What Causes Lung Cancer And Am I At Risk
There are about 235,760 new cases of lung cancer diagnosed in the United States each year. The average age of diagnosis is 71. Lung cancer is slightly more common in men than women across all racial groups. Lung cancer is the most common cause of cancer deaths.
Smoking is the greatest risk factor for developing lung cancer. Other causes of lung cancer include exposure to radon, exposure to radiation, environmental exposure to particular chemicals, and previous lung diseases.
Smoking
Every smoker is at risk for lung cancer. Your risk of getting lung cancer from cigarette smoking increases the longer you smoke, the more you smoke, and the deeper you inhale. Smoking low tar cigarettes does not prevent you from getting lung cancer. Importantly, if you quit smoking, your risk of getting lung cancer declines. The longer you go without smoking, the greater your risk declines. It is never too late to quit because your risk declines no matter how long you have been smoking. In addition, giving up smoking decreases the chance of developing another lung cancer after treatment for the current cancer.
Smoking also has an effect on people around you. Second-hand smoke or smoke inhaled when you are near someone smoking, is another risk factor for lung cancer.;
Radon
Radiation Exposure
Other Risk Factors
Lung Cancer in Never Smokers
Pearls And Other Issues
Lung cancer is the second most diagnosed cancer in the United States.
It is the leading cause of cancer death in both men and women, accounting for approximately a quarter of all cancer deaths.
Lung cancer is histologically divided into 2 main types: small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer .
Treatment is highly dependent on stage. Patients with limited-stage SCLC are candidates for curative-intent radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
Patients with extensive-stage disease are treated with chemotherapy with radiation reserved for select candidates and palliation.
Development And Early Warning Signs
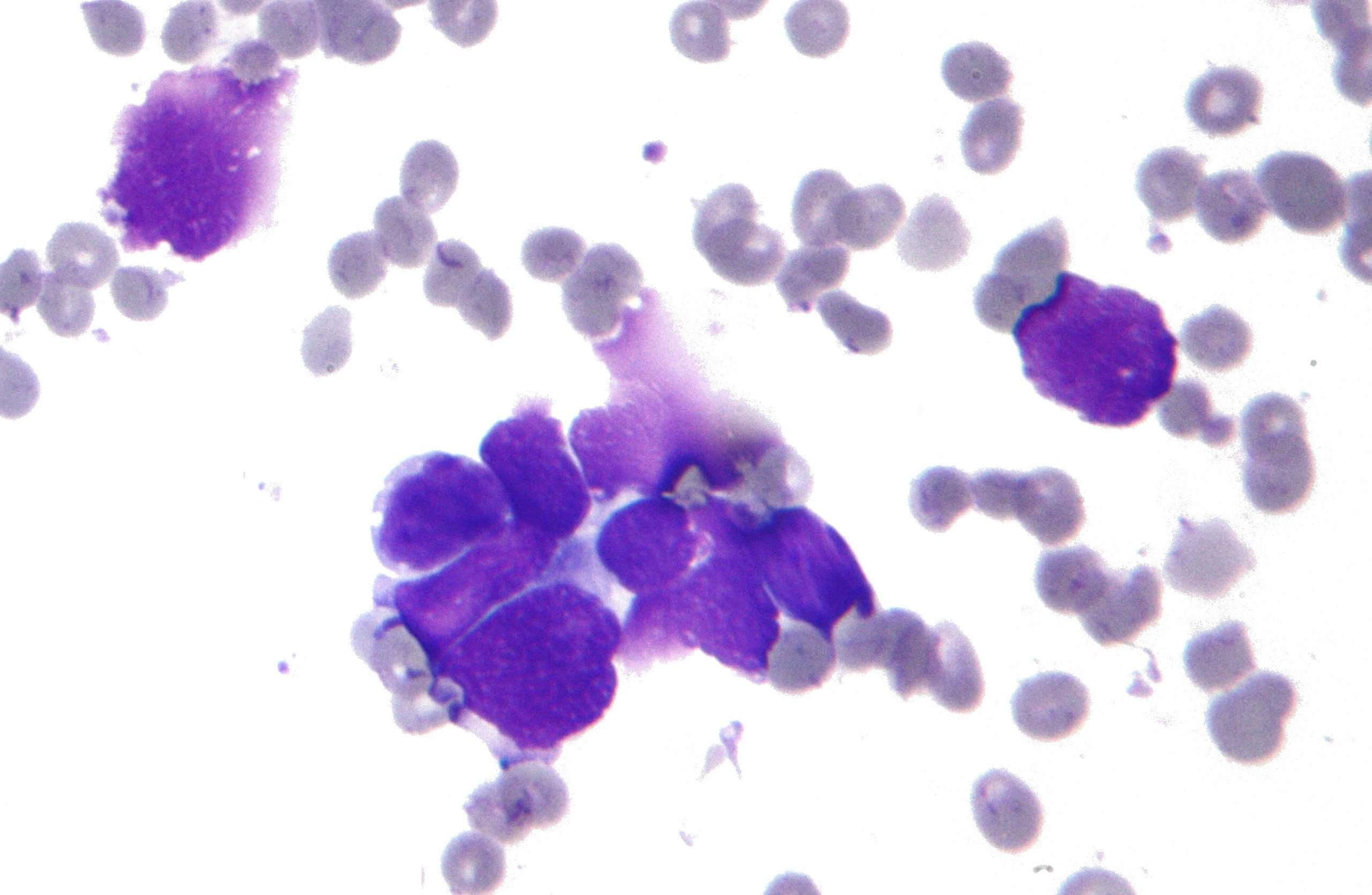
Small cell carcinoma begins in the cells found in the skin or lining of organs. Cancer is considered to be small cell carcinoma when it develops in cells smaller in size than normal cells, which are commonly found in the lung, prostate, and pancreas. Highly malignant, small cell carcinoma also develops in the breast, colon, and brain. But no area of the body is immune to the disease, as it is known to spread rapidly.
