Putative Genes For Basal Cell Carcinoma
BRCA1-associated protein 1
Pathogenic variants in the BAP1 gene are associated with an increased risk of a variety of cancers, including cutaneous melanoma and uveal melanoma. Although the BCC penetrance in individuals with pathogenic variants in BAP1 is not known, there are several BAP1 families that report diagnoses of BCC. In one study, pathogenic variant carriers from four families reported diagnoses of BCC. Tumor evaluation of BAP1 showed loss of BAP1 protein expression by immunohistochemistry in BCCs of two germline BAP1 pathogenic variant carriers but not in 53 sporadic BCCs. A second report noted that four individuals from families with BAP1 germline pathogenic variants were diagnosed with a total of 19 BCCs. Complete loss of BAP1 nuclear expression was observed in 17 of 19 BCCs from these individuals but none of 22 control BCC specimens. Loss of BAP1 nuclear expression was also reported in a series of 7 BCCs from individuals with loss of function BAP1 variants, but only in 1 of 31 sporadic BCCs.
Some Of The Signs And Symptoms Of Basal Cell Skin Cancer Include
- Sores that do not heal, bleed repeatedly and scab over
- Pearly white or waxy bumps that could bleed, form a skin depression or crust over
- Scaly, flat, fleshy-colored or brown patches
- Waxy scar that is white in color
It is important to visit a physician or a dermatologist, as soon the basal cell skin cancer symptoms become evident.
Major Genes For Melanoma
CDKN2A/p16 and p14/ARF
The major gene associated with melanoma is CDKN2A/p16, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A, which is located on chromosome 9p21. This gene has multiple names and is commonly called by the name of its protein, p16. It is an upstream regulator of the retinoblastoma gene pathway, acting through the cyclin D1/cyclin-dependent kinase 4 complex. This tumor suppressor gene has been intensively studied in multiple-case families and in population-based series of melanoma cases. CDKN2A controls the passage of cells through the cell cycle and provides a mechanism for holding damaged cells at the G1/S checkpoint to permit repair of DNA damage before cellular replication. Loss of function of tumor suppressor genesa good example of which is CDKN2Ais a critical step in carcinogenesis for many tumor systems.
CDKN2A encodes two proteins, p16INK4a and p14ARF, both inhibitors of cellular senescence. The protein produced when the alternate reading frame for exon 1 is transcribed instead of the standard reading frame exerts its biological effects through the p53 pathway. It mediates cell cycle arrest at the G1 and G2/M checkpoints, complementing p16s block of G1/S progressionthereby facilitating cellular repair of DNA damage.
There are models that can predict whether an individual has a pathogenic variant in CDKN2A. However, in the era of widely available and inexpensive multigene testing, these models are not widely utilized clinically.
Pancreatic cancer
POT1
Also Check: What Does Skin Cancer On The Face Look Like
How Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Staged
In rare situations, such as when the original lesion is more than 2 millimeters thick, or when it has invaded the lower layers of the skin, a stage may be assigned. The stages range from zero to four; higher numbers indicate more aggressive cancers. Most oncologists use the following scale:
- Stage 0 basal cell carcinoma These cancers are only present in the epidermis or the upper layer of the skin. They have not spread to any of the deeper layers or lymph nodes.
- Stage 1;basal cell carcinoma These cancers are smaller than 2 centimeters and have not spread to any nearby lymph nodes or organs, but may have one factor that increases the risk of spreading or recurrence .
- Stage 2;basal cell carcinoma These cancers are larger than 2 centimeters, and while they have not spread to other organs or lymph nodes, they have two or more factors that make them likely to return or spread.
- Stage 3;basal cell carcinoma These cancers have spread to local lymph nodes , but not to other organs.
- Stage 4;basal cell carcinoma These cancers have spread to several lymph nodes, bones or other organs, and they may be any size.
At Moffitt Cancer Center, we treat patients with all stages of basal cell carcinoma. Our skilled oncologists can determine whether a lesion is likely to spread and what treatments are expected to be most beneficial. No referral is necessary to meet with our team; call ;or complete a;new patient registration form;online.
- BROWSE
How Do You Prevent Basal Cell Skin Cancer
The best way to prevent basal cell carcinoma and other skin cancers is to protect the skin from the sun.
- Wear sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30. Apply sunscreen at least 30 minutes prior to sun exposure, and reapply every 2 hours or more frequently if swimming or sweating.
- Wear protective clothing and a wide-brimmed hat.
- Avoid the midday sun, between the hours of 10 a.m. to 4 p.m., when the sun’s rays are the strongest.
- Avoid tanning beds.
- Examine your skin regularly for new moles, spots, bumps, or growths, and inform your doctor of any skin changes.
