How Do People Find Bcc On Their Skin
Many people find it when they notice a spot, lump, or scaly patch on their skin that is growing or feels different from the rest of their skin. If you notice any spot on your skin that is growing, bleeding, or changing in any way, see a board-certified dermatologist. These doctors have the most training and experience in diagnosing skin cancer.
To find skin cancer early, dermatologists recommend that everyone check their own skin with a skin self-exam. This is especially important for people who have a higher risk of developing BCC. Youll find out what can increase your risk of getting this skin cancer at, Basal cell carcinoma: Who gets and causes.
Images used with permission of:
-
The American Academy of Dermatology National Library of Dermatologic Teaching Slides.
-
J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 80:303-17.
What Is Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is a cancer that grows on parts of your skin that get a lot of sun. It’s natural to feel worried when your doctor tells you that you have it, but keep in mind that it’s the least risky type of skin cancer. As long as you catch it early, you can be cured.
This cancer is unlikely to spread from your skin to other parts of your body, but it can move nearby into bone or other tissue under your skin. Several treatments can keep that from happening and get rid of the cancer.
The tumors start off as small shiny bumps, usually on your nose or other parts of your face. But you can get them on any part of your body, including your trunk, legs, and arms. If you’ve got fair skin, you’re more likely to get this skin cancer.
Basal cell carcinoma usually grows very slowly and often doesn’t show up for many years after intense or long-term exposure to the sun. You can get it at a younger age if you’re exposed to a lot of sun or use tanning beds.
What Are The Clinical Features Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
BCC is a locally invasive skin tumour. The main characteristics are:
- Slowly growing plaque or nodule
- Skin coloured, pink or pigmented
- Varies in size from a few millimetres to several centimetres in diameter
- Spontaneous bleeding or ulceration
BCC is very rarely a threat to life. A tiny proportion of BCCs grow rapidly, invade deeply, and/or metastasise to local lymph nodes.
Read Also: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
Skin Cancer Types: Basal Cell Carcinoma Overview
All content solely developed by the American Academy of Dermatology
The American Academy of Dermatology gratefully acknowledges the support from Sanofi Genzyme and Regeneron.
Basal cell carcinoma
What is basal cell carcinoma?The most common type of skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma can show up on the skin in many ways.
Is it contagious? No
What Is The Treatment For Advanced Or Metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma
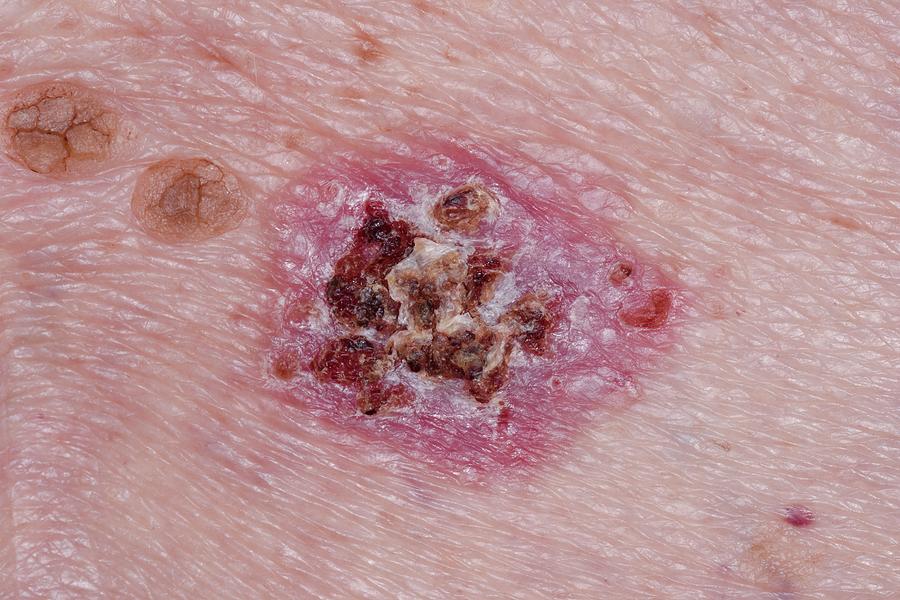
Locally advanced primary, recurrent or metastatic BCC requires multidisciplinary consultation. Often a combination of treatments is used.
