How Common Is Melanoma
Melanoma accounts for only about 1% of all skin cancers, but causes the great majority of skin cancer-related deaths. Its one of the most common cancers in young people under 30, especially in young women.
Melanoma incidence has dramatically increased over the past 30 years. Its widely accepted that increasing levels of ultraviolet exposure are one of the main reasons for this rapid rise in the number of melanoma cases.
Read Also: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
How Do People Find Signs Of Melanoma On Their Own Skin
Performing a skin self-exam as often as recommended by your dermatologist is the best way. While examining your skin, you want to look for the following:
-
Mole that is changing in any way
-
Spot that looks different from the rest of the spots on your skin
-
Growth or spot on your skin that itches, bleeds, or is painful
-
Band of color beneath or around a nail
-
Sore that doesnt heal or heals and returns
The ABCDEs of melanoma can help you find changes to a mole, freckle, or other spot on your skin.
Is A Melanoma Raised Or Flat
Usually melanomas develop in or around an existing mole. Signs and symptoms of melanoma vary depending on the exact type and may include: A flat or slightly raised, discolored patch with irregular borders and possible areas of tan, brown, black, red, blue or white
Read Also: Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer Prognosis
What Are The Survival Rates For Metastatic Melanoma
Survival rates for melanoma, especially for metastatic melanoma, vary widely according to many factors, including the patient’s age, overall health, location of the tumor, particular findings on the examination of the biopsy, and of course the depth and stage of the tumor. Survival statistics are generally based on 5-year survival rates rather than raw cure rates. Much of the success reported for the targeted therapies focuses on disease-free time because in many cases the actual 5-year survival is not affected. It is hoped that combination therapy discussed above will change that.
- For stage 1 , 5-year survival is ⥠90%.
- For stage 2 , 5-year survival is 80%-90%.
- For stage 3 , 5-year survival is around 50%.
- For stage 4 , 5-year survival is 10%-25% depending upon sex and other demographic factors.
What Are The Melanoma Stages And What Do They Mean
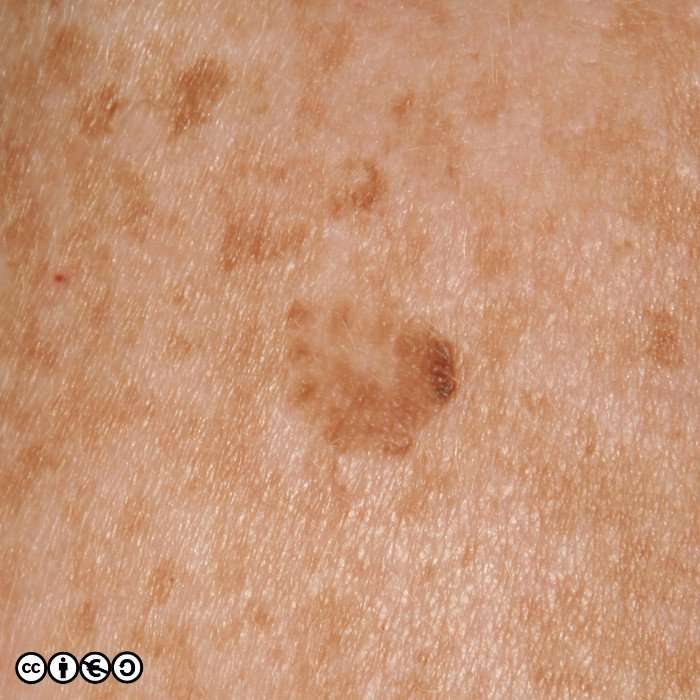
Early melanomas
Stage 0 and I are localized, meaning they have not spread.
- Stage 0: Melanoma is localized in the outermost layer of skin and has not advanced deeper. This noninvasive stage is also called melanoma in situ.
- Stage I: The cancer is smaller than 1 mm in Breslow depth, and may or may not be ulcerated. It is localized but invasive, meaning that it has penetrated beneath the top layer into the next layer of skin. Invasive tumors considered stage IA are classified as early and thin if they are not ulcerated and measure less than 0.8 mm.
Find out about treatment options for early melanomas.
Intermediate or high-risk melanomas
Localized but larger tumors may have other traits such as ulceration that put them at high risk of spreading.
