Symptoms Of Kaposi Sarcoma
Kaposi sarcoma usually appears as purple, pink, or red spots or bumps on the skin. The cancer may grow to several inches or more as a blue-violet to black, flat or slightly raised area. Swelling may be present. Sometimes the cancer grows deeper into soft tissues and invades bone. Cancer of mucosal surfaces, such as in the mouth, are blue to violet in color. In the digestive tract, the cancer can sometimes bleed excessively but usually causes no symptoms.
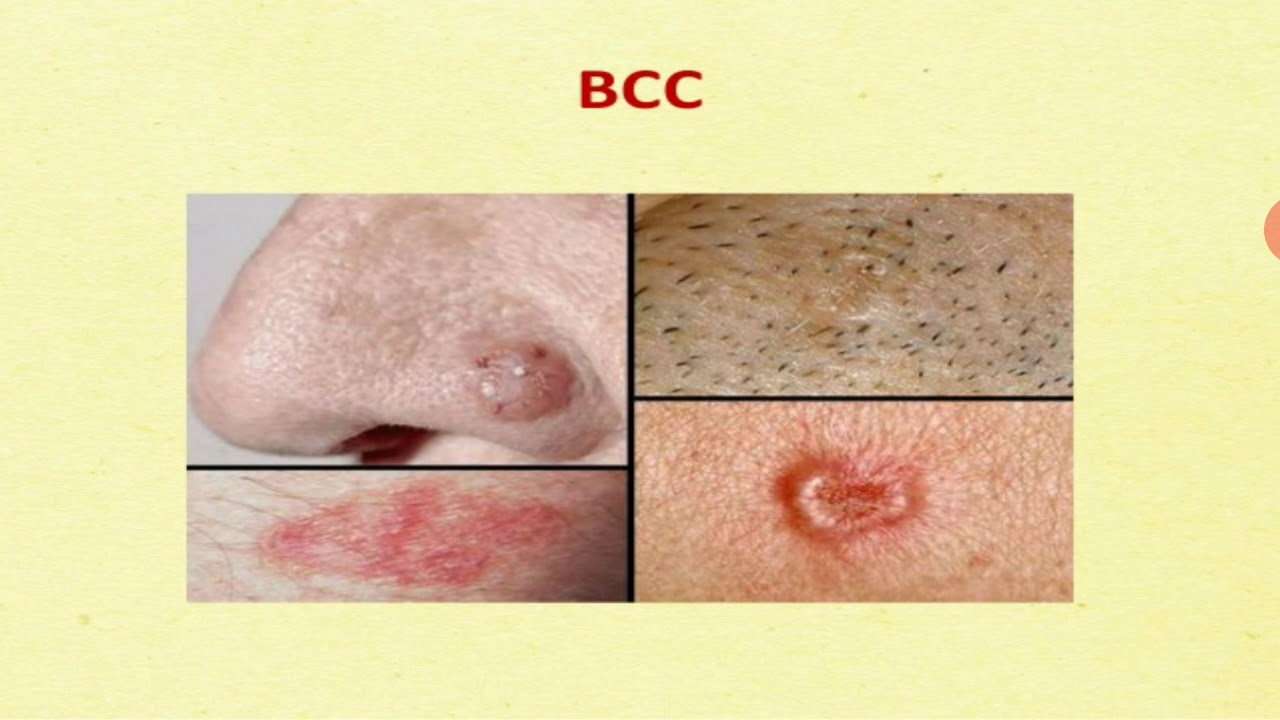
Basal Cell Carcinoma: The Most Common Skin Cancer
Basal cell carcinoma, which is also called basal cell skin cancer, is the most common form of skin cancer, accounting for about 80 percent of all cases.
Rates of basal cell carcinoma have been increasing. Experts believe this is due to more sun exposure, longer lives, and better skin cancer detection methods.
This type of cancer begins in the skins basal cells, which are found in the outermost layer, the epidermis. They usually develop on areas that are exposed to the sun, like the face, head, and neck.
