Prognosis Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Treatment of basal cell carcinoma is nearly always successful, and the cancer is rarely fatal. However, almost 25% of people with a history of basal cell carcinoma develop a new basal cell cancer within 5 years of the first one. Thus, anyone with one basal cell carcinoma should have a yearly skin examination.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stages
There are certain features that are considered to make the cancer at higher risk for spreading or recurrence, and these may also be used to stage squamous cell carcinomas. These include:
- Greater than 2 mm in thickness
- Invasion into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin
- Invasion into the tiny nerves in the skin
- Location on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip
After the TNM components and risk factors have been established, the cancer is assigned to one of the five squamous cell carcinoma stages, which are labeled 0 to 4. The characteristics and stages of squamous cell cancer are:
Stage 0: Also called carcinoma in situ, cancer discovered in this stage is only present in the epidermis and has not spread deeper to the dermis.
Stage 1 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer is less than 2 centimeters, about 4/5 of an inch across, has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs, and has one or fewer high-risk features.
Stage 2 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer is larger than 2 centimeters across, and has not spread to nearby organs or lymph nodes, or a tumor of any size with 2 or more high risk features.
Stage 3 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer has spread into facial bones or 1 nearby lymph node, but not to other organs.
Stage 4 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer can be any size and has spread to 1 or more lymph nodes which are larger than 3 cm and may have spread to bones or other organs in the body.
When Melanoma Can’t Be Cured
If your cancer has spread and it is not possible to cure it by surgery, your doctor may still recommend treatment. In this case, treatment may help to relieve symptoms, might make you feel better and may allow you to live longer.Whether or not you choose to have anti-cancer treatment, symptoms can still be controlled. For example, if you have pain, there are effective treatments for this. General practitioners, specialists and palliative care teams in hospitals all play important roles in helping people with cancer.
You May Like: What Stage Is Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- Do you know the stage of the cancer?
- If not, how and when will you find out the stage of the cancer?
- Would you explain to me what the stage means in my case?
- What will happen next?
There are many ways to treat skin cancer. The main types of treatment are:
- Surgery
- Immunotherapy
- Chemotherapy
Most basal cell and squamous cell cancers can be cured with surgery or other types of treatments that affect only the spot on the skin.
The treatment plan thats best for you will depend on:
- The stage and grade of the cancer
- The chance that a type of treatment will cure the cancer or help in some way
- Your age and overall health
- Your feelings about the treatment and the side effects that come with it
Staging For Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma usually do not spread to other parts of the body. On rare occasions, a persons lymph node may be removed to find out if the cancer has spread, which is called metastasis. Lymph nodes are bean-shaped organs that help fight infection. The doctor may recommend other tests to determine the extent of the disease, including blood tests, chest x-rays, and imaging scans of the lymph nodes and nerves, liver, bones, and brain, but this is uncommon.
You May Like: How Long Can You Live With Basal Cell Carcinoma
Recommended Reading: Braf And Melanoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma Stages
There are certain features that are considered to make the cancer at higher risk for spreading or recurrence, and these may also be used to stage basal cell carcinomas. These include:
- Greater than 2 mm in thickness
- Invasion into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin
- Invasion into the tiny nerves in the skin
- Location on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip
After the TNM components and risk factors have been established, the cancer is given a stage. For basal cell carcinoma staging, the factors are grouped and labeled 0 to 4. The characteristics and stages of basal cell carcinoma are:
Stage 0: Also called carcinoma in situ, cancer discovered in this stage is only present in the epidermis and has not spread deeper to the dermis.
Stage 1 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer is less than 2 centimeters, about 4/5 of an inch across, has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs, and has one or fewer high-risk features.
Stage 2 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer is larger than 2 centimeters across, and has not spread to nearby organs or lymph nodes, or a tumor of any size with 2 or more high-risk features.
Stage 3 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer has spread into facial bones or 1 nearby lymph node, but not to other organs.
