What Are The Treatments For Basal Cell Carcinoma
BCC is treated by removing it. The choice of treatment depends on many things, including patient health and age, the location of the tumor, and the extent and type of the cancer. Treatment may occur in many ways:
- Scratching off with a curette, an instrument that may end in a ring or a spoon, and then burning with a special electric needle. This method is called electrodessication and curettage.
- Surgical removal
- Mohs surgery: This is a specialized technique. The doctor first removes the visible cancer and then begins cutting around the edges. The tissues are examined during the surgery until no more cancer cells are found in tissues around the wound. If necessary, a skin graft or flap might be applied to help the wound heal.
- Excisional surgery: The growth and a bit of surrounding skin is removed with a scalpel.
If the BCC has advanced locally or spread to another location, which is very rare for BCC, the FDA has approved two medicines: vismodegib and sonidegib . These drugs are of a class called hedgehog inhibitors.
Our Approach To Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinoma
UCSF provides superior, proven care to prevent, detect and manage basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas, and will tailor cutting-edge treatment plans to the individual patient. Our dermatologists, medical and surgical oncologists, radiation oncologists and dermatopathologists are known for providing the best treatment options and cure rates for skin cancer, while giving outstanding cosmetic results.
Some of our new diagnostic and treatment techniques include lymph node mapping to detect early occurrences of cancer, electron beam radiation and Mohs micrographic surgery, which removes the smallest amount of healthy tissue in order to minimize scarring and preserve skin function. We also offer our patients access to educational programs, resources for emotional support and opportunities to participate in experimental treatments.
How Serious Is Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Basal cell skin cancer, also called basal cell carcinoma, is usually very curable, but it can cause disfigurement and complications if it’s not treated. In the majority of cases, basal cell carcinoma is very treatable.
It is unusual for basal cell carcinoma to cause death. Approximately 2,000 people in the U.S. die each year from basal and squamous skin cancers. In most cases, people who die from these types of skin cancer tend to be older, immunosuppressed, or have been diagnosed at a very late stage.
Read Also: What Does Stage 3b Melanoma Mean
Skin Cancer Types: Basal Cell Carcinoma Overview
All content solely developed by the American Academy of Dermatology
The American Academy of Dermatology gratefully acknowledges the support from Sanofi Genzyme and Regeneron.
Basal cell carcinoma
