Basal Cell Carcinoma Treatment Options
No matter how treatable cancer is, facing it can still feel overwhelming. You may wonder whether treatment will leave a scar, or if your cancer can come back. Mercy understands your concerns. Well make sure you feel comfortable and confident before beginning any treatment.
Your treatment strategy will depend on several factors. These include the size and location of your basal cell carcinoma. Your doctor may recommend you have one or more types of treatment, including:
- Medication, especially topical creams or ointments
- Cryotherapy
- Surgery to remove the cancer from your skin. Your surgeon will preserve as much healthy skin as possible.
- Radiation therapy
Your relationship with Mercy wont end when your treatments end. Well continue to watch your skin closely, so you can take your mind off cancerand turn it back to the people and activities you love.
Who Discovered Basal Cell Carcinoma
. Similarly one may ask, what does the beginning of basal cell carcinoma look like?
At first, a basal cell carcinoma comes up like a small “pearly” bump that looks like a flesh-colored mole or a pimple that doesn’t go away. Sometimes these growths can look dark. Or you may also see shiny pink or red patches that are slightly scaly. Another symptom to watch out for is a waxy, hard skin growth.
Similarly, what happens to untreated basal cell carcinoma? Basal cell carcinoma is a very slow growing type of non-melanoma skin cancer. If left untreated, basal cell carcinomas can become quite large, cause disfigurement, and in rare cases, spread to other parts of the body and cause death.
Additionally, what causes basal cell carcinoma?
Basal cell carcinoma is caused by damage and subsequent DNA changes to the basal cells in the outermost layer of skin. Exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun and indoor tanning is the major cause of BCCs and most skin cancers.
How serious is basal cell cancer?
Basal cell carcinoma is one of the exceptions, a skin cancer that is more an annoyance than a deadly foe. However, unlike most other malignancies, basal cell skin cancers are seldom aggressive. They rarely kill or spread through the body to cause damage elsewhere.
Excessive Sun Not Always A Factor
While most non-melanoma skin cancers result from sun or ultraviolet exposure, research shows that long-term inflammation and scar formation can also create cancerous change in the skin, says Dr. Tung.
Your dermatologist can confirm the diagnosis of skin cancer by performing a skin biopsy.
A scar looks a world of difference away from a skin cancer under the microscope.
Be on Lookout for Changing Scar
Have a changing scar? You owe to yourself to see a dermatologist to help determine if it has transformed into cancer.
Again, when skin cancer is detected in its early stages, its often fully curable with surgical removal.
Dr. Tungs specialties include general dermatology with skin cancer surveillance, moles, melanoma, surgery and cosmetic dermatology.
Lorra Garrick has been covering medical, fitness and cybersecurity topics for many years, having written thousands of articles for print magazines and websites, including as a ghostwriter. Shes also a former ACE-certified personal trainer.
Copyright Notice
All text is copyright property of this site’s authors. It is illegal to copy, reprint or republish any content or portions of content from this site without the author’s permission.
Disclaimer
Website Advertising Disclaimer
Also Check: How To Catch Skin Cancer Early
There Actually Are Cases In Which Basal Cell Carcinoma Sometimes Called A Non
Youve probably read that basal cell carcinoma cant spread or doesnt spread, but does cause local destruction if not treated.
But basal cell carcinoma CAN spreadand kill.
Unlike melanomas, basal cell carcinomas usually do not metastasize but instead spread locally, says Dr. Tess Mauricio, MD, FAAD, a leading board certified dermatologist from Stanford University Medical School and CEO of MBeautyClinic.com.
However, if BCCs are allowed to spread without treatment, there could be a chance for metastasis, warns Dr. Mauricio.
What are the chances of basal cell carcinoma metastasis?
