What You Can Do
If youve already had a BCC, you have an increased chance of developing another, especially in the same sun-damaged area or nearby.
A BCC can recur even when it has been carefully removed the first time, because some cancer cells may remain undetectable after surgery and others can form roots that extend beyond whats visible. BCCs on the nose, ears and lips are more likely to recur, usually within the first two years after surgery.
Heres what you can do to detect a recurrence and safeguard yourself against further skin damage that can lead to cancer:
Reviewed by:
Who Gets Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
- Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin generally affects elderly or older adults some cases rarely develop in children too
- Nodular BCC of Skin constitutes 80% of all Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin types. It is the most common type of BCC of Skin
- It can occur in both males and females however
- Among the older age group, males are affected more than females
- In the younger age group, females are affected more than males, which may be attributed to their tendency to acquire sun-tanned bodies or visit skin tanning parlors more
You May Like: Does Basal Cell Carcinoma Make You Tired
Other Risk Factors For Sporadic Bcc
The incidence of BCC is much more common in individuals who have received a solid organ transplant, in whom herpes virus like DNA sequences have been demonstrated, and in whom tumors appear to have an increased tendency for recurrence and metastasis. In concert with this more aggressive behavior, the histologic types are different in patients with immune suppression in whom infiltrative growth BCC is more common than nodular and/or superficial variants. In contrast, superficial BCC predominates in individuals with renal failure, diabetes mellitus and human immunodeficiency virus infection.
You May Like: What Does Early Squamous Skin Cancer Look Like
Recommended Reading: What Does Advanced Melanoma Look Like
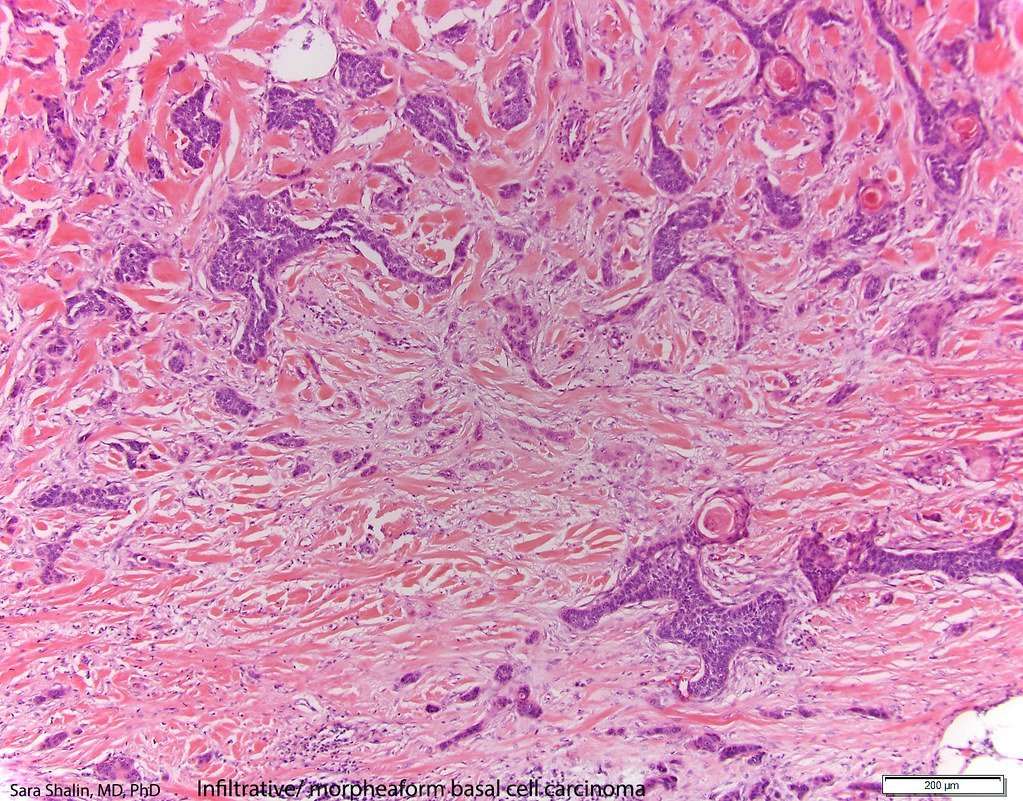
Infiltrative Basal Cell Carcinoma
Infiltrative basal cell carcinoma is an aggressive type of skin cancer that requires surgical treatment. Subtypes of infiltrative basal cell lesions include micronodular carcinoma and morpheaform carcinoma.
