How Does The Doctor Know I Have Skin Cancer
Basal and squamous skin cancer may look like:
- Flat, firm, pale or yellow areas that look a lot like a scar
- Raised reddish patches that might itch
- Rough or scaly red patches, which might crust or bleed
- Small, pink or red, shiny, pearly bumps, which might have blue, brown, or black areas
- Pink growths or lumps with raised edges and a lower center
- Open sores that dont heal, or that heal and then come back
- Wart-like growths
Staging For Merkel Cell Cancer
Doctors use the TNM system to describe the stage of Merkel cell cancer. Doctors use the results from diagnostic tests and scans to answer these questions:
-
Tumor : How large is the primary tumor? Where is it located?
-
Node : Has the tumor spread to the lymph nodes? If so, where and how many?
-
Metastasis : Has the cancer spread to other parts of the body? If so, where and how much?
The results are combined to determine the stage of Merkel cell cancer for each person.
There are 5 stages: stage 0 and stages I through IV . The stage provides a common way of describing the cancer, so doctors can work together to plan the best treatments.
Stage 0: This is called carcinoma in situ. Cancer cells are found only in the top layers of the skin. The cancer does not involve the lymph nodes, and it has not spread.
Stage I: The primary tumor is 2 centimeters or smaller at its widest part. The cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes or to other parts of the body.
Stage IIA: The tumor is larger than 2 cm and has not spread to the lymph nodes or other parts of the body.
Stage IIB: The tumor has grown into nearby tissues, such as muscles, cartilage, or bone. It has not spread to the lymph nodes or elsewhere in the body.
Stage III: The cancer has spread to the lymph nodes. The tumor can be any size and may have spread to nearby bone, muscle, connective tissue, or cartilage.
Stage IV: The tumor has spread to distant parts of the body, such as the liver, lung, bone, or brain.
Where Does Basal Cell Carcinoma Spread
It’s important to know that basal cell carcinoma can spread to other surrounding tissue and can grow around nerves. I had two separate basal cells that grew around nerves: one in my forehead and one in my upper lip. Both of those surgeries required moving the nerve to remove the cancer, and I was left with permanent numbness in both areas because of that.
Don’t Miss: How Fast Does Subungual Melanoma Grow
Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck Treatment
Surgery is the preferred management method for the majority of squamous cell skin cancers. Low-risk, early stage, small squamous cell cancers can be removed by Mohs surgery, which is a technique that spares normal tissue through repeated intraoperative margin testing, removing only the cancer and leaving adjacent normal tissue. Excision, curettage and desiccation, and cryosurgery can also be used to remove the cancer while sparing normal tissue. Radiation alone is an alternative for low-risk tumors when surgery is not desirable because of cosmetic concerns or medical reasons.
Large tumors and tumors with nerve or lymph node involvement are not suitable for Mohs surgery and require removal of at least 5-millimeter margins of normal tissue around the cancer and neck dissection for involved lymph nodes. Larger tumors require reconstruction, which can be done at the time of surgery if margin status is clear. Reconstruction should be staged when margins status is not clear.
Patients with high-risk tumors should meet with a radiation therapist to discuss postoperative radiation. Chemotherapy may be added to radiation for extensive lymph node involvement or positive margins that cannot be cleared with additional surgery. In patients with high-risk tumors who are not surgical candidates, systemic treatment with both radiation and chemotherapy is used. Such cases require multidisciplinary care by a team of surgeons, radiation oncologists and medical oncologists.
There Is Some Good News
There is some good news! According to the American Cancer Society, basal cell carcinomas rarely metastasize to lymph nodes, organs, or other areas of the body. This doesn’t mean, however, that they should be left untreated. Basal cell carcinoma can spread and do a lot of damage in the area where they form and can become quite disfiguring if they are left to grow.
Don’t Miss: Can You See Skin Cancer
When Should I Call My Doctor
You should have a skin examination by a doctor if you have any of the following:
- A personal history of skin cancer or atypical moles .
- A family history of skin cancer.
- A history of intense sun exposure as a young person and painful or blistering sunburns.
- New or numerous large moles.
- A mole that changes in size, color or shape.
- Any mole that itches, bleeds or is tender.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Receiving a diagnosis of melanoma can be scary. Watch your skin and moles for any changes and seeing your doctor regularly for skin examinations, especially if youre fair-skinned, will give you the best chances for catching melanoma early when its most treatable.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 06/21/2021.
References
Signs And Symptoms Of Melanoma
The most common sign of melanoma is the appearance of a new mole or a change in an existing mole.
