Dietary Sources Of Vitamin D
The best natural sources of vitamin D in the diet include fatty fish and fish liver oils. Small amounts of vitamin D are also found in egg yolks, beef liver, some mushrooms, ricotta cheese, and some cuts of pork. Vitamin D-fortified foods and beverages provide most of the vitamin D in the U.S. diet. Almost all of the milk in the United States is fortified with vitamin D, and many of the ready-to-eat breakfast cereals provide a small amount of added vitamin D. In addition, specific brands of soy beverages, orange juice, yogurt, margarine, and other foods are also fortified with vitamin D.
Medical Uses of UV Exposure
Dermatologists and other doctors sometimes use UV light to treat health conditions, such as psoriasis, rickets, and eczema. These providers are advised to carefully weigh the risks and benefits of UV treatment for individual patients and carefully monitor doses.,-
Benefits of Being Outdoors
Risks of Indoor Tanning Outweigh Any Potential Benefits
Low levels of sunlight in the winter months may contribute to seasonal affective disorder , and as a result, some indoor tanners may attempt to self-treat SAD with UV exposure through indoor tanning., Medical treatment of SAD frequently incorporates light treatment, but UV wavelengths are not generally recommended .,, In addition, light is thought to affect SAD through the retina, not the skin.
Preparing For Your Appointment
If you have any concerns about the health of your skin, it is important to share them with your doctor. After making an appointment, there are steps you can take to prepare yourself and make the most of your time with your doctor.
Here are some things to consider and be prepared to discuss before visiting the clinic or hospital:
-
What symptoms are you experiencing ?
-
When did you first notice your symptoms?
-
Have there been any major changes or stressors in your life recently?
-
What medications and/or vitamins are you taking?
-
What questions do you have for your doctor?
Merkel Cell Carcinoma: A Rare Skin Cancer On The Rise
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare type of skin cancer that affects about 2,000 people in the United States each year.
Though its an uncommon skin cancer, cases of Merkel cell carcinoma have increased rapidly in the last couple of decades.
This type of cancer starts when cells in the skin, called Merkel cells, start to grow out of control.
Merkel cell carcinomas typically grow quickly and can be difficult to treat if they spread.
They can start anywhere on the body, but Merkel cell carcinomas commonly affect areas exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, and arms.
They may look like pink, red, or purple lumps that are firm when you touch them. Sometimes, they can open up as ulcers or sores.
Risk factors include:
Read Also: Osteomyoma
What Is The Outlook For People With Skin Cancer
Nearly all skin cancers can be cured if they are treated before they have a chance to spread. The earlier skin cancer is found and removed, the better your chances for a full recovery. Ninety percent of those with basal cell skin cancer are cured. It is important to continue following up with a doctor to make sure the cancer does not return. If something seems wrong, call a doctor right away.
Articles On Skin Cancer
Skin cancer — abnormal cell changes in the outer layer of skin — is by far the most common cancer in the world. It can usually be cured, but the disease is a major health concern because it affects so many people. About half of fair-skinned people who live to age 65 will have at least one skin cancer. Most can be prevented by protecting your skin from the sun and ultraviolet rays.
Every malignant skin tumor will, over time, show up on the skin‘s surface. That makes this the only type of cancer that is almost always found in its early, curable stages.
Read Also: Basaloid Tumor
Current Trends In Sun Protection Sunburn And Indoor Tanning
Data on behaviors related to skin cancer risk among the U.S. population are collected by CDC through the national YRBS and NHIS. The national YRBS is a cross-sectional, school-based, biennial survey that monitors the prevalence of health risk behaviors among high school students. It is a nationally representative survey of students in grades 9â12 attending public and private schools. This survey includes questions about using sunscreen with an SPF of 15 or higher and indoor tanning. The NHIS is an annual, cross-sectional, nationally representative survey of the civilian, noninstitutionalized U.S. population. Interviews are conducted, mainly in person, with adults aged 18 years or older in each household, with follow-up interviews by telephone when necessary.
A periodic cancer control supplement to the NHIS includes questions about outdoor sun-protective behaviors , indoor tanning, sunburn, and sun sensitivity. This supplement is sponsored by CDC’s Division of Cancer Prevention and Control and the National Cancer Institute in the National Institutes of Health .