Stage 4 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer can be any size and has spread to 1 or more lymph nodes which are larger than 3 cm and may have spread to bones or other organs in the body.
Symptoms If Cancer Has Spread To The Bones
You may have any of these symptoms if your cancer has spread to the bones:
- an ache or pain in the affected bone
- a weakened bone which is more prone to break or fracture
Sometimes when bones are damaged by advanced cancer, the bones release calcium into the blood. This is called hypercalcaemia and can cause various symptoms such as:
- tiredness
Recommended Reading: What Does Stage 3b Melanoma Mean
Earlier Detection Methods Are Needed
Our findings highlight the need for earlier detection of cancer, Dr. Curtis said.
Cancer researchers are already exploring noninvasive methods that could detect cancer at an early stage by analyzing tumor cells, or pieces of DNA from tumor cells, that have escaped from the original tumor and are found in the blood.
This approach, often called a liquid biopsy, could help doctors identify patients at risk for metastasis and treat them with chemotherapy or targeted therapies, if available, to try to eliminate metastatic cells that have spread in the body before surgery, Dr. Boudreau said.
This is early-stage research, but it gives us the first quantitative evidence that metastasis can occur exceedingly early, while also providing clues as to how to identify individuals who are at risk of metastasis, Dr. Curtis said.
Before the new results can be used to guide patient care, the researchers will need to look at a much larger group of patients, to see how consistent their findings are, Dr. Boudreau said.
Indeed, Dr. Curtis said, her team plans to extend their analysis to more patients. The biggest task, she said, will be to follow patients with earlier-stage colorectal cancer and investigate whether these specific combinations of mutations are indeed predictive of disease progression. And then, if thats true, we will have a rationale to go forward with clinical studies.
Stage Ii Breast Cancer
There are basically four sub-categories of breast cancer within the category of stage II. Breast tumors in the Stage II classification are:
- A breast tumor that is 2cm in diameter or less. BUT the cancer cells have already spread to the lymph nodes.
- OR a breast tumor that is larger than 5 cm but has not yet spread to the lymph nodes.
- OR breast tumors in between 2 cm and 5 cm in diameter -whether there is evidence of spread to the lymph nodes or not.
There are actually quite a number of specific subcategories and letters and numbers to indicate a more precise description of the breast cancer at Stage II. .
In summary, stage II breast cancer is of intermediate size and threatening to spread. Without a doubt, staging for stage II breast cancers requires a thorough investigation of potential metastases.
Survival Rates for Stage II Breast Cancer
The average survival rate for stage II breast cancers is about 93% after five years and about 75% after 10 years. The rate of local recurrence is about 16% for stage II breast tumors. Furthermore, only about 16% of stage II breast cancers either have or will develop lymph node metastasis.
See also our new up-to-date survival rates by stageOR our general survival rates for breast cancer
A baseline bone scan is unlikely to detect bone metastasis with stage 2 tumors, but they are usually necessary just to be sure.
Treatment for Stage II Breast Cancer
You May Like: What Does Basal Cell Carcinoma Look Like On The Nose
Also Check: What Is Braf Testing In Melanoma
What Skin Cancer Looks Like
Skin cancer appears on the body in many different ways. It can look like a:
-
Changing mole or mole that looks different from your others
-
Dome-shaped growth
-
Non-healing sore or sore that heals and returns
-
Brown or black streak under a nail
It can also show up in other ways.
To find skin cancer on your body, you dont have to remember a long list. Dermatologists sum it up this way. Its time to see a dermatologist if you notice a spot on your skin that:
-
Differs from the others
-
Itches
-
Bleeds
To make it easy for you to check your skin, the AAD created the Body Mole Map. Youll find everything you need to know on a single page. Illustrations show you how to examine your skin and what to look for. Theres even place to record what your spots look like. Youll find this page, which you can print, at Body Mole Map.
