What Is The Prognosis For Merkel Cell Carcinoma
You can see the cure rate for this type of skin cancer in the adjacent section. This is a rare and very dangerous form of skin cancer. Successful prognosis invariably involves early detection. Almost 80 percent of cases found early have good five-year success rates. But if the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes and to other parts of the body, the prognosis is not good.
Thats why its important for you to regularly check your own skin and have an understanding of the growths, freckles, and the like on it. If you dont see a dermatologist regularly, you need to do so. Find one and see them once a year.
Merkel Cell Carcinoma: Prompt Treatment Is Best
Your doctor may use the following tests to help determine whether the cancer has spread beyond your skin:
- Sentinel node biopsy. A sentinel node biopsy is a procedure to determine whether cancer has spread to your lymph nodes. This procedure involves injecting a dye near the cancer. The dye then flows through the lymphatic system to your lymph nodes.
The first lymph node that receives the dye is called the sentinel node. Your doctor removes this lymph node and looks for cancerous cells under a microscope.
- Imaging tests. Your doctor may recommend a chest X-ray and a CT scan of your chest and abdomen to help determine whether the cancer has spread to other organs.
Your doctor may also consider other imaging tests such as a positron emission tomography scan or an octreotide scan a test that uses an injection of a radioactive tracer to check for the spread of cancer cells.
Dr. Allison has his skin cancer patients schedule regular checkups so he can monitor them for signs of recurrence. There is a possibility of skin cancer reappearing for individuals who have been successfuly treated, but avoiding sun exposure can help minimizing the risk.
Learn more about Merkel Cell Carcinoma from cancer.gov.
Sunlight & Merkel Cell Carcinoma
It is believed that ultraviolet radiation from the sun plays a significant role in the development of MCC. MCC is most commonly found on sun-exposed areas of the body in older Caucasian individuals, who may also have other sun-induced skin cancers. There are more MCC cases in sunny climates as opposed to areas with less sun . While extensive sun exposure is a risk factor for MCC, MCC can also occur on sun-protected skin, such as a hair-covered scalp.
You May Like: How Fast Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
You May Like: Ductal Carcinoma Breast Cancer Survival Rates
Diagnosing And Treating Mcc
One of the issues faced by healthcare providers is that an MCC lesion may look like a cyst or swelling from an inflamed hair follicle. In a clinical study, 56% of Merkel cell carcinomas were initially thought to be benign by physicians. If you notice any new or changing lesions on your skinno matter how minortalk with your healthcare provider. It is important not to delay time to detection.
If your healthcare provider suspects that a lesion on your skin may be MCC, he or she will likely take a careful medical history and perform a physical exam. If your healthcare provider thinks you may have MCC, he or she will do a skin biopsy. That means removing the lesion and sending it to a lab where it will be viewed under a microscope to examine and confirm whether there are any cancerous cells.
Treatment of MCC is based on the stage of the disease and the overall health of the patient. The main treatments are surgery , radiation, and chemotherapy and other systemic therapies .
Research is underway to better understand this disease and to discover treatments. For more information about available clinical trials for Merkel cell carcinoma, go to clinicaltrials.gov or Pfizer: Find a Trial.
Learn more about sun safety
Exposure to the sun is one risk factor for MCC that we can control. We all need some sun exposure, and its important to engage in some physical activity outdoors, but too much sun can be harmful. Find out what you can do to stay healthy in the sun.
Related Hot Topics
How Does An Mcc Differ In Appearance From A Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Unlike a squamous cell carcinomasquamous cell carcinomaSquamous cell carcinoma is a cancer that begins in squamous cells, which are thin, flat cells. Squamous cells are located in the middle layers of the epidermis, the lining of portions of the respiratory and digestive tracts, and the lining of some organs. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma affects about 100,000 Americans and has a mortality of roughly 2%., MCCs are rarely scaly and are rarely ulcerated unless a biopsy has just been carried out.