While some patients may not experience initial symptoms, red flags will begin to rise as small cell carcinoma develops. Many symptoms are unique to the location of the cancer, while others are shared between all types of small cell carcinoma. Symptoms may include:
- Pain in the bones, joints, chest, or other areas of the body
- A change in bathroom habits, such as increased frequency of urination
- Development of wheezing, hoarseness, chest pain, or consistent coughing
If you notice any of these symptoms, speak with your doctor immediately. He or she can perform testing to determine their cause and refer you for additional treatment if required.
Don’t Miss: What Does Skin Cancer Of The Vulva Look Like
How Can I Prevent Small Cell Lung Cancer
Because tobacco use is the top cause of small cell lung cancer, not smoking is the best way to protect your health. When you quit smoking regardless of your age or years of tobacco use your lungs start to heal, and cancer risk diminishes. These steps may also help:
- Eat a nutritious diet.
- Test your home for radon, a natural, odorless, radioactive gas.
- Install a mitigation system to remove radon from your home, if needed.
- Protect yourself from cancer-causing chemicals at work.
How Serious Is My Cancer
If you have lung cancer, the doctor will want to find out how far it has spread. This is called staging. Knowing the cancer’s stage helps your doctor decide what treatment is best for you.
For small cell lung cancer, a 2-stage system is most often used. Small cell lung cancers are staged as;limited stage and extensive stage.
- Limited stage means that the cancer is only in one lung and maybe in lymph nodes on the same side of the chest.
- It is called extensive stage if the cancer has spread to the other lung, to lymph nodes on the other side of the chest, or to distant organs. Many doctors also call cancer that has spread to the fluid around the lung extensive stage.
If your cancer is limited stage, you might get radiation or chemotherapy treatments to try to cure the cancer. An extensive stage cancer will be treated, but is less likely to be cured. Be sure to ask your doctor about your cancer’s stage and what it might mean.
Also Check: What Are Some Treatments For Melanoma
How Is Small Cell Lung Cancer Diagnosed
Chest X-rays are typically the first step to screen for any type of lung cancer. If images show suspicious spots on a lung, your healthcare provider may order one or more of these diagnostic tests:
- Imaging scans:Computed tomography and positron emission tomography scans detect lung tumors. These tests also can help gauge cancer spread. CT scans are the primary way to diagnose lung cancer.
- Sputum cytology: This test checks for cancer cells in sputum, mucus coughed up from the lungs.
- Biopsy: A needle biopsy removes tissue samples from the lungs. Lab pathologists check the biopsy for cancer cells.
- Bronchoscopy: Using a bronchoscope, your provider looks inside the lungs airways for tumors. At the same time, providers can remove tissue samples to biopsy.
How Can Uv Light Cause Skin Cancer
Every time UV light hits our skin, it can damage some of the DNA inside our skins cells. The body tries to repair this damage.
As UV light from the sun, indoor tanning equipment, or both, continues to hit our skin, the damage builds up. Eventually, it becomes too much for the body to repair. When the body cannot repair the damage, changes called mutations develop. When the mutations build up in the skin, we get skin cancer.
The type of skin cancer we get depends on where the mutations develop in the skin. Basal cells are found deep inside the first layer of our skin, so we get basal cell carcinoma when mutations develop inside these cells.
You May Like: Does Skin Cancer Hurt To The Touch
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Lungs
Squamous cell carcinoma of the lungs is one form of non-small cell lung cancer. Non-small cell lung cancers account for about 85 percent of lung cancers, and of these, roughly 30 percent are squamous cell carcinomas.
