Symptoms If Cancer Has Spread To The Bone
You might have any of the following symptoms if your cancer has spread to the bones:
- pain from breakdown of the bone the pain is continuous and people often describe it as gnawing
- backache, which gets worse despite resting
- weaker bones they can break more easily
- raised blood calcium , which can cause dehydration, confusion, sickness, tummy pain and constipation
- low levels of blood cells blood cells are made in the bone marrow and can be crowded out by the cancer cells, causing anaemia, increased risk of infection, bruising and bleeding
Cancer in the spinal bones can cause pressure on the spinal cord. If it isn’t treated, it can lead to weakness in your legs, numbness, paralysis and loss of bladder and bowel control . This is called spinal cord compression. It is an emergency so if you have these symptoms, you need to contact your cancer specialist straight away or go to the accident and emergency department.
Bone And Calcium Problems
Myeloma cells also interfere with cells that help keep bones strong. Bones are constantly being remade to keep them strong. Two kinds of bone cells work together to keep bones healthy and strong:
- Osteoclasts break down old bone
- Osteoblasts lay down new bone
Myeloma cells make a substance that tells the osteoclasts to speed up dissolving the bone. So old bone is broken down without new bone to replace it, making the bones weak and easy to break. Fractured bones are a major problem in people with myeloma. This increase in bone break-down can also raise calcium levels in the blood. Problems caused by high calcium levels are discussed in Signs and Symptoms of Multiple Myeloma.
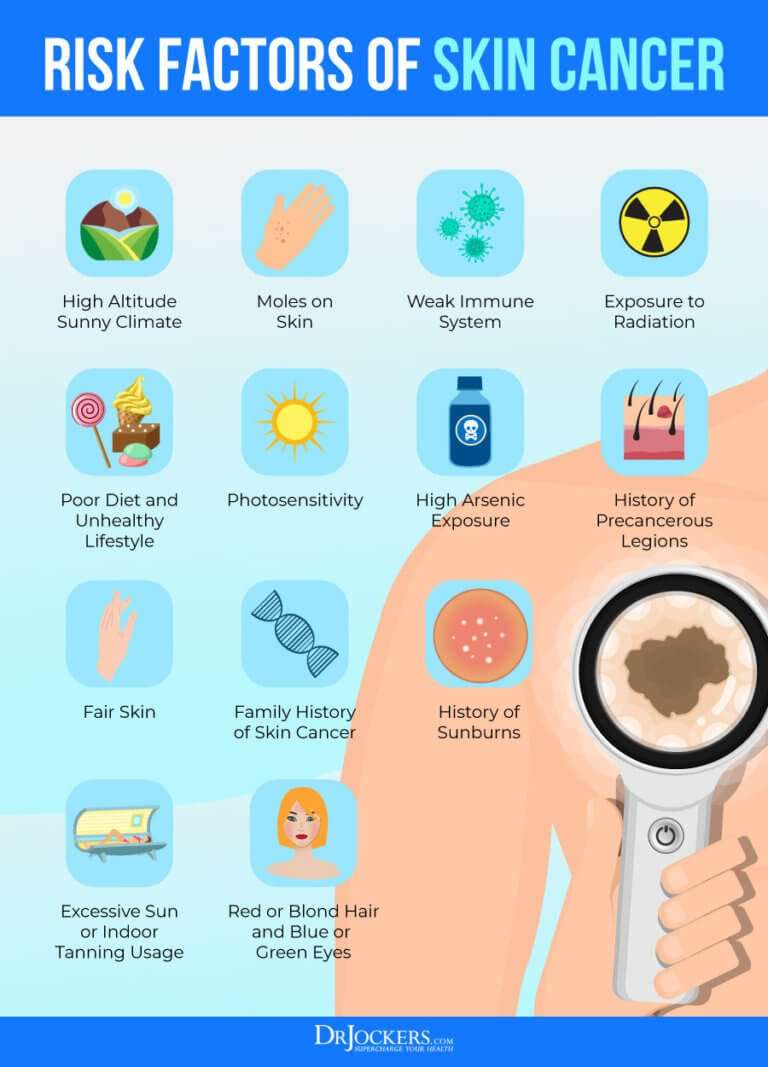
What Causes Melanoma Skin Cancer
Many risk factors for melanoma have been found, but its not always clear exactly how they might cause cancer.
For example, while most moles never turn into a melanoma, some do. Researchers have found some gene changes inside mole cells that may cause them to become melanoma cells. But its still not known exactly why some moles become cancerous while most dont.
DNA is the chemical in each of our cells that makes up our genes, which control how our cells function. We usually look like our parents because they are the source of our DNA. But DNA affects more than just how we look.
Some genes control when our cells grow, divide into new cells, and die:
- Genes that help cells grow, divide, and stay alive are called oncogenes.