Stages Of Melanoma: Growth Patterns And Stages Of Skin Cancer
Melanocytes, a layer of cells in the skin produce melanin, a brown-black skin pigment that determines skin and hair color and protect against the damaging rays of the sun. These melanocytes spread as the person ages and form clusters.
The controlled proliferation of melanocytes is non-cancerous and cause moles and freckles. At times, however the growth of melanocytes goes out of control and develops into cancerous and life-threatening melanoma. Such uncontrolled growth cause moles with uneven shape, dark color, or mixed color. The causes of such uncontrolled growth is usually excessive sun exposure during childhood, fair skin that burns easily, and certain hereditary conditions
Recommended Reading: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Metastasize
What To Look For:
Melanomas are lesions that usually look different from other moles.
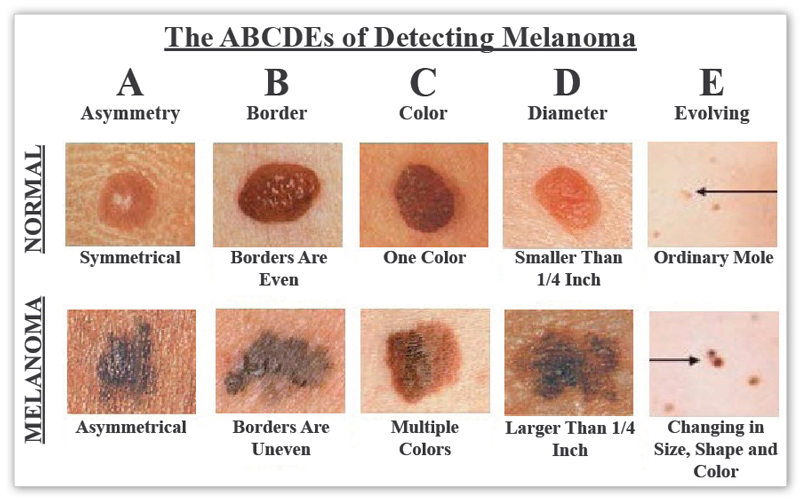
A new growth or any skin change, looking for the ABCDs of melanoma: Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Colour change, and a Diameter greater than 5mm. Most people have freckles, birthmarks, or moles, but any irregularities or a change in the shape, edge, colour or size can be warning signs of skin cancer if detected, see your doctor promptly:
Asymmetry
Common moles are round and symmetrical. Most early melanomas are asymmetrical. If a line divided through the middle of your mole doesnt create equal halves then ask your doctor to have a look.
Border irregularity
Common moles have fairly smooth and even borders. Most early melanomas have borders that are often uneven and may have rough edges.
Color change
Common moles usually are a single shade of brown. Varied shades of brown, tan or black are often the first sign of melanoma. As melanomas progress, the colors red, white and blue may appear.
Diameter > 5mm
Early melanomas tend to grow larger than common moles — generally to at least the size of a pencil eraser . Melanomas can be diagnosed at sizes much smaller than this – the smaller the melanoma when diagnosed, the better. Lesions under 7mm have a low risk of recurrence if removed.
The ABCD guide for the diagnosis of melanoma has been re-evaluated. New recommendations suggest adding E for describing pigmented skin lesions that suggest cancer.
Evolving
Surface
Sensation
Treatment Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
-
Removal of the tumor
Doctors may remove the cancer in the office by scraping and burning it with an electric needle or by cutting it out. Doctors may destroy the cancer by using extreme cold .
Certain chemotherapy drugs may be applied to the skin. Photodynamic therapy , in which chemicals and a laser are applied to the skin, also may be used. Occasionally, radiation therapy is used.
A technique called Mohs microscopically controlled surgery may be required for some basal cell carcinomas that are large or regrow or occur in certain areas, such as around the nose and eyes.