Read Also: Skin Cancer Mayo
Immune Function & Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Patients with weakened immune systems are at significantly higher risk of developing MCC. Conditions associated with weakened immunity include HIV/AIDS, kidney or heart transplantation, and autoimmune diseases requiring medications that suppress the immune system, chronic lymphocytic leukemiachronic lymphocytic leukemiaA slow-growing type of leukemia associated with immune suppression. Patients with CLL have a markedly increased risk and severity of Merkel cell carcinoma. and certain types of lymphoma. The risk of developing MCC is 8 times greater in HIV patients, 10 times greater in organ transplant patients, and about 40 times greater in CLL.234 Long-term suppression of the immune system appears to be a risk factor for MCC in some patients. While patients with profound immune suppression are at a higher risk of developing MCC, over 90% of all people who develop MCC have no known immune deficiency.3
The immune system is also very important after diagnosis of MCC. Patients whose tumors show a robust immune response with certain immune cells present in their tumor tend to do better.5 MCC patients without a primary tumor also do better, likely because their immune system was able to eliminate the primary tumor and thus are more likely to be able to fight small amounts of MCC elsewhere in the body as well.6 In contrast, patients on medications that reduce immune function are at higher risk of having their MCC recur.
Can Merkel Cell Carcinoma Be Prevented
You cannot prevent MCC. You can reduce your likelihood of developing this condition â and any skin cancer â by protecting your skin from exposure to ultraviolet light. Protecting your skin from UV light may include:
- Limiting your exposure to sunlight
- Applying and reapplying appropriate sunscreen products while outside
- Wearing protective clothing while outside
- Avoiding tanning beds or sunlamps
You can also examine your skin regularly for any signs of change. If you notice any skin changes, see your doctor as soon as possible.
Recommended Reading: Immunotherapy For Malignant Melanoma
Treatment Of Recurrent Merkel Cell Carcinoma
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
- Radiation therapy and/or surgery as palliative treatment to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
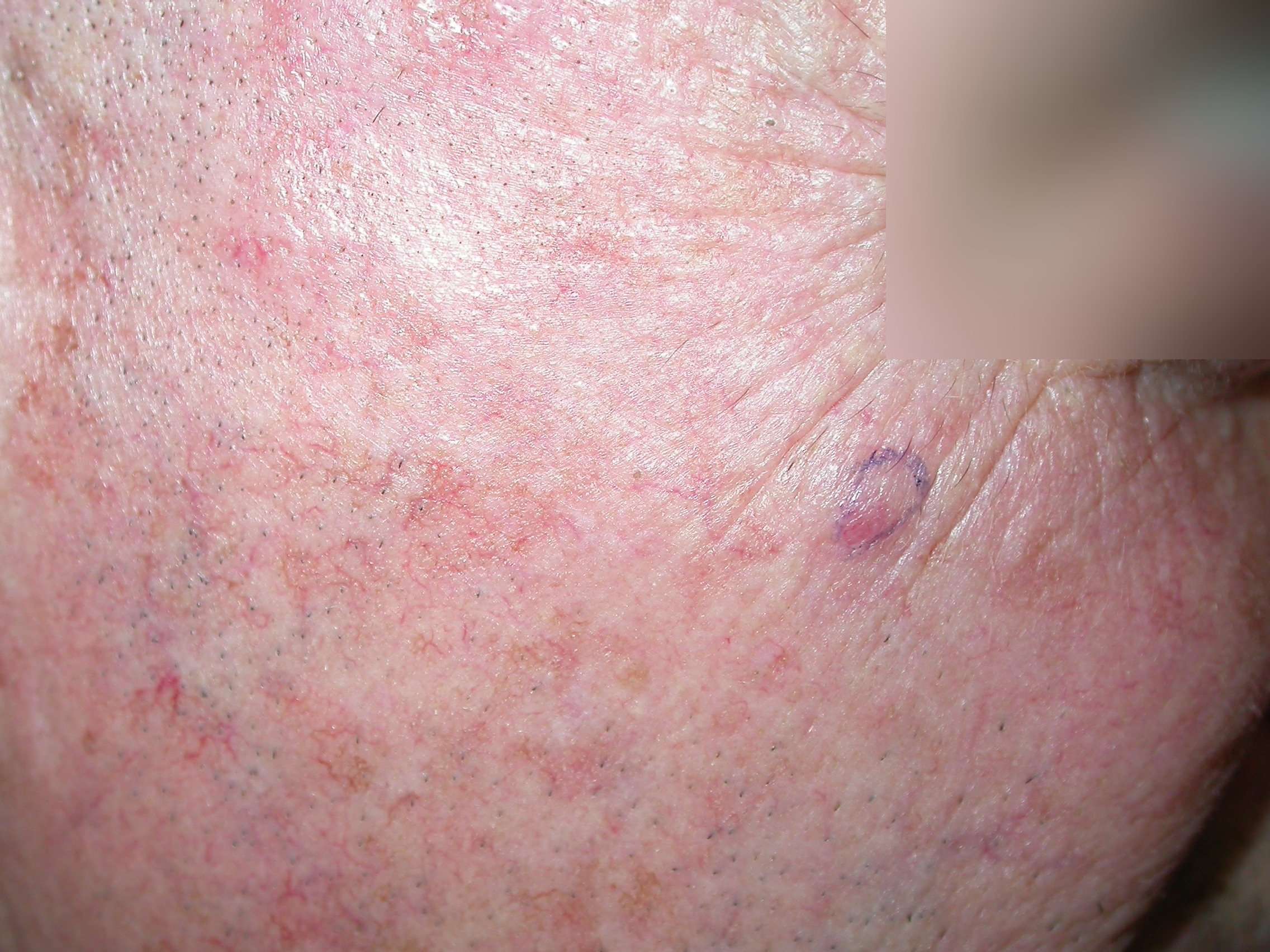
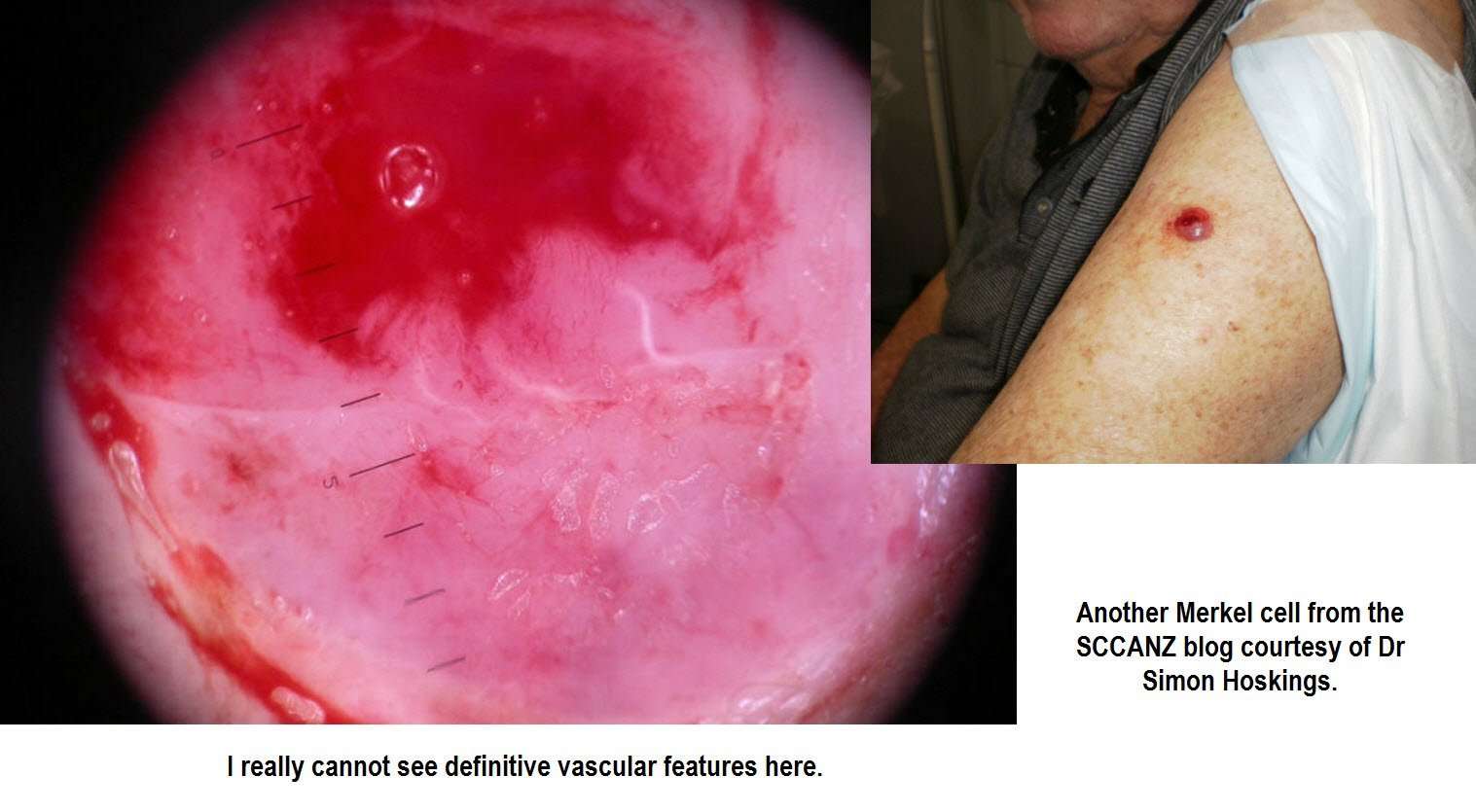
Appearance Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