Indoor Tanning
What Is Skin Cancer
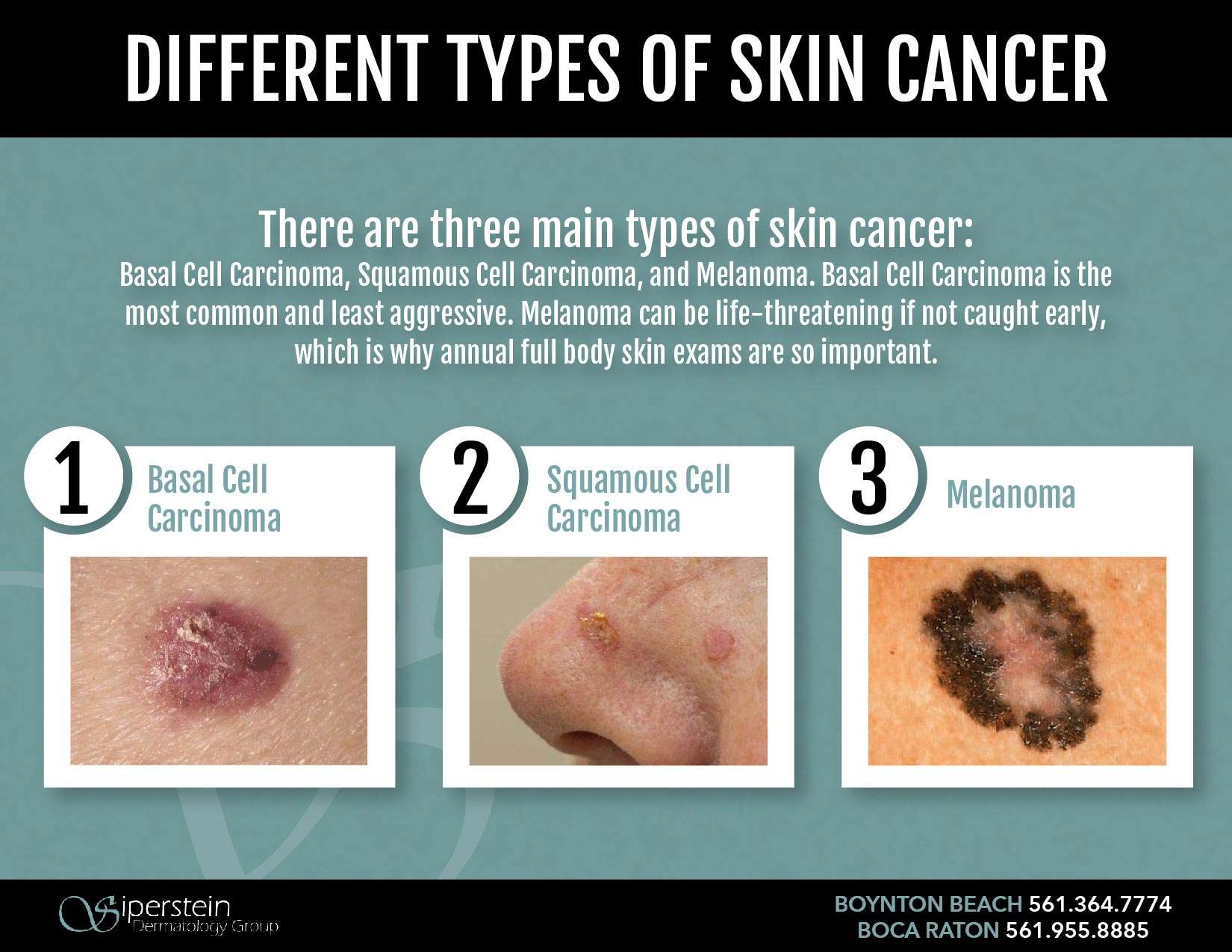
Basal cell carcinoma begins in the basal cell layer of the skin. Squamous cell carcinoma begins in the squamous layer of the skin. Melanoma begins in the melanocytes, which are the cells that make melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color.
Basal cell carcinoma begins in the basal cell layer of the skin. Squamous cell carcinoma begins in the squamous layer of the skin. Melanoma begins in the melanocytes, which are the cells that make melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color.