- Radiotherapy
- Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy refers to the hedgehog signalling pathway inhibitors, vismodegib and sonidegib. These drugs have some important risks and side effects.
Read Also: Large Cell Carcinoma Definition
Mohs Microscopically Controlled Surgery
|
Because skin cancer cells often have spread beyond the edges of the visible patch on the skin, doctors sometimes use a special surgical technique to make sure they remove all of the cancer. In this technique, called Mohs microscopically controlled surgery or Mohs micrographic surgery, doctors first remove the visible tumor and then begin cutting away the edges of the wound bit by bit. During surgery, doctors examine pieces of tissue to look for cancer cells. Tissue removal from the area continues until the samples no longer contain cancer cells. This procedure enables doctors to limit the amount of tissue removed and thus is especially useful for cancers near such important sites as the eye. After removing all of the cancer, doctors decide how best to replace the skin that has been cut away. They may bring the edges of the remaining skin together with sutures or use a skin graft or skin flap. Or they may place dressings on top of the wound and let the skin heal on its own. Mohs surgery reduces recurrence rates for skin cancers. This surgery is useful for basal cell and squamous cell cancers but is less often used for melanoma. |
What Is A Basal Cell
One of three main types of cells in the top layer of the skin, basal cells shed as new ones form. BCC most often occurs when DNA damage from exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or indoor tanning triggers changes in basal cells in the outermost layer of skin , resulting in uncontrolled growth.
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Prognosis
What Are The Advantages Of Mohs Surgery
The technique offers the highest possible cure rate for the treatment of skin cancer, compared to other therapeutic modalities. Mohs surgery also allows the physician to remove as little normal tissue as possible around the tumor, and thus in many cases can provide a superior cosmetic result. Our doctors also offer a variety of laser treatments to improve the appearance of scars after Mohs surgery. Another advantage is that with many large skin cancers, hospitalization can be avoided by performing Mohs surgery on an out-patient basis.
Treatments For Bowen’s Disease
There are a number of treatment options for Bowen’s disease. Talk to your dermatologist about which treatment is most suitable for you.
The main treatments are:
- cryotherapy liquid nitrogen is sprayed on to the affected skin to freeze it. The procedure may be painful and the skin may remain a bit uncomfortable for a few days. The affected skin will scab over and fall off within a few weeks.
- imiquimod cream or chemotherapy cream this is applied to the affected skin regularly for a few weeks. It may cause your skin to become red and inflamed before it gets better.
- curettage and cautery the affected area of skin is scraped away under local anaesthetic, where the skin is numbed, and heat or electricity is used to stop any bleeding, leaving the area to scab over and heal after a few weeks.
- a light-sensitive cream is applied to the affected skin and a laser is directed on to the skin a few hours later to destroy the abnormal cells. The treatment session lasts about 20 to 45 minutes. You may need more than 1 session.
- surgery the abnormal skin is cut out under local anaesthetic and stitches may be needed afterwards.
In a few cases, your dermatologist may just advise monitoring your skin closely for example, if it’s very slow growing and they feel the side effects of treatment will outweigh the benefits.
You May Like: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Treatment Of Facial Basal Cell Carcinoma: A Review
Vanessa Smith
1Department of Dermatology, Hull Royal Infirmary, Hull and Hull York Medical School , Hull HU2 3JZ, UK
Abstract
Basal cell carcinomas are locally destructive malignancies ofthe skin. They are the most common type of cancer in the westernworld. The lifetime incidence may be up to 39%. UV exposure is themost common risk factor. The majority of these tumours occur on thehead and neck. Despite BCCs being relatively indolent the highincidence means that their treatment now contributes a significant andincreasing workload for the health service. A good understanding ofthe options available is important. Management decisions may beinfluenced by various factors including the patients age andcomorbidities and the lesion subtype and location. Due to theimportance of a good cosmetic and curative outcome for facial BCCstreatment decisions may differ significantly to those that would bemade for BCCs arising elsewhere. There is little good randomizedcontrolled data available comparing treatment modalities. Althoughtraditionally standard excision has been the treatment of choicevarious other options are available including: Mohs micrographicsurgery, curettage and cautery, cryosurgery, radiotherapy, topicalimiquimod, photodynamic therapy and topical 5-fluorouracil. Wediscuss and review the literature and evidence base for the treatmentoptions that are currently available for facial BCCs.