What is basal cell carcinoma?The most common type of skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma can show up on the skin in many ways.
Is it contagious? No
Targeted Therapy Or Immunotherapy For Advanced Basal Cell Cancers
In rare cases where basal cell cancer spreads to other parts of the body or cant be cured with surgery or radiation therapy, a targeted drug such as vismodegib or sonidegib can often shrink or slow its growth.
If these drugs are no longer working , the immunotherapy drug cemiplimab can sometimes be helpful.
Also Check: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
What Is Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common kind of skin cancer. It can develop almost anywhere on the body.
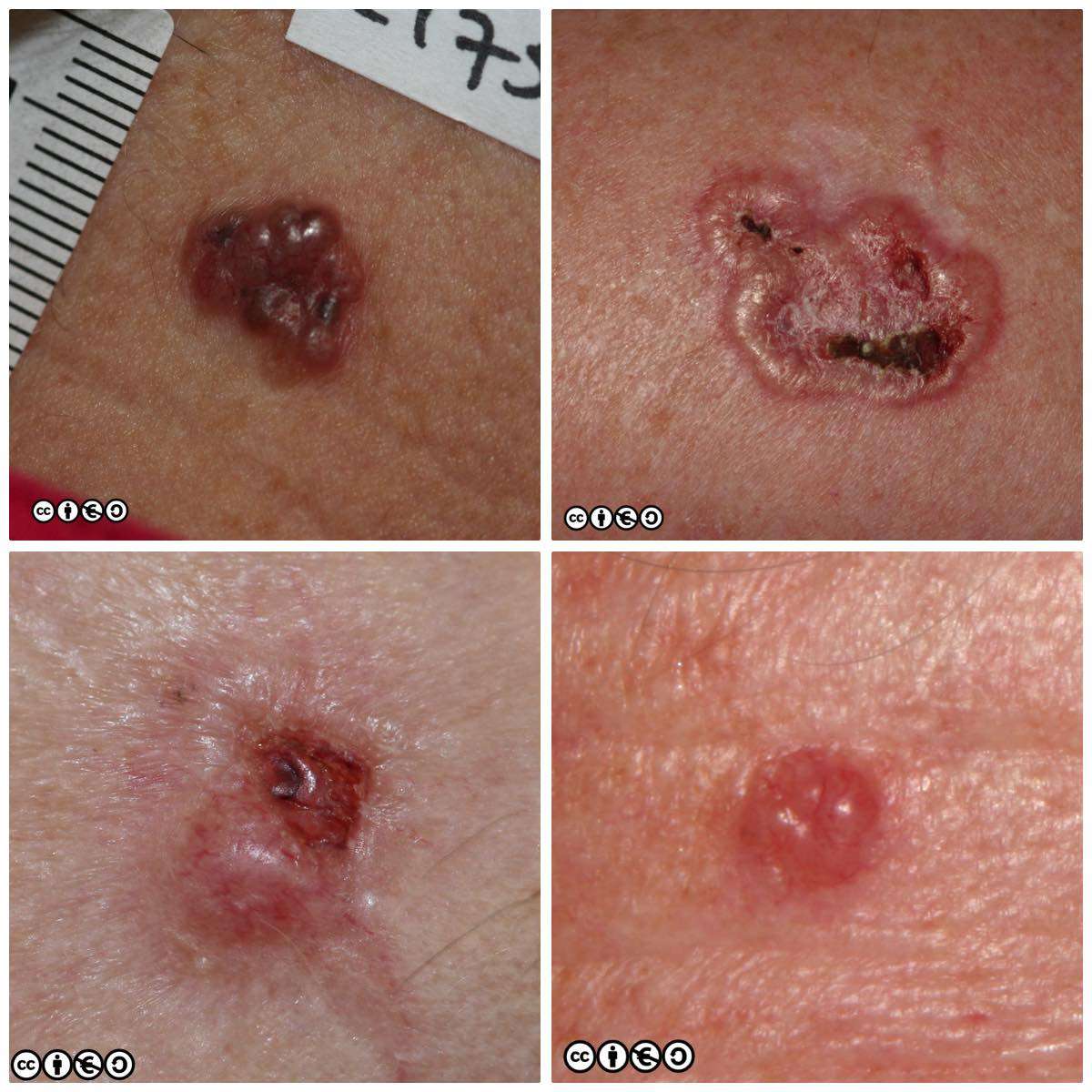
BCCs typically form in sun-exposed areas. They vary greatly in how they lookpink or red bumps, open sores, or waxy patches. For people with brown or black skin, BCCs may appear brown or almost black.
Treatment Of Facial Basal Cell Carcinoma: A Review
Vanessa Smith
1Department of Dermatology, Hull Royal Infirmary, Hull and Hull York Medical School , Hull HU2 3JZ, UK
Abstract
Basal cell carcinomas are locally destructive malignancies ofthe skin. They are the most common type of cancer in the westernworld. The lifetime incidence may be up to 39%. UV exposure is themost common risk factor. The majority of these tumours occur on thehead and neck. Despite BCCs being relatively indolent the highincidence means that their treatment now contributes a significant andincreasing workload for the health service. A good understanding ofthe options available is important. Management decisions may beinfluenced by various factors including the patients age andcomorbidities and the lesion subtype and location. Due to theimportance of a good cosmetic and curative outcome for facial BCCstreatment decisions may differ significantly to those that would bemade for BCCs arising elsewhere. There is little good randomizedcontrolled data available comparing treatment modalities. Althoughtraditionally standard excision has been the treatment of choicevarious other options are available including: Mohs micrographicsurgery, curettage and cautery, cryosurgery, radiotherapy, topicalimiquimod, photodynamic therapy and topical 5-fluorouracil. Wediscuss and review the literature and evidence base for the treatmentoptions that are currently available for facial BCCs.
1. Introduction
2.4. Cryosurgery
Also Check: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Basal Cell Carcinoma Affects A Wide Range Of People
| Basal Cell Carcinoma |
Men are somewhat more likely than women to get basal cell carcinoma. It is more common in the elderly. BCC is more common in people with fair complexion and bright eyes.
Although whites are 19 times more likely than blacks to be impacted, persons of colour may also be affected. People who have previously had BCC are more likely to acquire another lesion.