- Stage II: Intermediate, high-risk melanomas are tumors deeper than 1 mm that may or may not be ulcerated. Although they are not yet known to have advanced beyond the primary tumor, the risk of spreading is high, and physicians may recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy to verify whether melanoma cells have spread to the local lymph nodes. Thicker melanomas, greater than 4.0 mm, have a very high risk of spreading, and any ulceration can move the disease into a higher subcategory of stage II. Because of that risk, the doctor may recommend more aggressive treatment.
Learn more about sentinel lymph node biopsy and melanoma treatment options.
Advanced melanomas
Read Also: Can You Get Cancer In The Back Of Your Neck
What Are The Symptoms Of Skin Cancer
Talk to your doctor if you notice changes in your skin such as a new growth, a sore that doesnt heal, a change in an old growth, or any of the A-B-C-D-Es of melanoma.
A change in your skin is the most common sign of skin cancer. This could be a new growth, a sore that doesnt heal, or a change in a mole.external icon Not all skin cancers look the same.
For melanoma specifically, a simple way to remember the warning signs is to remember the A-B-C-D-Es of melanoma
- A stands for asymmetrical. Does the mole or spot have an irregular shape with two parts that look very different?
- B stands for border. Is the border irregular or jagged?
- C is for color. Is the color uneven?
- D is for diameter. Is the mole or spot larger than the size of a pea?
- E is for evolving. Has the mole or spot changed during the past few weeks or months?
Talk to your doctor if you notice changes in your skin such as a new growth, a sore that doesnt heal, a change in an old growth, or any of the A-B-C-D-Es of melanoma.
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Metastatic Melanoma
Look For The Signs Of Melanoma
When this skin cancer develops on a foot, you may see the ABCDEs of melanoma, but its also possible for a melanoma to have different features. Aside from looking like a changing mole, a melanoma on the foot can appear as a:
-
Brown or black vertical line under a toenail
-
Pinkish-red spot or growth
-
New spot or growth where you injured your foot
-
Rapidly growing mass on your foot, especially where you once injured your foot
-
Non-healing sore on your foot
-
Sore that looks like a diabetic ulcer
Sometimes, melanoma on the foot feels painful, bleeds, or itches, but not always. The bleeding tends to stop and start.
The following pictures show you what melanoma can look like on the foot.
Melanoma on the bottom of a toe
You can see some of the ABCDEs of melanoma. One half of this spot is unlike the other, it has an uneven border, and the color varies within the spot.
Melanoma on the bottom of a foot
Here, you can also see some of ABCDEs of melanoma, such as one half is unlike the other and it is larger than the eraser on a pencil.
Melanoma on the bottom of the foot
In this picture, you can see some of the ABCDEs of melanoma, such as more than one color, uneven border, and one half is unlike the other.
Melanoma beneath a toenail
On the feet and hands, melanoma can begin as a dark vertical line underneath a nail.
Melanoma on a callused heel
You may see melanoma that is brown, black, reddish pink, or flesh colored, and it can appear in just about any shape.
Read Also: Is Melanoma Cancer Curable
Who Gets Skin Cancer And Why
Sun exposure is the biggest cause of skin cancer. But it doesn’t explain skin cancers that develop on skin not ordinarily exposed to sunlight. Exposure to environmental hazards, radiation treatment, and even heredity may play a role. Although anyone can get skin cancer, the risk is greatest for people who have:
- Fair skin or light-colored eyes
- An abundance of large and irregularly-shaped moles
- A family history of skin cancer
- A history of excessive sun exposure or blistering sunburns
- Lived at high altitudes or with year-round sunshine
- Received radiation treatments
When Melanoma Can’t Be Cured
If your cancer has spread and it is not possible to cure it by surgery, your doctor may still recommend treatment. In this case, treatment may help to relieve symptoms, might make you feel better and may allow you to live longer.
Whether or not you choose to have anti-cancer treatment, symptoms can still be controlled. For example, if you have pain, there are effective treatments for this.
General practitioners, specialists and palliative care teams in hospitals all play important roles in helping people with cancer.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Cancer Prognosis
What Are The Signs Of Melanoma
Knowing how to spot melanoma is important because early melanomas are highly treatable. Melanoma can appear as moles, scaly patches, open sores or raised bumps.
Use the American Academy of Dermatology’s “ABCDE” memory device to learn the warning signs that a spot on your skin may be melanoma:
- Asymmetry: One half does not match the other half.
- Border: The edges are not smooth.
- Color: The color is mottled and uneven, with shades of brown, black, gray, red or white.
- Diameter: The spot is greater than the tip of a pencil eraser .