The skin is the bodys largest organ. Skin has several layers, but the two main layers are the epidermis and the dermis . Skin cancer begins in the epidermis, which is made up of three kinds of cells
- Squamous cells: Thin, flat cells that form the top layer of the epidermis.
- Basal cells: Round cells under the squamous cells.
- Melanocytes: Cells that make melanin and are found in the lower part of the epidermis. Melanin is the pigment that gives skin its color. When skin is exposed to the sun, melanocytes make more pigment and cause the skin to darken.
Basal and squamous cell carcinomas are the two most common types of skin cancer. They begin in the basal and squamous layers of the skin, respectively. Both can usually be cured, but they can be disfiguring and expensive to treat.
Don’t Miss: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Tracking Changes To Your Skin With An App
Some people find it helpful to photograph areas of their skin such as the back or individual lesions to be able to better spot any future changes.
Over the past years, smartphone apps that can help consumers track moles and skin lesions for changes over time have become very popular and can be a very helpful tool for at-home skin checks.
This page does not replace a medical opinion and is for informational purposes only.
Please note, that some skin cancers may look different from these examples. See your doctor if you have any concerns about your skin.
It might also be a good idea to visit your doctor and have an open talk about your risk of skin cancer and seek for an advice on the early identification of skin changes.
* Prof. Bunker donates his fee for this review to the British Skin Foundation , a charity dedicated to fund research to help people with skin disease and skin cancer.
Make a difference. Share this article.
How Common Is Skin Cancer
You may think places with sunnier, hotter weather have more cases of skin cancer. This isnt necessarily the case. In fact, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention notes California and Florida had fewer cases per 100,000 people than states with cooler climates, like Wyoming, Montana, and Idaho, in 2015.
The states with the fewest cases of skin cancer are:
- Alaska
- Wyoming
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 2 Survival Rate
Three Most Common Skin Cancers
It is estimated that one in seven people in the United States will develop some form of skin cancer during their lifetime. Although anyone can get skin cancer, people who burn easily and are fair-skinned are at higher risk. Researchers believe that one serious sunburn can increase the risk of skin cancer by as much as 50%. A yearly skin exam by a doctor is the best way to detect skin cancer early, when it is most treatable. If you have a new growth or any change in your skin, be sure to see your doctor to have it examined. Remember, protecting yourself from the sun is the best way to prevent all forms of skin cancer.
There Are Three Ways That Cancer Spreads In The Body
Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood:
- Tissue. The cancer spreads from where it began by growing into nearby areas.
- Lymph system. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the lymph system. The cancer travels through the lymph vessels to other parts of the body.
- Blood. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through the blood vessels to other parts of the body.
Read Also: Treatment For Stage 3 Melanoma
Who Gets Skin Cancer
Skin cancer tends to affect people of light skin color because they’re born with the least amount of protective melanin in their skin. The odds are highest if you’re:
- Redheaded
- A blue-eyed blonde
- Someone with a pigment disorder, such as albinism
People with many freckles or moles, particularly odd-looking ones, may be vulnerable to melanoma. It’s possible for dark-skinned people to get skin cancer, but it’s rare and usually on lighter areas of their body, such as the soles of the feet or under fingernails or toenails.
Where you live also plays a role. Places with intense sunshine, such as Arizona and Hawaii, have a larger share of people with skin cancer. It’s more common in places where fair-skinned people moved from less sunny areas, like Australia, which was settled largely by fair-skinned people of Irish and English descent.
About 3 times more men than women get skin cancer. It’s more likely when you’re older. Most people diagnosed are between ages 45 and 54, although more younger people are now being affected. If you or any close relatives have had skin cancer, your chances go up.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Common In Sun

Squamous cell carcinoma, also called squamous cell cancer, is the second most common type of skin cancer. It accounts for about 20 percent of cases.
This type of cancer starts in flat cells in the outer part of the epidermis. It commonly crops up on sun-exposed areas, such as the face, ears, neck, lips, and hands. It can also develop on scars or chronic sores.
Squamous cell carcinomas may develop from precancerous skin spots, known as actinic keratosis .
These cancers might look like:
- A firm, red bump
- A flat lesion with a scaly, crusted surface
- A sore that heals and then reopens
People with lighter skin are more at risk for developing squamous cell carcinoma, but the skin cancer can also affect those with darker skin.
