Treating Stage I Melanoma
Stage I melanoma is typically treated by wide excision . The width of the margin depends on the thickness and location of the melanoma. Most often, no other treatment is needed.
Some doctors may recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy to look for cancer in nearby lymph nodes, especially if the melanoma is stage IB or has other characteristics that make it more likely to have spread. You and your doctor should discuss this option.
If the SLNB does not find cancer cells in the lymph nodes, then no further treatment is needed, although close follow-up is still important.
If cancer cells are found on the SLNB, a lymph node dissection might be recommended. Another option might be to watch the lymph nodes closely by getting an ultrasound of the nodes every few months.
If the SLNB found cancer, adjuvant treatment with an immune checkpoint inhibitor or targeted therapy drugs might be recommended to try to lower the chance the melanoma will come back. Other drugs or perhaps vaccines might also be options as part of a clinical trial.
Permission To Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text. It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. However, a user would be allowed to write a sentence such as NCIs PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks in the following way: .
The best way to cite this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Adult Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Melanoma Treatment. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated <MM/DD/YYYY>. Available at: . Accessed <MM/DD/YYYY>.
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author, artist, and/or publisher for use in the PDQ summaries only. If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in Visuals Online. Visuals Online is a collection of more than 3,000 scientific images.
Symptoms Of Mucosal Melanoma
Unlike cutaneous melanomas, mucosal melanomas are hard to diagnose because they are hidden inside your body. The typical skin exams that help locate cancer lesions on visible skin aren’t practical for the skin you can’t see.
There are symptoms of mucosal melanoma. They vary depending on the location of the cancer.
Head and neck. Almost half of mucosal melanoma cases are in the mouth, nose, or throat. Symptoms include mouth ulcers, unexplained nosebleeds, and a lump in the neck, jaw, or mouth. You may have mouth pain or difficulty talking. You may be able to see lesions inside your mouth.â
Anus. Melanoma of the anus may cause bleeding from the anus. You may feel a growth or something protruding from your anus. You may also experience constipation, pain, or discomfort.â
