How To Protect Yourself From Melanoma
Fortunately, most melanomas are diagnosed in early, localized stages, says Dr. González, and most patients treated for melanoma make a full recovery. But we do have patients that have ignored that funny looking mole for way too long, and its not uncommon to see cases that have metastasized to other organs, she adds.
Melanoma tends to a very aggressive form of cancer, and it can progress quickly from one stage to another. Says Dr. González: As soon as you see something unusual you should get it checked out, and as soon as you get a diagnosis, you need to be on top of the appropriate treatment.
Risk factors for melanoma include ultraviolet light exposure , having fair skin and light hair, and having a close relative whos also had melanoma. But monitoring skin for abnormal growths and changes is important for everyone, whether or not they are predisposed to skin cancer.
Going to see your board-certified dermatologist yearly and doing regular skin exams may not seem that important, Dr. González says, but these are the things that could save your life.
What Does Stage 3 Cancer Mean
Stage 3 usually means the cancer is larger. It may have started to spread into surrounding tissues and there are cancer cells in the lymph nodes nearby. Stage 4 means the cancer has spread from where it started to another body organ. For example to the liver or lung. This is also called secondary or metastatic cancer.
Read Also: What Are The 4 Types Of Melanoma
How Long Will It Take To Get My Lab Results
Theres nothing more nerve-wracking than waiting on test results. Biopsies can take a matter of days or weeks, depending on how complex the specimen is to read, says Dr. Friedlander. As for those mutations, it may take a while to find out if you have one. Molecular profiling takes several weeks, he says. Having this expectation upfront will save you the stress of waiting by the phone.
Also Check: Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rates
What Are Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes are small structures that filter substances and help fight infection. They are part of a network that runs throughout the body. Cancer that reaches the lymph nodes is concerning because cancer cells can easily spread to other parts of the body through this interconnected system.
Whether or not a melanoma spreads to one or more lymph nodes, it also may affect nearby skin. Such melanoma tumors are called satellite tumors. They’re defined as being within 2 centimeters of the original tumor and can be seen without a microscope.
Melanoma tumors also may spread to lymphatic channels, thin tubes that resemble blood capillaries, through which lymph fluid flows.
Treating Stage Ii Melanoma
Wide excision is the standard treatment for stage II melanoma. The width of the margin depends on the thickness and location of the melanoma.
Because the melanoma may have spread to nearby lymph nodes, many doctors recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy as well. This is an option that you and your doctor should discuss.
If an SLNB is done and does not find cancer cells in the lymph nodes, then no further treatment is needed, although close follow-up is still important.
If the SLNB finds that the sentinel node contains cancer cells, then a lymph node dissection will probably be done at a later date. Another option might be to watch the lymph nodes closely by getting an ultrasound of the nodes every few months.
If the SLNB found cancer, adjuvant treatment with an immune checkpoint inhibitor or targeted therapy drugs might be recommended to try to lower the chance the melanoma will come back. Other drugs or perhaps vaccines might also be options as part of a clinical trial.
You May Like: In Situ Cancer Melanoma
Treating Stage I Melanoma
Stage I melanoma is typically treated by wide excision . The width of the margin depends on the thickness and location of the melanoma. Most often, no other treatment is needed.
Some doctors may recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy to look for cancer in nearby lymph nodes, especially if the melanoma is stage IB or has other characteristics that make it more likely to have spread. You and your doctor should discuss this option.
If the SLNB does not find cancer cells in the lymph nodes, then no further treatment is needed, although close follow-up is still important.
If cancer cells are found on the SLNB, a lymph node dissection might be recommended. Another option might be to watch the lymph nodes closely by getting an ultrasound of the nodes every few months.
If the SLNB found cancer, adjuvant treatment with an immune checkpoint inhibitor or targeted therapy drugs might be recommended to try to lower the chance the melanoma will come back. Other drugs or perhaps vaccines might also be options as part of a clinical trial.
Whats The Outlook For Stage 4 Melanoma
Once the cancer spreads, locating and treating the cancerous cells becomes more and more difficult. You and your doctor can develop a plan that balances your needs. The treatment should make you comfortable, but it should also seek to remove or slow cancer growth. The expected rate for deaths related to melanoma is 10,130 people per year. The outlook for stage 4 melanoma depends on how the cancer has spread. Its usually better if the cancer has only spread to distant parts of the skin and lymph nodes instead of other organs.