- Evolving: The spot is new or changing in size, shape or color.
Some melanomas don’t fit the ABCDE rule, so tell your doctor about any sores that won’t go away, unusual bumps or rashes or changes in your skin or in any existing moles.
Another tool to recognize melanoma is the ugly duckling sign. If one of your moles looks different from the others, its the ugly duckling and should be seen by a dermatologist.
What Are The Causes And Risk Factors For Melanoma
Guideline # 5: Individual sunburns do raise one’s risk of melanoma. However, slow daily sun exposure, even without burning, may also substantially raise someone’s risk of skin cancer.
Factors that raise one’s risk for melanoma include the following:
- Caucasian ancestry
- Fair skin, light hair, and light-colored eyes
- A history of intense, intermittent sun exposure, especially in childhood
- Many moles
- Large, irregular, or “funny looking” moles
- Close blood relatives — parents, siblings, and children — with melanoma
The presence of close family with melanoma is a high risk factor, although looking at all cases of melanoma, only 10% of cases run in families.
Having a history of other sun-induced skin cancers raises one’s risk of melanoma because they are markers of long-term sun exposure. The basic cell type is different, however, and a basal cell or squamous cell carcinoma cannot “turn into melanoma” or vice versa.
It is no longer recommended to do large batteries of screening tests on patients with thin, uncomplicated melanoma excisions, but patients who have had thicker tumors diagnosed or who already have signs and symptoms of metastatic melanoma may need to have MRIs, PET scans, CT scans, chest X-rays, or other X-rays of bones when there is a concern of metastasis.
The biopsy report may show any of the following:
In general, early localized melanoma is treated by surgery alone.
Recommended Reading: Survival Rate Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
How Do You Treat Stage 4 Melanoma
The good news is that even stage 4 melanoma can be treated. The sooner the cancer is found, the sooner it can be removed and the higher your chances are for recovery. Stage 4 melanoma also has the most treatment options, but these options depend on:
- where the cancer is
- how advanced the cancer has become
- your age and overall health
How you respond to treatment also affects your treatment options. The five standard treatments for melanoma are:
- surgery: to remove the primary tumor and affected lymph nodes
- chemotherapy: a drug treatment to stop growth of cancer cells
- radiation therapy: the application of high-energy X-rays to inhibit growth and cancer cells
- immunotherapy: treatment to boost your immune system
- targeted therapy: the use of drugs or other substances to attack cancer drugs
Other treatments may also depend on where the cancer has spread to. Your doctor will discuss your options with you to help map out a treatment plan.
You May Like: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Risk Of Further Melanomas
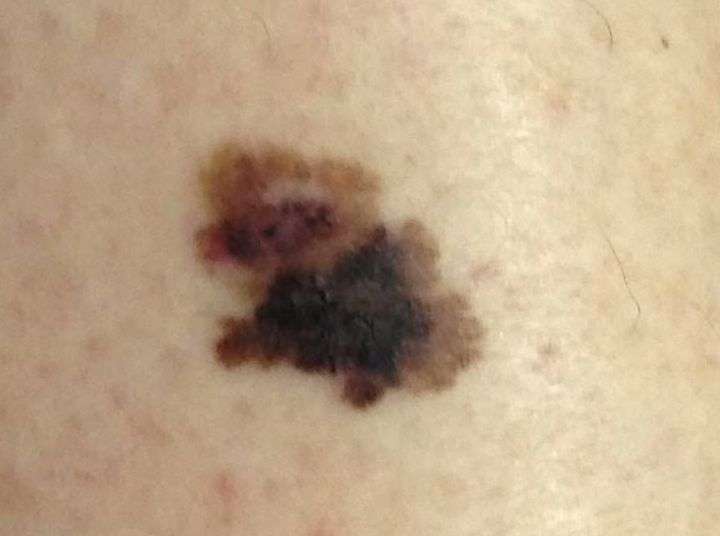
Most people treated for early melanoma do not have further trouble with the disease. However, when there is a chance that the melanoma may have spread to other parts of your body, you will need regular check-ups.
Your doctor will decide how often you will need check-ups everyone is different. They will become less frequent if you have no further problems.
After treatment for melanoma it is important to limit exposure to the sun’s UV radiation. A combination of sun protection measures should be used during sun protection times .
As biological family members usually share similar traits, your family members may also have an increased risk of developing melanoma and other skin cancers. They can reduce their risk by spending less time in the sun and using a combination of sun protection measures during sun protection times.
