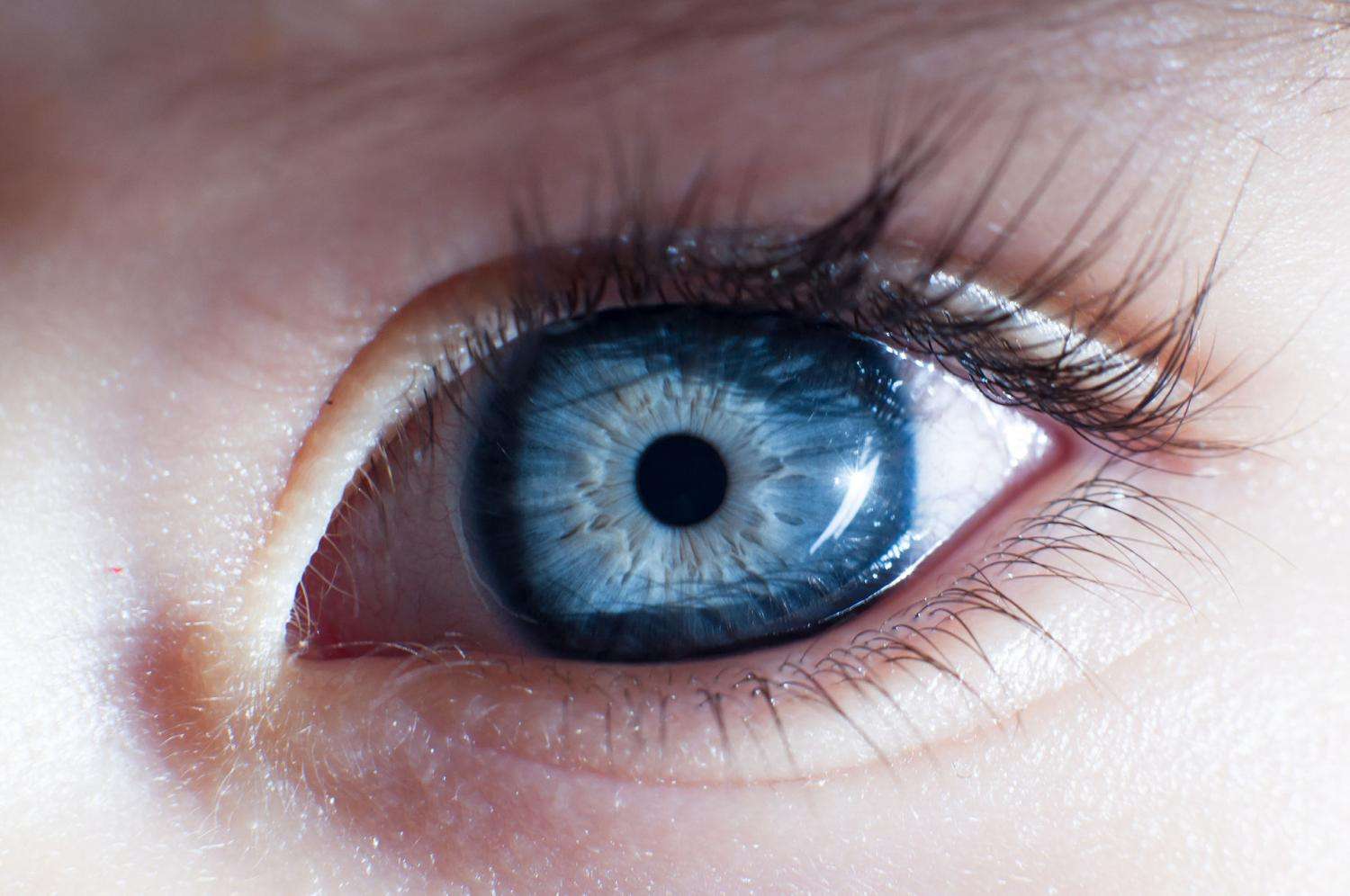
A small growth may not cause any symptoms. As it grows larger, your symptoms may include:
- Blurry vision or sudden vision loss
- Soreness in an eye, or bulging of the eye
- Flashes or floaters in your vision
- Dark spot on your iris, the colored ring at the front of your eye
- Change in the shape of your pupil, the black circle in the center of your eye
- A change in the way your eye moves or looks
Many of these may be caused by other health problems. So its important to see a healthcare provider if you have these symptoms. Your healthcare provider will do an exam and testing to find out if you have cancer.
