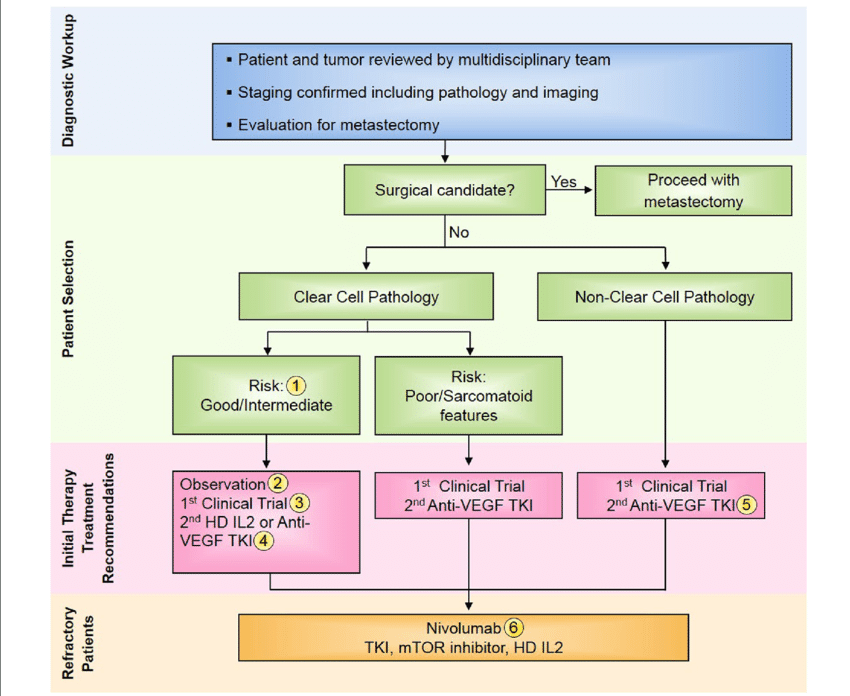
How Is The Treatment Done
Renal Cell Carcinoma is the most common type of kidney cancer, usually seen among adults. It occurs in the lining of proximal convoluted tubule which channelizes primary urine. The factors responsible for causing RCC are not clearly known, but the common symptoms include: blood in the urine, lump in the abdomen, drastic weight loss and fatigue, loss of appetite, vision problem, and abnormal hair growth.
If diagnosed with the above mentioned symptoms, the doctor would perform a few tests and physical examination in order to confirm RCC. The blood sample is sent for lab testing a CT scan is performed to examine any unusual growth in your kidney ultrasound waves are used to detect any sign of tumor in your kidney urine test is conducted to detect blood in the urine which shows evidence of cancer cells a biopsy is performed by eliminating a small portion of kidney tissue and the sample is sent for testing in order to confirm cancer.
The standard procedures for treating RCC include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, biologic therapy, targeted therapy, and clinical trials.
What Is The Treatment For Renal Cell Carcinoma
Treatment for renal cell carcinoma may involve local and/or systemic therapies.
Local therapies treat the tumor without affecting the rest of the body. These treatments are often used for earlier stage cancers and may include:
- Active surveillance
- Some small kidney tumors are benign and about 75% of small kidney cancers are slow growing
- This approach involves no treatment and watching the tumor carefully with imaging tests every 3 to 6 months to see if it grows
- Often used for elderly or frail patients to avoid the risks of treatment
Systemic treatments are medications taken orally or injected directly into the bloodstream that can reach cancer cells almost anywhere in the body. Depending on the type of kidney cancer, a number of different types of drugs might be used, such as:
- Targeted drug therapy
Renal Cell Carcinoma Staging
Doctors who diagnose and treat RCC and other types of cancer use a staging system. Each person with RCC is given a number designation ranging from 1 to 4. Stage 1 is the earliest stage of the disease and stage 4 is the latest and most advanced.