1. Introduction
2.4. Cryosurgery
What Does A Basal Cell Carcinoma Look Like
BCCs can vary greatly in their appearance, but people often first become aware of them as a scab that bleeds and does not heal completely or a new lump on the skin. Some BCCs are superficial and look like a scaly red flat mark on the skin. Others form a lump and have a pearl-like rim surrounding a central crater and there may be small red blood vessels present across the surface. If left untreated, BCCs can eventually cause an ulcer hence the name rodent ulcer. Most BCCs are painless, although sometimes they can be itchy or bleed if caught.
Read Also: Etiology Of Skin Cancer
Medical Treatment For Skin Cancer
Surgical removal is the mainstay of skin cancer treatment for both basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas. For more information, see Surgery.People who cannot undergo surgery may be treated by external radiation therapy. Radiation therapy is the use of a small beam of radiation targeted at the skin lesion. The radiation kills the abnormal cells and destroys the lesion. Radiation therapy can cause irritation or burning of the surrounding normal skin. It can also cause fatigue. These side effects are temporary. In addition, topical chemotherapy creams have been FDA approved for the treatment of certain low-risk nonmelanoma skin cancers. Patients with advanced or many basal cell carcinomas are sometimes prescribed oral pills to block the growth of these cancers. Side effects include muscle spasms, hair loss, taste changes, weight loss and fatigue.
In advanced cases of melanoma, immune therapies, vaccines, or chemotherapy may be used. These treatments are typically offered as clinical trials. Clinical trials are studies of new therapies to see if they can be tolerated and work better than existing therapies.
How Widespread Is Bcc
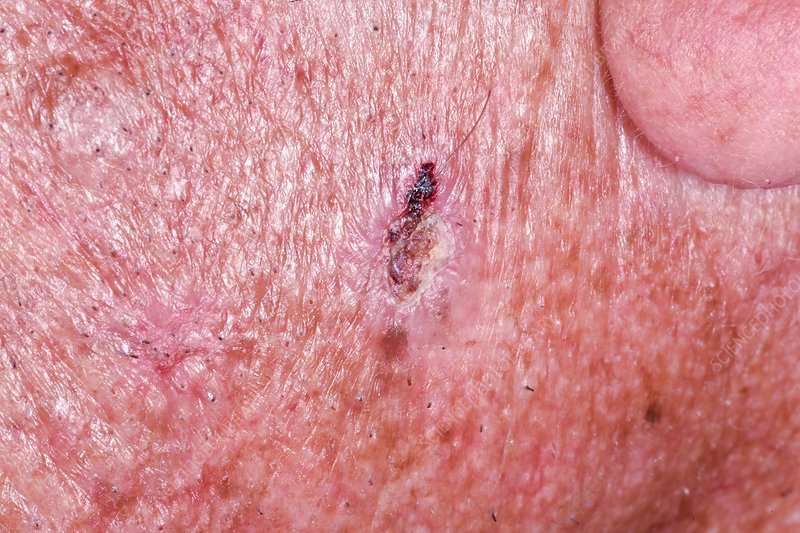
Basal cell carcinoma is quite common, and the number of reported cases in the U.S. has steadily increased.
- An estimated 3.6 million Americans are diagnosed with BCC each year.
- More than one out of every three new cancers are skin cancers, and the vast majority are BCCs.
- The diagnosis and treatment of nonmelanoma skin cancers, including BCC and squamous cell carcinoma , increased up to 77 percent between 1994 and 2014.
Reviewed by:
You May Like: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Prognosis For Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinomas rarely metastasize but may invade healthy tissues. Rarely, patients die because the carcinoma invades or impinges on underlying vital structures or orifices .