- Genes that keep cell growth in check, repair mistakes in DNA, or cause cells to die at the right time are called tumor suppressor genes.
Cancers can be caused by DNA mutations that keep oncogenes turned on, or that turn off tumor suppressor genes. These types of gene changes can lead to cells growing out of control. Changes in several different genes are usually needed for a cell to become a cancer cell.
Also Check: How To Check For Melanoma
What Are The Symptoms Of Melanoma Of The Head And Neck
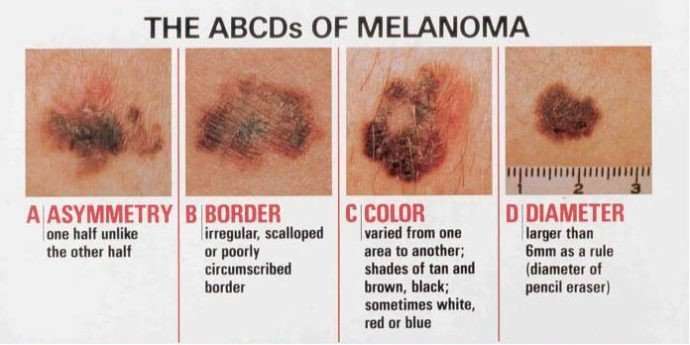
Melanomas usually present as an abnormal mole or growth on the skin. Many people have normal moles that are small, even, tan or brown in color, round or oval, and either flat or raised. Melanoma arises from abnormal melanocytes, or pigment cells, that become cancerous. These are usually brown or black in color because of melanin production by melanocytes. Any change in size of a mole, or the appearance of a new mole, should be evaluated for the ABCDE rule:
- A=Asymmetry: The appearance or shape of one half of the mole does not match the other side.
- B=Border irregularity: The mole has irregular or uneven borders, particularly if they are ragged or notched.
- C=Color variation: Variation in color throughout the lesion, with patches of different shades of brown or tan in a mole, is concerning.
- D=Diameter: Lesions that are larger than ¼ inch, or the size of a pencil eraser, may represent melanoma however, melanomas can be smaller than this.
- E=Evolving: A lesion that changes in size, color, shape or texture is suspicious for melanoma.
Melanomas may also have the appearance of a wart, crusty spot, ulcer, mole or sore. It may or may not bleed or be painful. If you have a preexisting mole, any change in the characteristics of this spot such as a raised or irregular border, irregular shape, change in color, increase in size, itching or bleeding is a warning sign of melanoma. Sometimes the first sign of head and neck melanoma is an enlarged lymph node in the neck.
New Types Of Treatment Are Being Tested In Clinical Trials
This summary section describes treatments that are being studied in clinical trials. It may not mention every new treatment being studied. Information about clinical trials is available from the NCI website.
Vaccine therapy
Vaccine therapy is a cancer treatment that uses a substance or group of substances to stimulate the immune system to find the tumor and kill it. Vaccine therapy is being studied in the treatment of stage III melanoma that can be removed by surgery.
You May Like: Are There Different Types Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
What Is Multiple Myeloma What Are Plasma Cells
Multiple myeloma definition
Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer of the plasma cells of the bone marrow. Plasma cells are protein-making cells that normally produce the different kinds of antibodies of the disease-fighting immune system. In multiple myeloma, the plasma cells undergo a malignant transformation and become cancerous. These myeloma cells stop making different forms of protein in response to the immune systems needs and instead start to produce a single abnormal type of protein sometimes termed a monoclonal or M protein. Multiple myeloma plasma cell populations accumulate in the bone marrow, and these collections of cells called plasmacytomas can erode the hard outer shell or cortex of the bone that normally surrounds the marrow. These weakened bones show thinning of the bone, as seen in nonmalignant osteoporosis or what appear to be punched out or lytic bone lesions. These lesions may cause pain and even breaks or fractures of the weakened bones. They may cause other systemic problems listed below. People often refer to multiple myeloma simply as myeloma . The disease usually occurs in people past middle age. However, rarely it can occur in a child.
You May Like: What Does Clear Cell Carcinoma Mean
Benign Tumors That Develop From Other Types Of Skin Cells
- Seborrheic keratoses: tan, brown, or black raised spots with a waxy texture
- Hemangiomas: benign blood vessel growths, often called strawberry spots
- Lipomas: soft growths made up of fat cells
- Warts: rough-surfaced growths caused by some types of human papilloma virus
Most of these tumors rarely, if ever, turn into cancers. There are many other kinds of benign skin tumors, but most are not very common.