The chances, in terms of percent, have not been determined. However, check out the following:
Metastasis of basal cell carcinoma rarely occurs. Few cases have been reported in the literature.
the occurrence of BCC metastasis is exceedingly rare, with an average rate of approximately 0.03%, typically involving a large, long-standing, locally destructive, recalcitrant tumor of the head or neck.
Cutis, July 2007
To put this in more perspective, here are intriguing excerpts from DermatologyTimes .
A search of the current literature shows that only about 350 cases of metastatic BCC have been reported.
However, with 1 million new cases of BCC every year in the United States alone, Dr. Giannelli says it is very hard to believe, and highly unlikely, that these metastases do not occur more frequently than they are actually reported.
From the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology :
What Is Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer
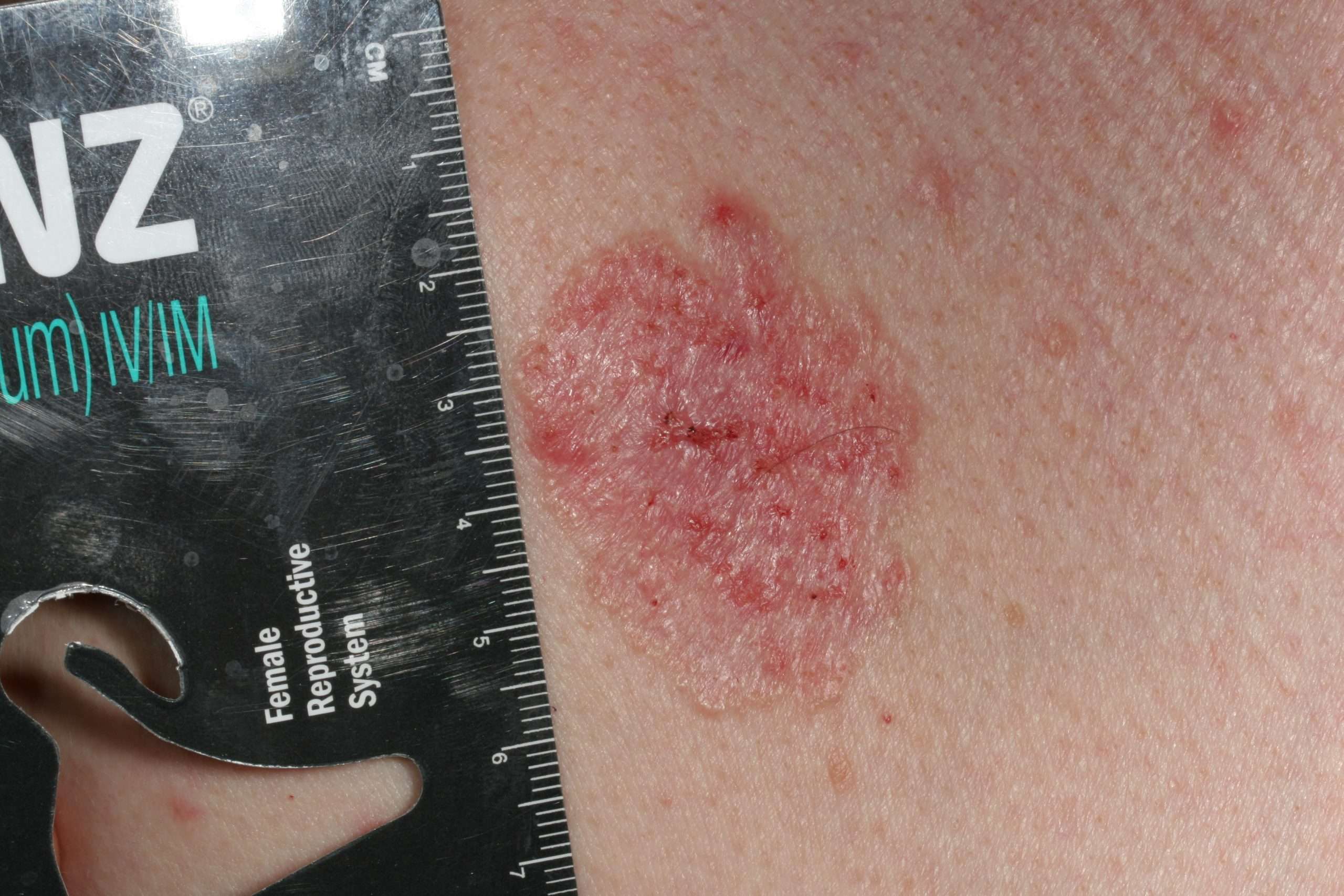
Skin cancer is a disease that begins in the cells of the skin. The area of skin with the cancer is often called a lesion. There are several types of skin cancer . Melanoma is the most serious. But there are others that are known as nonmelanoma skin cancer. These include:
-
Basal cell carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are by far the most common.