MCC usually develops on sun-exposed skin as a painless, firm bump that can be red-purple or skin-colored. Patients frequently point out a new MCC to their doctor because a bump is growing rapidly and/or does not look like anything the patient has ever had before. Most MCCs are diagnosed when a skin biopsybiopsyThe removal of cells or tissue in order to determine the presence, characteristics, or extent of a disease by a pathologist usually using microscopic analysis. is performed to rule out another sun-induced skin cancercancerA term used to describe diseases in which abnormal cells continually divide without normal regulation. Cancerous cells may invade surrounding tissues and may spread to other regions of the body via blood and the lymphatic system. or to remove a presumed cyst. In the vast majority of cases, both the doctor and the patient are surprised by the diagnosis of MCC. For more examples of MCC tumors beyond those presented on this page, visit the Clinical Photos page.
Recommended Reading: Metastatic Melanoma Cancer Life Expectancy
What Is The Outlook For Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Merkel call carcinoma is uncommon, so its difficult to estimate an accurate survival rate. The survival rate tells you what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive after a defined period of time after diagnosis.
According to the , the overall five-year survival rate for MCC is about 60 percent. This means that about 60 percent of people diagnosed with MCC will still be alive after five years.
Your outlook depends on how early the cancer is diagnosed. The following are based on stages 1 through 4 of diagnosis:
- stage 1A: 80 percent
What Are The First Symptoms Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma & How Do You Test For It
Merkel cell carcinoma is rare skin cancers that can metastasize to distant organs. It usually affects old people. Constant exposure to the sun and weak immune system can cause this cancer. It develops as a single red or purple lump on the skin. It is a rapidly growing cancer. It appears mainly on sun-exposed areas. It can be detected with a skin biopsy, X-ray, MRI scan, CT scan and others. It can be treated with surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
Recommended Reading: Stage Iii Melanoma Treatment
Merkel Cell Carcinoma Usually Appears As A Single Painless Lump On Sun