Vagina and vulva. Melanoma of the vagina or vulva can lead to unexplained vaginal bleeding. You may be able to feel a mass inside your vagina. You could have visible lesions on your vulva. You might experience pain or discomfort.
Don’t Miss: Can Renal Cell Carcinoma Be Benign
How Do People Find Signs Of Melanoma On Their Own Skin
Performing a skin self-exam as often as recommended by your dermatologist is the best way. While examining your skin, you want to look for the following:
-
Mole that is changing in any way
-
Spot that looks different from the rest of the spots on your skin
-
Growth or spot on your skin that itches, bleeds, or is painful
-
Band of color beneath or around a nail
-
Sore that doesnt heal or heals and returns
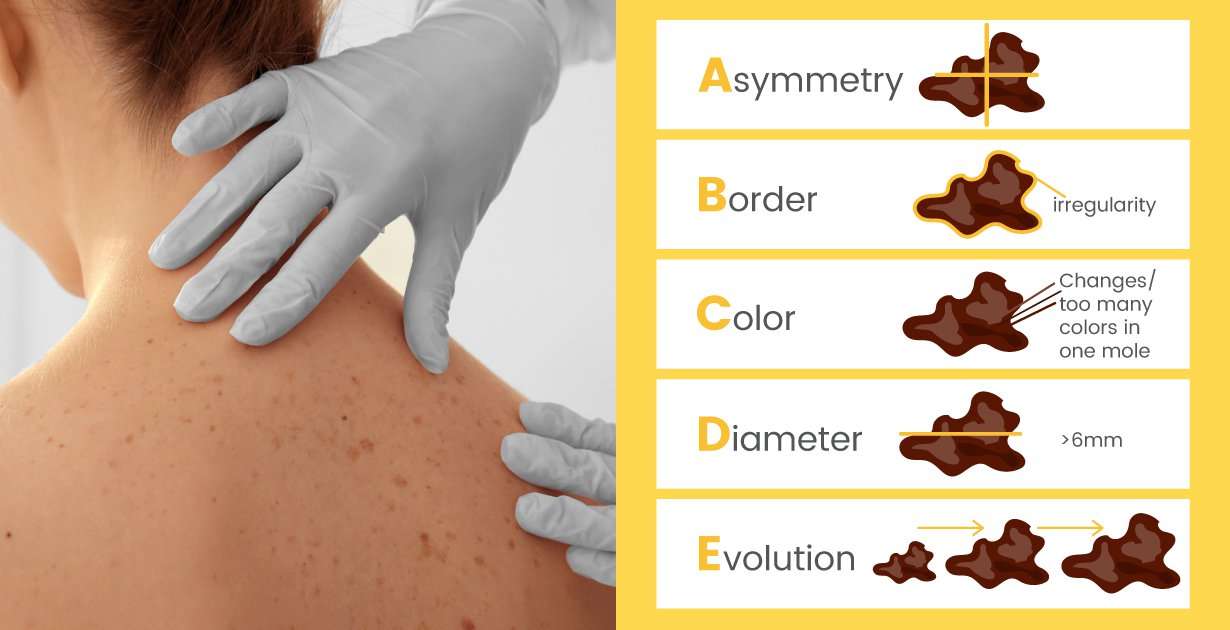
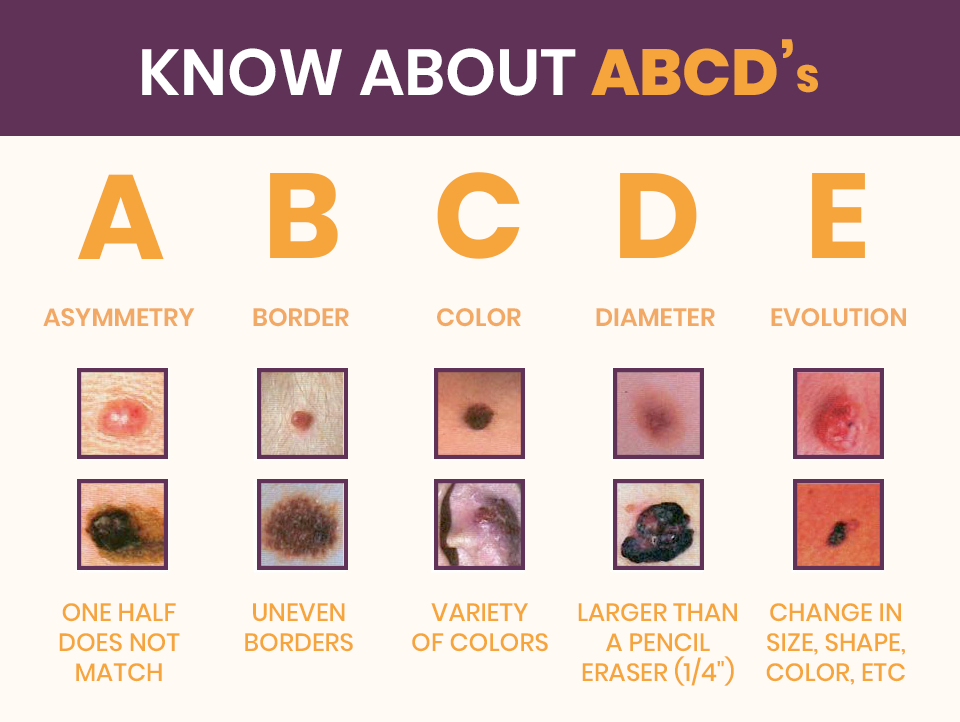
The ABCDEs of melanoma can help you find changes to a mole, freckle, or other spot on your skin.
What Tests Are Used To Stage Melanoma
There are several tests your doctor can use to stage your melanoma. Your doctor may use these tests:
- Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy: Patients with melanomas deeper than 0.8 mm, those who have ulceration under the microscope in tumors of any size or other less common concerning features under the microscope, may need a biopsy of sentinel lymph nodes to determine if the melanoma has spread. Patients diagnosed via a sentinel lymph node biopsy have higher survival rates than those diagnosed with melanoma in lymph nodes via physical exam.
- Computed Tomography scan: A CT scan can show if melanoma is in your internal organs.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging scan: An MRI scan is used to check for melanoma tumors in the brain or spinal cord.
- Positron Emission Tomography scan: A PET scan can check for melanoma in lymph nodes and other parts of your body distant from the original melanoma skin spot.
- Blood work: Blood tests may be used to measure lactate dehydrogenase before treatment. Other tests include blood chemistry levels and blood cell counts.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Tell If You Have Skin Cancer
Thinking About Taking Part In A Clinical Trial
Clinical trials;are carefully controlled research studies that are done to get a closer look at promising new treatments or procedures. Clinical trials are one way to get state-of-the art cancer treatment. In some cases they may be the only way to get access to newer treatments. They are also the best way for doctors to learn better methods to treat cancer. Still, they’re not right for everyone.