In patients who are at higher risk for recurrence of basal cell carcinoma, certain medications may be used, however, studies on the effectiveness of these medications have had mixed results.
- Celecoxib , a type of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug , may offer modest risk reduction, but studies on its effectiveness for preventing tumors are mixed.
- Oral nicotinamide is a vitamin supplement available over the counter. Additional studies are needed to determine its effectiveness in preventing skin cancers. Consult your doctor before taking any supplements because of possible side effects or drug interactions.
- Topical fluorouracil has been shown to help prevent other skin conditions and precursors to basal cell carcinoma, however, the data are mixed on whether it may help prevent BCC.
Recommended Reading: How Aggressive Is Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Diagnosing Basal Cell Carcinoma
The most common way dermatologists diagnose basal cell carcinoma is with a full body skin check.
Stevenson says during the diagnosis process dermatologists are looking for papules with skin cancer characteristics. Sometimes dermatologists will use a tool called a dermatoscope, which uses a polarized light to look for other signs of skin cancer. With their training, dermatologists should be able to tell patients if the lesion is benign or something that should be removed because of a skin cancer concern.
RELATED: Do You Need to Wear Sunscreen Indoors?
Structure Of The Skin
The genetics of skin cancer is an extremely broad topic. There are more than 100 types of tumors that are clinically apparent on the skin; many of these are known to have familial components, either in isolation or as part of a syndrome with other features. This is, in part, because the skin itself is a complex organ made up of multiple cell types. Furthermore, many of these cell types can undergo malignant transformation at various points in their differentiation, leading to tumors with distinct histology and dramatically different biological behaviors, such as squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell cancer . These have been called nonmelanoma skin cancers or keratinocyte cancers.
Figure 1 is a simple diagram of normal skin structure. It also indicates the major cell types that are normally found in each compartment. Broadly speaking, there are two large compartmentsthe avascular epidermis and the vascular dermiswith many cell types distributed in a connective tissue matrix, largely created by fibroblasts.
The true cytologic origin of BCC remains in question. BCC and basal cell keratinocytes share many histologic similarities, as is reflected in the name. Alternatively, the outer root sheath cells of the hair follicle have also been proposed as the cell of origin for BCC. This is suggested by the fact that BCCs occur predominantly on hair-bearing skin. BCCs rarely metastasize but can invade tissue locally or regionally, sometimes following along nerves.
Don’t Miss: How To Know You Have Skin Cancer
What Causes Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Environmental and genetic factors may predispose certain patients to develop basal cell carcinoma.
The main risk factor for developing basal cell carcinoma is exposure to ultraviolet rays from the sun or from tanning beds. Other risk factors for BCC include the following:
- Therapeutic exposure to psoralen plus ultraviolet A light for skin conditions such as psoriasis
- Drugs that cause photosensitivity , such as tetracyclineantibiotics or thiazide diuretics
- Dietary factors, such as high intake of citrus products that contain compounds called furocoumarins that are considered photocarcinogenic agents
- Chronic arsenic exposure
- Therapeutic ionizing radiation, such as that used to treat facial acne, psoriasis, or tinea capitis
- Having light skin, light hair, and light eye color, with poor tanning ability
- Personal history of basal cell carcinoma
- Certain genetic disorders
- Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome
- Xeroderma pigmentosum
- Smoking
How Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Be Prevented
The most important way to prevent BCC is to avoid sunburn. This is especially important in childhood and early life. Fair skinned individuals and those with a personal or family history of BCC should protect their skin from sun exposure daily, year-round and lifelong.
- Stay indoors or under the shade in the middle of the day
You May Like: How Bad Is Basal Cell Skin Cancer
What Are The Complications/side Effects Of The Treatments For Basal Cell Carcinoma
Most of the complications related to BCC treatments other than the hedgehog inhibitors are cosmetic, such as scarring or redness.
People who use sonidegib or vismodegib should make sure to use effective birth control to avoid pregnancy due to the risk of birth defects. In addition, sonidegib has other potential risks, including problems with nerves and muscles.
Where Does Bcc Develop
As the above pictures show, this skin cancer tends to develop on skin that has had lots of sun exposure, such as the face or ears. Its also common on the bald scalp and hands. Other common areas for BCC include, the shoulders, back, arms, and legs.
While rare, BCC can also form on parts of the body that get little or no sun exposure, such as the genitals.