Basal cell carcinomas may look like:
- A flesh-colored, round growth
- A pinkish patch of skin
- A bleeding or scabbing sore that heals and then comes back
They typically grow slowly and dont spread to other areas of the body. But, if these cancers arent treated, they can expand deeper and penetrate into nerves and bones.
Though its rare, basal cell carcinoma can be life-threatening. Experts believe that about 2,000 people in the United States die each year from basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma.
Some risk factors that increase your chances of having a basal cell carcinoma include:
- Being exposed to the sun or indoor tanning
- Having a history of skin cancer
- Being over age 50
- Having chronic infections, skin inflammation, or a weakened immune system
- Being exposed to industrial compounds, radiation, coal tar, or arsenic
- Having an inherited disorder, such as nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome or xeroderma pigmentosum
What Are The Risk Factors For Kaposi Sarcoma
You must already be infected with Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus to develop Kaposi sarcoma. However, most people who have the virus will never get Kaposi sarcoma. The cancer is usually triggered by a weakened immune system in people who are HIV-positive, who have received an organ transplant or whose immune systems are weakened for other reasons, including age.
Don’t Miss: What Does Stage 4 Skin Cancer Look Like
Stages Ii And Iii Soft Tissue Sarcoma
Most stage II and III sarcomas are high-grade tumors. They tend to grow and spread quickly. Some stage III tumors have already spread to nearby lymph nodes. Even when these sarcomas have not yet spread to lymph nodes, the risk of spread is very high. These tumors also tend to grow back in the same area after they’re removed.
For all stage II and III sarcomas, removing the tumor with surgery is the main treatment. Lymph nodes will also be removed if they contain cancer. Radiation may be given after surgery.
If the tumor is large or in a place that would make surgery difficult, but not in lymph nodes, the patient may be treated with chemo, radiation, or both before surgery. The goal of treatment is to shrink the tumor, making it easier to remove. Chemo, radiation, or both might also be given after surgery. These treatments lower the chance of the tumor coming back in or near the same place it started.
Smaller tumors may be treated with surgery first, then radiation to lower the risk of the tumor coming back.
In rare cases, amputation is needed to remove the entire limb with the tumor.
Radiation therapy with or without chemo can be used alone when the tumor’s location or size or the patient’s health in general makes surgery impossible.
What Does Kaposi Sarcoma Look Like
Kaposi sarcoma has some distinct features to keep an eye out for. If the affected area includes the skin, the most common kaposi sarcoma symptoms are flat skin lesions or spots that are red or purple on lighter skin bluish, brownish, or black on darker skin.
These skin lesions most often show up on the legs or face, and while they may look harmful, they typically cause no pain or have any symptoms. Furthermore, kaposi sarcoma skin lesions may look like bruises but dont change color when pressed, and they do not itch or drain.
Don’t Miss: How Often Does Melanoma Spread To Lymph Nodes
What Is Kaposi Sarcoma
A rare type of cancer, kaposi sarcoma develops in the lining of blood and lymph vessels. It typically shows up as tumors on the skin or mucosal surfaces, such as inside the mouth. Kaposi sarcoma tumors can form elsewhere in the body as well, including lymph nodes, genital area, digestive tract, and lungs.
Treatments For Kaposi Sarcoma
As mentioned above, we only treat the skin lesions or spots caused by kaposi sarcoma. Treatment will depend on the number of lesions, how big they are, where they are located, and the strength of the patients immune system.
Cumberland Skins top treatments for small skin lesions include:
- Cryotherapy
- Topicals
Treatment for more serious kaposi sarcoma cases typically involves the use of antiviral medications, radiation, or chemotherapy. In some cases, surgery may be needed.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does Skin Cancer Take To Develop After Sunburn
Common And Rare Tumors
The melanoma, sarcoma, and skin cancer program at the Dignity Health Cancer Institute at St. Josephs Hospital and Medical Center is dedicated to the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of all types of skin cancer, including rare skin cancers such as merkel cell carcinoma, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans and other rare cutaneous tumors. Our disease-specific, medical and surgical oncologists serve the needs of our patients, as well as participate in important research and clinical trials.