It is important to monitor your skin regularly and if you notice any changes in your skin, or enlarged lymph glands near to where you had the cancer, see your specialist as soon as possible.
You May Like: Stage 5 Cancer Symptoms
How Can You Tell If A Spot Is Melanoma See Your Doctor
If you are concerned about a mole or mark on your skin and have not had it examined by a doctor, the only safe thing to do is to make a doctors appointment and have it checked out.
Your doctor may inform you that you should just keep an eye on it and report back if you notice any changes.
In this case, you can ask your doctor whether tracking the lesion and the rest of your skin with photos is something they would recommend.
Mole Mapping Guide
Find out how Mole mapping can be a helpful solution for the early detection of skin cancer.
Looking For Signs Of Skin Cancer
Non melanoma skin cancers tend to develop most often on skin thats exposed to the sun.
To spot skin cancers early it helps to know how your skin normally looks. That way, youll notice any changes more easily.
To look at areas you cant see easily, you could try using a hand held mirror and reflect your skin onto another mirror. Or you could get your partner or a friend to look. This is very important if youre regularly outside in the sun for work or leisure.
You can take a photo of anything that doesnt look quite right. If you can its a good idea to put a ruler or tape measure next to the abnormal area when you take the photo. This gives you a more accurate idea about its size and can help you tell if its changing. You can then show these pictures to your doctor.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 2 Survival Rate
Also Check: Melanoma 3c
What Is Nodular Melanoma
All forms of melanoma occur when the melanocytes in your skin reproduce too fast and cause tumors to form. Melanocytes are the cells responsible for giving your skin its color.
In nodular melanoma, a bump, or nodule, will form on your skin. If not detected and treated early, the cancerous cells can spread into your skin and then to other parts of your body.
Nodular melanoma grows faster than other forms of melanoma, making it the most aggressive type of skin cancer.
Can You Get Melanoma In The Mouth
Because oral malignant melanomas are often clinically silent, they can be confused with a number of asymptomatic, benign, pigmented lesions. Oral melanomas are largely macular, but nodular and even pedunculated lesions occur. Pain, ulceration, and bleeding are rare in oral melanoma until late in the disease.
Read Also: Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rate
How Is Melanoma Diagnosed
If you have a mole or other spot that looks suspicious, your doctor may remove it and look at it under the microscope to see if it contains cancer cells. This is called a biopsy.
After your doctor receives the skin biopsy results showing evidence of melanoma cells, the next step is to determine if the melanoma has spread. This is called staging. Once diagnosed, melanoma will be categorized based on several factors, such as how deeply it has spread and its appearance under the microscope. Tumor thickness is the most important characteristic in predicting outcomes.
Melanomas are grouped into the following stages:
- Stage 0 : The melanoma is only in the top layer of skin .
- Stage I: Low-risk primary melanoma with no evidence of spread. This stage is generally curable with surgery.
- Stage II: Features are present that indicate higher risk of recurrence, but there is no evidence of spread.
- Stage III: The melanoma has spread to nearby lymph nodes or nearby skin.
- Stage IV: The melanoma has spread to more distant lymph nodes or skin or has spread to internal organs.
What Are The Signs Of Symptoms Of Metastatic Melanoma
Signs and symptoms depend upon the site of metastasis and the amount of tumor there. Metastases to the brain may first appear as headaches, unusual numbness in the arms and legs, or seizures. Spread to the liver may be first identified by abnormal blood tests of liver function long before the patient has jaundice, a swollen liver, or any other signs of liver failure. Spread to the kidneys may cause pain and blood in the urine. Spread to the lungs may cause shortness of breath, other trouble breathing, chest pain, and continued cough. Spread to bones may cause bone pain or broken bones called pathologic fractures. A very high tumor burden may lead to fatigue, weight loss, weakness and, in rare cases, the release of so much melanin into the circulation that the patient may develop brown or black urine and have their skin turn a diffuse slate-gray color. The appearance of multiple blue-gray nodules in the skin of a melanoma patient may indicate widespread melanoma metastases to remote skin sites.
Recommended Reading: Small Blue Cell Tumor Prognosis
What Does Early Signs Of Melanoma Look Like
What Does Melanoma Look Like?
- Asymmetry: The shape of one half does not match the other half.
- Border that is irregular: The edges are often ragged, notched, or blurred in outline.
- Color that is uneven: Shades of black, brown, and tan may be present.
- Diameter: There is a change in size, usually an increase.
13.10.2011