Read Also: How Often Does Basal Cell Carcinoma Spread
Don’t Miss: What Is Braf Melanoma
It Usually Starts With Suspicious Spot
Maybe you noticed a mole that stood out from the rest . Its edges were irregular, maybe it was asymmetrical in shape, unevenly pigmented, noticeably large , or rapidly changing . These are the spots that concern dermatologists. If you had one, your doc did a biopsy on your own ugly duckling. During this in-office procedure, your doctor either shaved off a layer of your mole, punched it out with a hole-punch-like tool, or removed it with surgical excision, along with a margin of healthy skin to check for wandering cancer cells.
Stage 3 Peritoneal Mesothelioma
Peritoneal mesothelioma is the second-most common form of the disease. Instead of a formal staging system to measure progression, physicians typically use the existing Peritoneal Cancer Index to grade tumors in the abdomen. In addition, the PCI helps doctors determine the stage in many other abdominal cancers.
The PCI ranges from 0 to 39, measuring the spread of tumors across 13 different abdominal sectors. A score between 21 and 30 indicates stage 3 peritoneal mesothelioma. The characteristics of this stage are tumors localized within the abdomen, with some spread to nearby lymph nodes.
If a doctor refers to peritoneal mesothelioma as stage 3, it usually means tumors have spread throughout the abdominal lining and to nearby lymph nodes.Dr. Daniel A. LandauOncologist and hematologist
Also Check: What Are The Early Stages Of Melanoma
Recommended Reading: Invasive Lobular Carcinoma Grade 2 Survival Rates
How Often Should You Follow Up With Your Doctor
After your treatment, your doctor will recommend a regular follow-up schedule to monitor your cancer. Theyll be checking to make sure the cancer hasnt come back or new cancerous lesions havent appeared. The types of follow-up include:
A yearly skin check: Skin checks are an important aspect of detecting melanoma in its earliest, most treatable stages. You should also conduct a skin check on yourself once per month. Look everywhere from the bottoms of your feet to behind your neck.
Imaging tests every three months to a year: Imaging studies, such as an X-ray, CT scan, or brain MRI, look for cancer recurrence.
Physical exam as needed: A physical exam to assess your overall health is important when you have had melanoma. For the first two years, youll want to get an exam every three to six months. Then for the next three years, the appointments can be every three months to a year. After the fifth year, the exams can be as needed. Do a monthly self-examination of your lymph nodes to check your progress.
Your doctor may recommend a different schedule based on your overall health.
Dont Miss: How Bad Is Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Staging And Grading For Stage 4 Cancer
Most cancers are staged using some form of the TNM system. Doctors may also use the TNM system to help determine the extent of certain cancers in each stage. The TNM system stands for:
- T , or the size of the original tumor
- N , or whether the cancer is present in the lymph nodes
- M , or whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body
Not all cancers are staged using the TNM system, though. Some cancers, especially liquid cancers, are staged through different established protocols. The Binet and Rai systems, for example, are used to stage certain types of leukemia. Female reproductive system cancers, such as cervical cancer, are staged with a separate staging system created by the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics .
As your care team gathers information about your cancer for the purposes of staging, they may need to order several tests, including:
Your care team may likely also need to perform a biopsy, a procedure that involves removing a sample of cells and analyzing it for signs of cancer. Imaging scans may be able to tell your care team where your cancer is, but looking at the cancer cells specifically tell them how fast they are likely to growor what grade they are.
Grading is different from staging and is done for most, but not all, cancers.
The grade of your cancer is part of how your cancer care team stages your cancer and determines your prognosis, or outlook.
Read Also: Stage 2 Cancer Symptoms
What Are The Stages Of Melanoma Skin Cancer
Melanoma Skin Cancer Stages. After someone is diagnosed with melanoma, doctors will try to figure out if it has spread, and if so, how far. This process is called staging. The stage of a cancer describes how much cancer is in the body. It helps determine how serious the cancer is and how best to treat it.