Read Also: What Causes Clear Cell Renal Carcinoma
Melanoma Symptoms And Signs
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that forms in pigment-forming cells . Melanoma is the most serious type of skin cancer. Rarely, melanomas can be found in other areas of the body that contain pigment-forming cells, including the eye, the tissues around the brain and spinal cord, or the digestive tract. Melanomas of the skin produce changes in the appearance of the skin, but these changes can sometimes be seen with other skin conditions. The characteristic symptoms include a change in an existing mole or new mole with asymmetric borders, uneven coloring, increasing size, scaling, or itching. Melanomas are typically not painful. It is always important to seek medical advice when you develop a new pigmented spot on the skin or have a mole that is growing or changing.
Where Do Skin Cancers Start
Most skin cancers start in the top layer of skin, called the epidermis. There are 3 main types of cells in this layer:
- Squamous cells: These are flat cells in the upper part of the epidermis, which are constantly shed as new ones form.
- Basal cells: These cells are in the lower part of the epidermis, called the basal cell layer. These cells constantly divide to form new cells to replace the squamous cells that wear off the skins surface. As these cells move up in the epidermis, they get flatter, eventually becoming squamous cells.
- Melanocytes: These are the cells that can become melanoma. They normally make a brown pigment called melanin, which gives the skin its tan or brown color. Melanin protects the deeper layers of the skin from some of the harmful effects of the sun.
The epidermis is separated from the deeper layers of skin by the basement membrane. When a skin cancer becomes more advanced, it generally grows through this barrier and into the deeper layers.
Recommended Reading: What Is Infiltrative Basal Cell Carcinoma
Heredity And Multiple Myeloma
The majority of people with multiple myeloma do not have a family history of the disease. Inherited genetic variations could increase a persons chance of developing the disease. According to the American Cancer Society, multiple myeloma is more than twice as common for African Americans than white Americans but its not clear why.
The overall chance of contracting the condition is very low. Its likely that other factors, such as environmental exposures, can also play a role.
What Are The Stages Of Multiple Myeloma
There are four stages of multiple myeloma. While many health care professionals use different staging, these are various stages cited by many clinicians:
- Smoldering: multiple myeloma with no symptoms
- Stage I: early disease with little anemia, relatively small amount of M protein and no bone damage
- Stage II: more anemia and M protein as well as bone damage
- Stage III: still more M protein, anemia, as well as signs of kidney damage
Because staging criteria differ according to different medical groups, some clinicians simply define the individuals multiple myeloma without assigning a stage and simply estimate a prognosis for their patient. In 2013, an international group divided stages into three stages based on two criteria, the concentration of beta-2-microglobulin and serum albumin levels over time, these defined criteria may become widely accepted.
However, each individual is unique and may do better or worse than the prediction based on the various stages.
Also Check: What Are The Kinds Of Skin Cancer
What Are The Four Main Types Of Melanoma Of The Skin
Superficial spreading melanoma
What you should know: This is the most common form of melanoma.
How and where it grows: It can arise in an existing mole or appear as a new lesion. When it begins in a mole that is already on the skin, it tends to grow on the surface of the skin for some time before penetrating more deeply. While it can be found nearly anywhere on the body, it is most likely to appear on the torso in men, the legs in women and the upper back in both.
What it looks like: It may appear as a flat or slightly raised and discolored, asymmetrical patch with uneven borders. Colors include shades of tan, brown, black, red/pink, blue or white. It can also lack pigment and appear as a pink or skin-tone lesion .
Lentigo maligna
What you should know: This form of melanoma often develops in older people. When this cancer becomes invasive or spreads beyond the original site, the disease is known as lentigo maligna melanoma.
How and where it grows: This form of melanoma is similar to the superficial spreading type, growing close to the skin surface at first. The tumor typically arises on sun-damaged skin on the face, ears, arms or upper torso.
What it looks like: It may look like a flat or slightly raised, blotchy patch with uneven borders. Color is usually blue-black, but can vary from tan to brown or dark brown.
Acral lentiginous melanoma
What you should know: This is the most common form of melanoma found in people of color, including individuals of African ancestry.
How Is Melanoma Diagnosed
If you have a mole or other spot that looks suspicious, your doctor may remove it and look at it under the microscope to see if it contains cancer cells. This is called a biopsy.
After your doctor receives the skin biopsy results showing evidence of melanoma cells, the next step is to determine if the melanoma has spread. This is called staging. Once diagnosed, melanoma will be categorized based on several factors, such as how deeply it has spread and its appearance under the microscope. Tumor thickness is the most important characteristic in predicting outcomes.
Melanomas are grouped into the following stages:
- Stage 0 : The melanoma is only in the top layer of skin .
- Stage I: Low-risk primary melanoma with no evidence of spread. This stage is generally curable with surgery.
- Stage II: Features are present that indicate higher risk of recurrence, but there is no evidence of spread.