This can happen anywhere on the body, but the most commonly affected areas are the back in men and the legs in women.
Melanomas are uncommon in areas that are protected from sun exposure, such as the buttocks and the scalp.
In most cases, melanomas have an irregular shape and are more than 1 colour.
The mole may also be larger than normal and can sometimes be itchy or bleed.
Look out for a mole that gradually changes shape, size or colour.
Superficial spreading melanoma are the most common type of melanoma in the UK.
They’re more common in people with pale skin and freckles, and much less common in people with darker skin.
They initially tend to grow outwards rather than downwards, so they do not pose a problem.
But if they grow downwards into the deeper layers of skin, they can spread to other parts of the body.
You should see a GP if you have a mole that’s getting bigger, particularly if it has an irregular edge.
Recommended Reading: What Is Large Cell Carcinoma
Tests That May Be Done
The doctor will ask you questions about when the spot on your skin first showed up and if it has changed in size or the way it looks or feels. The rest of your skin will be checked. During the exam your doctor will check the size, shape, color and texture of any skin changes. If signs are pointing to skin cancer, more tests will be done.
Skin biopsy
In a biopsy, the doctor takes out a small piece of tissue to check it for cancer cells. A biopsy is the only way to tell for sure if you have skin cancer and what kind it is.
There are many types of skin biopsies. Ask your doctor what kind you will need. Each type has pros and cons. The choice of which type to use depends on your own case.
In rare cases basal and squamous cell skin cancer can spread to the nearby lymph nodes Ask your doctor if your lymph nodes will be tested.
Basal and squamous cell cancers don’t often spread to other parts of the body. But if your doctor thinks your skin cancer might spread, you might need imaging tests, such as MRI or CT scans.
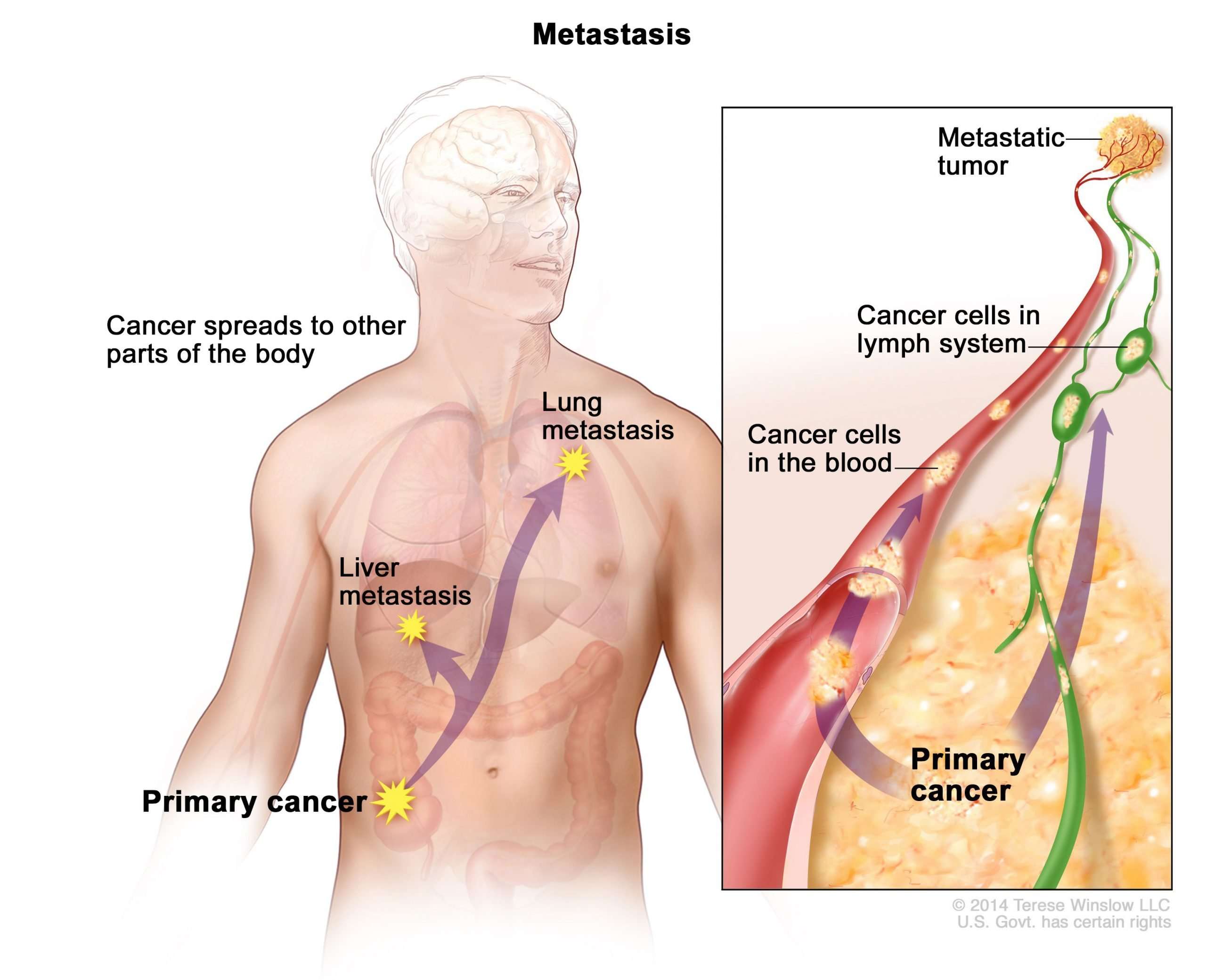
What Is Metastatic Cancer
In metastasis, cancer cells break away from where they first formed , travel through the blood or lymph system, and form new tumors in other parts of the body. The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor.