Also Check: What Does Squamous Skin Cancer Look Like
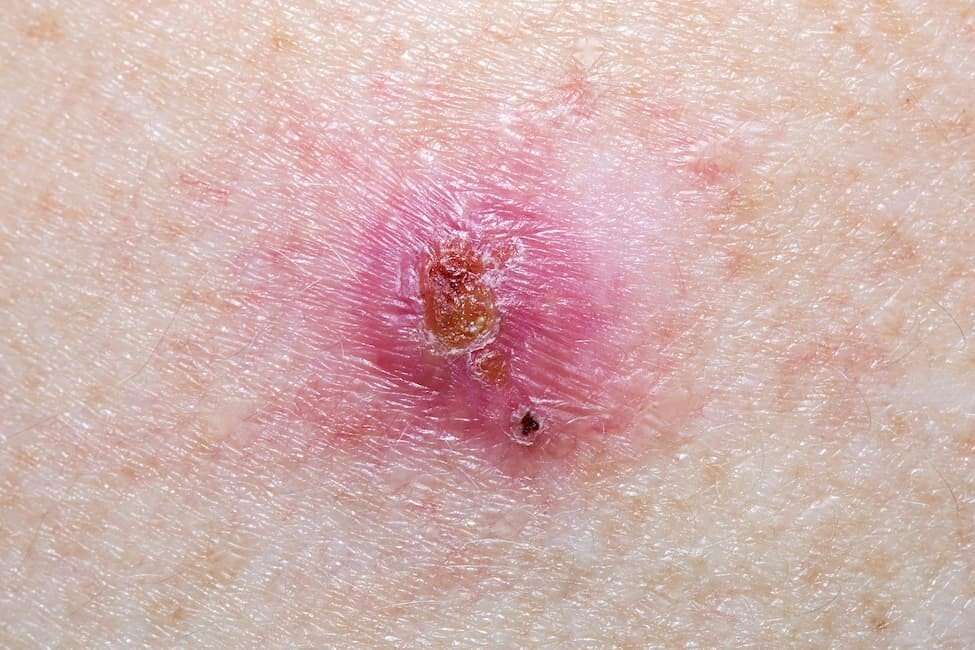
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that can show up on the skin in many ways. Also known as BCC, this skin cancer tends to grow slowly and can be mistaken for a harmless pimple, scar, or sore.
Common signs and symptoms of basal cell carcinoma
This skin cancer often develops on the head or neck and looks like a shiny, raised, and round growth.
To help you spot BCC before it grows deep into your skin, dermatologists share these 7 warning signs that could be easily missed.
If you find any of the following signs on your skin, see a board-certified dermatologist.
What Is The Staging For Basal Cell Skin Cancer
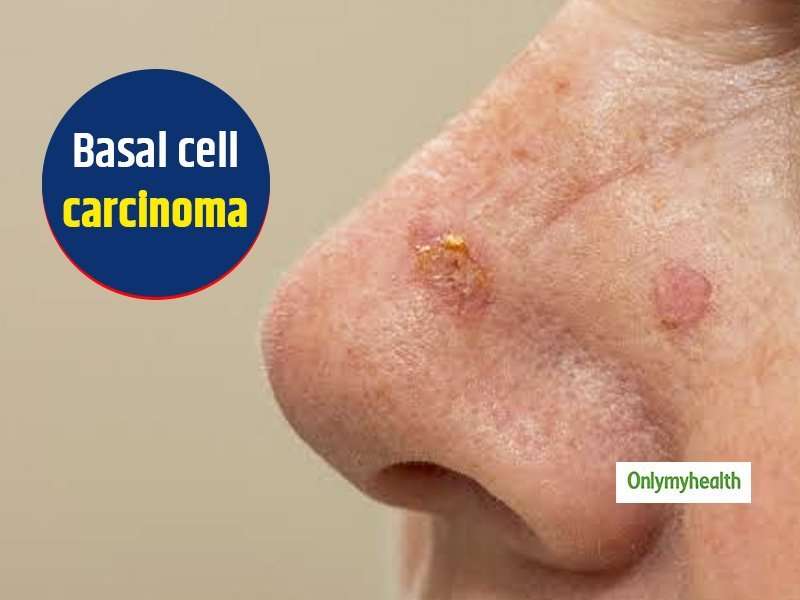
Basal cell carcinomas rarely spread so they are not typically staged. If the tumor is large and it is suspected of spreading to other parts of the body, then staging may be used.
Staging for basal cell carcinomas is similar to the staging for another type of skin cancer called squamous cell carcinoma :
- Stage 0: Cancer involves only the epidermis and has not spread to the dermis .
- Stage I: Cancer is not large and has not spread to the lymph nodes or other organs.
- Stage II: Cancer is large but has not spread to lymph nodes or other organs.
- Stage III: Cancer has spread to tissues beneath the skin such as muscle, bone, or cartilage, and/or to regional lymph nodes but not to other organs.
- Stage IV: Cancer can be any size and has spread to other organs.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Die From Melanoma
Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Cause Complications
The most common complication of basal cell carcinoma is recurrence. BCCs commonly recur, even after successful treatment. In some cases, BCC may reappear in the same place. It can also be disfiguring, especially if not treated promptly.
