How Is It Diagnosed
There are a variety of tests to diagnose invasive breast cancer. These include:
- Breast exam: During a breast exam, a healthcare professional will carefully feel your breasts for signs of lumps or other changes.
- Mammogram: During a mammogram, a device presses your breasts between two plates. X-ray images of the breast tissue are then taken and evaluated for signs of cancer.
- Imaging tests: A healthcare professional may order additional imaging tests to help them better visualize breast tissue. Some examples include ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging .
- Biopsy: During a biopsy, a sample of breast tissue is carefully removed and checked under a microscope for signs of cancer.
- Blood tests: Blood tests use a sample your blood to check for various markers of disease or illness.
If cancer is detected, additional tests can be used to help characterize the cancer and determine its stage. These tests can include things like:
- Receptor testing: Various tests can check for estrogen receptors, progesterone receptors, and HER2 status.
- Lymph node biopsy: A lymph node biopsy can determine if the cancer has spread to the nearby lymph nodes.
- Imaging tests: Imaging tests can look to see if cancer has spread to other areas. Some that may be used include bone scans, X-rays, CT scans, and positron emission tomography scans.
CE MM 4/8/2021: resolved
Treatment for invasive breast cancer depends on the stage of the cancer as well as other factors. Lets examine the most common treatment options.
Patient And Tumor Characteristics
summarizes the clinical and biological tumor characteristics of the three histologic types of breast cancers. Patients with IDC-L presented at a mean age similar to IDC. Compared to IDC, IDC-L were more likely to have lower histologic grade , be positive for ER and PR , and less likely to overexpress HER-2/neu . Despite having these good prognostic features, there was a higher frequency of nodal metastases . Although IDC-L tumors were larger than IDC tumors, even after correcting for size, the higher frequency of nodal metastases remained significant . Patients with IDC-L presented at a slightly younger age than ILC . Compared to ILC, IDC-L tended to have higher histologic grade and was more likely to be PR positive . There were no significant differences in ER and HER-2/neu expression, tumor size, or frequency of nodal metastases between IDC-L and ILC. Although not statistically significant, patients with IDC-L and ILC were more likely to present with stage III disease than patients with IDC .
Stage Ia & Ib Treatment Options
Stage I describes invasive breast cancer . Stage I is divided into subcategories known as IA and IB.
In general, stage IA describes invasive breast cancer in which:
- the tumor measures up to 2 centimeters and
- the cancer has not spread outside the breast no lymph nodes are involved
In general, stage IB describes invasive breast cancer in which:
- there is no tumor in the breast instead, small groups of cancer cells larger than 0.2 millimeter but not larger than 2 mm are found in the lymph nodes or
- there is a tumor in the breast that is no larger than 2 cm, and there are small groups of cancer cells larger than 0.2 mm but not larger than 2 mm in the lymph nodes
Still, if the cancer is estrogen-receptor-positive or progesterone-receptor-positive, it is likely to be classified as stage IA.
You May Like: Well Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Prognosis
What Are The Possible Complications Of Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma Of Breast
The complications of Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma of Breast may include:
- Emotional distress due to the presence of breast cancer
- 75% of the individuals have metastasis to the axillary lymph nodes at the time of diagnosis some studies report that almost 95% of the tumors would have metastasized during diagnosis
- The recurrence rate is high at 70%
- Side effects of chemotherapy, which may include nausea, vomiting, hair loss, decreased appetite, mouth sores, fatigue, low blood cell counts, and a higher chance of developing infections
- Side effects of radiation therapy that may include sunburn-like rashes, where radiation was targeted, red or dry skin, heaviness of the breasts, and general fatigue
- Lymphedema may occur after surgery or radiation therapy, due to restriction of flow of lymph fluid resulting in a build-up of lymph. It may form weeks to years after treatment that involves radiation therapy to the axillary lymph nodes
