What Are The Main Obstacles To Fight Melanoma For Good
There are many obstacles in the way of finding a cure for melanoma. Toxicity with any cancer therapy is always an obstacle. How can we treat only the malignant cells in the body, leaving healthy cells untouched?
Also, cancer cells from one person to the next are all very different. Cancer cells in general are genetically modified to proliferate and survive and have different mechanisms in place that allow them to continue to grow and survive, fighting the effects of treatment. Better characterizing these cancer cell pathways will allow us to offer better therapies and possibly help us predict who will respond and who may not respond to different treatment regimens.
Optimal combinations of medications, dosing regimens and maintenance plans will all come to play as we optimize patient specific treatment for melanoma.
We also lack biomarkers or tests that can indicated if a patient is responding to treatment or not or even tell us quickly if the cancer is coming back or recurring.
The pathways are complicated, but these advances along with targeted therapy specific to each patient cancer characteristics is an exciting area of melanoma research. Optimal combinations of medications, dosing regimens and maintenance plans will all come to play as we optimize patient specific treatment for melanoma.
What To Do When You Get Sunburnt
The best thing to do is to stay out of the sun, cover up when you have to go outside and give your skin time to heal. Drink plenty of water, use cool compresses and pain medication if necessary and see your GP if you think the burn is more severe than can be handled at home. For more advice, please see the NHS website on sunburn.
What Do Studies Show
Many studies have found that basal and squamous cell skin cancers are linked to certain behaviors that put people in the sun, as well as a number of markers of sun exposure, such as:
- Spending time in the sun for recreation
- Spending a lot of time in the sun in a swimsuit
- Living in an area that gets a lot of sunlight
- Having had serious sunburns in the past
- Having signs of sun damage to the skin, such as liver spots, actinic keratoses , and solar elastosis on the neck
Studies have also found links between certain behaviors and markers of sun exposure and melanoma of the skin, including:
- Activities that lead to intermittent sun exposure, like sunbathing, water sports, and taking vacations in sunny places
- Previous sunburns
- Signs of sun damage to the skin, such as liver spots, actinic keratoses, and solar elastosis
Because UV rays dont penetrate deeply into the body, they wouldnt be expected to cause cancer in internal organs, and most research has not found such links. However, some studies have shown possible links to some other cancers, including Merkel cell carcinoma and melanoma of the eye.
Studies have found that people who use tanning beds have a higher risk of skin cancer, including melanoma and squamous and basal cell skin cancers. The risk of melanoma is higher if the person started indoor tanning before age 30 or 35, and the risk of basal and squamous cell skin cancer is higher if indoor tanning started before age 25.
Read Also: What Do Skin Cancer Marks Look Like
Find Facts And Statistics For Reporting About Skin Cancer
Some types of skin cancer are more dangerous than others, but if you have a spot. It affects people of all races, genders and ages, which is why it’s absolutely critical for americans to learn about. In the united states, it’s estimated that doctors diagnose over 100,000 new skin cancer cases each year. Update your find a dermatologist profile, the academy’s directory that’s visited by over 1 million people a year. According to the american cancer society, just over 100,000 new cases of skin cancer are diagnosed in the united states each year. We may earn commission from links on this page, but we only recommend products we back. Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer in the united states by a pretty large margin, and it does not discriminate. But this common form of cancer can also occur on areas of your skin not ordinarily ex. Learn about the academy’s efforts to refocus its brand on education. Make this melanoma monday your fresh start we may earn commission from links on this page, but we only recommend products we back. Learn what skin cancer is and what causes it. Skin cancer is one of the most common types of cancer. If you have skin cancer, it is important to know which type you have because it affects your treatment options and your outlook .
Widespread Rash: Drug Allergy
A rash that covers a wide area could be a sign of drug hypersensitivity syndrome when a medication causes an allergy.DRESS can take a few weeks to appear after you start a new drug, and continue for a while even if you stop taking it.
Patients report a diverse range of rashes from blistering and lesions to eczema and facial swelling.DRESS can lead to issues with internal organs, which is why its so serious. It could cause multi organ failure, or lead to lung disease, inflammation of the heart and seizures.
You May Like: Can Stage 3 Melanoma Be Cured
What Should I Do If I Get Sunburnt
If you notice your skin becoming pink or red, you should come out of the sun and cover up to help stop any more damage from happening. Putting on more sunscreen wont help and wont let you safely stay out in the sun for longer.
After sun lotion can help sunburnt skin feel better, but it cant repair any DNA damage.
Getting sunburnt once doesnt mean you will definitely develop skin cancer. But the more you get sunburnt the higher your risk of melanoma skin cancer. Reduce your risk of sunburn and protect your skin in the future by using a combination of shade, clothing and sunscreen.