People whose cancer has spread to nearby tissues or spread to other parts of the body and who are not candidates for surgery or radiation therapy may be given the drug vismodegib or sonidegib taken by mouth.
You May Like: What Is Nodular And Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma
Breast Cancer Doubling Time
An easier way to envision how fast a breast cancer grows is by looking at the growth rate or volume doubling time. Tumor doubling time is the period of time that it takes for the tumor to double in size.
Since it would be unethical to leave a cancer untreated to see how rapidly it grew, doubling time is estimated in a number of ways. Looking at these estimates, however, doubling times have varied widely from study to study.
A 2019 study estimated doubling time by looking at serial ultrasounds between diagnosis and surgery. It was found that growth varied significantly based on the estrogen receptor status of the breast tumors.
During an average interval of 57 days, 36 percent of tumors did not change in size, while 64 percent grew. Of those tumors that increased in size, the average gain in volume was 34.5 percent.
Tumors that were triple negative had greater increases in volume and shorter doubling times than those that were estrogen receptor positive and HER2 negative tumors.
In a 2016 study that similarly looked at growth based on ultrasound between diagnosis and surgery over a 31 day period, tumors increased from 1.47 centimeters to 1.56 centimeters in diameter. Daily growth rate based on type was:
- 1.003 percent per day increase for triple negative tumors
- 0.859 percent per day increase for HER2 positive/estrogen receptor negative tumors
- 0.208 percent per day increase for estrogen receptor-positive tumors
Also Check: Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Hurt
Can Lung Cancer Become Skin Cancer
Skin lesions that arise from lung cancer may develop before the primary tumor is recognized and can be spread by the venous, arterial, or lymphatic system. The most common primary malignancies that metastasize to the skin are lung cancer in men and breast cancer in women.
Don’t Miss: What Is Braf Testing In Melanoma
Certain Factors Affect Prognosis And Treatment Options
The prognosis for squamous cell carcinoma of the skin depends mostly on the following:
- Stage of the cancer.
- Whether the patient is immunosuppressed.
- Whether the patient uses tobacco.
- The patient’s general health.
Treatment options for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin depend on the following:
- The type of cancer.
- The stage of the cancer, for squamous cell carcinoma.
- The size of the tumor and what part of the body it affects.
- The patients general health.
Stem Cell Or Bone Marrow Transplant
A stem cell transplant, sometimes called bone marrow transplant, replaces damaged blood-forming cells with healthy ones. The procedure takes place following large-dose chemotherapy or radiation therapy to kill cancer cells and to stop your stem cells from producing cancerous cells.
Stem cell transplants can be used for several types of cancer, including multiple myeloma and some kinds of leukemia.
Also Check: Cure For Melanoma Stage 4
Can Changing My Diet Help Prevent Melanoma
The American Cancer Society advocates eating a plant-based diet over an animal-based diet as part of a healthy plan to avoid all cancers. Growing evidence suggests that plants pack a powerful punch in any fight against cancer because they’re nutritious, cholesterol-free and fiber-rich.
Theres no doubt that a healthy diet can protect your immune system. Having a strong immune system is important to help your body fight disease. Some research has shown that a Mediterranean diet is a healthy choice that may help prevent the development of cancer. Talk to your healthcare provider about the role food plays in lowering your cancer risks.
Some skin and immune-system healthy foods to consider include:
- Daily tea drinking: The polyphenols in tea help strengthen your immune system. Green tea contains more polyphenols than black tea.
- High vegetable consumption: Eating carrots, cruciferous and leafy vegetables is linked to the prevention of cutaneous melanoma.
- Weekly fish intake: Study participants who ate fish weekly seemed to avoid developing the disease when compared to those who did not eat fish weekly.
