Risk Factors For Basal Cell Carcinoma
Anyone with a history of sun exposure can develop basal cell carcinoma. The disease is rarely seen in children, but occasionally a teenager is affected.
Men with BCC have outnumbered women with the disease, but more women are getting BCCs than in the past.
Workers in occupations that require long hours outside and people who spend a lot of time in the sun are particularly susceptible.
People who are at highest risk have fair skin, blond or red hair, and blue, green, or grey eyes.
Also Check: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
Common Skin Cancer Can Signal Increased Risk Of Other Cancers
Frequent skin cancers due to mutations in genes responsible for repairing DNA are linked to a threefold risk of unrelated cancers, according to a Stanford study. The finding could help identify people for more vigilant screening.
Basal cell carcinomas are common. More than 3 million cases a year are diagnosed nationwide.jax10289/Shutterstock.com
People who develop abnormally frequent cases of a skin cancer known as basal cell carcinoma appear to be at significantly increased risk for developing of other cancers, including blood, breast, colon and prostate cancers, according to a preliminary study by researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine.
The increased susceptibility is likely caused by mutations in a panel of proteins responsible for repairing DNA damage, the researchers found.
We discovered that people who develop six or more basal cell carcinomas during a 10-year period are about three times more likely than the general population to develop other, unrelated cancers, said Kavita Sarin, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology. Were hopeful that this finding could be a way to identify people at an increased risk for a life-threatening malignancy before those cancers develop.
Sarin is the senior author of the study, which was published online Aug. 9 in JCI Insight. Medical student Hyunje Cho is the lead author.
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The two most common kinds of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, which are sometimes called nonmelanoma skin cancer. These cancers are carcinomas that begin in the cells that cover or line an organ.
Basal cell carcinoma accounts for more than 90 percent of all skin cancers in the United States and is the most common of all cancers. Typically, it is a slow-growing cancer that seldom spreads to other parts of the body.
Squamous cell carcinoma also rarely spreads, but does so more often than basal cell carcinoma. It is important that skin cancers are found and treated early because they can invade and destroy nearby tissue. Organ transplant recipients have a 65-fold higher risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma than others. UCSF Medical Center offers a High Risk Skin Cancer Clinic for those at high risk for non-melanoma skin cancers, such as transplant recipients.
Recommended Reading: What To Do When You Get Skin Cancer
Don’t Miss: What Is Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
How Widespread Is Bcc
Basal cell carcinoma is quite common, and the number of reported cases in the U.S. has steadily increased.
- An estimated 3.6 million Americans are diagnosed with BCC each year.
- More than one out of every three new cancers are skin cancers, and the vast majority are BCCs.
- The diagnosis and treatment of nonmelanoma skin cancers, including BCC and squamous cell carcinoma , increased up to 77 percent between 1994 and 2014.
Reviewed by:
Risk Factors For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
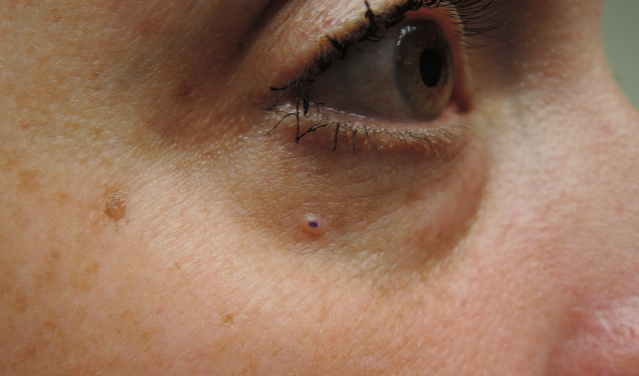
Sun exposure and other risk factors
Sun exposure is the major known environmental factor associated with the development of skin cancer of all types however, different patterns of sun exposure are associated with each major type of skin cancer. Unlike basal cell carcinoma , SCC is associated with chronic exposure, rather than intermittent intense exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Occupational exposure is the characteristic pattern of sun exposure linked with SCC. Other agents and factors associated with SCC risk include tanning beds, arsenic, therapeutic radiation , chronic skin ulceration, and immunosuppression.
Characteristics of the skin
Like melanoma and BCC, SCC occurs more frequently in individuals with lighter skin than in those with darker skin. A case-control study of 415 cases and 415 controls showed similar findings relative to Fitzpatrick type I skin, individuals with increasingly darker skin had decreased risks of skin cancer . The same study found that blue eyes and blond/red hair were also associated with increased risks of SCC, with crude ORs of 1.7 for blue eyes, 1.5 for blond hair, and 2.2 for red hair.