Causes: Infiltrative forms of basal cell cancer, like those of the nodular and superficial types, are linked to both genetic factors and environmental factors such as prolonged sun exposure in youth.
Symptoms: The symptoms of infiltrative basal cell lesions vary according to subtype. Micronodular lesions are typically firm, yellowish-white in color, and have a distinct border. Morpheaform lesions resemble plaque or scar tissue, have vague and far-reaching borders, and are prone to crusting and bleeding.
Diagnosis and Treatment: A thorough skin biopsy is necessary for this type of basal cell cancer, as infiltrative lesions are visually easy to mistake for other non-cancerous forms of scar tissue. Surgical excision with margin examination, radiation therapy, and Mohs micrographic surgery are the most effective treatment options.
Once a patient has been diagnosed with one of the types of basal cell cancer, he or she can discuss treatment options with medical professionals and can proceed with having the cancer removed. Because several effective basal cell surgical procedures and medication options are available, patients who are diagnosed while the disease is in early stages often have a very good prognosis.
What Are The Possible Complications Of Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
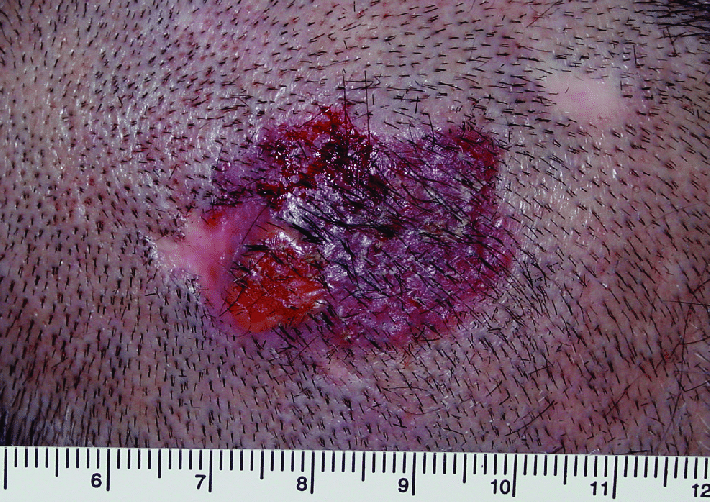
The complications of Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin could include:
- If the tumor becomes big, develops into a firm mass and ulcerates, it can get secondarily infected with bacteria or fungus
- Metastasis to regional lymph nodes can occur. The tumor can also infiltrate into surrounding structures
- Nodular BCC of Skin can cause cosmetic issues, since these skin tumors can cause large ulceration
- Recurrence of the tumor after a period of time recurrence is frequently common with large tumors
- Side effects of chemotherapy and radiation
Recommended Reading: How Does Immunotherapy Work For Melanoma
What Are The Risk Factors For Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
The risk factors that contribute to Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin formation include:
- Prolonged sun exposure, exposure to ultraviolet light
- Use of tanning beds, tanning parlors
- Arsenic exposure
- Ionizing radiation
- Smoking
- The presence of certain genetic syndromes such as basal cell nevus syndrome increases the risk
- Caucasians are more vulnerable compared to other darker-toned individuals
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases one’s chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What Is The Treatment For Advanced Or Metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma
Locally advanced primary, recurrent or metastatic BCC requires multidisciplinary consultation. Often a combination of treatments is used.
- Radiotherapy
- Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy refers to the hedgehog signalling pathway inhibitors, vismodegib and sonidegib. These drugs have some important risks and side effects.