Staging for RCC is based on:
- size of the primary tumor in the kidney
- spread of cancerous cells from the primary tumor to nearby tissues
- degree of metastasis
- spread of the cancer to other organs in the body
Stage 4 RCC can include different combinations of staging criteria:
- When the primary tumor is large and has spread throughout the kidney and into nearby tissues. In this instance, the cancer cells may or may not have spread into other organs in the body.
- When the cancer has metastasized and is present in distant organs. In this case, the primary tumor may be of any size, and there may or may not be any cancer in the tissues immediately surrounding the kidney.
Also Check: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Overview Of The Market
Therapeutic options for advanced or mRCC have expanded significantly since the approval of the first VEGFR-targeted therapy sorafenib in 2005 and continue to grow. First-line treatment options for metastatic or surgically unresectable locally advanced disease include VEGFR-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors sunitinib or pazopanib , cabozantinib targeting VEGFR as well as the receptor tyrosine kinases MET and AXL, cytokine-based immunotherapy in the form of high-dose interleukin-2, combination bevacizumab plus interferon alpha, the mTOR inhibitor temsirolimus, and most recently the combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab. In addition, patients with disease refractory to first-line agents may receive single-agent nivolumab, axitinib, lenvatinib plus everolimus , everolimus monotherapy, or most of the aforementioned first-line treatment options.
The randomized phase III studies in RCC have largely focused on patients with clear cell histology disease and excluded non-clear cell RCC. Because non-clear cell RCC typically carries a poorer prognosis compared to clear cell RCC, clinical trial enrollment is recommended. For non-clear cell mRCC patients who are not enrolled in a clinical study, the treatment approach is generally similar to those with clear cell histology.
Drugs That Target The Mtor Protein
Temsirolimus
Temsirolimus works by blocking a protein known as mTOR, which normally helps cells grow and divide. This drug has been shown to be helpful against advanced kidney cancers that have a poorer prognosis because of certain factors and may help some people live longer. It is given as an intravenous infusion, typically once a week.
The most common side effects of this drug include skin rash, weakness, mouth sores, nausea, loss of appetite, fluid buildup in the face or legs, and increases in blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Rarely, more serious side effects have been reported.
Everolimus
Everolimus also blocks the mTOR protein. It is used to treat advanced kidney cancers after other drugs such as sorafenib or sunitinib have been tried. It can be used by itself or along with lenvatinib after at least one other treatment has been tried. Everolimus is taken as a pill once a day.
Common side effects of this drug include mouth sores, an increased risk of infections, nausea, loss of appetite, diarrhea, skin rash, feeling tired or weak, fluid buildup , and increases in blood sugar and cholesterol levels. A less common but serious side effect is lung damage, which can cause shortness of breath or other problems.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Remission And The Chance Of Recurrence
A remission is when cancer cannot be detected in the body and there are no symptoms. This may also be called having no evidence of disease or NED.
A remission may be temporary or permanent. This uncertainty causes many people to worry that the cancer will come back. While many remissions are permanent, it is important to talk with your doctor about the possibility of the cancer returning. Understanding your risk of recurrence and the treatment options may help you feel more prepared if the cancer does return. Learn more about coping with the fear of recurrence.
If the cancer returns after the original treatment, it is called recurrent cancer. It may come back in the same place , nearby , or in another place . If you have had a partial nephrectomy already, a new tumor may form in the same kidney. The recurrent tumor can be removed with another partial nephrectomy or with a radical nephrectomy .
People with recurrent cancer often experience emotions such as disbelief or fear. You are encouraged to talk with the health care team about these feelings and ask about support services to help you cope. Learn more about dealing with cancer recurrence.