Immunosuppression
Personal history of BCC, SCC, and melanoma skin cancers
Family history of squamous cell carcinoma or associated premalignant lesions
Read Also: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Metastatic Melanoma
Where Do Skin Cancers Start
Most skin cancers start in the top layer of skin, called the epidermis. There are 3 main types of cells in this layer:
- Squamous cells: These are flat cells in the upper part of the epidermis, which are constantly shed as new ones form. When these cells grow out of control, they can develop into squamous cell skin cancer .
- Basal cells: These cells are in the lower part of the epidermis, called the basal cell layer. These cells constantly divide to form new cells to replace the squamous cells that wear off the skins surface. As these cells move up in the epidermis, they get flatter, eventually becoming squamous cells. Skin cancers that start in the basal cell layer are called basal cell skin cancers or basal cell carcinomas.
- Melanocytes: These cells make the brown pigment called melanin, which gives the skin its tan or brown color. Melanin acts as the bodys natural sunscreen, protecting the deeper layers of the skin from some of the harmful effects of the sun. Melanoma skin cancer starts in these cells.
The epidermis is separated from the deeper layers of skin by the basement membrane. When a skin cancer becomes more advanced, it generally grows through this barrier and into the deeper layers.
Is It Time For Your Annual Skin Check
One of the best ways to prevent basal cell carcinoma is to take steps to protect your skin from the sun, including daily sunscreen, protective clothing, and seeking shade whenever possible. If you have a high risk of developing skin cancer, then make sure that you dont miss your yearly skin check-up with your dermatologist.
Are you experiencing any symptoms that concern you? Schedule an appointment with the dermatologists at the Center for Surgical Dermatology. Were now accepting patients for telemedical appointments!
Don’t Miss: How To Remove Skin Cancer
Treatment For Advanced Or Metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma
Locally advanced primary, recurrent or metastatic basal cell carcinoma requires multidisciplinary consultation. Often a combination of treatments is used.
- Surgery
- Radiotherapy
- Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy refers to the hedgehog signalling pathway inhibitors, vismodegib and sonidegib. These drugs have some important risks and side effects.
References
Basal Cell Carcinoma Prevention
- Stay indoors or under the shade in the middle of the day
- Wear covering clothing, hat and sunglasses
- Use broadspectrum sunscreens SPF 50+ generously to exposed skin if outdoors and sun avoidance
- Avoid indoor tanning
- Nicotinamide in a dose of 500 mg twice daily may reduce the number and severity of basal cell carcinomas.
A recent placebo-controlled study of 386 patients who had been diagnosed with at least two skin cancers â such as basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma â in the past five years, showed that taking 500 milligrams twice daily of nicotinamide reduced the subsequent risk of non-melanoma skin cancers by 23%. When patients stopped taking the supplements, their risk of getting skin cancer rose again about six months later.
A prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of acitretin 25 mg/day 5 days a week over 2 years did not show any reduction in the development of basal cell carcinoma in patients with a history of multiple basal cell carcinomas 6).
Topical tretinoin and tazarotene have been shown to not be effective in preventing basal cell carcinoma 7).
Don’t Miss: How To Protect Against Skin Cancer
What Should I Do If I Think I Have A Basal Cell Carcinoma
If you notice a change to or growth on your skin, make an appointment to see your doctor straight away. Your doctor will assess the size, location and look of the growth. They will also ask you how long you have had it, whether it bleeds or itches, etc.
If your doctor thinks the growth may be cancer, they may take a small sample of tissue . The tissue sample will be sent to a laboratory and examined under a microscope. Your doctor will let you know whether the sample showed any cancer cells, and will recommend appropriate treatment if necessary.
Recommended Reading: How Quickly Can Melanoma Metastasis
Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Turn Into Melanoma
No, basal cell carcinoma cannot develop into melanoma, as they are entirely separate and unique skin cancers. Melanoma is usually scaly in physical appearance and feel, while basal cell carcinoma is more common and nonmelanoma, which means skin cancer doesnt originate from melanin-producing skin cells.
You May Like: What Are The 4 Types Of Skin Cancer
Basal Cell Carcinoma Prognosis
Most basal cell carcinomas are cured by treatment. Cure is most likely if treatment is undertaken when the lesion is small.
About 50% of people with basal cell carcinoma develop a second one within 3 years of the first. They are also at increased risk of other skin cancers, especially melanoma. Regular self-skin examinations and long-term annual skin checks by an experienced health professional are recommended.