You May Like: What Is Sarcoma Skin Cancer
Differentiating Squamous Cell Carcinoma And Basal Cell Carcinoma Skin Cancers
Understanding the type of skin cancer you have been diagnosed with will allow you to ask the right questions when it comes to understanding your treatment. The difference between two of the most common forms of non-melanoma skin cancer will be described here to better understand what skin cancer looks like.
Skin cancer is determined by which type of cells are present when a lesion is biopsied.
The skin is divided into three layers, with many cells and tissues throughout each. Both basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma take place in the outermost layer, the epidermis. The epidermis is a sensitive area, vulnerable to many outside elements that it must work against to protect the body. Both mentioned skin cancers are in effect when basal cells and squamous cells are mutated.
What Are Signs And Symptoms Of Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Basal cell carcinoma typically occurs on areas of the skin exposed to the sun, such as the face, around the eyes, ears, head and scalp, and neck. In rare cases, basal cell cancer may occur on the hands.
Characteristics of the tumors may include the following:
- A pearly white bump
Donât Miss: What Are The Early Stages Of Melanoma
You May Like: How Do You Detect Skin Cancer
How Do People Find Bcc On Their Skin
Many people find it when they notice a spot, lump, or scaly patch on their skin that is growing or feels different from the rest of their skin. If you notice any spot on your skin that is growing, bleeding, or changing in any way, see a board-certified dermatologist. These doctors have the most training and experience in diagnosing skin cancer.
To find skin cancer early, dermatologists recommend that everyone check their own skin with a skin self-exam. This is especially important for people who have a higher risk of developing BCC. Youll find out what can increase your risk of getting this skin cancer at, Basal cell carcinoma: Who gets and causes.
Images used with permission of:
-
The American Academy of Dermatology National Library of Dermatologic Teaching Slides.
-
J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 80:303-17.
What Is A Basal Cell
One of three main types of cells in the top layer of the skin, basal cells shed as new ones form. BCC most often occurs when DNA damage from exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or indoor tanning triggers changes in basal cells in the outermost layer of skin , resulting in uncontrolled growth.
Don’t Miss: Does Medicare Cover Skin Cancer
What Is Aggressive Basal Cell Carcinoma
Superficial and nodular BCC subtypes behave with relatively indolent malignant behaviour. More aggressive BCC subtypes include micronodular, infiltrating, morphoeic or sclerosing, and BCC with squamous differentiationthese aggressive subtypes were assessed combined as aggressive subtype, in this study.
Taking Care Of Yourself
After you’ve been treated for basal cell carcinoma, you’ll need to take some steps to lower your chance of getting cancer again.
Check your skin. Keep an eye out for new growths. Some signs of cancer include areas of skin that are growing, changing, or bleeding. Check your skin regularly with a hand-held mirror and a full-length mirror so that you can get a good view of all parts of your body.
Avoid too much sun. Stay out of sunlight between 10 a.m. and 2 p.m., when the sun’s UVB burning rays are strongest.