If you would like to learn more about clinical trials that might be right for you, start by asking your doctor if your clinic or hospital conducts clinical trials.;
What Is The Process Of Liquid Nitrogen Skin Cancer Treatment
With this process, a dermatologist will destroy the skin cancer cells by freezing the lesion with liquid nitrogen. The liquid nitrogen is applied to the cells with a cotton applicator or a spray. The method is also known for being used to remove warts, so it may sound familiar. This method can call for numbing prior to the process, depending on how large the lesion is and how sensitive the individual is.
Also Check: What Happens If I Have Melanoma
Tests Or Procedures That Examine The Skin Are Used To Diagnose Basal Cell Carcinoma And Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin
The following procedures may be used:
- Physical exam and health history: An exam of the body to check general signs of health, including checking for signs of disease, such as lumps or anything else that seems unusual. A history of the patients health habits and past illnesses and treatments will also be taken.
- Skin exam: An exam of the skin for bumps or spots that look abnormal in color, size, shape, or texture.
- Skin biopsy: All or part of the abnormal-looking growth is cut from the skin and viewed under a microscope by a pathologist to check for signs of cancer. There are four main types of skin biopsies:
- Shave biopsy: A sterile razor blade is used to shave-off the abnormal-looking growth.
- Punch biopsy: A special instrument called a punch or a trephine is used to remove a circle of tissue from the abnormal-looking growth. Enlarge Punch biopsy. A hollow, circular scalpel is used to cut into a lesion on the skin. The instrument is turned clockwise and counterclockwise to cut down about 4 millimeters to the layer of fatty tissue below the dermis. A small sample of tissue is removed to be checked under a microscope. Skin thickness is different on different parts of the body.
- Incisional biopsy: A scalpel is used to remove part of a growth.
- Excisional biopsy: A scalpel is used to remove the entire growth.
What Are Targeted Therapies
A targeted therapy is a drug that blocks the growth of cancer by interfering with specific molecules involved in tumour growth. This is different to non-specific treatments like chemotherapy that simply aim to kill rapidly dividing cells.;
This new generation of drugs has resulted in a big improvement in melanoma treatment for patients with the spread of the disease to other organs.
Researchers have identified some of the key genetic mutations that drive the growth of melanoma in patients. These discoveries are opening new avenues for treatment options using drugs that selectively block activity of these driving mutations, known as targeted therapy.
The genetic mutations involved in melanoma development that have been discovered so far have interesting names. They include:
- BRAF
More mutations are continuing;to be discovered.
Also Check: Does Melanoma Metastasize To The Brain
Remission And The Chance Of Recurrence
A remission is when cancer cannot be detected in the body and there are no symptoms. This may also be called having no evidence of disease or NED.
A remission may be temporary or permanent. This uncertainty causes many people to worry that the cancer will come back. While many remissions are permanent, it is important to talk with your doctor about the possibility of the cancer returning. Understanding your risk of recurrence and the treatment options may help you feel more prepared if the cancer does return.;Learn more about coping with the fear of recurrence.
If the melanoma returns after the original treatment, it is called recurrent cancer. It may come back in the same place , nearby , or in another part of the body .
When this occurs, a new cycle of testing will begin to learn as much as possible about the recurrence. After this testing is done, you and your doctor will talk about the treatment options. Often the treatment plan will include the treatments described above, such as surgery, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and radiation therapy, but they may be used in a different combination or given at a different pace. Your doctor may suggest clinical trials that are studying new ways to treat this type of recurrent cancer. Whichever treatment plan you choose, palliative care will be important for relieving symptoms and side effects.
After Melanoma Has Been Diagnosed Tests May Be Done To Find Out If Cancer Cells Have Spread Within The Skin Or To Other Parts Of The Body
The process used to find out whether cancer has spread within the skin or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment.
For melanoma that is not likely to spread to other parts of the body or recur, more tests may not be needed. For melanoma that is likely to spread to other parts of the body or recur, the following tests and procedures may be done after surgery to remove the melanoma:
The results of these tests are viewed together with the results of the tumor biopsy to find out the stage of the melanoma.
Don’t Miss: What Does Skin Cancer Of The Lip Look Like
Basal Cell Carcinoma: The Most Common Skin Cancer
Basal cell carcinoma, which is also called basal cell skin cancer, is the most common form of skin cancer, accounting for about 80 percent of all cases.