Putative Genes For Basal Cell Carcinoma
BRCA1-associated protein 1
Pathogenic variants in the BAP1 gene are associated with an increased risk of a variety of cancers, including cutaneous melanoma and uveal melanoma. Although the BCC penetrance in individuals with pathogenic variants in BAP1 is not known, there are several BAP1 families that report diagnoses of BCC. In one study, pathogenic variant carriers from four families reported diagnoses of BCC. Tumor evaluation of BAP1 showed loss of BAP1 protein expression by immunohistochemistry in BCCs of two germline BAP1 pathogenic variant carriers but not in 53 sporadic BCCs. A second report noted that four individuals from families with BAP1 germline pathogenic variants were diagnosed with a total of 19 BCCs. Complete loss of BAP1 nuclear expression was observed in 17 of 19 BCCs from these individuals but none of 22 control BCC specimens. Loss of BAP1 nuclear expression was also reported in a series of 7 BCCs from individuals with loss of function BAP1 variants, but only in 1 of 31 sporadic BCCs.
Don’t Miss: What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Head And Neck
Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Be Cured
In the vast majority of cases, basal cell skin cancer can be cured. The survival rates are excellent however, the exact statistics remain unknown. Unlike other cancers, basal and squamous cell skin cancers are not tracked by cancer registries, so the statistics are not available.
In some cases, basal skin cancer can recur. The risk of recurrence appears to be linked to the type of treatment used to treat the cancer.
Research has indicated that the recurrence risk is:
- Just above 10% after surgical excision
- Slightly less than 8% after electrodesiccation and curettage
- Approximately 7.5% after cryotherapy
- Less than 1% after Mohs micrographic surgery
Treatment options vary depending on the subtype, staging, and location of the basal skin cancer.
Deterrence And Patient Education
Prevention is the key to address BCC and other skin cancers. This is especially true for those individuals who have already had skin cancer, even after successful treatment. This includes avoiding direct sunlight , wearing protective clothing to cover exposed skin, and using broad-spectrum sunscreens.
Recommended Reading: Does The Sun Cause Skin Cancer
What Is Spongiosis Of Esophagus
Background:The histological diagnosis of GERD is not based on a single feature in esophageal biopsies. However, the presence of eosinophils is considered a sensitive marker for GERD. A morphological finding that can also be seen in GERD is spongiosis, which is the presence of edema between squamous cells.
The Difference Between Basal Cell Carcinoma And Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the two most common types of skin cancers. According to the American Cancer Society, over 5 million cases of basal cell and squamous cell cancers are diagnosed every year. Though, basal cell carcinoma occurs more often, taking credit for about 80% of these cases. Other than the disparities in occurrence, what is the difference between basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas? You may also be wondering is squamous cell worse than basal cell, or vice versa. Here is some insight.
You May Like: What Does In Situ Melanoma Mean
What Is Advanced Bcc
An estimated 1% of all BCC cases will progress to advanced BCC and either invade the surrounding tissue or spread to other parts of the body . This may result in debilitating effects, severe deformities and even death.
Advanced BCCs are often open lesions that may bleed, become infected, and produce unpleasant odours.
Donât Miss: How Do You Know If You Have Melanoma
Minor Genes For Melanoma
MC1R
The MC1R gene, otherwise known as the alpha melanocyte-stimulating hormone receptor, is located on chromosome 8. Partial loss-of-function pathogenic variants, of which there are at least ten, are associated not only with red hair, fair skin, and poor tanning, but also with increased skin cancer risk independent of cutaneous pigmentation. A comprehensive meta-analysis of more than 8,000 cases and 50,000 controls showed the highest risk of melanoma in individuals with MC1R variants associated with red hair however, alleles not associated with red hair have also been linked to increased melanoma risk. Additional phenotypic associations have been found. In different studies, MC1R variants were found to be associated with lentigo maligna melanoma and increased risk of melanoma for individuals with no red hair, no freckles, and Fitzpatrick type III or IV skin . Pooled studies of 5,160 cases and 12,119 controls from 17 sites calculated that melanoma risk attributable to MC1R variants is 28%, suggesting that these variants may be an important contributor to melanoma risk in the general population.
Other pigmentary genes
Pathogenic variants in albinism genes may also account for a small proportion of familial melanoma. For example, variants in TYRP1, TYR, and OCA2 were observed at an increased frequency in one study of individuals with familial cutaneous melanoma compared with population controls. Further studies are needed to confirm these findings.