Key Differences Between Invasive And Metastatic Breast Cancer
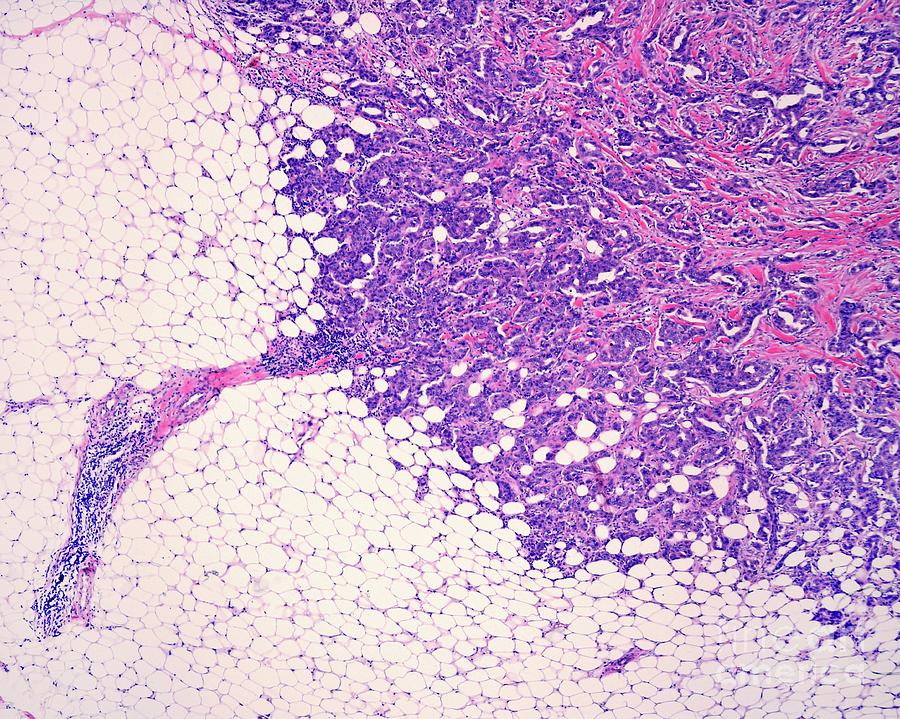
Metastatic breast cancer isnât a specific type of breast cancer, but is the most advanced stage of breast cancer. Both invasive and metastatic breast cancer have spread beyond the exact point where they started. Invasive breast cancers may have spread within the breast only, or to nearby lymph nodes or tissues, or may have spread to distant body parts. All metastatic breast cancers have spread outside of the breast and nearby lymph nodes to distant body parts. If a cancer is only invasive within the breast, itâs usually easier for doctors to treat than metastatic disease.
Recommended Reading: Large Cell Carcinoma Lung Cancer
Rare Types Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Medullary ductal carcinoma accounts for only 3%5% of breast cancers. It may appear on a mammogram, and it does not always feel like a lump rather, it can feel like an abnormally spongy area in the breast tissue.
Mucinous ductal carcinoma is also called colloid breast cancer. It occurs when cancer cells within the milk duct of the breast produce mucous, which also contains breast cancer cells. The cells and mucous combine to form a tumor. Pure mucinous ductal carcinoma tends to grow slowly, and has a better prognosis than some other types of IDCs.
Papillary carcinoma forms finger-like projections that can be seen under a microscope. Many papillary tumors are benign, but even those that become cancerous are usually very treatable with a good prognosis. Papillary carcinoma most commonly occurs in people older than 60.
Tubular ductal carcinoma is a rare diagnosis of IDC, comprising only 2% of breast cancer diagnoses. The name comes from how the cancer looks under the microscope like hundreds of tiny tubes. Tubular breast cancer has an excellent prognosis.
Can Breast Cancer Be Both Invasive And Metastatic
Yes. But thatâs not always the case.
Most metastatic breast cancers were invasive breast tumors before traveling to another body part. Many doctors even consider metastatic breast cancer a type of invasive breast cancer that has spread further. This means that everyone who has metastatic disease has invasive breast cancer. Sometimes, a person already has metastatic breast cancer when they are diagnosed, if it wasnât found before it spread.
But all invasive breast cancers arenât metastatic. Earlier stage breast cancers may have invaded other parts of the breast or nearby lymph nodes but havenât spread to further parts of the body.
Show Sources
Also Check: Body Cancer Symptoms
Grading Breast Cancer Cells
Three cancer cell features are studied and each is assigned a score. The scores are then added to get a number between 3 and 9 that is used to get a grade of 1, 2, or 3, which is noted on your pathology report. Sometimes the terms well differentiated, moderately differentiated, and poorly differentiated are used to describe the grade instead of numbers:
- Grade 1or well differentiated . The cells are slower-growing, and look more like normal breast tissue.
- Grade 2 or moderately differentiated . The cells are growing at a speed of and look like cells somewhere between grades 1 and 3.
- Grade 3or poorly differentiated . The cancer cells look very different from normal cells and will probably grow and spread faster.
Our information about pathology reports can help you understand details about your breast cancer.
Also Check: What Is The Latest Treatment For Melanoma
Symptoms Of Invasive Breast Cancer
Make an appointment to see your doctor if you notice anything different or unusual about the look and feel of your breasts.
The symptoms of breast cancer include:
- a new lump or thickening in your breast or armpit
- a change in size, shape or feel of your breast
- skin changes in the breast such as puckering, dimpling, a rash or redness of the skin
- fluid leaking from the nipple in a woman who isnt pregnant or breast feeding
- changes in the position of nipple
You May Like: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Is Invasive Mammary Carcinoma Genetic
Scientists funded by Breast Cancer Now have confirmed inherited genetic links between non-invasive cancerous changes found in the milk ducts known as ductal carcinoma in situ and the development of invasive breast cancer, meaning that a family history of DCIS could be as important to assessing a womans risk
Special Types Of Invasive Breast Cancer
These are less common forms of invasive ductal breast cancer, and all have particular distinguishing features, which are seen under a microscope.