Use sunscreen. The suns UVA rays are present all day long — thats why you need daily sunscreen. Make sure you apply sunscreen with at least a 6% zinc oxide and a sun protection factor of 30 to all parts of the skin that aren’t covered up with clothes every day. You also need to reapply it every 60 to 80 minutes when outside.
Dress right. Wear a broad-brimmed hat and cover up as much as possible, such as long-sleeved shirts and long pants.
Continued
You May Like: How Fast Does Melanoma Develop
Additional And Relevant Useful Information For Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Vulva:
Although dirty skin is not considered a risk factor for developing Basal Cell Carcinoma of Vulva, keeping the skin clean helps avoid infections and other complications. However, it must be noted that aggressive cleaning of the skin and use of harsh chemicals and soaps should be avoided, so as to not worsen the condition.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Common In Sun
Squamous cell carcinoma, also called squamous cell cancer, is the second most common type of skin cancer. It accounts for about 20 percent of cases.
This type of cancer starts in flat cells in the outer part of the epidermis. It commonly crops up on sun-exposed areas, such as the face, ears, neck, lips, and hands. It can also develop on scars or chronic sores.
Squamous cell carcinomas may develop from precancerous skin spots, known as actinic keratosis .
These cancers might look like:
- A firm, red bump
- A flat lesion with a scaly, crusted surface
- A sore that heals and then reopens
People with lighter skin are more at risk for developing squamous cell carcinoma, but the skin cancer can also affect those with darker skin.
Other risk factors include:
- Having light eyes, blond or red hair, or freckles
- Being exposed to the sun or tanning beds
- Having a history of skin cancer
- Having a history of sunburns
- Having a weakened immune system
- Having the genetic disorder xeroderma pigmentosum
RELATED: 10 Things You May Know Cause Skin Cancer
You May Like: How To Check For Melanoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma: The Most Common Skin Cancer
Basal cell carcinoma, which is also called basal cell skin cancer, is the most common form of skin cancer, accounting for about 80 percent of all cases.
Rates of basal cell carcinoma have been increasing. Experts believe this is due to more sun exposure, longer lives, and better skin cancer detection methods.
This type of cancer begins in the skins basal cells, which are found in the outermost layer, the epidermis. They usually develop on areas that are exposed to the sun, like the face, head, and neck.
Basal cell carcinomas may look like:
- A flesh-colored, round growth
- A pinkish patch of skin
- A bleeding or scabbing sore that heals and then comes back
They typically grow slowly and dont spread to other areas of the body. But, if these cancers arent treated, they can expand deeper and penetrate into nerves and bones.
Though its rare, basal cell carcinoma can be life-threatening. Experts believe that about 2,000 people in the United States die each year from basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma.
Some risk factors that increase your chances of having a basal cell carcinoma include:
- Being exposed to the sun or indoor tanning
- Having a history of skin cancer
- Being over age 50
- Having chronic infections, skin inflammation, or a weakened immune system
- Being exposed to industrial compounds, radiation, coal tar, or arsenic
- Having an inherited disorder, such as nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome or xeroderma pigmentosum
How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinomas look like flesh-colored, pearl-like bumps or pinkish patches of skin. They can develop into sores. They tend to grow most often on areas of the skin that are exposed to the sun, such as your arms, face, and neck. Often the first detected symptom of a basal cell carcinoma is a bleeding spot without a preceding cause. It is extremely rare to see regional spread or metastasis to other locations in the body. However, if left untreated, the lesion will expand and destroy more tissue locally where it is found.
Don’t Miss: How To Remove Skin Cancer Yourself
What Causes Squamous Cell Cancer
Most squamous cell skin cancers are caused by repeated and unprotected skin exposure to ultraviolet light from sunlight and tanning beds.
Risk factors for developing squamous cell skin cancer include:
- Ultraviolet light exposure
- Having light-colored skin
- Excisional biopsy: removes the entire tumor
- Incisional biopsy: removes only a portion of the tumor
How Do You Prevent Squamous Cell Cancer
Squamous cell skin cancers may be prevented in some cases.