Does Uv Radiation Cause Cancer
Most skin cancers are a result of exposure to the UV rays in sunlight. Both basal cell and squamous cell cancers tend to be found on sun-exposed parts of the body, and their occurrence is typically related to lifetime sun exposure. The risk of melanoma, a more serious but less common type of skin cancer, is also related to sun exposure, although perhaps not as strongly. Skin cancer has also been linked to exposure to some man-made sources of UV rays.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Basal Cell Carcinoma
Uv Radiation And Skin Cancer
Skin cells in the top layer of skin produce a pigment called melanin. Melanin gives skin its natural colour. When skin is exposed to UV radiation, more melanin is produced, causing the skin to darken. This is what we call a tan. A tan is not a sign of good health, but of damaged skin cells in trauma.
Tanning can contribute to DNA damage, premature skin ageing and skin cancer. Every time skin is exposed to the sun or a solarium, the total lifetime dose of UV radiation is increased. Over time, this damage adds up, even when no sunburn is experienced.
All types of sunburn, whether serious or mild, can cause permanent and irreversible skin damage that can lead to the development of skin cancer later in life.
It is recommended that all people, regardless of skin type, use a combination of sun protection measures during the daily sun protection times. The sun protection times are issued whenever the UV level is forecast to be 3 or above, and sun protection is recommended.
Does Sunlight Cause Skin Cancer
There is evidence that sunlight causes skin cancer. Skin cancer can be treated and cured without serious consequences. However, in some cases the condition can be life-threatening if not diagnosed in time.
Skin cancer is an occupational concern for people who work under the sun. The risk however, may be reduced through awareness of the problem, and by taking measures to prevent exposure to sunlight.
Don’t Miss: How Fast Can You Get Skin Cancer From The Sun
Prognosis For Skin Cancer
It is not possible for a doctor to predict the exact course of a disease. However, your doctor may give you the likely outcome of the disease. If detected early, most skin cancers are successfully treated.
Most non-melanoma skin cancers do not pose a serious risk to your health but a cancer diagnosis can be a shock. If you want to talk to someone see your doctor. You can also call Cancer Council 13 11 20.
Recommended Reading: How Likely Is Skin Cancer
Debunking Skin Cancer Myths
Skin cancer is the most common cancer in the United States. May is skin cancer awareness month and we debunk some common myths about this disease and provide some tips to reduce your risk.
Woman applying sunscreen on her shoulder
Skin cancer is the most common cancer in the United States. May is skin cancer awareness month and we debunk some common myths about this disease and provide some tips to reduce your risk.
Before we start myth-busting, lets get clear on what is skin cancer and the dangers it carries. Skin cancer happens when skin cells start growing rapidly and uncontrollably. Your skin has 3 layers: epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis. The epidermal bottom layer or basal layer creates new skin cells that move to the top layer. These cells also contain melanin, which multiplies to protect our skin from harsh sun exposure. Melanin is often called the bodys natural sunscreen. Sometimes, these cells can multiply uncontrollably, causing a tumor.
Myth 1: Skin cancer is not a deadly disease.
Fact: More than 11,500 people in the United States are expected to lose their lives from melanoma and other nonepithelial skin cancers this year. Most deaths are due to melanoma, the most dangerous form of skin cancer.
Myth 2: A tanning bed is safer than UV rays from the sun.
Myth 3: A base tan prevents sunburns.
Sunburn happens when the UV rays are more than the skin can handle and repair.
Myth 4: People who tan easily and rarely burn will not get cancer.
Practice Skin Safety
Don’t Miss: What Are The Symptoms Of Melanoma
How Is Scalp Cancer Diagnosed
You might go to your doctor if you notice a suspicious spot on your scalp, or a doctor might notice it during a skin check. No matter how the spot is found, skin cancer diagnosis will happen roughly the same way.
First, your doctor will ask you about your family history of cancer, if you spend a lot of time in the sun, use protection in the sun, and if you use tanning beds. If you noticed the lesion, your doctor may ask if youve noticed any changes over time or if its a new growth.
Then your doctor will do a skin exam to look more closely at the lesion and determine if you need further testing. Theyll look at its size, color, shape, and other features.
If your doctor thinks it might be skin cancer on your scalp, theyll take a biopsy, or small sample, of the growth for testing. This testing can tell your doctor if you have cancer, and if you do, what type. A biopsy might be enough to completely remove a small cancerous growth, especially basal cell carcinoma.
If the spot is cancerous but not basal cell carcinoma, your doctor might recommend more testing to see if it has spread. This will usually include imaging tests of lymph nodes in your head and neck.