Also Check: Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch
Life With An Artificial Eye
Mom describes the space where her eye used to be as like the inside of your cheek. She removes the prosthetic eye to clean it occasionally and treats the area with natural tears when it gets dry . Every few years, usually when the prosthetic starts to get uncomfortable, she visits an ocularist someone who specializes in creating and fitting artificial eyes to have the eye refitted or replaced. Over the years, her lower lid has thickened, so the ocularist thins out the bottom of the prosthetic to make it fit better. She has also experienced some drooping of her top lid where the bone has receded. Its possible that cosmetic surgery might help, but Mom is reluctant to have a procedure when there are no guarantees it will work. These days the appearance of it annoys me, Mom says. But I know that I cant worry about that every day or Id go crazy.
Over the years Mom has found ways to adapt. She knows where to sit in a restaurant booth or around a conference table, so she can see everyone. She learned to tell new coworkers about her eye, so they knew she wasnt ignoring them if they happened to approach her from the left. I have a constant bruise on my left forearm from walking into doorknobs, she says, but things could be so much worse.
On March 17, 1978, almost exactly two years to the day after her surgery, she met my Dad. They were married a year later, on St. Patricks Day 1979. My brother, sister and I were born over the next six years.
Detect Health Problems With Eye Exams
Scheduling an eye exam can be an effective way to spot diseases that can be very dangerous to your health in the long run. Conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol may be first identified in eye exams.
Many eye problems share symptoms with serious conditions. However, that does not mean that all symptoms point to serious conditions. You may simply have normal periodic bouts of dry eyes, itchy eyes, or redness.
Don’t Miss: Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Metastasis
In My Mothers Eyes: Her Ocular Melanoma Story
Jeanne Wiley in 1978, a few years after her cancer diagnosis
When I was growing up, I noticed my mom, Jeanne, had a peculiar habit: if I was on her left side when we walked together, she would always move me over to her right. I can still remember the sensation of her stopping, gently grabbing my hand or my waist, and maneuvering us until I was on her right side, so she could see me.
When 3-D movies became popular in the 1990s, Mom didnt have much interest in seeing them. Because she doesnt have any depth perception, the blurry images that you see without 3-D glasses stay blurry for her even with the glasses on.
I vaguely knew that my mother had a special eye that she couldnt see out of, but I didnt really think much about it until I was in high school. Thats when she told me about her ocular melanoma.
I remember one of the first times we talked about it: I was sitting at the kitchen table while she made dinner. I said something about hating my pale legs and the taunts of Casper from my classmates and mentioned that I was thinking of going to a tanning salon. I burned badly when I was in the sun, but some of my friends went to tanning salons and they said I wouldnt get hurt.
Mom stopped what she was doing and looked over at me. Oh Becky, dont do it, she said. My cancer may have been caused by a sunlamp.
What Is Melanoma Of The Eyelid
The eyelid is made mainly of skin and blood capillaries. The eyelids are there to protect our eyes from external factors such as dust, water etc. By the reflex action, our eyelids close immediately when certain object is brought near our eyes. Also the eyelids protects the eyes from dust and other tiny particles to enter the eyes. Eyelids even though are used mainly for protection and covering the eyes are very soft and delicate in nature.
Melanoma is the growth of pigments on various parts of the body. It mainly grows on skin for women, it is often seen on legs. Sometimes, even though not quite often, melanoma may be seen to be growing on the intestine, on the mouth or on the eye.
The cells which contain the pigments and grow on the skin or on the eye are often cancerous in nature. Therefore, melanoma of the eyelid is also known as malignant melanoma of the eyelid. Sometimes, the abnormal development on the mole like the mole gets itchy, the color changes or the size of the mole grows, the skin starts breaking down and the edges of the mole gets irregular may also indicate melanoma.
Don’t Miss: Osteomyoma
Cancers Of The Eyeball
- sensation of something in the eye
- white painless growth on the surface of the eye
Treatment includes surgery to remove the cancer, freezing therapy or chemotherapy eye drops .
Conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia
Sometimes cells on the surface of the conjunctiva can look abnormal. These cell changes are called conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia and are usually diagnosed with a biopsy. You may have treatment with surgery or topical chemotherapy.
CIN is a pre-cancerous change. If left untreated, it may turn into invasive squamous cell cancer and may spread to other parts of the body.
Living With Eye Cancer
After treatment has finished, you will still need regular checks with your specialists and ongoing tests. Eye melanoma can come back in other parts of the body, such as the liver, so your ophthalmologist will want to keep a close watch on you.
If you have had an eye removed, you should still be able to see adequately with just one eye. But it may take a few months for your vision to adjust. You may always have problems with judging distance.
You will need to learn to care for your artificial eye, if you have one. You can find more information on the website Artificial Eyes.
After you have been treated for cancer, it is normal to feel afraid that the cancer will return. If you are struggling, it is important to seek support from your doctor, a therapist or other people who have been through cancer.