What Are The Stages Of Melanoma
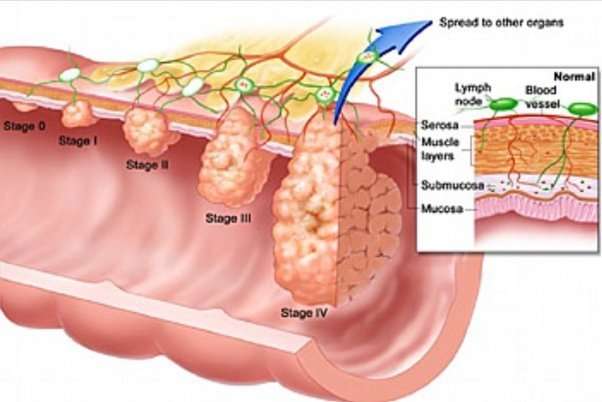
When a melanoma has been diagnosed, the pathology report provides information to determine the stage of the disease.
The prognosis of melanoma and the treatment options available depend on the stage at which the cancer is diagnosed.
One of the most common areas of confusion is the difference between the levels of melanoma and the staging of melanoma. The level of melanoma relates to the depth of the melanoma in the skin and the staging of melanoma refers to how limited or advanced the melanoma is at the time of diagnosis.
The stages of melanoma are determined by reviewing different factors including:
Read Also: How To Treat Melanoma In Nails
Don’t Miss: Metastatic Melanoma Cancer Life Expectancy
Treatments For Stage Ii Melanoma
As with stage I, stage II melanoma is typically treated with wide excision surgery, which cuts out the melanoma along with a margin of healthy surrounding skin. In the case of stage II melanoma, many doctors will recommend looking for cancer in nearby lymph nodes by performing a sentinel lymph node biopsy, which may necessitate further treatment if cancer cells are found.
What Are The Melanoma Stages And What Do They Mean
Early melanomas
Stage 0 and I are localized, meaning they have not spread.
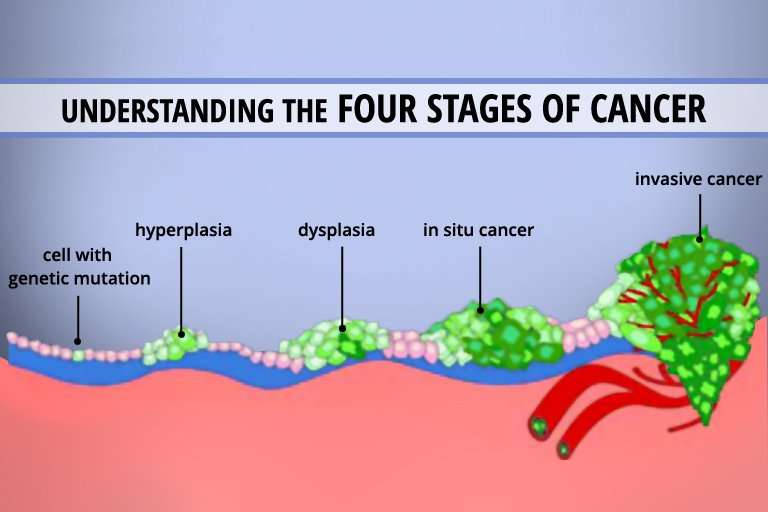
- Stage 0: Melanoma is localized in the outermost layer of skin and has not advanced deeper. This noninvasive stage is also called melanoma in situ.
- Stage I: The cancer is smaller than 1 mm in Breslow depth, and may or may not be ulcerated. It is localized but invasive, meaning that it has penetrated beneath the top layer into the next layer of skin. Invasive tumors considered stage IA are classified as early and thin if they are not ulcerated and measure less than 0.8 mm.
Find out about treatment options for early melanomas.
Intermediate or high-risk melanomas
Localized but larger tumors may have other traits such as ulceration that put them at high risk of spreading.
- Stage II: Intermediate, high-risk melanomas are tumors deeper than 1 mm that may or may not be ulcerated. Although they are not yet known to have advanced beyond the primary tumor, the risk of spreading is high, and physicians may recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy to verify whether melanoma cells have spread to the local lymph nodes. Thicker melanomas, greater than 4.0 mm, have a very high risk of spreading, and any ulceration can move the disease into a higher subcategory of stage II. Because of that risk, the doctor may recommend more aggressive treatment.
Learn more about sentinel lymph node biopsy and melanoma treatment options.