If You Have One Of The Two Types Of Non
- A sore that crusts, bleeds, or oozes without scabbing over and healing for a period of several weeks
- One patch of skin appears tight and shiny like a scar
- A red, raised patch with or without itching
- A dip in the skin with a raised border
- A shiny, pearl-like bump
The terms basal cell and squamous cell refer to the layer of the skin where a doctor diagnoses a carcinoma, which means the skin contains cancer cells. Basal cell skin cancer means that cancer is present in the skins epidermis. Squamous cell skin cancer resides in the skins subcutaneous layer.
Read Also: How Do You Cure Melanoma
How The Government Of Canada Protects You
The Public Health Agency of Canada monitors cancer in Canada. PHAC identifies trends and risk factors for cancer, develops programs to reduce cancer risks, and researches to evaluate risks from the environment and human behaviours. Health Canada also promotes public awareness about sun safety and the harmful effects of UV rays.
What Is Ultraviolet Radiation
Energy from the sun reaches the earth as visible, infrared, and ultraviolet rays.
-
Ultraviolet A is made up of wavelengths 320 to 400 nm in length.
-
Ultraviolet B wavelengths are 280 to 320 nm.
-
Ultraviolet C wavelengths are 100 to 280 nm.
Only UVA and UVB ultraviolet rays reach the earth’s surface. The earth’s atmosphere absorbs UVC wavelengths.
-
UVB rays cause a much greater risk of skin cancer than UVA.
-
But UVA rays cause aging, wrinkling, and loss of elasticity.
-
UVA also increases the damaging effects of UVB, including skin cancer and cataracts.
In most cases, ultraviolet rays react with melanin. This is the first defense against the sun. Thats because melanin absorbs the dangerous UV rays that can do serious skin damage. A sunburn develops when the amount of UV damage exceeds the protection that the skin’s melanin can provide. A suntan represents the skin’s response to injury from the sun. A small amount of sun exposure is healthy and pleasurable. But too much can be dangerous. Measures should be taken to prevent overexposure to sunlight. These preventive measures can reduce the risks of cancers, premature aging of the skin, the development of cataracts, and other harmful effects.
#TomorrowsDiscoveries: Protecting Against UV Radiation Anna Chien, M.D.
Also Check: How Fast Does Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Spread
Hereditary Factors And Skin Cancer
Family history and hereditary factors , play an important part in the risk of developing skin cancer.
If one or both of your parents have had a skin cancer, you too could be at risk, especially as you are likely to have the same skin type as them.
When combined with UV exposure, traits such as:
- red or blonde hair
are genetic risk factors for developing skin cancers.
Sun Exposure Induces Genetic Mutations In The Skin
Research indicates that sun exposure causes a type of mutation known as p53 in skin cancers at a higher frequency compared to other types of cancer. The p53 genetic mutation has been shown to arise in lab studies as early as one week within chronic sun exposure and reaches its maximum at four to eight weeks of exposure. Another genetic mutation known as patched has been found on the skin of sun-exposed areas of the skin as well.