Who Is Eligible For The Treatment
Depending on the cause and seriousness of the condition, RCC can be treated in the following ways: Surgery- depending on how far the cancer has spread, partial removal or complete removal of your kidney may be necessary. In case of a life-threatening situation radical nephrectomy is performed wherein the surrounding tissue, lymph nodes and the adrenal gland is removed. Dialysis or transplant is inevitable in certain cases where both the kidneys need to be removed. Radiation- high-energy X-rays are given either through a machine or by using internal seeds and wires which help to kill the cancer cells. Chemotherapy- the drugs given during chemotherapy channelizes through your bloodstream and helps to destroy the cancer cells which may have spread to other parts or organs of your body. They can be given either orally or intravenously. Biologic therapy- this refers to the process where the enzymes or substances present in your body fight the cancer cells. Targeted therapy- drugs are used to target specific cancer cells without causing damage to the healthy cells. For instance, certain drugs stop the flow of blood from blood vessels to the tumor.
Read Also: What Stage Is Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
After Renal Cell Cancer Has Been Diagnosed Tests Are Done To Find Out If Cancer Cells Have Spread Within The Kidney Or To Other Parts Of The Body
The process used to find out if cancer has spread within the kidney or to otherparts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from thestaging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to knowthe stage in order to plan treatment. The following tests andprocedures may be used in the staging process:
- CT scan : A procedure that makes a series of detailed pictures of areas inside the body, such as the chest or brain, taken from different angles. The pictures are made by a computer linked to an x-ray machine. A dye may be injected into a vein or swallowed to help the organs or tissues show up more clearly. This procedure is also called computed tomography, computerized tomography, or computerized axial tomography.
- MRI : A procedure that uses a magnet, radio waves, and a computer to make a series of detailed pictures of areas inside the body, such as the brain. This procedure is also called nuclear magnetic resonance imaging .
- Chest x-ray: An x-ray of the organs and bones inside the chest. An x-ray is a type of energy beam that can go through the body and onto film, making a picture of areas inside the body.
- Bone scan: A procedure to check if there are rapidly dividing cells, such as cancer cells, in the bone. A very small amount of radioactive material is injected into a vein and travels through the bloodstream. The radioactive material collects in the bones with cancer and is detected by a scanner.
Stage Information For Renal Cell Cancer
The staging system for renal cell cancer is based on the degree of tumor spreadbeyond the kidney. Involvement of blood vessels may not be a poorprognostic sign if the tumor is otherwise confined to the substance of thekidney. Abnormal liver function test results may be caused by a paraneoplasticsyndrome that is reversible with tumor removal, and these types of results do not necessarily representmetastatic disease. Except when computed tomography examination isequivocal or when iodinated contrast material is contraindicated, CT scanningis as good as or better than magnetic resonance imaging for detectingrenal masses.
Also Check: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
What Is Kidney Cancer
Kidney cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the kidney. The most common type of kidney cancer is renal cell carcinoma , accounting for about 90% of all cases. Usually only one kidney is affected, but in rare cases the cancer may develop in both kidneys.
Other less common types include:
- Uroethelial carcinoma which can begin in the ureter or renal pelvis where the kidney and ureter meet. It is generally treated like bladder cancer.
- Wilms tumour, which is most common in younger children although it is still rare.
It is estimated that 4377 people in Australia will be diagnosed with kidney cancer in 2021. Kidney cancer is more common in men – the risk of being diagnosed by age 85 is 1 in 47 for men compared to 1 in 100 for women.
The five year survival rate for kidney cancer is 79%.
How Renal Cell Carcinoma Spreads
Renal cell carcinoma can spread from the kidney to other areas of the body. It can enlarge within the kidney and grow into the adrenal glands, which are adjacent to the kidneys. Adrenal glands are small organs that make and release hormones. Each kidney has one adrenal gland located right above it.
Cancer cells can also enter into the bloodstream or the lymphatic vessels, spreading to other areas of the body. The cancer can then grow in other organs, such as the lungs, bones, or brain, causing serious harm to these areas.
Read Also: Treatment For Stage 3 Melanoma
Patients May Want To Think About Taking Part In A Clinical Trial
For some patients, taking part in a clinical trial may be the best treatment choice. Clinical trials are part of the cancer research process. Clinical trials are done to find out if new cancer treatments are safe and effective or better than the standard treatment.