Cancer that spreads from where it started to a distant part of the body is called metastatic cancer. For many types of cancer, it is also called stage IV cancer. The process by which cancer cells spread to other parts of the body is called metastasis.
When observed under a microscope and tested in other ways, metastatic cancer cells have features like that of the primary cancer and not like the cells in the place where the metastatic cancer is found. This is how doctors can tell that it is cancer that has spread from another part of the body.
Metastatic cancer has the same name as the primary cancer. For example, breast cancer that spreads to the lung is called metastatic breast cancer, not lung cancer. It is treated as stage IV breast cancer, not as lung cancer.
Sometimes when people are diagnosed with metastatic cancer, doctors cannot tell where it started. This type of cancer is called cancer of unknown primary origin, or CUP. See the Carcinoma of Unknown Primary page for more information.
You May Like: Is Melanoma The Worst Cancer
Different Kinds Of Skin Cancer
There are many types of skin cancer. Some are very rare. Your doctor can tell you more about the type you have.
The two most common kinds of skin cancers are:
- Basal cell cancer, which starts in the lowest layer of the skin
- Squamous cell cancer, which starts in the top layer of the skin
Another kind of skin cancer is called melanoma. These cancers start from the color-making cells of the skin . You can read about melanoma in If You Have Melanoma Skin Cancer.
More Information About Basal Cell Carcinoma
The following are some English-language resources that may be useful. Please note that THE MANUAL is not responsible for the content of these resources.
See the following sites for comprehensive information about basal cell carcinoma, including detection, prevention, treatment options, and other resources:
Don’t Miss: How Do You Remove Skin Cancer
What Is The Prognosis Of Metastatic Cancer To Skin
- The prognosis of Metastatic Cancer to Skin depends on many factors such as the severity of signs and symptoms, the number of organ systems affected, and the individual response to treatment
- Individuals, who respond well to treatment, have better prognosis than those who do not respond to treatment
- However, the prognosis is usually poor because skin metastasis often indicates a high-stage cancer. It can result in death
What Are The Different Types Of Melanoma
Melanomas fall into four basic categories.
You May Like: What Happens When Melanoma Spreads
Treatment Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
-
Removal of the tumor
Doctors may remove the cancer in the office by scraping and burning it with an electric needle or by cutting it out. Doctors may destroy the cancer by using extreme cold .
Certain chemotherapy drugs may be applied to the skin. Photodynamic therapy , in which chemicals and a laser are applied to the skin, also may be used. Occasionally, radiation therapy is used.
A technique called Mohs microscopically controlled surgery may be required for some basal cell carcinomas that are large or regrow or occur in certain areas, such as around the nose and eyes.
People whose cancer has spread to nearby tissues or spread to other parts of the body and who are not candidates for surgery or radiation therapy may be given the drug vismodegib or sonidegib taken by mouth.
What Is Metastatic Melanoma
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer. When it spreads to other places in your body, it’s called metastatic, or advanced. You may also hear your doctor refer to it as stage IV melanoma.
Melanoma often spreads to:
Although in many cases metastatic melanoma canât be cured, treatments and support can help you live longer and better. Doctors have therapies that have greatly increased survival rates. And researchers are working to find new medications that can do even more.
Remember: You still have control over the decisions you make about your treatment and your life. It’s important to have people you can talk to about your plans, your fears, and your feelings. So find support and learn about your treatment options. That will help you make the most of your life.