This and other changes in the skin may be caused by Merkel cell carcinoma or by other conditions. Check with your doctor if you see changes in your skin.
Merkel cell carcinoma usually appears on sun-exposed skin as a single lump that is:
- Fast-growing.
- Firm and dome-shaped or raised.
- Red or violet in color.
Causes And Risk Factors: Who Gets Merkel Cell Carcinoma

Its not fully understood what causes MCC, but researchers recently discovered that a common virus, called the Merkel cell polyomavirus , plays a role in many cases. 37219-5/fulltext” rel=”nofollow”> 5)
MCP lives on the skin of most people without any signs or symptoms and without ever developing into MCC. Just how this virus triggers a dangerous skin cancer in some people and not others has yet to be determined, but researchers have identified a number of factors that markedly increase your risk.
These include:
- Excessive exposure to UV light Chronic exposure to light from the sun or tanning beds damages the DNA of genes that control skin-cell growth. This puts you at risk of all skin cancers and MCC is no exception. The vast majority of MCCs appear on skin surfaces that are frequently exposed to the sun.
- Older age Though MCC can occur at any age, your risk significantly increases as you get older. More than half of MCC patients are over the age of 65 years at the time of diagnosis. The average age of diagnosis is 74.
- A weakened immune system If your immune system is suppressed , you are about 15 times more likely to develop MCC than people with healthy immune function.
- Light skin color More than 9 out of 10 cases of MCC in the United States are diagnosed in whites.
RELATED: Cancer Risk Genes: Everything You Need to Know About ATM
Read Also: Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Who Is Likely To Have Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Anyone can develop MCC. You are at higher risk of developing this type of cancer if you:
- Have lighter-colored skin
- Have a weakened immune system
- Use tanning beds or ultraviolet light therapy for psoriasis
- Have another type of cancer, especially another type of skin cancer
The incidence of MCC in the US is about 0.6 per 100,000 people per year. This is up about 4X since 1986. However, it must be noted that diagnosis has improved, the population is getting older, and immunosuppressant medications are rising. It is estimated that about 700 people with MCC die per year. The rate of death is about one in three. Melanoma, also a dangerous cancer, is said to kill about one in nine people per year.