Squamous cell carcinoma begins in the tissues that line the air passages in the lungs. It is also known as epidermoid carcinoma. Most squamous cell carcinomas of the lungs are located centrally, usually in the larger;bronchi;that join the;trachea;to the lung.
Diagnosing Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The main way to diagnose squamous cell carcinoma is with a biopsy. This involves having a small piece of tissue removed from the suspicious area and examined in a laboratory.
In the laboratory, a pathologist will examine the tissue under a microscope to determine if it is a skin cancer. He or she will also stage the cancer by the number of abnormal cells, their thickness, and the depth of penetration into the skin. The higher the stage of the tumor, the greater the chance it could spread to other parts of the body.
Squamous cell carcinoma on sun-exposed areas of skin usually does not spread. However, squamous cell carcinoma of the lip, vulva, and penis are more likely to spread. Contact your doctor about any sore in these areas that does not go away after several weeks.
You May Like: What Are The Chances Of Skin Cancer
Can A Person Have Both Types
Around
After making a diagnosis, the doctor will describe the treatment options and develop a treatment plan.
Factors that affect the plan will include:- the type of cancer
- how far it has spread
- the individuals age and overall health
- the availability of therapies
Because each persons situation is different, treatment will vary accordingly.
How Does Treatment Differ
Like most cancers, the treatment options are dependent on the stage the disease. The pace of treatment for SCLC is generally faster than NSCLC due to the tumors ability to quickly spread. NSCLC is less aggressive; however, it is typically identified at a later stage. In fact, only an approximate 25% of NSCLC patients are diagnosed at stage 1 or 2. For the minority who are diagnosed at stage 1 or 2, surgery to remove the tumor is often an option. Patients in the later stages are typically treated with chemotherapy and radiation.
The treatment for SCLC is typically done at a much faster pace, seeing as the tumor is able to quickly spread. Chemotherapy and radiation put approximately a quarter of patients into remission, however this type of cancer is likely to spread to other parts of the body. Some healthcare professionals may preventatively treat the brain with radiation, as these cancer cells are likely to end up in the brain.
Recommended Reading: How Do They Remove Basal Cell Carcinoma
What Will Happen After Treatment
Youll be glad when treatment is over. But its hard not to worry about cancer coming back. Even when cancer never comes back, people still worry about this.
For years after treatment ends, you will see your cancer doctor. Be sure to go to all of these follow-up visits. You will have exams, blood tests, and maybe other tests to tell if the cancer has come back.
For the first year after treatment, your visits may be every 2 to 3 months. You may have CT scans and blood tests. After the first year or so, your visits might be every 6 months, and then at least once a year after 5 years.
Having cancer and dealing with treatment can be hard, but it can also be a time to look at your life in new ways. You might be thinking about how to improve your health.;Call us at 1-800-227-2345 or talk to your cancer care team to find out what you can do to feel better.;
You cant change the fact that you have cancer. What you can change is how you live the rest of your life making healthy choices and feeling as well as you can.
What Are The Risks For Developing Sclc

The leading risk for developing SCLC is smoking tobacco. The more you smoke and the earlier in life you began smoking, the greater your risk for SCLC. Other risk factors include exposure to secondhand smoke, workplace carcinogens, radiation and/or environmental pollution, as well as family history of lung cancer and previous HIV infection.
Read Also: How Aggressive Is Merkel Cell Carcinoma
About Small Cell Lung Cancer
There are 2 main classifications of lung cancer: small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer . There are different treatments for each type of lung cancer. This guide provides information on SCLC. Learn more about NSCLC in a different guide. This website also offers a separate guide on neuroendocrine tumors of the lung.
SCLC begins when healthy cells in the lung change and grow out of control, forming a mass called a tumor, a lesion, or a nodule. SCLC begins in the nerve cells or hormone-producing cells of the lung. The term “small cell” refers to the size and shape of the cancer cells as seen under a microscope.
When a cancerous lung tumor grows, it can shed cancer cells. These cells can be carried away in blood or float away in the fluid, called lymph, that surrounds lung tissue. Lymph flows through tubes called lymphatic vessels that drain into lymph nodes.
Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped organs that help fight infection. They are located in the lungs, the center of the chest, and elsewhere in the body. The natural flow of lymph out of the lungs is toward the center of the chest, which explains why SCLC often spreads there first. When a cancer cell moves into a lymph node or to a distant part of the body through the bloodstream, it is called metastasis. SCLC often spreads quickly and many people are diagnosed after SCLC has already spread to other parts of the body.
What Are The Stages Of Small Cell Lung Cancer
Healthcare providers use a two-stage system to diagnose the spread of small cell lung cancer. This information also helps guide treatment. The two stages of small cell lung cancer are:
- Limited: Cancer is confined to one lung and nearby lymph nodes.
- Extensive: Cancer has spread to the other lung and lymph nodes. It also may have spread to bones, the brain and other organs.