Advanced melanomas
Recommended Reading: Skin Cancer Pictures Mayo Clinic
Systemic Adjuvant Treatment Of Stage Iii Melanoma
Systemic therapy is any treatment directed at destroying cancer cells throughout the body. Many patients with stage III melanoma are at high risk for disease recurrence because undetectable cancer cells referred to as micrometastases have already broken away from the primary cancer and traveled through the lymph and blood system to other locations in the body. The delivery of systemic cancer treatment following surgery is referred to as adjuvant therapy.
Adjuvant treatment of stage III melanoma with newer precision cancer medicines and immunotherapy drugs is the standard of care because they delay the time to cancer recurrence and prolong survival.
Dont Miss: What Type Of Skin Cancer Spreads The Fastest
What Is A Five
Five-year survival rate refers to the average number of people with a particular disease or condition who are alive five years after being diagnosed.
Cancer experts based five-year survival rates for melanoma on information from a database called SEER, which stands for the National Cancer Institute’s Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program.
Survival statistics from the SEER database are not based on AJCC melanoma staging. Instead, they’re based on if and how far the melanoma has spread:
| Type |
|---|
The five-year survival rate for all three SEER stages combined is 93%.
The five-year survival rate for all three SEER stages combined is 93%.
Recommended Reading: Treatment For Stage 3 Melanoma
Unusual Moles Exposure To Sunlight And Health History Can Affect The Risk Of Melanoma
Anything that increases your risk of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer not having risk factors doesnât mean that you will not get cancer. Talk with your doctor if you think you may be at risk.
Risk factors for melanoma include the following:
- Having a fair complexion, which includes the following:
- Fair skin that freckles and burns easily, does not tan, or tans poorly.
- Blue or green or other light-colored eyes.
- Red or blond hair.
Being White or having a fair complexion increases the risk of melanoma, but anyone can have melanoma, including people with dark skin.
See the following PDQ summaries for more information on risk factors for melanoma:
Read Also: How Quickly Does Renal Cell Carcinoma Grow
How Fast Does Melanoma Spread
Melanoma is a deadly form of skin cancer because of its ability to metastasize to local lymph nodes and other organs. It is estimated that melanoma kills, on average, over 10,000 people in the United States every year.
The first sign of flat melanoma is usually a new spot or an existing mole or freckle that changes in appearance. Some changes can include:
- A spot that has grown in size
- A spot where the edges are looking irregular versus smooth and even
- A spot that has a range of colors such as brown, black, blue, red, white or light gray.
- A spot that has become itchy or is bleeding
According to Dr. Andrew Duncanson, board-certified dermatologist at Forefront Dermatology, It is important to know that melanoma can appear on areas of the skin not normally exposed to the sun such as under the arm, chest, and buttocks. It can also appear in areas that you are not able to see easily on your own including the ears, scalp, back of legs, and bottom of feet. I always recommend to my patients to look for the ugly duckling spot the new spot that doesnt look like any others. Additionally, ask a family member to look over the hard to see areas monthly, while also getting an annual skin cancer exam by a board-certified dermatologist to detect skin cancer early.
Read Also: Is Melanoma The Same As Skin Cancer
You May Like: Lobular Breast Cancer Stage 1
What To Do After A Stage 3 Mesothelioma Diagnosis
After receiving a mesothelioma diagnosis, the most crucial step is finding a team of well-equipped specialists to treat this rare cancer. It is essential to seek treatment as soon as possible following a stage 3 mesothelioma diagnosis.
Working with doctors who have successfully treated patients through surgery and the latest therapies gives you the best chance of improving your mesothelioma prognosis. Additionally, improving overall health through proper nutrition and exercise can help extend your mesothelioma life expectancy.
Joining a mesothelioma support group is a great way to connect with resources such as clinical trials and physicians who specialize in this rare cancer. These specialists know the intricacies of mesothelioma, and they understand the challenges patients face. Not all hospitals or major metropolitan cancer centers have doctors who focus on mesothelioma.
Watch: 14-year mesothelioma survivor Tamron Little explains the importance of joining a support group.
Support groups, such as the one offered by Asbestos.com, help patients and their families come to terms with their mesothelioma diagnosis and provide resources for improving quality of life and mental health awareness.