Recommended Reading: How Fast Does Melanoma Metastasis
Benign And Malignant Tumors
Several benign and malignant tumors can have a clinical appearance similar to that of SGC. These include BCC, SCC, melanoma, Merkel cell carcinoma, lymphoma, sweat gland neoplasm, junctional squamous papilloma, hereditary benign intraepithelial dyskeratosis, metastatic carcinoma, and other rare tumors.1
Basal cell carcinoma
The nodular BCC is more common on the lower lid and is white rather than yellow. BCC is also more likely to become ulcerated than SGC. Although diffuse sclerosing BCC may closely simulate SGC, it very rarely exhibits diffuse invasion of the conjunctiva. Histologically, BCC typically shows peripheral palisading of nuclei and retraction artifact that are not seen in SGC.
Squamous cell carcinoma
SCC is more superficial and lacks a yellow color. Conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia can be very similar to diffuse epithelial invasion by SGC, except for eyelid involvement, which is less likely to be present in SGC. Histopathologically, SCC is the lesion most often confused with SGC.6,14,15 Unlike SGC, SCC cells have more abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, lack lipid vacuoles, and demonstrate eddy formation and keratin cysts.
Melanoma
Nodular or diffuse cutaneous melanoma in the eyelid or conjunctiva can usually be distinguished from SGC by its black or brown pigmentation, but amelanotic melanoma can resemble SGC.
Other tumors
You May Like: Can Laser Hair Removal Cause Skin Cancer
Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Risk Factors Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma: High Risk And Low Risk
Mohs surgeon Erica Lee researches ways to improve quality of life in people with skin cancer.
When any type of cancer is diagnosed, its classified according to certain characteristics. Basal cell carcinomas are classified based on the risk of recurrence , which depends mostly on where the tumor is located.
Basal cell carcinomas are considered to be high risk if:
- they are located in the middle or central part of the face, such as the eyelids, nose, ears, and lips
- they have come back after first treatment
- they are wider than 2 centimeters
Basal cell carcinomas are considered to be a low risk for coming back if:
- they are small and superficial
- they have a clear, defined edge
- they havent been treated before
How Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Diagnosed
BCC is diagnosed clinically by the presence of a slowly enlarging skin lesion with typical appearance. The diagnosis and histological subtype is usually confirmed pathologically by a diagnostic biopsy or following excision.
Some typical superficial BCCs on trunk and limbs are clinically diagnosed and have non-surgical treatment without histology.
Also Check: What Is Skin Cancer Caused By
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
An evidence-based approach to basal cell cancer
Basal cell cancer is relatively common. Patients often first present to the primary care provider with complaints of an abnormal skin lesion. When diagnosed early, it has an excellent prognosis, but if there is a delay in diagnosis, the tumor can advance and lead to significant morbidity. Basal cell cancer is best managed by an interprofessional team that includes a dermatologist, mohs surgeon, plastic surgeon, nurse practitioner, primary care provider, and a dermatopathologist. Basal cell carcinomas typically have a slow growth rate and tend to be locally invasive. Tumors around the nose and eye can lead to vision loss. In most cases, surgical excision is curative. However, because recurrences can occur, these patients need long-term follow up.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
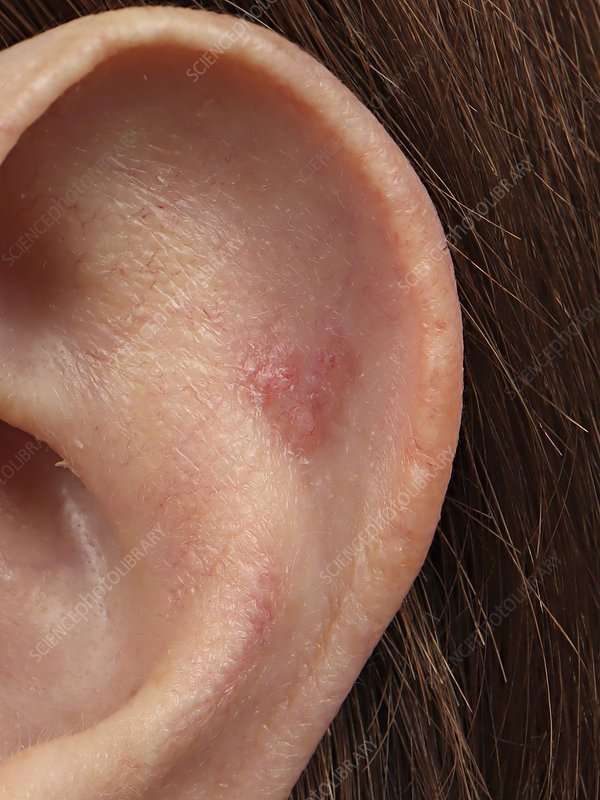
Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin signs and symptoms may include:
- Nodular BCC of Skin is a slow-growing malignant tumor. The tumor is a typical skin lesion that has a nodular appearance
- The surface of the nodule may be red, if intact. Else, it may appear as an ulcer, if the surface is eroded