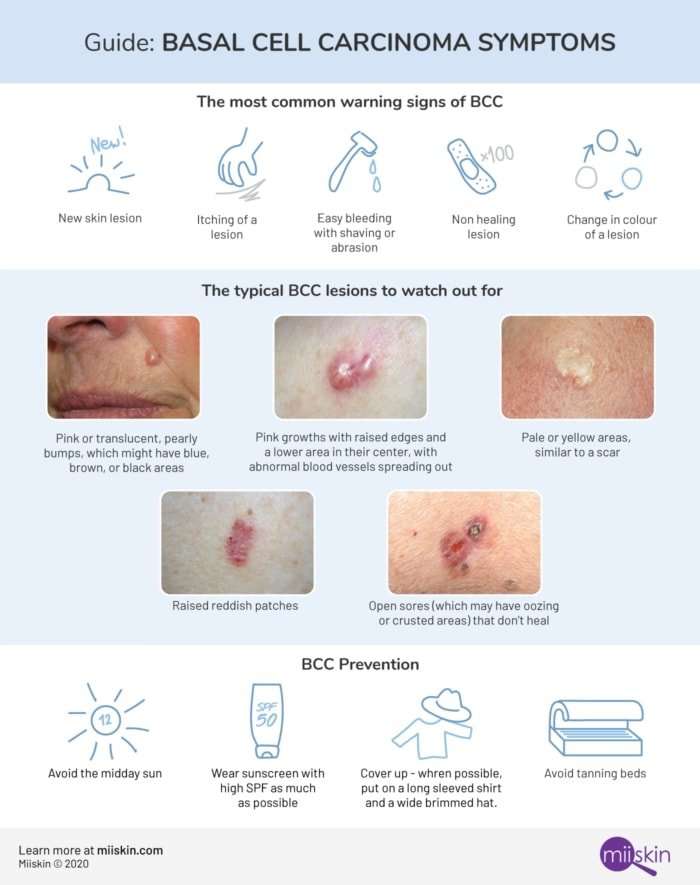
Early Detection And Prevention
Many dermatologists do not have experience in treating people with darker skin. Implicit bias during assessment and diagnosis can also play a role, so it is important that Black people know the signs of skin cancer.
No matter what type of skin cancer a person has, detecting it early improves their outlook. Knowing the signs and symptoms of skin cancer can help a person detect suspicious skin growths early.
An individual can try :
- Doing regular skin checks every few months: When a person is familiar with their skin, it makes it easier to detect potentially harmful changes in moles and freckles.
- Visiting a dermatologist for an annual skin cancer screening: This is particularly important if a person has a family history of skin cancer.
- Wearing sunscreen in the sun: Black people can burn, too. The melanin in Black skin has an estimated
usually begins as a change in the skin. This can be a new growth like a freckle or a mole or changes to an existing growth.
Being familiar with their skin can help a person detect abnormalities. Regular skin self-exams can help a person get to know their skin and how their moles and freckles typically look.
When people find a questionable mole or freckle, they can wonder whether or not it may be melanoma. Try using the acronym ABCDE to check growths when doing a skin exam:
Diagnosing skin cancer starts with an exam. A doctor will use a scope to look at suspicious skin growths.
Don’t Miss: How Fast Does Cancer Spread Without Treatment
Prognosis Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Treatment of basal cell carcinoma is nearly always successful, and the cancer is rarely fatal. However, almost 25% of people with a history of basal cell carcinoma develop a new basal cell cancer within 5 years of the first one. Thus, anyone with one basal cell carcinoma should have a yearly skin examination.
How Widespread Is Bcc
Basal cell carcinoma is quite common, and the number of reported cases in the U.S. has steadily increased.
- An estimated 3.6 million Americans are diagnosed with BCC each year.
- More than one out of every three new cancers are skin cancers, and the vast majority are BCCs.
- The diagnosis and treatment of nonmelanoma skin cancers, including BCC and squamous cell carcinoma , increased up to 77 percent between 1994 and 2014.
Reviewed by:
You May Like: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
Get To Know Your Skin And Check It Regularly
Look out for changes such as:
- A mole that changes shape, color, size, bleeds, or develops an irregular border
- A new spot on the skin that changes in size, shape, or color
- Sores that don’t heal
- New bumps, lumps, or spots that don’t go away
- Shiny, waxy, or scar type lesions
- New dark patches of skin that have appeared
- Rough, red, scaly, skin patches
If you notice any changes to your skin, seek advice from a medical professional. Basal cell carcinoma is very treatable when caught early.
How Is Basal Cell Cancer Of The Head And Neck Diagnosed
Diagnosis is made by clinical exam and a biopsy. Basal cell cancers are staged by size and extent of growth. These cancers rarely metastasize to lymph nodes or other organs, but they can grow quite large and invade small nerves and local structures.