Pagets Disease of the Breast This rare type of breast cancer accounts for approximately 2% of all breast cancers and usually presents with a red, scaly or ulcerated nipple, sometimes accompanied by a burning sensation or discharge. The cancer cells accumulate in the ducts of the nipple but may extend out to the nipple surface. The skin changes sometimes extend to the areola but they first arise on the nipple. Pagets Disease is often initially confused with eczema or other skin conditions. A full-thickness skin biopsy taken from the nipple/areola is usually required for diagnosis.Occasionally the disease is confined solely to the nipple, but the majority of people with Pagets Disease will also have underlying DCIS or, in some cases, an invasive tumour in the breast.
Mucinous carcinoma This is a rare form of invasive ductal cancer in which cancer cells are surrounded by mucin, a principal component of mucous. It accounts for 2-3% of all breast cancers, and tends to occur in women over 60. It is extremely rare in men. It is generally less aggressive and less likely to spread to the lymph nodes than other types.
Micropapillary carcinoma This is an aggressive form of breast cancer with a high rate of lymph node involvement. The cells form in clusters with distinct clear spaces between them.
Mixed tumours
Don’t Miss: Skin Cancer Prognosis
How Is Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Diagnosed
About 80% of cases are found by mammograms. On the mammogram, it appears as a shadowy area.
If your mammogram suggests that you may have DCIS, your doctor should order a biopsy to analyze the cells and confirm the diagnosis. Biopsies for DCIS are typically done using needles to remove tissue samples from the breast.
If you have DCIS, your doctor may do more tests to gather information about your cancer. These tests may include an ultrasound or MRI. Based on the results of various tests, your doctor will be able to tell the size of your tumor and how much of your breast is affected by the cancer.
What Is Invasive Lobular Carcinoma

Invasive lobular carcinoma is a cancer that starts in the breasts lobules and invades surrounding tissue. ILC is the second most common form of invasive breast cancer, accounting for 10 to 15% of breast cancer cases. ILC doesnt always form a lump, but women who have it may notice a thick or full area that doesnt feel like the rest of the breast.
Read Also: Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rate
What Are Lobular Carcinoma In Situ And Atypical Lobular Hyperplasia
Lobular carcinoma in situ is not considered breast cancer or a precancer because it doesnt turn into invasive cancer if untreated. LCIS and atypical lobular hyperplasia , a similar noncancerous condition, are subtypes of lobular neoplasia, a disorder marked by abnormal cells in the breasts lobules . Since LCIS and ALH raise your risk for breast cancer in the future, if youve been diagnosed with either of them, talk to your doctor about how often you should be screened for breast cancer and whether you should have any additional screening tests.
Examples Using The Full Staging System
Because there are so many factors that go into stage grouping for breast cancer, its not possible to describe here every combination that might be included in each stage. The many different possible combinations mean that two women who have the same stage of breast cancer might have different factors that make up their stage.
Here are 3 examples of how all of the factors listed above are used to determine the pathologic breast cancer stage:
Recommended Reading: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda
Read Also: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stage 2 Survival Rate
Nonsurgical Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Treatment
Radiation. Radiation therapy might be part of your treatment plan if you are undergoing a lumpectomy. Studies show that lumpectomy followed by radiation can be as effective in treating IDC as mastectomy. We dont usually treat patients with radiation after a mastectomy unless theres some cancer in the lymph nodes, Wright says.
Chemotherapy. Deciding on whether to treat invasive ductal breast cancer with chemotherapy, or chemo, depends on features of the tumor cells themselves their genes and proteins. The more the doctor can learn about the characteristics of the cancer cells, the easier it is to determine what type of chemotherapy is likely to be effective.
Hormone therapy. Breast cancers with positive hormone receptors can be treated with estrogen or progesterone. These medications come in pill form, and may be prescribed for several years.
Biologic therapy. This approach uses antibodies or small molecule drugs to activate your bodys immune system to fight the invasive ductal cancer cells.
What Does It Mean If My Report Mentions Paget Disease
Paget disease is when cells resembling the cells of ductal carcinoma in situ are found in the skin of the nipple and the nearby skin . Paget disease of the nipple is usually associated with DCIS or invasive carcinoma in the underlying breast tissue. If Paget disease is found on needle or punch biopsy, more tissue in that area usually needs to be removed with the goal of entirely removing the area of Paget disease. Talk to your doctor about the best treatment for you.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Breast Cancer Prognosis
What Does It Mean If My Doctor Asks For A Special Molecular Test To Be Performed On My Specimen
Molecular tests such as Oncotype DX® and MammaPrint® may help predict the prognosis of certain breast cancers, but not all cases need these tests. If one of these tests is done, the results should be discussed with your treating doctor. The results will not affect your diagnosis, but they might affect your treatment.