A diagnosis of BCC increases the chance of developing other types of skin cancer. This includes melanoma, which can metastasize and is the most life-threatening form of skin cancer.
Rare, aggressive forms of BCC can invade the body beyond the skin. It can destroy bone, nerves, and muscles. In rare cases it can metastasize to other parts of the body, including key organs, and become life-threatening.
Basal Cell Carcinomas Topical Treatment
Topical treatments can be successful on superficial basal cell carcinomas with little depth. These drugs work by inflaming the area where they are applied. The body responds by sending white blood cells to attack the inflammation. These white blood cells go after the mutated basal cells. Aldara, Efudex, and Fluoroplex are three of the most used drugs.
You May Like: What Happens If I Have Melanoma
Dna Repair Defects And Increased Cancer Risk
Many cancer syndromes are due to an inherited impairment in DNA repair capability. When an inherited mutation is present in a DNA repair gene, the repair gene will either not be expressed or expressed in an altered form. Then the repair function will likely be deficient, and, as a consequence, DNA damages will tend to accumulate. Such DNA damages can cause errors during DNA synthesis leading to mutations, some of which may give rise to cancer. Germ-line DNA repair mutations that increase the risk of cancer are listed in the Table.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Stages
There are certain features that are considered to make the cancer at higher risk for spreading or recurrence, and these may also be used to stage basal cell carcinomas. These include:
- Greater than 2 mm in thickness
- Invasion into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin
- Invasion into the tiny nerves in the skin
- Location on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip
After the TNM components and risk factors have been established, the cancer is given a stage. For basal cell carcinoma staging, the factors are grouped and labeled 0 to 4. The characteristics and stages of basal cell carcinoma are:
Stage 0: Also called carcinoma in situ, cancer discovered in this stage is only present in the epidermis and has not spread deeper to the dermis.
Stage 1 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer is less than 2 centimeters, about 4/5 of an inch across, has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs, and has one or fewer high-risk features.
Stage 2;basal cell carcinoma: The cancer is larger than 2 centimeters across, and has not spread to nearby organs or lymph nodes, or a tumor of any size with 2 or more high-risk features.
Stage;3 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer has spread into facial bones or 1 nearby lymph node, but not to other organs.
Stage 4 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer can be any size and has spread to 1 or more lymph nodes which are larger than 3 cm and may have spread to bones;or other organs in the body.
Don’t Miss: Is Melanoma The Worst Cancer
More Pictures Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
While the above pictures show you some common ways that BCC can appear on the skin, this skin cancer can show up in other ways, as the following pictures illustrate.
Scaly patch with a spot of normal-looking skin in the center
On the trunk, BCC may look like a scaly patch with a spot of normal-looking skin in the center and a slightly raised border, as shown here.
Basal cell carcinoma can be lighter in some areas and darker in others
While BCC tends to be one color, it can be lighter in some areas and darker in others, as shown here.
Basal cell carcinoma can be brown in color
Most BCCs are red or pink; however, this skin cancer can be brown, as shown here.
Basal cell carcinoma can look like a group of shiny bumps
BCC can look like a group of small, shiny bumps that feel smooth to the touch.
Basal cell carcinoma can look like a wart or a sore
The BCC on this patients lower eyelid looks like a wart* in one area and a sore** in another area.
If you see a spot or growth on your skin that looks like any of the above or one that is growing or changing in any way, see a board-certified dermatologist.
What Is Skin Cancer
Basal cell carcinoma begins in the basal cell layer of the skin. Squamous cell carcinoma begins in the squamous layer of the skin. Melanoma begins in the melanocytes, which are the cells that make melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color.
Basal cell carcinoma begins in the basal cell layer of the skin. Squamous cell carcinoma begins in the squamous layer of the skin. Melanoma begins in the melanocytes, which are the cells that make melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color.
The skin is the bodys largest organ. Skin has several layers, but the two main layers are the epidermis and the dermis . Skin cancer begins in the epidermis, which is made up of three kinds of cells
- Squamous cells: Thin, flat cells that form the top layer of the epidermis.
- Basal cells: Round cells under the squamous cells.
- Melanocytes: Cells that make melanin and are found in the lower part of the epidermis. Melanin is the pigment that gives skin its color. When skin is exposed to the sun, melanocytes make more pigment and cause the skin to darken.
Basal and squamous cell carcinomas are the two most common types of skin cancer. They begin in the basal and squamous layers of the skin, respectively. Both can usually be cured, but they can be disfiguring and expensive to treat.
Don’t Miss: Can Skin Cancer Look Like Psoriasis