Biopsy can help determine if the basal cell cancer is a low-risk tumor or a high-risk tumor that requires more aggressive treatment. Low-risk tumors are often nodular and do not have nerve involvement. High-risk tumors in the head and neck are those that involve the central face, nose and eye area, as well as those tumors that are greater than or equal to 10 millimeters on the cheeks, scalp and neck tumors that are recurrent or arising from previously radiated tissue and tumors arising in patients who are immunosuppressed. An aggressive growth pattern on the pathology evaluation and perineural invasion are also features of high-risk basal cell cancers.
Read Also: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
What Is A Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that occurs when there is damage to the DNA of basal cells in the top layer, or epidermis, of the skin. They are called basal cells because they are the deepest cells in the epidermis. In normal skin, the basal cells are less than one one-hundredth of an inch deep, but once a cancer has developed, it will spread deeper.
Who Is At Risk
Anyone can develop skin cancer, but its more common in older people. The risk is also higher in people who have:
- fair or freckled skin, especially if it burns easily and doesnt tan
- red or fair hair and light-coloured eyes
- had short, intense periods of exposure to UV radiation, e.g. on weekends or holidays or when playing sport, especially if it caused sunburn
- actively tanned or used solariums
- worked outdoors
- a weakened immune system, which could be caused by taking certain medicines after an organ transplant or by ongoing blood conditions such as chronic leukaemia
- lots of moles on their body or moles with an irregular shape and uneven colour
- a previous skin cancer or a family history of skin cancer
- certain skin conditions such as sunspots.
People with olive or very dark skin have more protection against UV radiation because their skin produces more melanin than fair skin does. However, they can still develop skin cancer.
| Slip, slop, slap, seek and slide during sun protection times to protect your skin from overexposure to the sun and sun damage. |
Read Also: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
An evidence-based approach to basal cell cancer
Basal cell cancer is relatively common. Patients often first present to the primary care provider with complaints of an abnormal skin lesion. When diagnosed early, it has an excellent prognosis, but if there is a delay in diagnosis, the tumor can advance and lead to significant morbidity. Basal cell cancer is best managed by an interprofessional team that includes a dermatologist, mohs surgeon, plastic surgeon, nurse practitioner, primary care provider, and a dermatopathologist. Basal cell carcinomas typically have a slow growth rate and tend to be locally invasive. Tumors around the nose and eye can lead to vision loss. In most cases, surgical excision is curative. However, because recurrences can occur, these patients need long-term follow up.
How Do People Find Bcc On Their Skin
Many people find it when they notice a spot, lump, or scaly patch on their skin that is growing or feels different from the rest of their skin. If you notice any spot on your skin that is growing, bleeding, or changing in any way, see a board-certified dermatologist. These doctors have the most training and experience in diagnosing skin cancer.
To find skin cancer early, dermatologists recommend that everyone check their own skin with a skin self-exam. This is especially important for people who have a higher risk of developing BCC. Youll find out what can increase your risk of getting this skin cancer at, Basal cell carcinoma: Who gets and causes.
Images used with permission of:
-
The American Academy of Dermatology National Library of Dermatologic Teaching Slides.
-
J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 80:303-17.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
What Is The Best Treatment For A Basal Cell Carcinoma
Pro Tip
If treated when small, basal cell carcinomas are easily removed. Dr. MacCormack
If you think you may have skin cancer, make an appointment with a dermatologist . They will examine the lump or sore and also the rest of your body for any other suspicious spots.
If skin cancer is suspected, the doctor will want to scrape or cut off a small piece of the lesion so it can be examined and tested for basal cell carcinoma cells in a laboratory.
If a biopsy confirms BCC, the dermatologist will likely offer several treatment options. Possibilities include in-office surgical procedures to remove the lesion, radiation therapy, or certain medications.
The type of treatment will depend on the size and location of the tumor, plus patient preference where possible. Your dermatologist will help you decide which approach is right for you.
Know That Surgery Sites Heal In Time
Had basal cell on the side of my nose going toward the corner of my eye. Couldnt see anything on the skin, but thanks to the keen eye of my derm she saw it, and did a biopsy, and sent me to a Mohs specialist at UAB. He removed it along with surrounding tissue, sutured, sent me on my way looking, well, terrible! Within 1 year, the scare is completely gone & cant tell anything was done. Thankful for those yearly scans. Debbie
I had Mohs done on a very small spot on side of nose right by eye. They had to put me to sleep and did a flap on forehead. Also had Mohs on lip. It went about 2 inches outside of mouth and about an inch in mouth. Great results. Almost unnoticeable. Joy
Recommended Reading: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
What Causes Basal Cell Carcinomas
The main cause of damage leading to BCC is sun exposure. This is usually a combination of:
- long-term, everyday sun exposure, and
- occasional intense exposure, usually leading to sunburn.
In some cases, they are the result of damage caused by things such as burns, scars, infections, vaccinations or tattoos.
What Should I Do If I Think I Have A Basal Cell Carcinoma
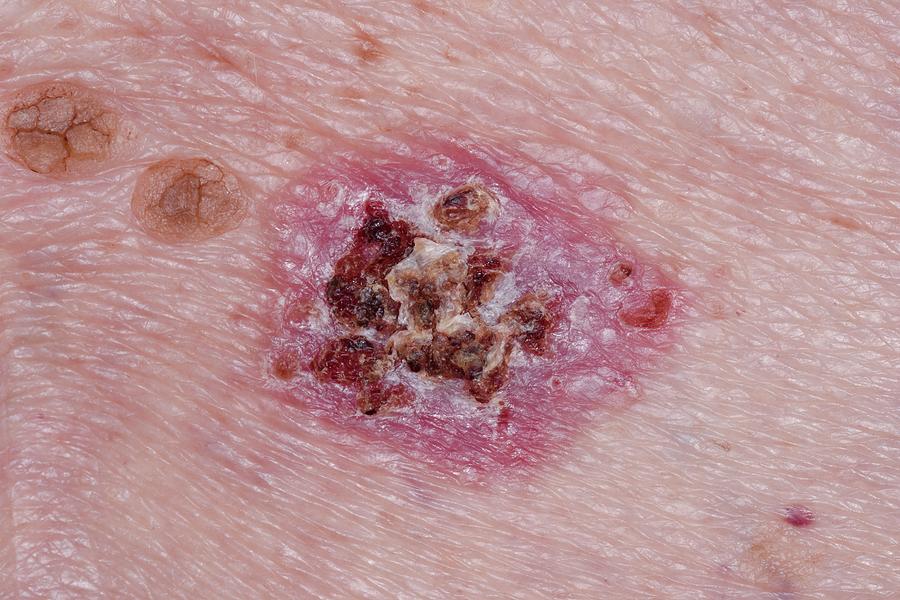
If you notice a change to or growth on your skin, make an appointment to see your doctor straight away. Your doctor will assess the size, location and look of the growth. They will also ask you how long you have had it, whether it bleeds or itches, etc.
If your doctor thinks the growth may be cancer, they may take a small sample of tissue . The tissue sample will be sent to a laboratory and examined under a microscope. Your doctor will let you know whether the sample showed any cancer cells, and will recommend appropriate treatment if necessary.
Read Also: Etiology Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
What Causes Basal Cell Carcinoma
The commonest cause is exposure to ultraviolet light from the sun or from sunbeds. BCCs can occur anywhere on the body, but are most common on areas that are exposed to the sun such as your face, head, neck and ears. It is also possible for a BCC to develop in a longstanding scar. BCCs are not infectious.
BCCs mainly affect fair skinned adults, but other skin types are also at risk. Those with the highest risk of developing a basal cell carcinoma are:
- People with pale skin who burn easily and rarely tan .
- Those who have had a lot of exposure to the sun, such as people with outdoor hobbies or outdoor workers, and people who have lived in sunny climates.
- People who have used sun beds or have regularly sunbathed.
- People who have previously had a basal cell carcinoma.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Common In Sun
Squamous cell carcinoma, also called squamous cell cancer, is the second most common type of skin cancer. It accounts for about 20 percent of cases.
This type of cancer starts in flat cells in the outer part of the epidermis. It commonly crops up on sun-exposed areas, such as the face, ears, neck, lips, and hands. It can also develop on scars or chronic sores.
Squamous cell carcinomas may develop from precancerous skin spots, known as actinic keratosis .
These cancers might look like:
- A firm, red bump
- A flat lesion with a scaly, crusted surface
- A sore that heals and then reopens
People with lighter skin are more at risk for developing squamous cell carcinoma, but the skin cancer can also affect those with darker skin.
Other risk factors include:
- Having light eyes, blond or red hair, or freckles
- Being exposed to the sun or tanning beds
- Having a history of skin cancer
- Having a history of sunburns
- Having a weakened immune system
- Having the genetic disorder xeroderma pigmentosum
RELATED: 10 Things You May Know Cause Skin Cancer
Read Also: What Does Stage 3b Melanoma Mean