Sun Exposure And Having A Weak Immune System Can Affect The Risk Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Anything that increases your risk of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer not having risk factors doesn’t mean that you will not get cancer. Talk with your doctor if you think you may be at risk. Risk factors for Merkel cell carcinoma include the following:
- Being exposed to a lot of natural sunlight.
- Having an immune system weakened by disease, such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia or HIVinfection.
- Taking drugs that make the immune system less active, such as after an organ transplant.
- Having a history of other types of cancer.
- Being older than 50 years, male, or White.
You May Like: Prognosis For Skin Cancer
How Do You Test For Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma is detected by some procedures and tests. Your physician will perform a physical examination of the skin by closely examining the unusual moles, freckles, pigmented spots, and other skin ailments. He will remove the tumor cells to send it to the laboratory to find out any signs of cancer. This process is called a skin biopsy. He will also order you some tests such as sentinel node biopsy and imaging tests. Sentinel node biopsy helps to know whether the lymph nodes are also involved. In this process, a dye is injected into the lymph nodes near cancer and your doctor removes these lymph nodes and cancerous cells are observed for microscopic study.
Imaging tests such as MRI scans, CT scans, and X-rays are also advised to know the spread of cancer. In some cases, PET is advised to evaluate the spread of the cancer cells.
When Should I See A Doctor
- You should see your doctor if you have any new or changing marks on your skin. Be aware of any lumps, growths, moles, or other abnormal areas on your skin. Watch for new spots or areas that are changing. This can include skin marks that grow larger, bleed, crust, or itch.
- Early diagnosis and treatment is important to prevent the cancer from spreading. Your healthcare provider may recommend you do a skin self-exam once a month or more.
Also Check: Lobular Carcinoma Survival Rate
How Is Merkel Cell Cancer Treated
Your treatment choices depend on the number of Merkel cell cancer tumors, test results, and the stage of the cancer. The goal of treatment may be to cure you, control the cancer, or to help ease problems caused by cancer. Talk with your healthcare team about your treatment choices, the goals of treatment, and what the risks and side effects may be.
Types of treatment for cancer are either local or systemic. Local treatments remove, destroy, or control cancer cells in one area. Surgery and radiation are local treatments. Systemic treatment is used to destroy or control cancer cells that may have traveled around your body. When taken by pill or injection, chemotherapy and targeted therapy are systemic treatments. You may have just one type of treatment or a combination of treatments.
Sometimes more than 1 type of treatment is used. Treatment may include:
Talk with your healthcare providers about your treatment options. Make a list of questions. Think about the benefits and possible side effects of each option. Some treatments may affect your ability to have children in the future. Talk about your concerns with your healthcare provider before making a decision.
Treatment Of Stage Iii Merkel Cell Carcinoma
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
- A clinical trial of chemotherapy.
- A clinical trial of immunotherapy .
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Recommended Reading: What Is Large Cell Carcinoma
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Mcc
MCC usually appears as a single, painless bump on the skin. These bumps are called lesions. The most common site for MCC to occur is the head and neck, followed by the arms and legs. The lesion is typically red/pink, although blue/purple is also common. MCC lesions vary in size but when the cancer is found, they are on average about 17 mm .
Patients Can Enter Clinical Trials Before During Or After Starting Their Cancer Treatment
Some clinical trials only include patients who have not yet received treatment. Other trials test treatments for patients whose cancer has not gotten better. There are also clinical trials that test new ways to stop cancer from recurring or reduce the side effects of cancer treatment.
Clinical trials are taking place in many parts of the country. Information about clinical trials supported by NCI can be found on NCIs clinical trials search webpage. Clinical trials supported by other organizations can be found on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
Read Also: What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Head And Neck
Stanford Expertise In Merkel Cell Carcinoma
The multispecialty Merkel Cell Carcinoma Program at Stanford provides a comprehensive treatment approach for patients with MCC and is investigating novel targeted-and immunotherapies to treat patients with advanced disease.
For this reason, the Stanford Merkel Cell Carcinoma Program offers a multispecialty approach to the treatment of MCC, utilizing the expertise of Stanford surgeons for wide local excision and sentinel lymph node biopsy staging.