How Does Skin Cancer Start
Raleigh Medical Group, P.A.General Posts, Skin Cancer, Skin Care
Would you risk your life for a good tan? It may sound absurd, but if you spend time sunbathing or in tanning beds, thats exactly what youre doing. Exposure to the suns ultraviolet rays puts you at risk for skin cancer, even if youre not trying to get bronzed.Half of Americans who live to be 65 will have skin cancer at least once, and 1 in 5 will develop it over the course of a lifetime. It is the most common type of cancer. The statistics are even more grim for those who started using a tanning bed before they turned 35.If you fall into this category, youve just increased your risk of melanoma, a serious form of skin cancer, by 75 percent.
Read Also: Osteomyoma
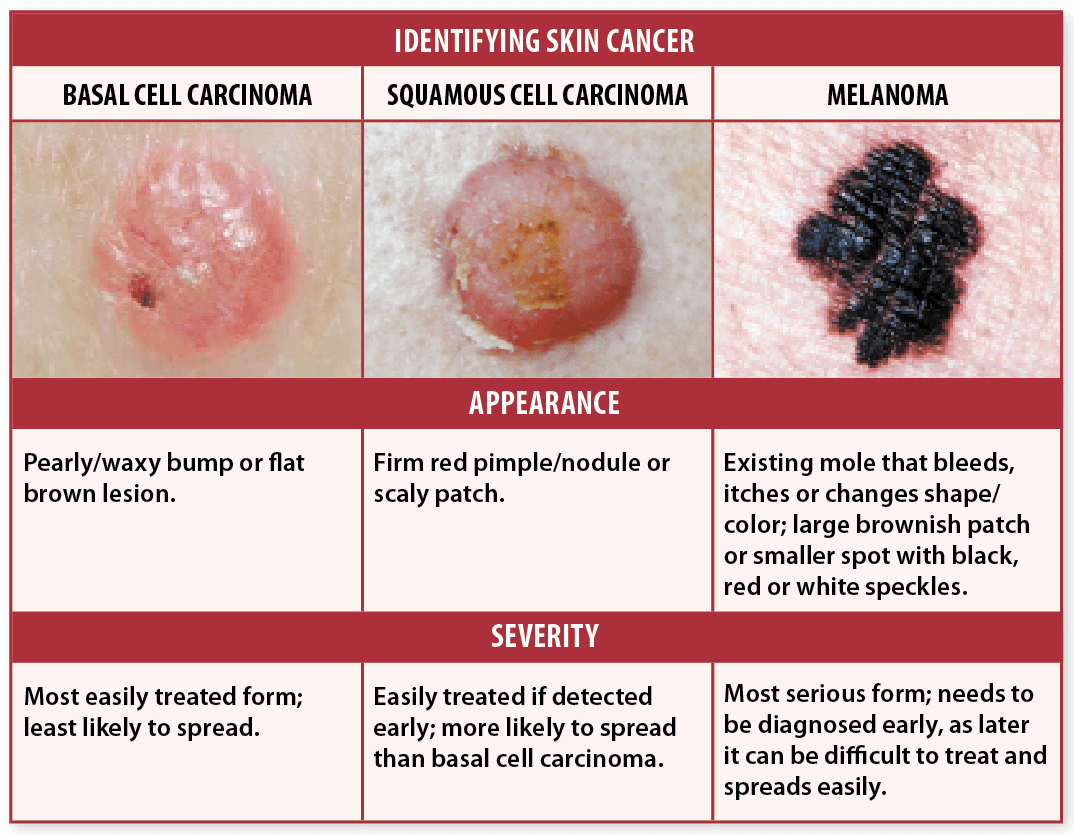
Different Kinds Of Skin Cancer
There are many types of skin cancer. Some are very rare. Your doctor can tell you more about the type you have.
The two most common kinds of skin cancers are:
- Basal cell cancer, which starts in the lowest layer of the skin
- Squamous cell cancer, which starts in the top layer of the skin
Another kind of skin cancer is called melanoma. These cancers start from the color-making cells of the skin . You can read about melanoma in If You Have Melanoma Skin Cancer.