Read Also: Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Deadly
What Exams And Tests Help Diagnose Small
Initial examinations and tests for suspected lung cancer can include the following:
Once a medical professionals diagnoses a patient with lung cancer, examinations and tests are performed to find out whether the cancer has spread to other organs of the person’s body. These examinations and tests help to determine the stage of the cancer. Staging is important because lung cancer treatment depends on the stage of the cancer. Examinations and tests used to detect the spread of cancer may include the following:
Staging of small-cell lung cancer
Staging of the cancer provides important information about the outlook of the patient’s condition and helps the doctor plan the best treatment. Although doctors stage other cancers from stage I to stage IV, small-cell lung cancer is classified into two stages.
- Limited stage: In this stage, the tumor is confined to a single radiation field. This includes the lung and the lymph nodes, within and between the lungs.
- Extensive stage: In this stage, cancer has spread from the lung to other organs of the body. This includes the presence of fluid in the lining of the lung .
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
The most effective treatment for small-cell lung cancer is chemotherapy , either alone or in combination with radiation therapy .
The Following Stages Are Used For Small Cell Lung Cancer:
Limited-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer
In limited-stage,cancer is in the lung where it started and may have spread to the area between the lungs or to the lymph nodes above the collarbone.
Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer
In extensive-stage,cancer has spread beyond the lung or the area between the lungs or the lymph nodes above the collarbone to other places in the body.
Recommended Reading: What Happens If You Have Skin Cancer
Immunotherapy For Small Cell Lung Cancer
Immunotherapy is treatment that either boosts your own immune system or uses man-made versions of parts of the immune system that attack the small cell lung cancer cells. These drugs may be given into a vein.
Side effects of immunotherapy
Immunotherapy can cause many different side effects depending on which drug is used. These drugs often make you feel tired, sick to your stomach, and cause a skin rash. Most of these problems go away after treatment ends.
There are ways to treat most of the side effects caused by immunotherapy. If you have side effects, talk to your cancer care team so they can help.
Small Cell Lung Cancer Vs Non
Lung cancer diagnoses are broken down into two main groups: small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer .
SCLC often starts in the bronchi, or the airways that lead from the trachea into the lungs and then branch off into progressively smaller structures. After affecting the bronchi, SCLC quickly grows and spread to other parts of the body, including the lymph nodes. This type of lung cancer represents fewer than 20% of lung cancers and is typically caused by tobacco smoking. SCLC itself is broken down into another two categories: small cell carcinoma and combined small cell carcinoma. These two categories are used to distinguish the small cells when viewed under a microscope. Small cell carcinoma is the most common type of SCLC and looks flat under a microscope, much like oats. Combined small cell carcinoma refers to a tumor made up of small cell carcinoma cells and a small number of non-small cell lung cancer cells.
Recommended Reading: How Fast Does Subungual Melanoma Grow
Dna Repair Deficiency In Nsclc
Deficiencies in DNA repair underlie many forms of cancer. If DNA repair is deficient, the frequency of unrepaired DNA damages increases, and these tend to cause inaccurate translesion synthesis leading to mutation. Furthermore, increased damages can elevate incomplete repair, leading to epigenetic alterations.
As indicated as in the article Carcinogenesis, mutations in DNA repair genes occasionally occur in cancer, but deficiencies of DNA repair due to epigenetic alterations that reduce or silence DNA repair-gene expression occur much more frequently in cancer.
Epigenetic gene silencing of DNA repair genes occurs frequently in NSCLC. At least nine DNA repair genes that normally function in relatively accurate DNA repair pathways are often repressed by promoter hypermethylation in NSCLC. One DNA repair gene, FEN1, that functions in an inaccurate DNA repair pathway, is expressed at an increased level due to hypo-, rather than hyper-, methylation of its promoter region in NSCLC.
Epigenetic promoter methylation in DNA repair genes in NSCLC
| Gene |
|---|
Smoking Is The Major Risk Factor For Small Cell Lung Cancer
Anything that increases your chance of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer; not having risk factors doesn’t mean that you will not get cancer. Talk to your doctor if you think you may be at risk for lung cancer.
Risk factors for lung cancer include the following:
- Smoking cigarettes, pipes, or cigars, now or in the past. This is the most important risk factor for lung cancer. The earlier in life a person starts smoking, the more often a person smokes, and the more years a person smokes, the greater the risk of lung cancer.
- Being exposed to secondhand smoke.
- Being exposed to asbestos, arsenic, chromium, beryllium, nickel, soot, or tar in the workplace.
- Being exposed to radiation from any of the following:
- Radiation therapy to the breast or chest.
- Radon in the home or workplace.
Older age is the main risk factor for most cancers. The chance of getting cancer increases as you get older.
When smoking is combined with other risk factors, the risk of lung cancer is increased.
Recommended Reading: What Is Metastatic Merkel Cell Carcinoma