MITF
BRCA1 and BRCA2
Don’t Miss: How Fast Does Melanoma Develop
Major Genes For Melanoma
CDKN2A/p16 and p14/ARF
The major gene associated with melanoma is CDKN2A/p16, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A, which is located on chromosome 9p21. This gene has multiple names and is commonly called by the name of its protein, p16. It is an upstream regulator of the retinoblastoma gene pathway, acting through the cyclin D1/cyclin-dependent kinase 4 complex. This tumor suppressor gene has been intensively studied in multiple-case families and in population-based series of melanoma cases. CDKN2A controls the passage of cells through the cell cycle and provides a mechanism for holding damaged cells at the G1/S checkpoint to permit repair of DNA damage before cellular replication. Loss of function of tumor suppressor genesa good example of which is CDKN2Ais a critical step in carcinogenesis for many tumor systems.
CDKN2A encodes two proteins, p16INK4a and p14ARF, both inhibitors of cellular senescence. The protein produced when the alternate reading frame for exon 1 is transcribed instead of the standard reading frame exerts its biological effects through the p53 pathway. It mediates cell cycle arrest at the G1 and G2/M checkpoints, complementing p16s block of G1/S progressionthereby facilitating cellular repair of DNA damage.
There are models that can predict whether an individual has a pathogenic variant in CDKN2A. However, in the era of widely available and inexpensive multigene testing, these models are not widely utilized clinically.
Pancreatic cancer
POT1
What Does Early Stage Basal Cell Carcinoma Look Like
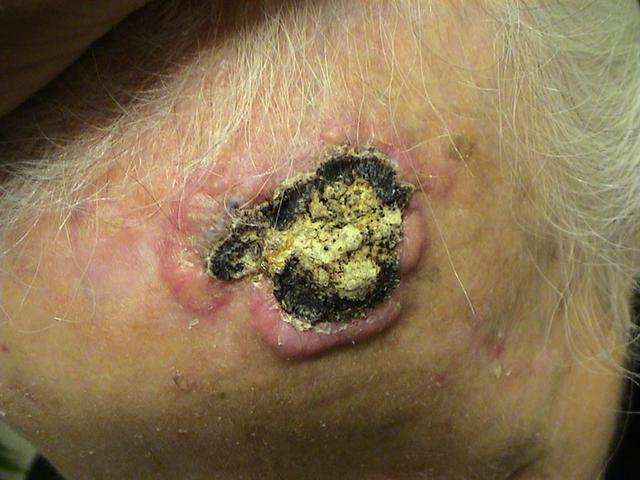
In the early stages, basal cell carcinoma comes up like small shiny bumps that look like fleshy moles or pimples. In some cases, they can look dark or with reddish, scaly skin . Additionally, they can also be skin growths that are hard and waxy. To have a clearer image of what they look like, please check our patients galleryhere.
Recommended Reading: What Does Skin Cancer Look Like On Your Head
Basal Cell Carcinoma Complications
Recurrent basal cell carcinoma
Recurrence of basal cell carcinoma after initial treatment is not uncommon. Characteristics of recurrent basal cell carcinoma often include:
- Incomplete excision or narrow margins at primary excision
- Morphoeic, micronodular, and infiltrative subtypes
- Location on head and neck
Advanced basal cell carcinoma
Advanced basal cell carcinomas are large, often neglected tumours.
- They may be several centimetres in diameter
- They may be deeply infiltrating into tissues below the skin
- They are difficult or impossible to treat surgically
Metastatic basal cell carcinoma
- Very rare
Basal cell carcinoma is a locally invasive skin tumor. The main characteristics are:
- Slowly growing plaque or nodule
- Skin colored, pink or pigmented
- Varies in size from a few millimetres to several centimetres in diameter
- Spontaneous bleeding or ulceration
Basal cell carcinoma is very rarely a threat to life. A tiny proportion of basal cell carcinomas grow rapidly, invade deeply, and/or metastasise to local lymph nodes.
Figure 11. Basal cell carcinoma
How Long Does It Take To Recover From Basal Cell Carcinoma Surgery
Wound recovery from basal cell carcinoma would typically take up to 4 to 6 weeks, depending on the size. Symptoms such as infection, bleeding, and pain are highly unlikely. The wound is closed with stitches, which is important in minimizing the scar or when the skins natural healing is not enough. For more information on basal cell carcinoma, visit our website by clicking this link.
You May Like: What To Do When You Get Skin Cancer