- It is typically observed on sun-exposed areas of the body common sites include the head and neck region
- The tumor may be solitary or many in number. In children, if it is associated with basal cell nevus syndrome, then multiple lesions may be observed
- Some Nodular BCC of Skin may have pigmented appearance and may resemble a melanoma
- Most lesions are less than 1-2 cm, but some may grow to larger sizes of even 10 cm
- The nodular lesion may grow and there may be itching sensation, ulceration, and bleeding
Also Check: Are There Different Types Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Mohs May Be Your Best Treatment Option
Because of its ability to invade the surrounding area, typical location in high-risk areas, and high risk of recurrence, your doctor may recommend Mohs surgery for treating morpheaform basal cell carcinoma. It is possible that excision alone would not remove all the cancer. Removing all the cancer with excision would also remove a large amount of healthy tissue.2-4
Have you or someone you know been diagnosed with morpheaform basal cell carcinoma?
Infiltrative Basal Cell Carcinoma Treatment
Due to the visually challenging element of this kind of skin cancer, the most recommended infiltrative basal cell carcinoma treatment method is Mohs surgery. This surgical procedure aims to remove unhealthy cells from the skin by cutting them out with a scalpel, allowing the healthy tissue to heal around the area. Depending on the patients circumstances, other non-melanoma skin cancer treatments include topical creams, chemotherapy, and IG-SRT, a radiotherapy treatment that helps avoid surgery but with similar results.
Read Also: How Does Skin Cancer Occur
What Is The Prognosis Of Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
- In general, the prognosis of Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin is excellent, if it is detected and treated early. However, if it metastasizes to the local lymph nodes, the prognosis is guarded or unpredictable
- In such cases of metastatic BCC, its prognosis depends upon a set of several factors that include:
- Stage of tumor: With lower-stage tumors, when the tumor is confined to site of origin, the prognosis is usually excellent with appropriate therapy. In higher-stage tumors, such as tumors with metastasis, the prognosis is poor
- The surgical resectability of the tumor
- Overall health of the individual: Individuals with overall excellent health have better prognosis compared to those with poor health
- Age of the individual: Older individuals generally have poorer prognosis than younger individuals
- Whether the tumor is occurring for the first time, or is a recurrent tumor. Recurring tumors have a poorer prognosis compared to tumors that do not recur
- Response to treatment: Tumors that respond to treatment have better prognosis compared to tumors that do not respond so well to treatment
What Is Basal Cell Carcinoma
The basal cells are the bottom layer of the epidermis, which is the uppermost layer of skin. They are responsible for producing new skin cells when old ones die. Basal cell carcinoma occurs when the basal cells begin to reproduce out of control.
The most common cause of BCC is unprotected and excessive exposure to UV rays, either from the sun or tanning beds. UV light damages the skin and, over time, can cause mutations in the different types of skin cells. When the mutation occurs in the basal cells, it causes basal cell carcinoma.
BCC is slow growing and, unlike many other types of cancer, doesnt spread to other areas of the body easily. The most common areas to develop BCC are the places that get the most sun exposure, including the ears, nose, head, neck, and arms. However, any area of the body can develop basal cell carcinoma.
Early diagnosis and treatment are key to a great prognosis. When you catch it early, your dermatologist can often treat most types of basal cell carcinoma in-office with very little downtime for recovery. However, the tumor can grow deep into the skin, which can cause injury to the nerves and blood vessels. As it grows, it can leave the surrounding tissue permanently damaged and disfigured.