- Limit exposure to ultraviolet rays
- Stay in the shade
- Wear a shirt and hat
- Wear sunglasses to protect eyes
- Avoid tanning beds and sun lamps
Also Check: How Do You Remove Skin Cancer
Rarer Types Of Non Melanoma Skin Cancer
There are other less common types of skin cancer. These include:
- Merkel cell carcinoma
- T cell lymphoma of the skin
- Sebaceous gland cancer
These are all treated differently from basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers.
Merkel cell carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma is very rare. Treatment is with surgery or radiotherapy, or both. This usually works well, but sometimes the cancer can come back in the same place. And sometimes it spreads to nearby lymph nodes.
Sebaceous gland cancer
Sebaceous gland cancer is another rare type of skin cancer affecting the glands that produce the skin’s natural oils. Treatment is usually surgery for this type of cancer.
Kaposi’s sarcoma
Kaposis sarcoma is a rare condition. It’s often associated with HIV but also occurs in people who don’t have HIV. It’s a cancer that starts in the cells that form the lining of lymph nodes and the lining of blood vessels in the skin. Treatment is surgery or radiotherapy, and sometimes chemotherapy.
T cell lymphoma of the skin
T cell lymphoma of the skin can also be called primary cutaneous lymphoma. It’s a type of non Hodgkin lymphoma. There are a number of different types of treatment for this type of cancer.
How Dangerous Is Bcc
While BCCs rarely spread beyond the original tumor site, if allowed to grow, these lesions can be disfiguring and dangerous. Untreated BCCs can become locally invasive, grow wide and deep into the skin and destroy skin, tissue and bone. The longer you wait to have a BCC treated, the more likely it is to recur, sometimes repeatedly.
There are some highly unusual, aggressive cases when BCC spreads to other parts of the body. In even rarer instances, this type of BCC can become life-threatening.
Don’t Miss: Where Does Skin Cancer Metastasis To
Different Kinds Of Skin Cancer
There are many types of skin cancer. Some are very rare. Your doctor can tell you more about the type you have.
The two most common kinds of skin cancers are:
- Basal cell cancer, which starts in the lowest layer of the skin
- Squamous cell cancer, which starts in the top layer of the skin
Another kind of skin cancer is called melanoma. These cancers start from the color-making cells of the skin . You can read about melanoma in If You Have Melanoma Skin Cancer.
What Happens If A Basal Cell Carcinoma Is Not Treated

Posted on September 26, 2015 in Skin Cancer, Mohs Micrographic Surgery, Practice News, Skin Tumor, Basal Cell Carcinoma, malignancy
A basal cell carcinoma is one of the more common forms of skin cancers and, fortunately, one of the most treatable, says Dr. Adam Mamelak, board certified dermatologist and skin cancer specialist in Austin, Texas.
Basal cell carcinoma is most commonly caused by exposure of the skin to ultraviolet light, either from the sun or a tanning bed. Gradually, the effects of exposure damage the DNA, resulting in the development of cancer. The process can take anywhere from weeks to months to several years before it becomes noticeable.
Basal cell carcinomas can look different. They can appear as tiny, pearl shaped bumps. They can also manifest as shiny red or pink patches that feel slightly scaly. They are fragile and can bleed easily. Some appear to be dark against the surrounding skin, while others will break down and create a sore or ulcer on the skin.
If Dr. Mamelak suspects his patients have a basal cell carcinoma, he often does a biopsy on the growth to see if cancer cells are present. Dr. Mamelak also asks his patients a number of questions about their potential risk factors, including how often they are out in the sun, whether or not they use a tanning bed, and what kind of sunblock they use, if any.
What happens if a basal cell carcinoma is not treated?
Contact Us
Don’t Miss: What Causes Small Cell Carcinoma