Read Also: How Fast Can Skin Cancer Kill You
How Cancer Can Spread To Other Areas Of The Body
Cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system . There they can start to grow into new tumours.
Cancers are named according to where they first started developing. For example, bowel cancer that has spread to the liver is called bowel cancer with liver metastases or secondaries. It is not called liver cancer. This is because the cancerous cells in the liver are cancerous bowel cells. They are not liver cells that have become cancerous.
Who Gets Metastatic Melanoma
Melanoma usually starts as a single lesion on the skin or mucous membrane. This lesion can progress to the formation of metastases if it is not recognised and treated effectively at an early stage.
Risk factors for the development of melanoma include:
- Age
- A history of previous skin cancer
- A family history of melanoma
- Having large numbers of moles especially atypical moles
- Having fair skin which burns easily
- Having sun-damaged skin.
The risk of melanoma metastasising is highest in an individual with an aggressive rapidly growing melanoma, an unrecognised melanoma, advanced primary melanoma, melanoma that was not completely excised , and/or is immunosuppressed.
Recommended Reading: Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Slow Growing
Basal Cell Carcinoma Staging
Staging is the process of determining whether cancer has spread and, if so, how far. The stage of the disease may affect the treatment plan.
The stage is based on the size of the tumor, how deeply into the skin it has grown, and whether cancer has spread beyond the tumor to the lymph nodes. Your doctor will look at the results of the biopsy to determine the stage. In rare cases, your doctor may recommend imaging such as CT or PET-CT scan to see if the cancer has spread beyond the skin
Stages are numbered in Roman numerals between 0 and IV.
Most non-melanoma skin cancers are Stage 0 or Stage 1. Stage 3 and 4 are relatively rare. Based on the type of cancer, the stage of cancer, your overall health, and other factors, your doctor works with you to develop a treatment plan.
High risk features for primary tumor staging
- Depth/invasion: > 2 mm thickness , Clark level IV, Perineural invasion
- Anatomic: Primary site ear
- Location: Primary site hair-bearing lip
- Differentiation: Poorly differentiated or undifferentiated
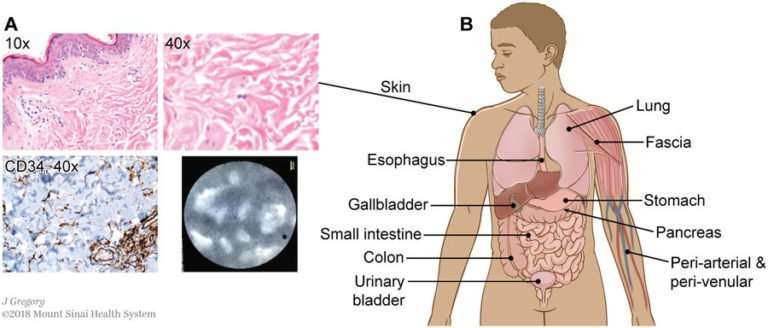
What Is Metastatic Cancer To Skin
Basic information on Metastatic Cancer to Skin is as follows:
- Metastatic Cancer of Skin is a condition where cancers originating from various parts of the body spread to the skin. Metastasis can occur on the skin, either as a single nodule or multiple nodules. If these nodules get large in size, then they can ulcerate and bleed
- Some cancers metastasize to skin more often than other cancer types. Common cancers that metastasize to skin include:
- Melanoma
- Cancer of nasal cavities and nasal sinuses
- Cancer of larynx
- Cancers of endocrine glands
- Cancer of esophagus
- Cancers of kidney
- Stomach cancer
Also Check: What Does Melanoma Under The Toenail Look Like
Mohs Microscopically Controlled Surgery
|
Because skin cancer cells often have spread beyond the edges of the visible patch on the skin, doctors sometimes use a special surgical technique to make sure they remove all of the cancer. In this technique, called Mohs microscopically controlled surgery or Mohs micrographic surgery, doctors first remove the visible tumor and then begin cutting away the edges of the wound bit by bit. During surgery, doctors examine pieces of tissue to look for cancer cells. Tissue removal from the area continues until the samples no longer contain cancer cells. This procedure enables doctors to limit the amount of tissue removed and thus is especially useful for cancers near such important sites as the eye. After removing all of the cancer, doctors decide how best to replace the skin that has been cut away. They may bring the edges of the remaining skin together with sutures or use a skin graft or skin flap. Or they may place dressings on top of the wound and let the skin heal on its own. Mohs surgery reduces recurrence rates for skin cancers. This surgery is useful for basal cell and squamous cell cancers but is less often used for melanoma. |