Don’t Miss: Can You Die From Melanoma Skin Cancer
Who Gets Basal Cell Carcinoma
Risk factors for BCC include:
- Age and sex: BCCs are particularly prevalent in elderly males. However, they also affect females and younger adults
- Repeated prior episodes of sunburn
- Fair skin, blue eyes and blond or red hairnote BCC can also affect darker skin types
- Previous cutaneous injury, thermal burn, disease
- Inherited syndromes: BCC is a particular problem for families with basal cell naevus syndrome , Bazex-Dupré-Christol syndrome, Rombo syndrome, Oley syndrome and xeroderma pigmentosum
- Other risk factors include ionising radiation, exposure to arsenic, and immune suppression due to disease or medicines
What Is The Treatment For Primary Basal Cell Carcinoma
The treatment for a BCC depends on its type, size and location, the number to be treated, patient factors, and the preference or expertise of the doctor. Most BCCs are treated surgically. Long-term follow-up is recommended to check for new lesions and recurrence the latter may be unnecessary if histology has reported wide clear margins.
Also Check: Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treatable
Infiltrative Basal Cell Carcinoma Prognosis
8 out of 10 patients who are diagnosed with non-melanoma skin cancer will have basal cell carcinoma, which can present in a wide variety of colors, shapes, and sizes. Many basal cell carcinoma lesions are red or pink sores that refuse to heal, and can also be itchy or uncomfortable. Receiving an infiltrative basal cell carcinoma prognosis is unique because unlike many other forms of basal cell carcinoma, this variant is typically white and harder to see, due to it developing in between the skins collagen fibers. This growth pattern is more unusual, as basal cell carcinoma typically forms on the top-most layer of the skin.
Pigment Basal Cell Carcinoma
The pigmentation can be found in different clinical versions of basal cell carcinoma including nodular, micronodular, multifocal and superficial BCC, and the color varies from dark brown to black . Histology showed nests of basaloid cells, abundance of melanin and melanophages, and moderate inflammatory infiltrate. The melanocytes are located among tumor nests, while the melanophages are present in the stroma. The differential diagnosis has to be made with malignant melanoma.
An irregular, periphery spreading erosive pigmented plaque on head of a 78 years old woman
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Melanoma Skin Cancer
How Is Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin Treated
In general, the treatment of Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin depends upon a variety of factors including:
- The subtype of BCC
- The location of the tumor
- The number of tumors
- The size of the tumor
- Whether the tumor has metastasized
A combination of treatment methods may be used to treat Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin. The type of surgery may include:
- Shave biopsy of skin: This procedure is used for small tumors. There is no requirement of sutures after the surgery
- Excision of tumor: In this procedure, the tumor and surrounding tissue are removed with clear margins. Depending upon the amount of skin removed, surgical sutures may be necessary
- Mohs surgery: In this procedure, the tumor is removed layer by layer precisely, until clear margins are achieved. Each layer removed is examined under a microscope through a âfrozen sectionâ procedure, for the presence of residual tumor
In most cases, a surgical removal of the entire tumor is the preferred treatment option. This can result in a cure.
Other techniques to treat this skin cancer may include:
- Cryotherapy: Here the tumor tissue is destroyed through a freezing technique. Typically liquid nitrogen is used to freeze the tumor
- Topical creams, such as 5-fluorouracil cream and imiquimod cream, are two examples that can be used for topical treatment. These creams may be applied for several weeks, which slowly destroys the tumor
Dont Miss: What Is The Main Cause Of Skin Cancer
Identifying The Types Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Did you know that skin cancer is the most frequently diagnosed cancer in the US and globally? Of the various kinds of skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma is the most common, with up to 4.3 million new cases discovered annually in America. The good news? In the early stages, most types of basal cell carcinoma have a high cure rate and cause very little damage.
This month, were exploring the types of basal cell carcinoma, including the causes, symptoms, and prognosis for recovery.
Read Also: What Cancer Can Cause Itchy Skin