Skin cancer is the most frequently diagnosed cancer in the United States. According to the American Academy of Dermatology, 5.4 million cases of non-melanoma skin cancer occurred in the U.S. in 2012, including basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. In the same year, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 67,753 Americans were diagnosed with melanomas of the skin.
Types Of Soft Tissue Sarcoma
There are many different types of soft tissue sarcoma, depending on where in the body it develops.
Examples include:
- leiomyosarcoma develops in muscle tissue
- liposarcoma develops in fat tissue
- angiosarcoma develops in the cells of the blood or lymph glands
- gastrointestinal stromal tumours develop in the connective tissues that support the organs of the digestive system
You May Like: What To Do If I Have Skin Cancer
How To Reduce Your Risk Of Skin Cancer
According to the Centers for Disease Control , protecting yourself and those you love from ultraviolet radiation is important year-round, not just during the summer months. Easy options for protection from UV radiation include the following:
- Stay in the shade, especially during midday hours.
- Wear clothing that covers your arms and legs.
- Wear a hat with a wide brim to shade your face, head, ears, and neck.
- Wear sunglasses that wrap around and block both UVA and UVB rays.
- Use sunscreen with sun protection factor 30 or higher, and both UVA and UVB protection.
- Avoid indoor tanning booths or lamps.
For more information on how to reduce your risks of skin cancer, visit .
Soft Tissue Sarcoma Treatment
The treatment for soft tissue sarcoma depends heavily on the specific subtype of sarcoma, location, size and grade. Multi-modality care is used frequently to provide patients with the best outcome. All patients with sarcoma should be discussed in a multi-disciplinary tumor board to determine treatment plan.
- Surgery Removal of all cancer with intent of getting negative margins. Surgery remains the standard treatment of primary tumors. Important factors to consider are obtaining negative margins, re-operating if possible to get negative margins and not disrupting the tumor.
- Radiation in certain cases, can be given before or after surgery. Radiation is typically used in larger, higher grade tumors.
- Targeted therapy newer agents are being developed to target specific genes or proteins.
- Chemotherapy can be used alone or in combination with surgery and radiation. Some subtypes have better responses to chemotherapy and should be evaluated at a center that routinely treats sarcoma.
- Immunotherapy ongoing clinical trials are evaluating the role of immunotherapy in soft tissue sarcomas.
You May Like: What Are The Symptoms Of Renal Cell Carcinoma
What Causes Kaposi Sarcoma
Kaposi sarcoma is always caused by an infection with a virus called human herpesvirus 8, which is also known as Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus . The virus, which is in the same family as Epstein-Barr virus, is rare in the United States. In fact, less than 1 percent of the general U.S. population is a carrier. The virus and the tumor are much more common in some other parts of the world.
How the virus is initially acquired and spread is poorly understood, but scientists have identified four distinct populations that represent nearly all cases of the disease. There is some evidence within those populations as to how KSHV is acquired and what causes some carriers to develop Kaposi sarcoma.
Sarcoma Vs Carcinoma: Differences And Similarities
There are a number of differences between sarcomas and carcinomas, though individual cancers within each category can vary tremendously. Carcinomas account for the majority of cancers with only 1% of cancers in adults being sarcomas. In children, however, sarcomas account for over 15% of cancers, making research critical. Carcinomas arise out of epithelial cells that line the surface and organs of the body, whereas sarcomas arise from connective tissues such as bone, cartilage, fibrous tissue, blood vessels, and nerves. Learn about the similarities and differences with regard to subtypes, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatments, and prognosis.
Read Also: How Treatable Is Skin Cancer
Merkel Cell Carcinoma: A Rare Skin Cancer On The Rise
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare type of skin cancer that affects about 2,000 people in the United States each year.
Though its an uncommon skin cancer, cases of Merkel cell carcinoma have increased rapidly in the last couple of decades.
This type of cancer starts when cells in the skin, called Merkel cells, start to grow out of control.
Merkel cell carcinomas typically grow quickly and can be difficult to treat if they spread.