You May Like: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
What Causes Eye Cancer
We dont fully understand why eye cancer develops, but there are some things that increase your risk, including:
- having lighter-coloured eyes
- having a lot of moles on your skin
- having a close relative who has had eye cancer
UV radiation from sunlight has also been suggested as a possible risk factor for melanoma of the eye, but this has not been proven.
Learning To See Again
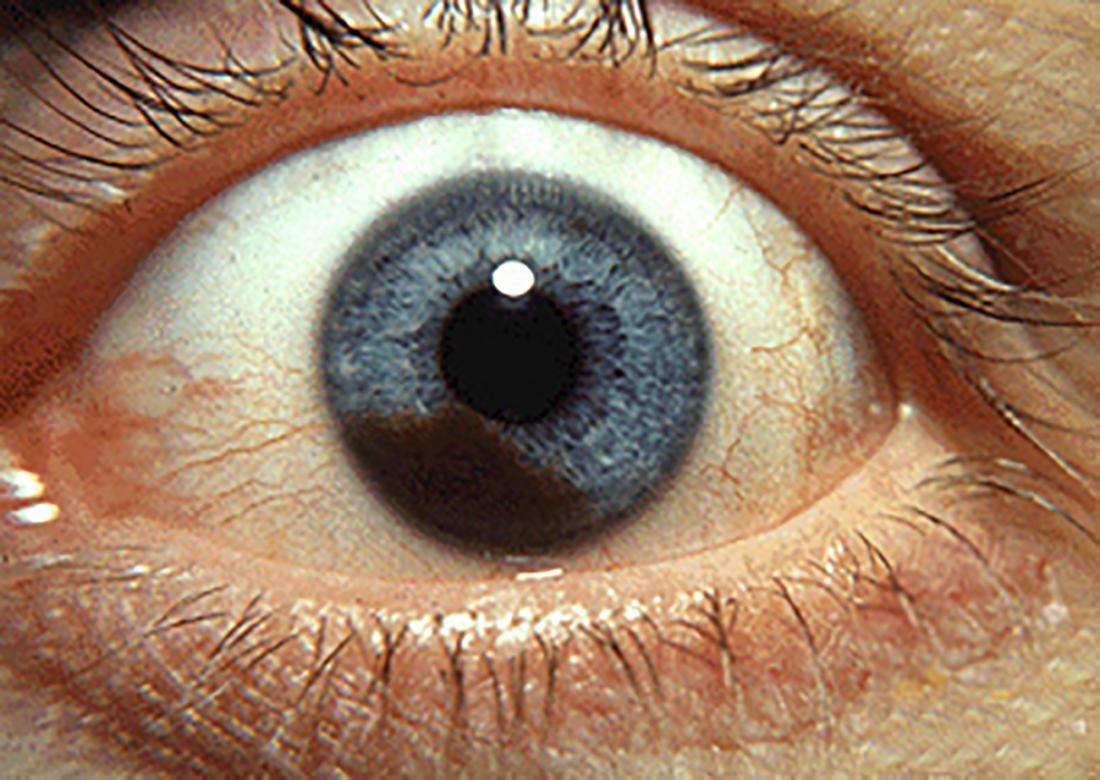
As predicted, the surgery went well. Mom spent five days in the hospital, though these days enucleation is typically an outpatient procedure. She remembers a bit of dizziness for the first day or two, and headaches that went away within a week.
The hardest part was adjusting to monocular vision. Mom had to retrain her right eye and brain to work together without the benefit of depth perception. For example, she remembers trying to paint her nails in the hospital and not being able to line up the nail polish brush with her nails. Something as simple as pouring a cup of water from a pitcher required practice. An occupational therapist at the hospital recommended she use a cup-and-ball toy to improve her hand-eye coordination, and she spent hours practicing.
It was annoying, but everyone told me that my depth perception would get better, Mom says. In the grand scheme of things, it really wasnt that bad.
She was worried about driving, but my grandfather took her out to practice, just like when she was 16. It took a little while to judge the distance to stop signs and stoplights, but eventually I got the hang of it. The only trouble I had was with parallel parking, but I was never any good at that anyway. To this day I just avoid it.
At first Mom only had a piece of gauze over her eye, with a metal shield and a piece of tape. One of her aunts sewed her a selection of cloth patches and she wore them for a month before she was fitted for an artificial eye.
Recommended Reading: Etiology Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
How Is This Cancer Diagnosed
This cancer is diagnosed in large part by the clinical signs and the appearance of the tumor.