Many of today’s standard treatments for cancer are based on earlier clinical trials. Patients who take part in a clinical trial may receive the standard treatment or be among the first to receive a new treatment.
Patients who take part in clinical trials also help improve the way cancer will be treated in the future. Even when clinical trials do not lead to effective new treatments, they often answer important questions and help move research forward.
Combined Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors And Antiangiogenic Targeted Therapies
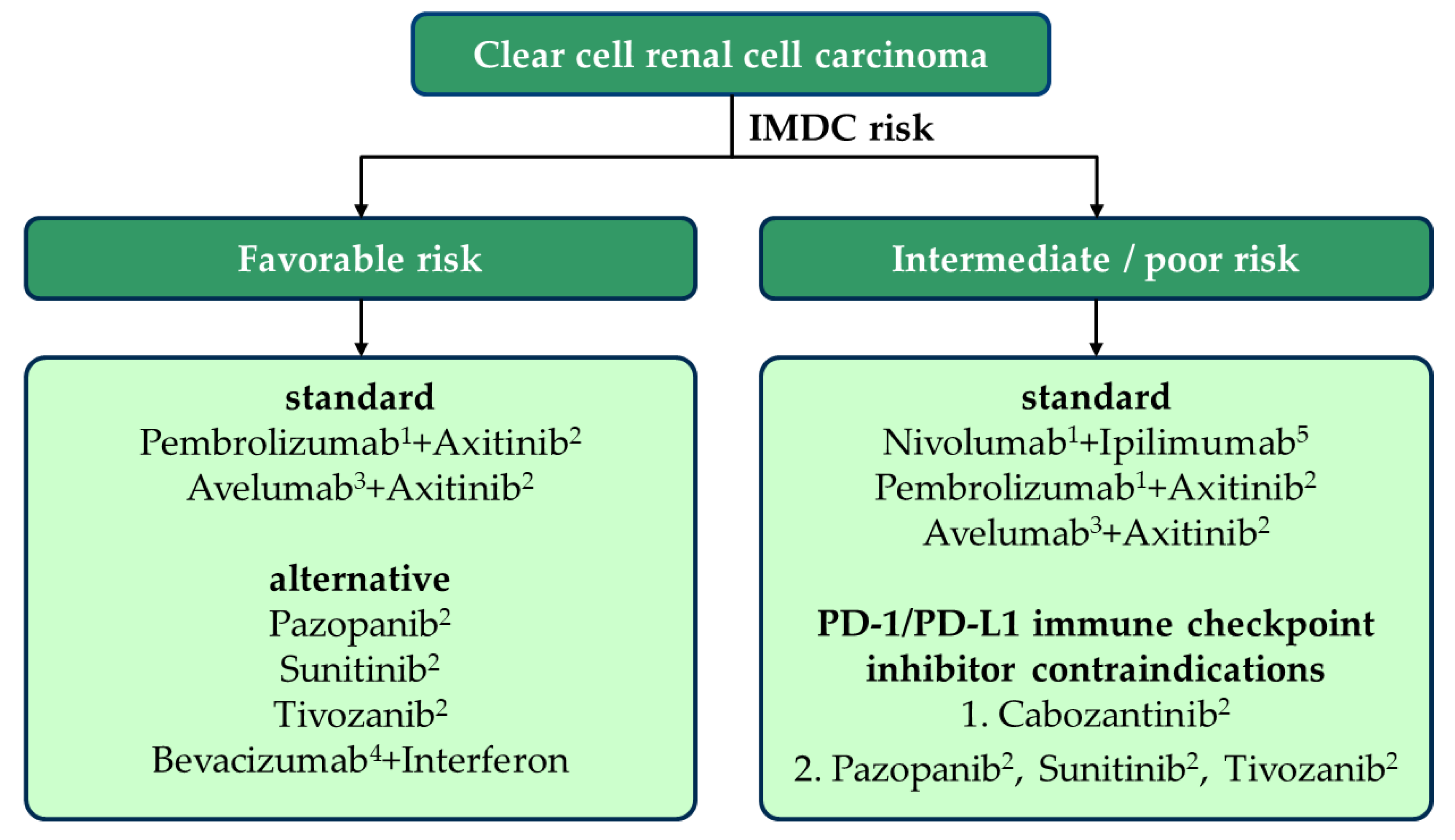
After immune checkpoint inhibitors and antiangiogenic targeted therapies were found to improve outcomes, the combination of these two approaches has been studied in clinical trials and shown to result in longer OS when compared with monotherapy.