- Stage III: The melanoma has spread to nearby lymph nodes or nearby skin.
- Stage IV: The melanoma has spread to more distant lymph nodes or skin or has spread to internal organs.
Also Check: Is Skin Cancer The Same As Melanoma
Establish A Support System
Establish a support system by gathering a group of friends and family members that can lend a helping hand or emotional support when you need it. Support groups can also be helpful and may be found online. If you prefer to meet with a support group in person, visit the website to find groups in your area.
Recommended Reading: What Is Good For Skin Cancer
What Screening Tests Are Available
The most important screening test for melanoma is a skin examination because the vast majority of cutaneous melanomas are visible on the skin. Generally speaking, it is recommended that everyone get annual skin checks with a healthcare provider who works in the dermatology field. Your doctor may recommend something called Mole Mapping, or a similar system by which you can track changes to moles and other lesions through periodic photographs. Additionally, you should be examining your skin routinely at home. Because you see your skin every single day, you are the most likely person to notice any changes to it. At least once a monthwe suggest after you get out of the showeryou should do a self-check of your skin, using the ABCDEs as a guide, and look for any itching or bleeding moles or lesions. Also look for any spots that dont appear like others on your skinthese are called Ugly Ducklings. The prognosis for melanoma is best when it is found early, making skin examinations very important.
If you have a family and/or personal history of melanoma, you may want to talk to your healthcare provider about whether genetic testing would be beneficial.
You May Like: What Are Symptoms Of Melanoma That Has Spread
Melanoma Of The Head And Neck Treatment
Surgical resection with wide margins and often sentinel lymph node biopsy is required for melanoma that has not spread. Thin tumors, up to 1 millimeter thick, can be resected with 1-centimeter margins around the tumor. The greater the depth of invasion, the larger the margin required, up to 2 centimeters. Mohs surgery is not suitable for melanoma because the diagnosis often requires special pathologic staining that is not part of the Mohs technique.
To obtain a sentinel lymph node biopsy, a preoperative sentinel node localization study is performed: A radionuclide tracer is injected in the melanoma, then a radionuclide uptake SPECT or SPECT-CT scan shows which nodes the tracer spreads to first. These sentinel nodes may or may not contain melanoma: They are the nodes that a melanoma that has spread would first encounter, and contain melanoma cells when melanoma has spread to lymph nodes. Because there are hundreds of lymph nodes in the head and neck, your surgeon will use a gamma probe at surgery to identify and confirm that the nodes selected for removal are the sentinel nodes.
When enlarged lymph nodes are present, a neck dissection is performed at the time of surgery. If distant spread is detected during the workup that is, melanoma has spread to other organs immunotherapy and sometimes radiation therapy are used for treatment.
Johns Hopkins Head and Neck Cancer Surgery
What Is A Melanocyte
Melanocytes are skin cells found in the upper layer of skin. They produce a pigment known as melanin, which gives skin its color. There are two types of melanin: eumelanin and pheomelanin. When skin is exposed to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or tanning beds, it causes skin damage that triggers the melanocytes to produce more melanin, but only the eumelanin pigment attempts to protect the skin by causing the skin to darken or tan. Melanoma occurs when DNA damage from burning or tanning due to UV radiation triggers changes in the melanocytes, resulting in uncontrolled cellular growth.
About Melanin
Naturally darker-skinned people have more eumelanin and naturally fair-skinned people have more pheomelanin. While eumelanin has the ability to protect the skin from sun damage, pheomelanin does not. Thats why people with darker skin are at lower risk for developing melanoma than fair-skinned people who, due to lack of eumelanin, are more susceptible to sun damage, burning and skin cancer.
You May Like: What Kind Of Cancer Causes Skin Rashes
What Is The Cause Of Melanoma
Melanoma, like all cancers and diseases, is linked to poor nutrition and environmental pollutants. More and more research is produced regarding actual causation of melanoma.
Melanoma is clearly linked to sugar intake. A recently published study found that glycemic load was linked to a 240% higher risk of melanoma in women . Foods with the highest glycemic load include: refined grains , sugar-sweetened beverages, and dried fruit.
Further evidence of sugar as the culprit includes the fact that diabetics have a 15% higher risk than non-diabetics, per a meta-analysis of 11 studies . When you have diabetes, your risk of cancer, dementia, and heart disease are higher. Elevated blood sugar causes damage to cellular proteins. If the proteins that regulate cancer gene expression are damaged, the final outcome is obvious.
Insulin resistance increases the risk of melanoma . Obese people have a higher risk of insulin resistance. In short, if insulin is not able to do its job, poor health will follow. You see, insulin is responsible for energy utilization and storage. If we cant get energy into the cell, necessary intracellular activities cannot occur. Cancer will flourish.