They can start anywhere on the body, but Merkel cell carcinomas commonly affect areas exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, and arms.
They may look like pink, red, or purple lumps that are firm when you touch them. Sometimes, they can open up as ulcers or sores.
Risk factors include:
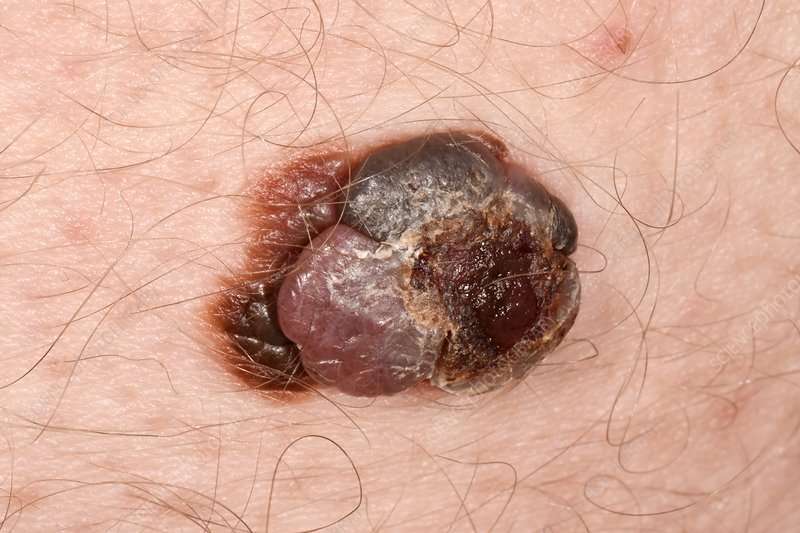
What Are The Symptoms Of Sarcoma
The symptoms of sarcomas vary. For example, in their early stages, some sarcomas may not cause noticeable symptoms. Sarcomas may appear as a painless lump under the skin. Other sarcomas may form in the abdomen, and may not cause symptoms until they grow very large and press on an organ.
Other sarcomas can present as long-lasting bone pain or swelling in an arm or leg that gets worse at night, or decreased mobility.
Sarcoma symptoms that should be investigated are masses that grow larger, painless masses that have become painful or masses larger than a golf ball .
In the case of children, a child who has bone pain that does not get better on its own, and that did not occur with an injury, should have an imaging test to investigate.
You May Like: What Are Some Treatments For Melanoma
Diagnosis Screening And Staging
The diagnostic process for sarcomas can be similar to carcinomas, and often begins with scans , or in the case of digestive tract sarcomas, endoscopy. Similarly, a biopsy is needed to determine the type of cancer as well as the tumor grade . Special stains may likewise be helpful.
As with carcinomas, DNA testing is often helpful, but in the case of some sarcomas, RNA testing may be helpful as well.
Survival Rate Of Soft Tissue Sarcoma:
The overall survival rate of the soft tissue sarcoma is better than other cancer forms. The survival rate counted on the basis of 5 year survival has found that almost 90 % of the patientâs diagnosed in the Stage A have survived for 5 or more years. However the rate decreases to 75 % for the Stage B and 56 % for the early Stage C of the disease.
Don’t Miss: Where Can You Get Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Cancer Terminology: Oma Vs Sarcoma Etc
Most of the time , the description of a tumor differentiates benign connective tissue tumors from malignant sarcomas.
For example, a lipoma is a benign tumor of fat , and a liposarcoma is a cancerous tumor of the tissue. A hemangioma is a benign tumor of blood vessels, whereas a hemangiosarcoma is a malignant tumor.
There are exceptions in this classification as well. For example, a chordoma is malignant. A glioma is a cancer of glial cells in the brain. Sometimes, the word malignant is used to distinguish benign and malignant tumors. For example, a meningioma refers to a benign tumor of the meninges , whereas a cancerous tumor is referred to as malignant meningioma.