Pembrolizumab plus axitinib
Evidence :
Avelumab plus axitinib
Evidence :
You May Like: Carcinoma Cancer Symptoms
We Service What We Sell
My dealership is proud to carry STIHL outdoor power equipment. As you can see from this guide, we offer a wide range of STIHL power tools.
STIHL products are designed to meet uncompromising standards of quality and durability. When you shop at my dealership you get great prices, expert product advice and the best customer service in the business. Best of all, you get STIHL quality at a price much less than you would expect. That’s why STIHL is the Number One Selling Brand in Canada*.
Thank you for your business, Glen Hall
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Renal Cell Carcinoma
Renal cell carcinoma is often asymptomatic in most people until it has reached an advanced stage.
In just 10 percent of the cases, this cancer may present in its typical form that consists of the following:
- Flank pain
- A mass in the flank or abdomen
Hematuria may not always be visible to the naked eye . In most cases, the blood cells are seen in urine on microscopic examination . Some people may pass blood clots in urine.
Other signs and symptoms of RCC include:
Read Also: Stage Iii Melanoma Treatment
Treatment Of Stage Iv And Recurrent Renal Cell Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
- Surgery .
- Surgery to reduce the size of the tumor.
- Radiation therapy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve the quality of life.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Cellular Classification Of Renal Cell Cancer
Approximately 85% of renal cell cancers are adenocarcinomas, and most of those are of proximal tubular origin. Most of the remainder are transitional cellcarcinomas of the renal pelvis. Adenocarcinomas may be separated into clear cell and granular cell carcinomas however, the two cell types may occur together in some tumors. Someinvestigators have found that granular cell tumors have a worse prognosis, butthis finding is not universal. Distinguishing between well-differentiatedrenal adenocarcinomas and renal adenomas can be difficult. The diagnosis isusually made arbitrarily on the basis of the size of the mass, but size aloneshould not influence the treatment approach, because metastases can occur withlesions as small as 0.5 centimeter.
Also Check: How Do You Die From Melanoma
Stage Ii Renal Cell Cancer Treatment
Stage II renal cell cancer is defined by the American Joint Committee on Cancer’s TNM classification system:
- T2, N0, M0
Radical resection is the accepted, often curative, therapy for stage II renalcell cancer. The operation includes removal ofthe kidney, adrenal gland, perirenal fat, and Gerota’s fascia, with or withouta regional lymph node dissection. Lymphadenectomy is commonly employed, butits effectiveness has not been definitively proven. External-beam radiation therapy has been given before or after nephrectomy without conclusive evidence thatthis improves survival when compared with the results of surgery alone however, it may be ofbenefit in selected patients with more extensive tumors.
In patients who arenot candidates for surgery, arterial embolization can provide palliation.
Standard treatment options:
Who Is Not Eligible For The Treatment
Renal Cell Carcinoma is a common kidney cancer normally seen among adults. This disease is more common in men aging between 50-70 years than in women. Anybody showing symptoms of weight loss, fatigue, loss of appetite, pain or lump in the abdomen, blood in the urine etc, or those who have a medical history of kidney stones or cancer are eligible for the treatment.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Prognosis For Skin Cancer