Almost 25% of patients with a history of basal cell carcinoma develop a new basal cell cancer within 5 years of the original carcinoma. Consequently, patients with a history of basal cell carcinoma should be seen annually for a skin examination.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Stages
There are several stages of basal cell carcinoma. They start with stage 0, which means cancer has not spread to the deeper layers of skin and is only present in the upper layer. Then the stages progress in the following order:
- Stage 1: The tumor is smaller than one inch wide.
- Stage 2: The tumor is larger than one inch wide.
- Stage 3: Cancer has spread into facial bones and to one lymph node.
- Stage 4: Cancer has spread to one or more lymph nodes and might have spread to bones and organs.
Also Check: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
Read Also: Mayo Clinic Skin Cancer
When To Seek Medical Care For Skin Cancer
Many people, especially those who have fair coloring or have had extensive sun exposure, periodically check their entire body for suspicious moles and lesions.
Have your primary health care provider or a dermatologist check any moles or spots that concern you.
See your health care provider to check your skin if you notice any changes in the size, shape, color, or texture of pigmented areas .
If you have skin cancer, your skin specialist or cancer specialist will talk to you about symptoms of metastatic disease that might require care in a hospital.
Diagnosing Basal Cell Carcinoma
To diagnose basal cell carcinoma your dermatologist will ask about your symptoms, risk factors, family history and other skin conditions and might also look at the suspect area with a dermatoscope a lighted magnifying lens.
If it looks suspicious, your doctor might remove it and send it to a lab. For basal cell carcinoma, its likely that the whole tumor will be removed as part of this skin biopsy.
You May Like: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
You May Like: Malignant Breast Cancer Survival Rate
More Pictures Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
While the above pictures show you some common ways that BCC can appear on the skin, this skin cancer can show up in other ways, as the following pictures illustrate.
Scaly patch with a spot of normal-looking skin in the center
On the trunk, BCC may look like a scaly patch with a spot of normal-looking skin in the center and a slightly raised border, as shown here.
Basal cell carcinoma can be lighter in some areas and darker in others
While BCC tends to be one color, it can be lighter in some areas and darker in others, as shown here.
Basal cell carcinoma can be brown in color
Most BCCs are red or pink however, this skin cancer can be brown, as shown here.
Basal cell carcinoma can look like a group of shiny bumps
BCC can look like a group of small, shiny bumps that feel smooth to the touch.
Basal cell carcinoma can look like a wart or a sore
The BCC on this patients lower eyelid looks like a wart* in one area and a sore** in another area.
If you see a spot or growth on your skin that looks like any of the above or one that is growing or changing in any way, see a board-certified dermatologist.
The Most Common Skin Cancer
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer and the most frequently occurring form of all cancers. In the U.S. alone, an estimated 3.6 million cases are diagnosed each year. BCCs arise from abnormal, uncontrolled growth of basal cells.
Because BCCs grow slowly, most are curable and cause minimal damage when caught and treated early. Understanding BCC causes, risk factors and warning signs can help you detect them early, when they are easiest to treat and cure.
You May Like: Treatment For Stage 3 Melanoma
Is Bowen’s Disease Serious
Bowen’s disease itself is not usually serious. It tends to grow very slowly over months or years, and there are several very effective treatments for it.
The concern is that Bowen’s disease can eventually develop into a different type of skin cancer called squamous cell skin cancer if it’s left undiagnosed or neglected.
It’s estimated this happens in up to 1 in 20 to 1 in 30 people with untreated Bowen’s disease.
Squamous cell skin cancer is often treatable, but it can spread deeper into the body and is sometimes very serious.