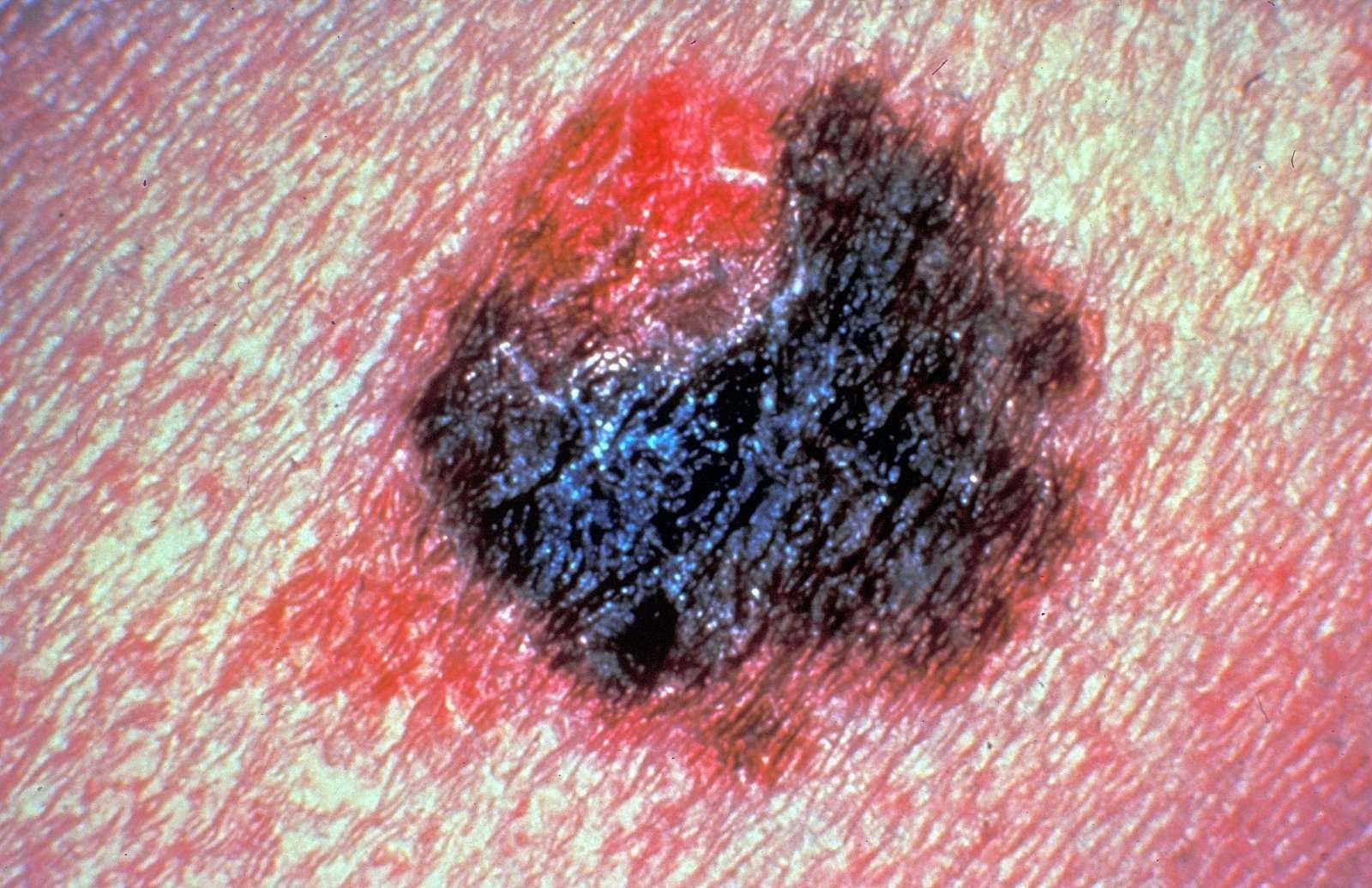
What Melanoma Skin Cancer Looks Like
Melanoma can look a lot like age spots and can develop in moles. That being said, it does not really look like sarcoma at all. Melanoma is the most dangerous form of skin cancer in the world. Though it only accounts for less than one percent of skin cancer cases, melanoma causes the majority of deaths from skin cancer, according to the Skin Cancer Foundation. Thats why its imperative to see a doctor if youre worried you have skin cancer. Melanoma is most commonly caused by UV rays from the sun or tanning beds.