Rates of basal cell carcinoma have been increasing. Experts believe this is due to more sun exposure, longer lives, and better skin cancer detection methods.
This type of cancer begins in the skins basal cells, which are found in the outermost layer, the epidermis. They usually develop on areas that are exposed to the sun, like the face, head, and neck.
Basal cell carcinomas may look like:
- A flesh-colored, round growth
- A pinkish patch of skin
- A bleeding or scabbing sore that heals and then comes back
They typically grow slowly and dont spread to other areas of the body. But, if these cancers arent treated, they can expand deeper and penetrate into nerves and bones.
Though its rare, basal cell carcinoma can be life-threatening. Experts believe that about 2,000 people in the United States die each year from basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma.
Some risk factors that increase your chances of having a basal cell carcinoma include:
- Being exposed to the sun or indoor tanning
- Having a history of skin cancer
- Being over age 50
- Having chronic infections, skin inflammation, or a weakened immune system
- Being exposed to industrial compounds, radiation, coal tar, or arsenic
- Having an inherited disorder, such as nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome or xeroderma pigmentosum
After Squamous Cell Cancer Of The Skin Has Been Diagnosed Tests Are Done To Find Out If Cancer Cells Have Spread Within The Skin Or To Other Parts Of The Body
The process used to find out if cancer has spread within the skin or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment for squamous cell carcinoma of the skin.
Basal cell carcinoma of the skin rarely spreads to other parts of the body. Staging tests to check whether basal cell carcinoma of the skin has spread are usually not needed.
The following tests and procedures may be used in the staging process for squamous cell carcinoma of the skin:
Don’t Miss: Is Non Melanoma Skin Cancer Deadly
Treating Stage 0 Melanoma
Stage 0 melanoma has not grown deeper than the top layer of the skin . It is usually treated by surgery to remove the melanoma and a small margin of normal skin around it. The removed sample is then sent to a lab to be looked at with a microscope. If cancer cells are seen at the edges of the sample, a second, wider excision of the area may be done.
Some doctors may consider the use of imiquimod cream or radiation therapy instead of surgery, although not all doctors agree with this.
For melanomas in sensitive areas on the face, some doctors may use Mohs surgery or even imiquimod cream if surgery might be disfiguring, although not all doctors agree with these uses.
Unusual Moles Exposure To Sunlight And Health History Can Affect The Risk Of Melanoma
Anything that increases your risk of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer; not having risk factors doesn’t mean that you will not get cancer. Talk with your doctor if you think you may be at risk.
Risk factors for melanoma include the following:
- Having a fair complexion, which includes the following:
- Fair skin that freckles and burns easily, does not tan, or tans poorly.
- Blue or green or other light-colored eyes.
- Red or blond hair.
Being White or having a fair complexion increases the risk of melanoma, but anyone can have melanoma, including people with dark skin.
See the following PDQ summaries for more information on risk factors for melanoma:
Recommended Reading: What Types Of Melanoma Are There
If Treatment Does Not Work
Recovery from melanoma is not always possible. If the cancer cannot be cured or controlled, the disease may be called advanced or terminal.
This diagnosis is stressful, and for many people, advanced cancer is difficult to discuss. However, it is important to have open and honest conversations with your health care team to express your feelings, preferences, and concerns. The health care team has special skills, experience, and knowledge to support patients and their families and is there to help. Making sure a person is physically comfortable, free from pain, and emotionally supported is extremely important.
People who have advanced cancer and who are expected to live less than 6 months may want to consider hospice care. Hospice care is designed to provide the best possible quality of life for people who are near the end of life. You and your family are encouraged to talk with the health care team about hospice care options, which include hospice care at home, a special hospice center, or other health care locations. Nursing care and special equipment can make staying at home a workable option for many families.;Learn more about advanced cancer care planning.
After the death of a loved one, many people need support to help them cope with the loss.;Learn more about grief and loss.
Patients May Want To Think About Taking Part In A Clinical Trial
For some patients, taking part in a clinical trial may be the best treatment choice. Clinical trials are part of the cancer research process. Clinical trials are done to find out if new cancer treatments are safe and effective or better than the standard treatment.
Many of today’s standard treatments for cancer are based on earlier clinical trials. Patients who take part in a clinical trial may receive the standard treatment or be among the first to receive a new treatment.
Patients who take part in clinical trials also help improve the way cancer will be treated in the future. Even when clinical trials do not lead to effective new treatments, they often answer important questions and help move research forward.
Don’t Miss: Can Skin Cancer Look Like Psoriasis