Understanding Your Pathology Report: Breast Cancer
When your breast was biopsied, the samples taken were studied under the microscope by a specialized doctor with many years of training called a pathologist. The pathologist sends your doctor a report that gives a diagnosis for each sample taken. Information in this report will be used to help manage your care. The questions and answers that follow are meant to help you understand medical language you might find in the pathology report from a breast biopsy, such as a needle biopsy or an excision biopsy.
In a needle biopsy, a needle is used to remove a sample of an abnormal area. An excision biopsy removes the entire abnormal area, often with some of the surrounding normal tissue. An excision biopsy is much like a type of breast-conserving surgery called a lumpectomy.
Read Also: Stage 3 Melanoma Life Expectancy
What Is The Prognosis Of Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma Of Breast
What Does It Mean If My Carcinoma Is Well Differentiated Moderately Differentiated Or Poorly Differentiated
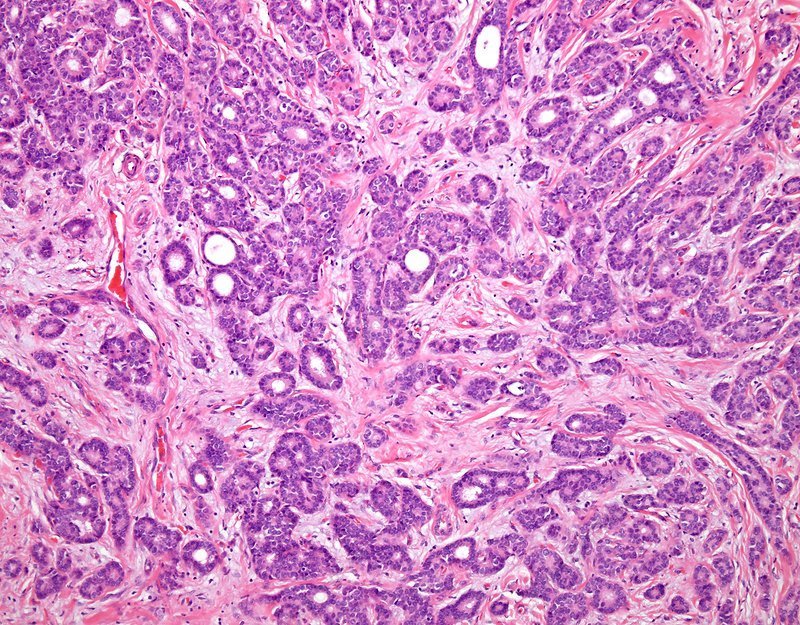
When looking at the cancer cells under the microscope, the pathologist looks for certain features that can help predict how likely the cancer is to grow and spread. These features include the arrangement of the cells in relation to each other, whether they form tubules , how closely they resemble normal breast cells , and how many of the cancer cells are in the process of dividing . These features taken together determine how differentiated the cancer is .
- Well-differentiated carcinomas have relatively normal-looking cells that do not appear to be growing rapidly and are arranged in small tubules for ductal cancer and cords for lobular cancer. These cancers tend to grow and spread slowly and have a better prognosis .
- Poorly differentiated carcinomas lack normal features, tend to grow and spread faster, and have a worse prognosis.
- Moderately differentiated carcinomas have features and a prognosis in between these two.
You May Like: Skin Cancer 1st Stage
Diagnosing Invasive Breast Cancer
In many people the cancer is found during breast screening.
Its important that you see your GP if you have any symptoms. They may refer you to a specialist breast clinic. At the breast clinic the doctor or specialist nurse takes your medical history and examines your breasts. They also feel for any swollen lymph nodes under your arms and at the base of your neck.
You may have some or all of the following tests:
- a mammogram
- an ultrasound
- a biopsy a small sample of cells or tissue is taken from your breast and looked at under a microscope
Changes seen on the mammogram or ultrasound could be due to cancer, so you may have a biopsy of the breast. You might also have an ultrasound of the lymph nodes under your arm. You may also have lymph node biopsies if they look abnormal.
You should get your results within 1 or 2 weeks at a follow up appointment.
- drugs that help prevent or slow down bone thinning or bone damage
- a combination of these treatments
You may have surgery to your armpit called a sentinel lymph node biopsy. This means having about 3-5 lymph nodes removed. Sometimes surgeons have to remove more lymph nodes. Your doctor will let you know whether you need this.
You might have chemotherapy or hormone therapy before surgery called neoadjuvant therapy. The aim is to shrink the cancer down. This means that some people may be able to have breast conserving surgery, who might have needed removal of the breast .