Basal Cell Carcinoma: The Most Common Skin Cancer
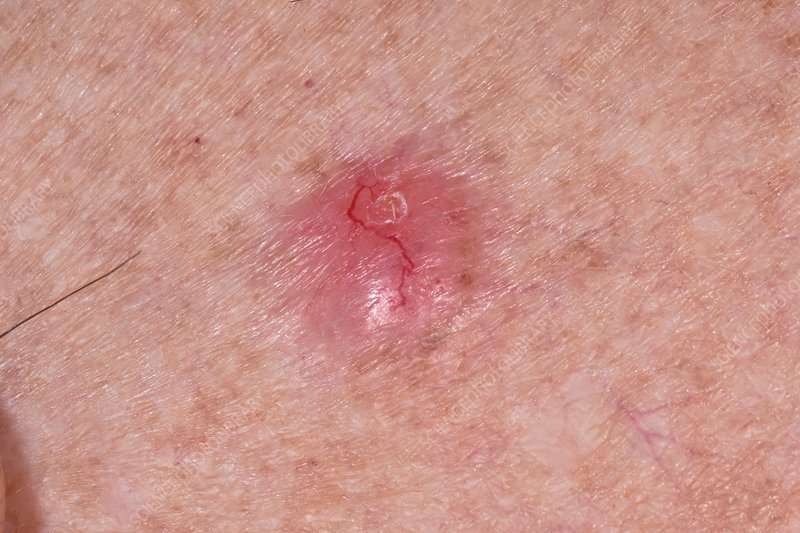
Basal cell carcinoma, which is also called basal cell skin cancer, is the most common form of skin cancer, accounting for about 80 percent of all cases.
Rates of basal cell carcinoma have been increasing. Experts believe this is due to more sun exposure, longer lives, and better skin cancer detection methods.
This type of cancer begins in the skins basal cells, which are found in the outermost layer, the epidermis. They usually develop on areas that are exposed to the sun, like the face, head, and neck.
Basal cell carcinomas may look like:
- A flesh-colored, round growth
- A pinkish patch of skin
- A bleeding or scabbing sore that heals and then comes back
They typically grow slowly and dont spread to other areas of the body. But, if these cancers arent treated, they can expand deeper and penetrate into nerves and bones.
Though its rare, basal cell carcinoma can be life-threatening. Experts believe that about 2,000 people in the United States die each year from basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma.
Some risk factors that increase your chances of having a basal cell carcinoma include:
- Being exposed to the sun or indoor tanning
- Having a history of skin cancer
- Being over age 50
- Having chronic infections, skin inflammation, or a weakened immune system
- Being exposed to industrial compounds, radiation, coal tar, or arsenic
- Having an inherited disorder, such as nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome or xeroderma pigmentosum
Also Check: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma: The most common type of skin cancer, which commonly presents as a sore that seems to get better and then recurs and may start to bleed. Basal cell carcinoma often occurs on the face and neck, where the skin is exposed to sunlight. These tumors are locally invasive and tend to burrow in but not metastasize to distant locations.
©1996-2021 MedicineNet, Inc. All rights reserved. Terms of Use.
MedicineNet does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. See additional information.
Health Categories
What Causes Basal And Squamous Cell Skin Cancers
While many risk factors for basal and squamous cell skin cancers have been found, its not always clear exactly how these factors might cause cancer.
Most basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers are caused by repeated and unprotected skin exposure to ultraviolet rays from sunlight, as well as from man-made sources such as tanning beds.
UV rays can damage the DNA inside skin cells. DNA is the chemical in each of our cells that makes up our genes, which control how our cells function. We usually look like our parents because they are the source of our DNA. But DNA affects more than just how we look.
Some genes help control when our cells grow, divide into new cells, and die:
- Genes that help cells grow, divide, and stay alive are called oncogenes.
- Genes that keep cell growth in check by slowing down cell division or causing cells to die at the right time are called tumor suppressor genes.
Cancers can be caused by DNA changes that keep oncogenes turned on, or that turn off tumor suppressor genes. These types of gene changes can lead to cells growing out of control.
Researchers dont yet know all of the DNA changes that result in basal or squamous cell skin cancer, but they have found that in many skin cancers the cells have changes in tumor suppressor genes.
These are not the only gene changes that play a role in the development of skin cancer. There are many others as well.
Recommended Reading: Does Skin Cancer Itch And Burn
You May Like: Squamous Cell Carcinoma Skin Metastasis