Don’t Miss: What Does Oral Melanoma Look Like
Read The Full Article Here
Excellent article from the U.K. Why is Europe and Australia and New Zealand embracing new technology while here in the USA we seem to be avoiding the obvious advantages of imaging? Get an FBI investigation of your skin today at a convenient time and location near you. Only $99 and you get all the images to share with your medical professional.
What Happens When You Get Sunburnt
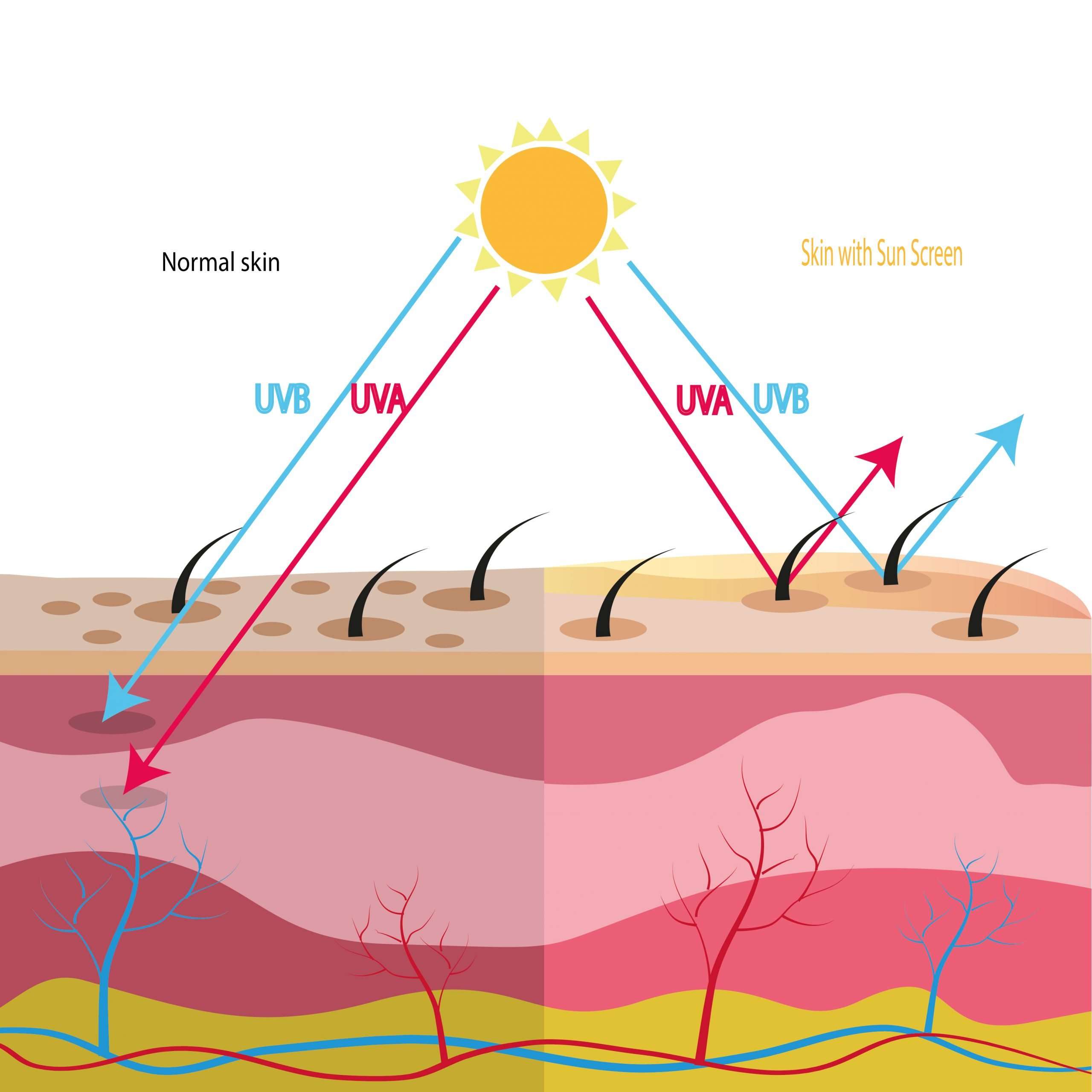
UV radiation from the sun is always present, whether its a cloudy day or blazing hot outside. Some types of UV radiation can even get to you through windows, which is why its a good idea to wear some form of SPF every day. There are three main types of UV radiation UVA, UVB and UVC. You dont really need to worry about UVC as it is absorbed by the Earths atmosphere. UVA and UVB rays are the ones that cause serious harm by penetrating into the skin and damaging proteins, membranes and the DNA in your skin cells.
UVA rays A as in ageing penetrate deep into the skin where they cause damage to elastic fibres and DNA. They are thought to be responsible for 80% of visible skin ageing.
UVB rays B as in burn hit the top layer of your skin and cause the typical symptoms of sunburn. They damage DNA and kickstart an inflammatory response, leading to swelling, redness, heat and pain in the affected area. This immune response already begins while youre still enjoying the warming rays from the sun and peaks about one or two days later, which is why you sometimes wont realise how badly you got sunburnt until its too late. Some of the cells in your skin will also start producing melanin to protect the skin, resulting in a tan. But any form of tan means that DNA in your skin cells has been damaged, so unfortunately there is no safe amount of tanning.
Read Also: How To Know I Have Skin Cancer
How Can I Protect Myself From Skin Cancer
Have your doctor check your skin if you are concerned about a change.Your doctor may take a sample of your skin to check for cancer cells.
Ask your doctor about your risk of skin cancer:
- Some skin conditions and certain medicines may make your skin more sensitive to damage from the sun.
- Medicines or medical conditions that suppress the immune system may make you more likely to develop skin cancer.
- Having scars or skin ulcers increases your risk.
- Exposure to a high level of arsenic increases your risk.
Stay out of the sun as much as you can. Whenever possible, avoid exposure to the sun from10 a.m. to 4 p.m. If you work or play outside, then
- Try to wear long sleeves, long pants, and a hat that shades your face, ears, and neck with a brim all around.
- Use sunscreen with a label that says it is broad spectrum or is at least SPF 15 and can filter both UVA and UVB rays.
- Wear sunglasses that filter UV to protect your eyes and the skin around your eyes.
- If you are concerned about having a low level of vitamin D from not being in the sun, talk with your doctor about supplements.
Dont use tanning beds, tanning booths, or sunlamps.
Related Resources