Your veterinarian will perform a full physical examination on your cat, followed by a complete ophthalmic examination. The ophthalmic examination will include inspecting the interior structures of the eyes using an ophthalmoscope and measuring the intraocular pressures using a tonometer. Other diagnostic procedures may be performed, usually by a veterinary ophthalmologist. X-rays and ultrasound may also be helpful to determine the size of tumor and extent of spread within the eye. Ultrasound is also helpful to differentiate tumors from cysts, which are benign and of no concern.
Since diffuse iris melanomas are malignant and spread not just locally , but also to other areas of the body , your veterinarian may recommend staging. Staging is the process of determining the extent to which a cancer has grown and spread. Staging may include bloodwork, urinalysis, chest and abdominal X-rays or ultrasound, and FNA of the nearby lymph nodes.
Size Category Classification Table For Ciliary Body And Choroid Melanoma
|
Thickness |
Used with permission of the American Joint Committee on Cancer , Chicago, Illinois.
T1: The tumor is size category 1.
T1a: The tumor is size category 1 and does not involve the ciliary body or other parts of the eye.
T1b: The tumor is a category 1 and involves the ciliary body.
T1c: The tumor is size category 1 that does not involve the ciliary body. But, there is a very small area of visible spread beyond the eyeball. This is called extraocular spread.
T1d: Thetumor is a size category 1 that involves the ciliary body with extraocular spread less than 5 mm.
T2: The tumor is size category 2.
T2a: The tumor is size category 2 and does not involve the ciliary body or other parts of the eye.
T2b: The tumor is size category 2 and involves the ciliary body.
T2c: The tumor is size category 2 that does not involve the ciliary body. But, there is a very small area of visible spread beyond the eyeball.
T2d: The tumor is size category 2 that involves the ciliary body with extraocular spread less than 5 mm.
T3: The tumor is size category 3.
T3a: The tumor is size category 3 and does not involve the ciliary body or other parts of the eye.
T3b: The tumor is size category 3 and involves the ciliary body.
T3c: The tumor is size category 3 that does not involve the ciliary body. But, there is a very small area of visible spread beyond the eyeball.
T3d: The tumor is size category 3 that involves the ciliary body with extraocular spread less than 5 mm.
Recommended Reading: Does Skin Cancer Itch And Burn
Different Types Of Melanoma Of The Eye Include:
Uveal Melanoma
The uvea is three-layered part of the eye. It is made up of the choroid, iris and ciliary body. Uveal melanoma can form in any of these layers and is named for where it forms:
- Choroidal melanoma begins in the layer of blood vessels the choroid beneath the retina. It is the most common type of uveal melanoma. A 2012 article by the American Academy of Ophthalmology discusses the differences between choroidal nevi and choroidal melanoma.2
- Iris melanoma occurs in the front, colored part of the eye. Iris melanomas usually grow slowly and do not typically metastasize, or spread, to other parts of the body outside the eye.
- Ciliary melanoma occurs in the back part of the eye in the ciliary body. Melanomas in the ciliary body tend to grow and metastasize to the liver more quickly than iris melanomas.
The conjunctiva is the clear tissue that covers the white part of the eye, as well as the inside of the eyelids. Conjunctival melanoma is very rare. It often appears as a raised tumor and may contain little or even no pigment. Conjunctival melanoma most commonly occurs in the bulbar conjunctiva the mucous membrane that covers the outer surface of the eyeball. Unlike other forms of ocular melanoma that spread most often to the liver, when conjunctival melanoma spreads, it most often spreads to the lungs.1
What Is Intraocular Melanoma
Melanoma is a serious kind of skin cancer. This cancer starts in cells called melanocytes. These cells produce the pigment that colors your skin. You also have melanocytes in your eyes. When these cells become cancer, its called intraocular melanoma. Its not as common as skin melanoma, but it can be just as serious.
Intraocular melanoma is rare. But it is the most common type of cancer that starts in the eye in adults. In most cases, it starts in a layer of the eye called the choroid. This thin, pigmented layer of blood vessels brings oxygen and nutrients to the eye.
Intraocular melanoma can spread to other parts of your body. These include both nearby tissues and more distant parts of the body. This happens if the cancer cells travel through your lymph system or blood. It can also affect other tissues in and around your eye. These include the colored part of the eye , part of the middle layer of the eye , the thin membrane that covers the eye , and the eyelid.
Also Check: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Orbital And Adnexal Cancers
The orbit consists of the tissues surrounding the eyeball. These include muscles that move the eyeball in different directions and the nerves attached to the eye. Cancers of these tissues are called orbital cancers.
Adnexal structures include the eyelids and tear glands. Cancers that develop in these tissues are called adnexal cancers.
Cancers of the orbit and adnexa develop from tissues such as muscle, nerve, and skin around the eyeball and are like cancers in other parts of the body. For example: