What Does A Blue Dot On Your Skin Mean
Theyre formally called congenital dermal melanocytosis. These marks are flat and blue-gray. They typically appear on the buttocks or lower back, but may also be found on the arms or legs. Theyre generally present at birth or develop soon after. These birthmarks are noncancerous and present no health danger.
What Is The Treatment
Unfortunately, research shows that treatment or removal of most toenail melanomas is done whilst they are in a later stage of growth. These are technically tumors but are often benign, meaning that they can be removed quite quickly and easily with surgery.
Important note: They are usually done later because they are identified late which again prompts me to remind you to make an appointment if you think you have something like this.
However, one thing to note is that because it is covered by a nail, the toe or thumbnail will most likely be partially or completely removed to allow access to the affected area.
The surgery should only last for around an hour and it will be completed under local aesthetic, meaning a lengthy stay in hospital is not likely unless there are complications from the surgery.
If there is cancer, your doctor may follow up with chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
It is also possible that a small part of your toe will be removed if there is cancer and it has spread. However, if the diagnosis is very late and the cancer has spread to other parts of your body, the treatment will become more general as specifically targeting your toe will not help as much as having proper cancer treatments.
Skin Exam And Physical
You may have had a complete skin exam during your last dermatology appointment. Dermatologists often perform this exam when a patient has a suspicious spot on their skin that could be skin cancer.
During a complete skin exam, your dermatologist examines you head to toe. This exam includes a look at all of your skin, including the skin on your scalp, face, genitals, and the bottoms of your feet. Your dermatologist will also examine your nails and look inside your mouth.
If you did not have a complete skin exam before being diagnosed with melanoma, youll have one at your next appointment.
During a complete skin exam, your dermatologist may use a device called a dermatoscope
This device provides a closer look at the spots on your skin.
At your next appointment, youll receive a physical. During your physical, your dermatologist will ask how youre feeling and about your health, illnesses, and injuries. Your dermatologist will also want to know what diseases run in your family and the medications you take.
During your physical, your dermatologist will check your lymph nodes to find out if any feel swollen. There are many reasons for swollen lymph nodes. For example, if you have an infection or recently received a vaccination, lymph nodes can feel swollen. When you have melanoma, the swelling might be a sign that the cancer has spread.
If youre unsure what diseases your close blood relatives have had, try to find out
Don’t Miss: Small Blue Cell Tumor Prognosis
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Subungual Melanoma
In cases of suspected subungual melanoma you should expect your foot specialist to perform a simple surgical procedure called a nail matrix biopsy, right where the pigmented lesion is originating from. A nail matrix biopsy is a full thickness biopsy through the nail plate and down to the nail bed.
The specimen should then be sent to a certified pathology lab where the pathologist will look at the lesion under the microscope. The lab should also perform a special staining technique to the sample lesion to determine if the growth is malignant, pre-malignant or benign.
If the diagnosis is melanoma of the nail unit then the definitive treatment is a digital amputation. Melanoma is potentially life-threatening so if you have melanoma of the toe it needs to be dealt with aggressively. You need a quick diagnosis and surgery to remove any chance of it spreading.
Can Melanoma Be Prevented
You can’t control how fair your skin is or whether you have a relative with cancerous moles. But there are things you can do to lower your risk of developing melanoma. The most important is limiting your exposure to the sun.
Take these precautions:
- Avoid the strongest sun of the day between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Use broad-spectrum sunscreen whenever you’re in the sun.
- Wear a wide-brimmed hat and cover up with long, loose cotton clothing if you burn easily.
- Stay out of the tanning salon. Even one indoor tanning session increases your risk of getting melanoma.
Also, be sure to check your moles often . Keep dated records of each mole’s location, size, shape, and color, and get anything suspicious checked out right away.
Not all skin cancer is melanoma, but every case of melanoma is serious. So now that you know more about it, take responsibility for protecting yourself and do what you can to lower your risk.
You can find more information online at:
Don’t Miss: Is Melanoma Cancer Curable
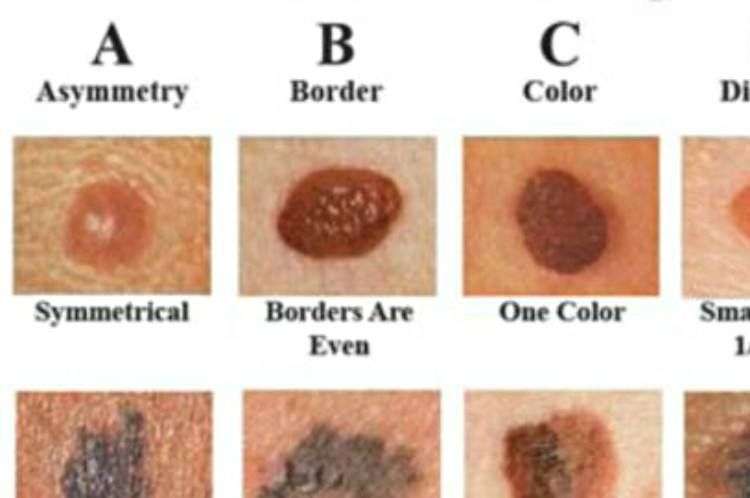
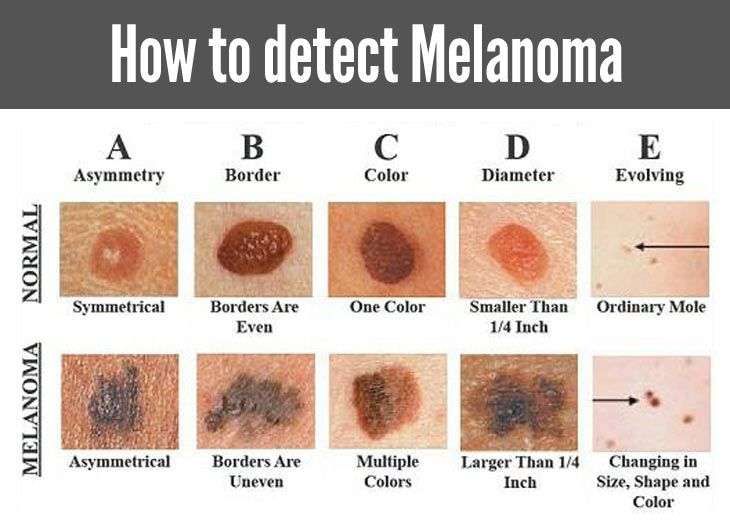
A Stands For Asymmetry
A benign, or non-cancerous mole is symmetrical. If you draw a line down the middle of it, the two sides will match. But, one of the first things that dermatologist Dr. Perri will check for in his skin cancer screenings is asymmetrical moles moles whose two sides do not match. If Dr. Perri notices you have an asymmetrical mole, he will likely recommend that it be biopsied to check for Melanoma.
What Causes Skin Cancer
Ultraviolet radiation from the sun is the number one cause of skin cancer, but UV light from tanning beds is just as harmful. Exposure to sunlight during the winter months puts you at the same risk as exposure during the summertime.
Cumulative sun exposure causes mainly basal cell and squamous cell skin cancer, while episodes of severe blistering sunburns, usually before age 18, can cause melanoma later in life. Other less common causes are repeated X-ray exposure, scars from burns or disease, and occupational exposure to certain chemicals.
Ultraviolet A and Ultraviolet B rays also affect the eyes and the skin around the eyes. Sun exposure may lead to cataracts, cancer of the eyelids, and possibly macular degeneration.
Also Check: Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Malignant
You May Like: Skin Cancer Mayo
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- How far has the melanoma spread under my skin?
- Has it spread anywhere else?
- What treatment do you think is best for me?
- Whats the goal of this treatment? Do you think it could cure the cancer?
- Will treatment include surgery? If so, who will do the surgery?
- What will the surgery be like?
- Will I need other types of treatment, too?
- Whats the goal of these treatments?
- What side effects could I have from these treatments?
- What can I do about side effects that I might have?
- Is there a clinical trial that might be right for me?
- What about special vitamins or diets that friends tell me about? How will I know if they are safe?
- How soon do I need to start treatment?
- What should I do to be ready for treatment?
- Is there anything I can do to help the treatment work better?
- Whats the next step?
What Is Metastatic Melanoma
Metastatic melanoma is melanoma that has spread beyond its original site in the skin to distant tissue sites. There are several types of metastatic melanoma. There may be spread through the lymphatic system to local lymph nodes. This may show up as swollen lymph glands or as a string of skin tumors along a lymphatic chain. Melanoma may also spread through the bloodstream , where it may appear in one or more distant sites, such as the lungs, liver, brain, remote skin locations, or any other body location.
Read Also: What Does Melanoma In Situ Look Like
What Is A Biopsy
An excisional biopsy is a simple surgical procedure in which the lesion is removed and sent to a laboratory for analysis. Sometimes this might be done by your GP or by a specialist. You will be given a local anaesthetic and then a scalpel is used to remove the mole and some of the surrounding tissue. You may have stitches to help the wound to heal.
The tissue that is removed is sent to a pathology laboratory for examination and it takes one to two weeks to get the results a followup appointment may be arranged. You will find out if melanoma is present and what stage it is, how thick it is, and other information such as how rapidly the cells are dividing , ulceration, regression and excision margins.
If the tests show you have melanoma, you may have surgery to remove a wider margin of surrounding skin see page 15 for information on treatment.
If melanoma is confirmed and confined to the epidermis, then it is in situ if it has spread to the dermis it is invasive and if it has spread to other parts of your body it is metastatic.
Depending on the results of the biopsy additional testing may be recommended. This is more likely for thicker melanomas or if you have other risk factors.
Signs And Symptoms Of Melanoma
The most common sign of melanoma is the appearance of a new mole or a change in an existing mole. This can occur anywhere on the body, but the most commonly affected areas are the back in men and the legs in women. Melanomas are uncommon in areas which are protected from sun exposure, such as the buttocks and the scalp.
In most cases, melanomas have an irregular shape and are more than one colour. The mole may also be larger than normal and can sometimes be itchy or bleed. Look out for a mole which changes progressively in shape, size and/or colour.
You May Like: Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Flat Red Patches And Rashes
One type of cancer that affects the skin, T-cell lymphoma, often begins with very itchy, flat, red patches and plaques that are easily mistaken for eczema or psoriasis.
One type of T-cell lymphoma, mycosis fungoids, transitions from these patches to dome-shaped nodules, and then to extensive reddened areas on multiple areas of the body. It may spread to lymph nodes and other regions of the body such as the lungs, liver, and bones. T-cell lymphomas most often begin on the buttocks, groin, hips, armpits, and chest.
Other cancers, such as breast cancer, may spread to the skin and initially be mistaken for a benign rash. Inflammatory breast cancer is a type of breast cancer that originates in the skin and appears, at first, to be an eczematous type of rash.
What Are The Symptoms Of Melanoma That Has Spread
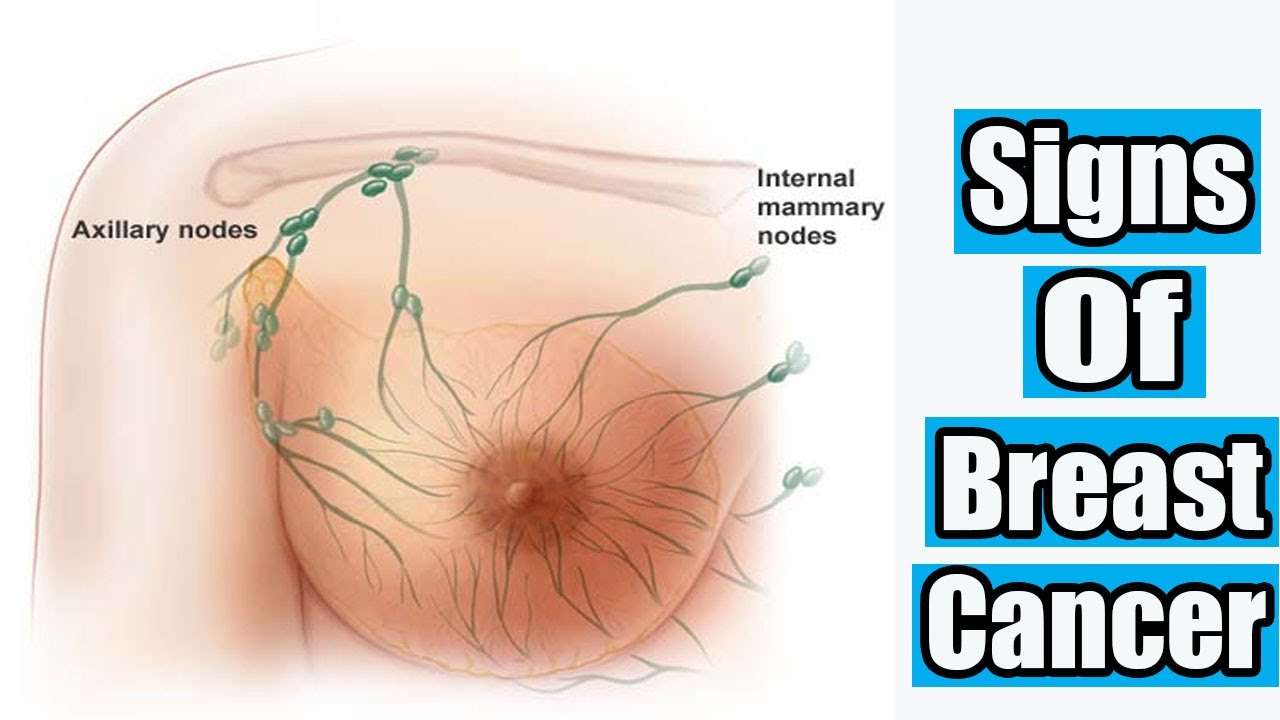
Metastatic melanoma is cancer that has spread from the skin to another part of the body. It most often spreads to the lymph nodes, brain, bones, liver or lungs, with patients experiencing symptoms based on where it has spread to:
- Lymph nodes Swollen or painful lymph nodes or hardened lumps felt under the skin
- Brain Headaches or seizures
Also Check: What Does Cancer Tumor Look Like
What Are The Survival Rates For Metastatic Melanoma
Survival rates for melanoma, especially for metastatic melanoma, vary widely according to many factors, including the patient’s age, overall health, location of the tumor, particular findings on the examination of the biopsy, and of course the depth and stage of the tumor. Survival statistics are generally based on 5-year survival rates rather than raw cure rates. Much of the success reported for the targeted therapies focuses on disease-free time because in many cases the actual 5-year survival is not affected. It is hoped that combination therapy discussed above will change that.
- For stage 1 , 5-year survival is ⥠90%.
- For stage 2 , 5-year survival is 80%-90%.
- For stage 3 , 5-year survival is around 50%.
- For stage 4 , 5-year survival is 10%-25% depending upon sex and other demographic factors.
E Stands For Evolving
One of the biggest warning signs of Melanoma is a mole that evolves or changes over time. Any change in a mole can be cause for concern, including a change in size, shape, color, elevation. Also, if the mole has recently started bleeding, itching or crusting its important you dont delay making an appointment to see Dr. Perri.
What Will Dr. Perri Do if He Suspects I have Melanoma? If dermatologist Dr. Perri suspects you have Melanoma, your safety and health will be his primary priority. Dr. Perri will apply a local anesthetic around the area of the mole, then use a blade to biopsy the mole from your skin. . The biopsied area will then be sutured and bandaged.
The biopsy will involve a lab looking at the mole under a microscope to check for any malignant skin tissue. The biopsy typically takes 2 weeks to perform.
Don’t Miss: Ductal Invasive Carcinoma Survival Rate
Biological Therapies And Melanoma
Biological therapies are treatments using substances made naturally by the body. Some of these treatments are called immunotherapy because they help the immune system fight the cancer, or they occur naturally as part of the immune system.
There are many biological therapies being researched and trialled, which in the future may help treat people with melanoma. They include monoclonal antibodies and vaccine therapy.
You Can Find Skin Cancer On Your Body
The best way to find skin cancer is to examine yourself. When checking, you want to look at the spots on your skin. And you want to check everywhere from your scalp to the spaces between your toes and the bottoms of your feet.
If possible, having a partner can be helpful. Your partner can examine hard-to-see areas like your scalp and back.
Getting in the habit of checking your skin will help you notice changes. Checking monthly can be beneficial. If you have had skin cancer, your dermatologist can tell you how often you should check your skin.
People of all ages get skin cancer
Checking your skin can help you find skin cancer early when its highly treatable.
Don’t Miss: Ductal Carcinoma Breast Cancer Survival Rates
What Is Recurrent Melanoma
Recurrent melanoma refers to a recurrence of tumor at the site of removal of a previous tumor, such as in, around, or under the surgical scar. It may also refer to the appearance of metastatic melanoma in other body sites such as skin, lymph nodes, brain, or liver after the initial tumor has already been treated. Recurrence is most likely to occur within the first five years, but new tumors felt to be recurrences may show up decades later. Sometimes it is difficult to distinguish recurrences from new primary tumors.
What If The Skin Changes Are Rapid Or Dramatic
Guideline # 4: The more rapid and dramatic the change, the less serious the problem.
When changes such as pain, swelling, or even bleeding come on rapidly, within a day or two, they are likely to be caused by minor trauma, often a kind one doesn’t remember . If a spot changes rapidly and then goes back to the way it was within a couple of weeks, or falls off altogether, it is not likely to represent anything serious. Nevertheless, this would be a good time to say once again: Nobody can diagnose him- or herself. If one sees a spot that looks as though it is new or changing, show it to a doctor. If one see a spot that doesn’t look like one’s other spots, it should be evaluated.
You May Like: Treatment For Stage 4 Melanoma
Symptoms Of Subungual Melanoma
- Over weeks to months the pigment band may become wider, especially at its base.
- It usually becomes more irregular in pigmentation and can extend to involve the nail fold, known as Hutchinson Sign.
- The pigmented lesion may ulcerate or bleed.
- The nail bed will be painful.
- A nodule may develop under the nail plate, lifting it up.
- You may see a thinning, cracking or distortion of the nail plate.
- In many cases a subungual melanoma is not pigmented.
How Does The Doctor Know I Have Melanoma
A new spot on your skin or a spot thats changing in size, shape, or color may be a warning sign of melanoma. If you have any of these changes, have your skin checked by a doctor.
The doctor will ask you questions about when the spot on your skin first showed up and if it has changed in size or the way it looks. The rest of your skin will be checked. During the exam your doctor will check the size, shape, color and texture of any skin changes. If signs are pointing to melanoma, more tests will be done.
Also Check: Well Differentiated
When Melanoma Can’t Be Cured
If your cancer has spread and it is not possible to cure it by surgery, your doctor may still recommend treatment. In this case, treatment may help to relieve symptoms, might make you feel better and may allow you to live longer.
Whether or not you choose to have anti-cancer treatment, symptoms can still be controlled. For example, if you have pain, there are effective treatments for this.
General practitioners, specialists and palliative care teams in hospitals all play important roles in helping people with cancer.
The Risks The Causes What You Can Do
Skin cancers like melanoma have damaged DNA in skin cells that lead to uncontrolled growth of these cells. Ultraviolet rays from the sun or tanning beds damage DNA in your skin cells. Your immune system repairs some of this damage but not all. Over time, the remaining DNA damage can lead to mutations that cause skin cancer. Many other factors also play a role in increasing the risk for melanoma, including genetics , skin type or color, hair color, freckling and number of moles on the body.
Understanding what causes melanoma and whether youre at high risk of developing the disease can help you prevent it or detect it early when it is easiest to treat and cure.
These factors increase your melanoma risk:
- Unprotected or excessive UV exposure from the sun or indoor tanning.
- Weakened immune system due to a medical condition or medications.
- Many moles: The more moles you have on your body, the higher your risk for melanoma. Also, having large moles , or any atypical moles, increases the risk for melanoma.
- Fair skin: Melanoma occurs more frequently in people with fair skin, light eyes and light or red hair.
- Skin cancer history: People who have already had melanoma or nonmelanoma skin cancers run a greater risk of developing melanoma in the future.
- Genetics: Melanoma can run in families one in every 10 patients has a family member who also has had the disease.
Read Also: Braf And Melanoma