Other risk factors include:
- Having light eyes, blond or red hair, or freckles
- Being exposed to the sun or tanning beds
- Having a history of skin cancer
- Having a history of sunburns
- Having a weakened immune system
- Having the genetic disorder xeroderma pigmentosum
RELATED: 10 Things You May Know Cause Skin Cancer
Read Also: Carcinoma Cancer Symptoms
Cancer May Spread From Where It Began To Other Parts Of The Body
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if skin cancer spreads to the lung, the cancer cells in the lung are actually skin cancer cells. The disease is metastatic skin cancer, not lung cancer.
Staging For Basal Cell Carcinoma And Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin Depends On Where The Cancer Formed
Staging for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the eyelid is different from staging for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma found on other areas of the head or neck. There is no staging system for basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma that is not found on the head or neck.
Surgery to remove the primary tumor and abnormal lymph nodes is done so that tissue samples can be studied under a microscope. This is called pathologic staging and the findings are used for staging as described below. If staging is done before surgery to remove the tumor, it is called clinical staging. The clinical stage may be different from the pathologic stage.
You May Like: Show Me What Skin Cancer Looks Like
What Are Basal And Squamous Cell Skin Cancers
Basal and squamous cell skin cancers are the most common types of skin cancer. They start in the top layer of skin , and are often related to sun exposure.
Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow out of control. Cells in nearly any part of the body can become cancer cells. To learn more about cancer and how it starts and spreads, see What Is Cancer?
What Causes Skin Cancer
The main cause of skin cancer is overexposure to sunlight, especially when it results in sunburn and blistering. Ultraviolet rays from the sun can damage the skin and, over time, lead to skin cancer. The UV light damages DNA in the skin and causes it to grow abnormally. Exposure to certain chemicals such as tar and coal can cause skin cancer for those with jobs that require them to frequently be in contact with these chemicals. Those with a weakened immune system also have an increased risk for skin cancer.
You May Like: Mayo Clinic Skin Cancer
Other Cancers On The Face
A few other rare skin cancers that might happen on the face:
- Lymphoma of the skin is an uncommon type of white blood cell cancer.
- Kaposi’s sarcoma is cancer caused by a herpes virus in immunosuppressed patients that causes skin lesions on the face. They look like painless purplish spots.
- Skin adnexal tumors is a rare cancer type that starts in hair follicles or skin glands.
- Sarcomas are tumors of the connective tissuesspecifically the fat, nerves, bone, skin, and muscles 80% of which occur in the face, head, or neck.
- Cutaneous leiomyosarcoma is an uncommon soft-tissue sarcoma that can happen on the face.
Determining If The Cancer Has Spread
As part of your diagnosis, your doctor will also determine what stage the cancer is in. The different stages refer to whether and how far the cancer has spread in your body, on a Roman numeral scale of I to IV. A stage I cancer is small and contained to the body part where it originated, whereas a stage IV cancer has spread aggressively to other parts of the body.
Depending on the type of skin cancer that a person has, it may be more or less likely that it has spread through the body. For instance, basal cell skin cancer rarely spreads beyond the skin where it starts. However, melanomas and large squamous cell carcinomas are more likely to spread into other regions of the body. Cases of melanoma, in particular, may call for further tests to determine the specific stage theyre in.
Your doctor may evaluate multiple factors in order to stage the cancer. Using biopsies and imaging tests, your doctor may take a look at:
-
The size and thickness of the tumor, and whether it has grown into surrounding tissues
-
Nearby lymph nodes, to check for signs of cancer spread
Recommended Reading: Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rates
Skin Color And Being Exposed To Sunlight Can Increase The Risk Of Basal Cell Carcinoma And Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin
Anything that increases your chance of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer not having risk factors doesnt mean that you will not get cancer. Talk with your doctor if you think you may be at risk.
Risk factors for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin include the following:
- Being exposed to natural sunlight or artificial sunlight over long periods of time.
- Having a fair complexion, which includes the following:
- Fair skin that freckles and burns easily, does not tan, or tans poorly.
- Blue, green, or other light-colored eyes.
- Red or blond hair.
Although having a fair complexion is a risk factor for skin cancer, people of all skin colors can get skin cancer.
Older age is the main risk factor for most cancers. The chance of getting cancer increases as you get older.