If you see a strange spot on your skin or notice that a spot is changing, make sure you look for the ABCDE signs of melanoma, according to the Skin Care Foundation:
- Asymmetry: If you draw an invisible line between the two sides of your mole and notice that they dont match, then there is a chance you may have melanoma.
- Border: In the early stages of melanoma, the border of your mole is typically scalloped, notched, or uneven.
- Color: Melanoma moles can be made up of multiple shades of color, including brown, tan, black, red, white, or blue.
- Diameter: While melanoma may be smaller when first detected, its diameter is usually larger than the eraser on a pencil tip.
- Evolving: Melanoma tends to evolve or change over time. Be on the lookout for changes in size, color, elevation, shape, or any other feature. You should also check for symptoms like bleeding, crusting or itching.
Read Also: What Does Sebaceous Carcinoma Look Like
Remember: All Omas Arent Cancer
In cancers, including carcinoma and sarcoma, cells divide uncontrollably, invade nearby tissues and can eventually spread to distant sites.
It is important to know that benign masses may also end in oma, which means tumor, but these cells behave and are treated quite differently, says Dr. Shepard.
For example, cells in benign tumors such as adenomas, fibromas and angiomas will not invade nearby tissues or spread to other sites.
Thus, the tumors dont have the same negative consequences as a carcinoma or sarcoma.
Overlap Between Sarcomas And Carcinomas
The region of the body does not always distinguish sarcomas and carcinomas. For example, breast sarcomas arise in the connective tissue of the breasts rather than milk ducts or lobules. Most “colon cancers” are adenocarcinomas, but 1% to 2% of tumors in this region are leiomyosarcomas of the colon and rectum.
Some tumors may have characteristics of both carcinomas and sarcomas and may be referred to as carcinosarcomas or sarcomatoid carcinomas.
Also Check: Are There Any Symptoms Of Skin Cancer
Causes Of Soft Tissue Sarcomas
In most cases there are no obvious reasons why a soft tissue sarcoma develops, but there are a number of things known to increase the risk, including:
- age soft tissue sarcomas can happen at any age, including in children, but they’re more common in middle-aged or elderly people and your risk increases as you get older
- certain genetic conditions, such as neurofibromatosis type 1 and retinoblastoma, are associated with an increased risk of soft tissue sarcomas
- previous radiotherapy some people who have previously had radiotherapy for another type of cancer develop a soft tissue sarcoma, often many years later
- exposure to certain chemicals, including vinyl chloride, dioxins and phenoxyacetic herbicides, has been associated with increased rates of soft tissue sarcoma
Kaposi’s sarcoma is a very rare sarcoma caused by the human herpesvirus 8 infecting someone with a weakened immune system .
Melanoma: The Deadliest Skin Cancer
Melanoma is the most serious type of skin cancer, because it tends to spread if its not treated early.
This cancer starts in the melanocytes cells in the epidermis that make pigment.
About 100,350 new melanomas are diagnosed each year.
Risk factors for melanoma include:
- Having fair skin, light eyes, freckles, or red or blond hair
- Having a history of blistering sunburns
- Being exposed to sunlight or tanning beds
- Living closer to the equator or at a higher elevation
- Having a family history of melanoma
- Having many moles or unusual-looking moles
- Having a weakened immune system
Melanoma can develop within a mole that you already have, or it can pop up as a new dark spot on your skin.
This cancer can form anywhere on your body, but it most often affects areas that have had sun exposure, such as the back, legs, arms, and face. Melanomas can also develop on the soles of your feet, palms of your hands, or fingernail beds.
Signs to watch out for include:
- A mole that changes in color, size, or how it feels
- A mole that bleeds
RELATED: The Difference Between Chemical and Mineral Sunscreen
Also Check: What Is Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma