Prognostic Systems For Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
Two similar prognostic systems are commonly used to calculate risk in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma . The Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center /Motzer score includes the following criteria :
- Time from diagnosis to systemic treatment less than 1 year
- Hemoglobin concentration below the lower limit of normal
- Serum calcium concentration > 10 mg/dL
- Lactate dehydrogenase level more than 1.5 times the upper limit of normal
- Performance status less than 80%
The International Metastatic RCC Database Consortium risk model, validated and further developed by Heng et al, includes the following prognostic criteria :
- Time from diagnosis to systemic treatment less than 1 year
- Karnofsky performance status less than 80%
- Hemoglobin concentration below LLN
- Platelet count above the ULN
- Neutrophil count above the ULN
Both systems categorize patients into the following 3 risk groups:
- Favorable risk â Median survival 20 months 2-year overall survival 75%
- Intermediate risk â Median survival 10 months 2y OS 53%
- Poor/high risk group â Median survival 4 months 2y OS 7%
Review of an external validation cohort of 4657 patients treated for kidney cancer in clinical trials from 2003 to 2013 also demonstrated longer overall survival in obese patients, with median overall survivals of 23.4 months versus 14.5 months for those with low BMI.
How Is Renal Cell Carcinoma Diagnosed
If your doctor suspects that you may have RCC, theyll ask about your personal and family medical history. Theyll then do a physical exam. Findings that can indicate RCC include swelling or lumps in the abdomen, or, in men, enlarged veins in the scrotal sac .
If RCC is suspected, your doctor will order a number of tests to get an accurate diagnosis. These may include:
- complete blood count a blood test conducted by drawing blood from your arm and sending it to a lab for evaluation
- CT scan an imaging test that allows your doctor to take a closer look at your kidneys to detect any abnormal growth
- abdominal and kidney ultrasounds a test that uses sound waves to create a picture of your organs, allowing your doctor to look for tumors and problems within the abdomen
- urine examination tests used to detect blood in the urine and to analyze cells in the urine looking for evidence of cancer
- biopsy the removal of a small piece of kidney tissue, done by inserting a needle into the tumor and drawing out a tissue sample, which is then sent to a pathology lab to rule out or confirm the presence of cancer
If you are found to have RCC, more tests will be done to find out if and where the cancer has spread. This is called staging. RCC is staged from stage 1 to stage 4, in order of ascending severity. Staging tests can include a bone scan, PET scan, and chest X-ray.
Approximately one-third of individuals with RCC have cancer that has spread at the time of diagnosis.
What Is Renal Cell Carcinoma
It’s the most common type of kidney cancer. Although itâs a serious disease, finding and treating it early makes it more likely that youâll be cured. No matter when youâre diagnosed, you can do certain things to ease your symptoms and feel better during your treatment.
Most people who have renal cell carcinoma are older, usually between ages 50 and 70. It often starts as just one tumor in a kidney, but sometimes it begins as several tumors, or itâs found in both kidneys at once. You might also hear it called renal cell cancer.
Doctors have different ways to treat renal cell carcinoma, and scientists are testing new ones, too. Youâll want to learn as much about your disease as you can and work with your doctor so you can choose the best treatment.
Don’t Miss: Non Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Renal Cell Carcinoma: Diagnosis And Management
RICHARD E. GRAY, DO, and GABRIEL T. HARRIS, MD, Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, Bethesda, Maryland
Am Fam Physician. 2019 Feb 1 99:179-184.
Kidney cancer is one of the 10 most common cancers in the United States with 90% being attributed to renal cell carcinoma. Men, especially black men, are more likely to be affected than women. Renal masses, either cystic or solid, are best detected with contrast-enhanced, triple-phase computed tomography. Renal tumors are often detected incidentally during a computed tomography scan of the abdomen or chest that was ordered for unrelated symptoms. Hematuria serves as a warning sign that necessitates further evaluation and imaging leading to a diagnosis and treatment plan. Treatment options include active surveillance, ablation, nephron-sparing tumor excision, nephrectomy, and systemic treatment. Predictors of a poor prognosis include poor functional status and metastasis. In recent years new therapies have improved the prognosis for patients with metastatic disease. The family physician should be aware of risk factors and lifestyle and dietary modifications that may reduce risk.
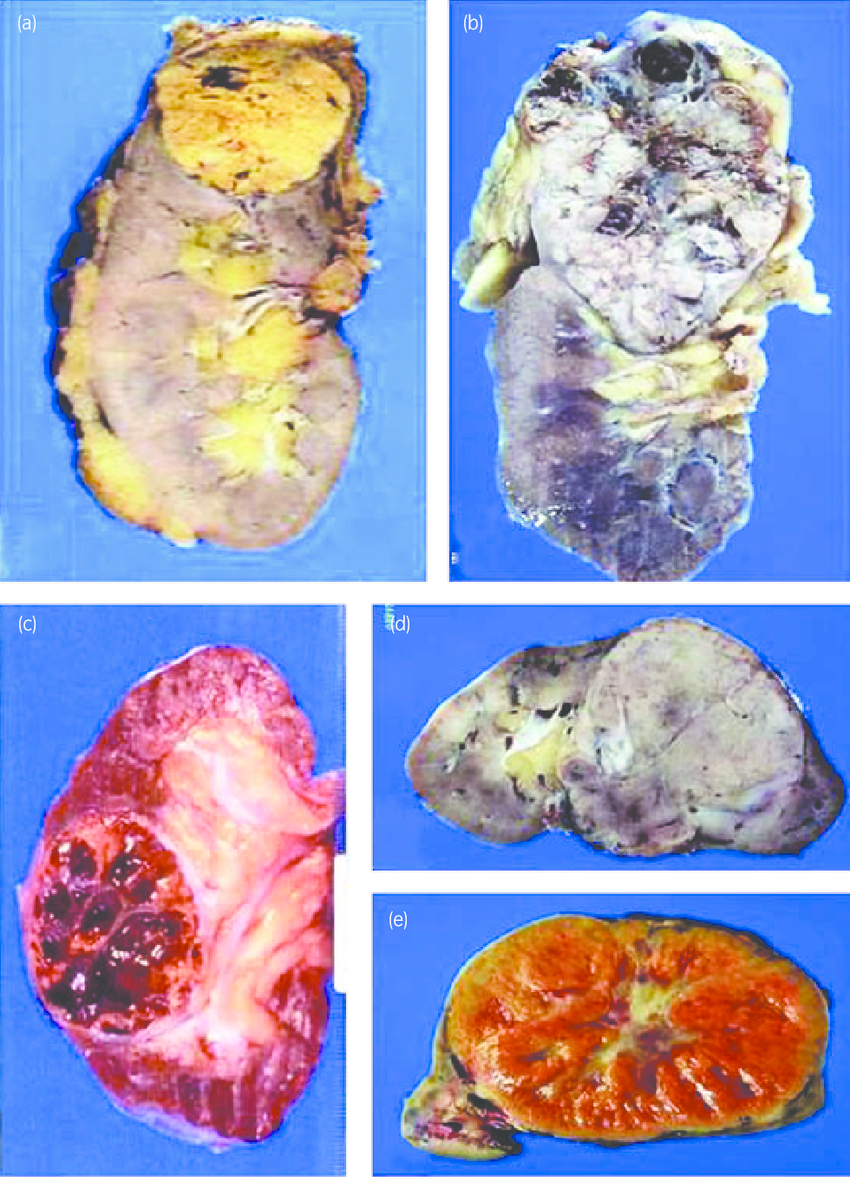
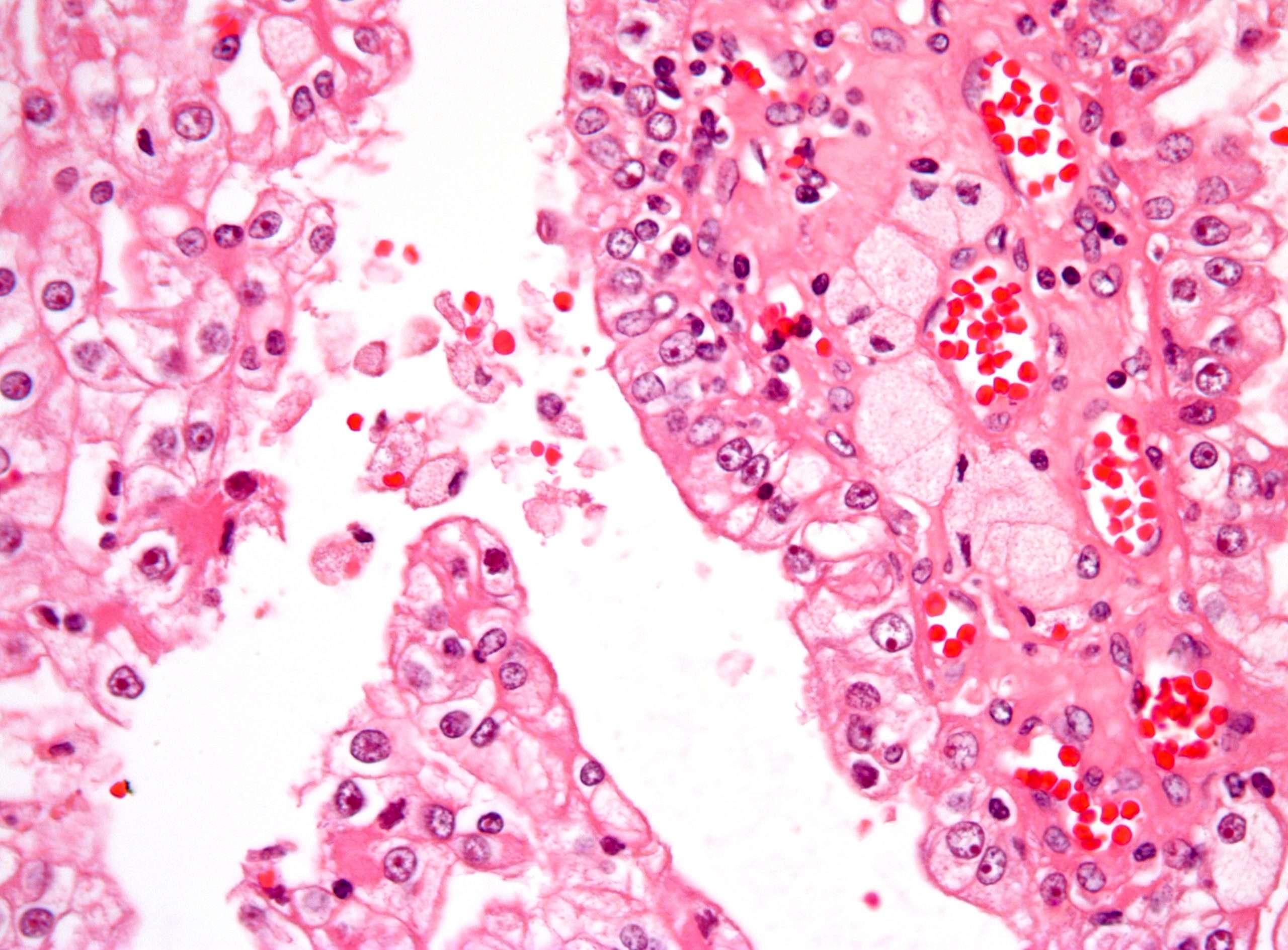
Renal cell carcinoma is classified in three major histological subtypes: clear cell , papillary , and chromophobe .4 Disease-specific survival is worst with clear cell renal cell carcinoma as it tends to be discovered at a more advanced stage.5
Also Check: Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Be Fatal
Patients May Want To Think About Taking Part In A Clinical Trial
For some patients, taking part in a clinical trial may be the best treatment choice. Clinical trials are part of the cancer research process. Clinical trials are done to find out if new cancer treatments are safe and effective or better than the standard treatment.
Many of today’s standard treatments for cancer are based on earlier clinical trials. Patients who take part in a clinical trial may receive the standard treatment or be among the first to receive a new treatment.
Patients who take part in clinical trials also help improve the way cancer will be treated in the future. Even when clinical trials do not lead to effective new treatments, they often answer important questions and help move research forward.
Also Check: Well Differentiated Carcinoma
Collecting Duct And Other Rare Forms Of Rcc
Collecting duct RCC is a rare but highly aggressive tumor of the distal nephron that shows LOH of chromosome 1q, 6p, 8p, 13q and 21q . Mapping of chromosome 1q , 8p and 13q have narrowed down the region but not yet identified the target suppressor genes. Renal medullary carcinoma described in African-Americans and associated with sickle cell trait, mucinous tubulocystic RCC and other rare forms of RCC have been reviewed in Srigley and Delahunt 2009 .
How Common Is Kidney Cancer
The American Cancer Societys most recent estimates for kidney cancer in the United States for 2021 are:
- About 76,080 new cases of kidney cancer will be diagnosed.
- About 13,780 people will die from this disease
These numbers include all types of kidney and renal pelvis cancers.
Most people with kidney cancer are older. The average age of people when they are diagnosed is 64 with most people being diagnosed between ages 65 and 74. Kidney cancer is very uncommon in people younger than age 45.
Kidney cancer is about twice as common in men than in women and it is more common in African Americans and American Indian /Alaska Natives.
You May Like: How Common Is Renal Cell Carcinoma
Also Check: Skin Cancer Prognosis
What Is The Treatment For Renal Cell Carcinoma
Treatment for renal cell carcinoma may involve local and/or systemic therapies.
Local therapies treat the tumor without affecting the rest of the body. These treatments are often used for earlier stage cancers and may include:
- Active surveillance
- Some small kidney tumors are benign and about 75% of small kidney cancers are slow growing
- This approach involves no treatment and watching the tumor carefully with imaging tests every 3 to 6 months to see if it grows
- Often used for elderly or frail patients to avoid the risks of treatment
Systemic treatments are medications taken orally or injected directly into the bloodstream that can reach cancer cells almost anywhere in the body. Depending on the type of kidney cancer, a number of different types of drugs might be used, such as:
- Targeted drug therapy
Treatment Of Stage Ii Renal Cell Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
- Surgery , before or after radiation therapy.
- Radiation therapy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms in patients who cannot have surgery.
- Arterial embolization as palliative therapy.
- A clinical trial of a new treatment.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Read Also: How Long Until Melanoma Spreads
Cancer May Spread From Where It Began To Other Parts Of The Body
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if renal cell cancer spreads to the bone, the cancer cells in the bone are actually cancerous renal cells. The disease is metastatic renal cell cancer, not bone cancer.
Risk Prevention And Early Detection Of Rcc
Individuals with inherited syndromes that predispose to RCC and long-term dialysis patients are at high risk but account for a minority of RCC cases. Algorithms of relative risk of RCC according to smoking status, body mass index and blood pressure have been investigated and a decrease in risk was observed for men who had stopped smoking for 30 years or more . The only evidence for the potential of chemoprevention for RCC are studies which show diets rich in fruit and vegetables as well as high vitamin D levels to be preventive . Candidates for a future chemopreventive strategy would be inherited RCC, ESRD patients and also RCC patients at high risk of recurrence.
Molecular early detection strategies must be designed with careful regard to the abundance of tumor cells in the clinical specimen as well as the frequency and timing of the alteration to be detected . LOH of 3p and point mutation of VHL are frequent and early in clear cell RCC but urine or blood contain a low ratio of DNA from renal tumor cells to DNA from normal cells that is insufficient for the robust detection of these alterations by polymorphic marker and sequencing analysis respectively. Because point mutations occur throughout the VHL gene, rather than at hotspots of particular codons like RAS, the design of more sensitive oligonucleotide molecular tests is very complicated. However, if a tumor cell-rich biopsy specimen is available, LOH and point mutation can be assessed as prognostic markers.
Recommended Reading: What Is Clear Cell Carcinoma
Symptoms Of Kidney Cancer
In many cases, there are no obvious symptoms at first and kidney cancer may only be found during tests for another condition or reason.
If there are symptoms, they can include:
- blood in your pee you may notice your pee is darker than usual or reddish in colour
- a persistent pain in your lower back or side, just below your ribs
- a lump or swelling in your side
Treatments For Renal Cell Carcinoma
There are five kinds of standard treatments for RCC. One or more may be used to treat your cancer.
Also Check: Well Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Prognosis
On This World Cancer Day We Bring Your Attention To Renal Cell Carcinoma A Deadly Oncological Disease Which Is Two Times More Common In Men Than Women
Written by Editorial Team | Updated : February 4, 2022 2:31 PM IST
Renal cell carcinoma is one of the deadliest urological malignancy and accounts for three per cent of oncological diseases in men. It occurs in sporadic and familial forms. The familial RCC occurs more in the young, usually bilateral and multifocal. The sporadic form occurs mainly in the sixth and seventh decade of life. It is usually unilateral and fairly predictable however, its clinical presentation tends to vary with age. An insidious onset and late presentation were documented in the older adults. Most of the renal cell carcinoma are seen in 60-70 years of life, Young onset renal cell carcinomas are rare and accounts for four to seven per cent of total incidences. This type of cancer is also two times more common in men than women.
Treatment Of Stage I Renal Cell Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
- Arterial embolization as palliative therapy.
- A clinical trial of a new treatment.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Also Check: What Does Early Squamous Skin Cancer Look Like
Don’t Miss: Well Differentiated
Tnm Staging And The Stages Of Kidney Cancer
Kidney cancer is described in stages that the American Joint Committee on Cancer developed. The system is better known as the TNM system.
- T refers to the tumor. Doctors assign a T with a number thats based on the size and growth of the tumor.
- N describes whether the cancer has spread to any nodes in the lymph system.
- M means the cancer has metastasized.
Based on the characteristics above, doctors assign RCC a stage. The stage is based on the size of the tumor and the spread of the cancer.
There are four stages:
- Stages 1 and 2 describe cancers in which the tumor is still in the kidney. Stage 2 means that the tumor is larger than seven centimeters across.
- Stages 3 and 4 mean the cancer has either spread into a major vein or nearby tissue or to lymph nodes.
- Stage 4 is the most advanced form of the disease. Stage 4 means that the cancer has spread to the adrenal gland or has spread to distant lymph nodes or other organs. Because the adrenal gland is attached to the kidney, the cancer often spreads there first.
Five-year survival rates for kidney cancer are based on the percentage of people who live at least 5 years with the disease after its been diagnosed.
The reports the percentage of people living 5 years or more after diagnosis according to three stages based on data from the National Cancer Institute.
These stages are:
- localized
- regional
- distant
According to the ACS, the RCC survival rates based on these three stages are:
- localized:
Treatments may include:
Changes To This Summary
The PDQ cancer information summaries are reviewed regularly and updated as new information becomes available. This section describes the latest changes made to this summary as of the date above.
Inheritance and Risk of Renal Cell Carcinoma
Added text about the results of several studies in which patients with renal cell carcinoma were found to have pathogenic variants in genes not previously associated with hereditary RCC .
This summary is written and maintained by the PDQ Cancer Genetics Editorial Board, which iseditorially independent of NCI. The summary reflects an independent review ofthe literature and does not represent a policy statement of NCI or NIH. Moreinformation about summary policies and the role of the PDQ Editorial Boards inmaintaining the PDQ summaries can be found on the About This PDQ Summary and PDQ® – NCI’s Comprehensive Cancer Database pages.
You May Like: Lobular Breast Cancer Stage 3
Aerobic And Strength Training Exercises
Both strength and aerobic training are important for optimal physical fitness. But they affect you in different ways.
Aerobic exercises help your body utilize the oxygen you breathe in. They also strengthen your heart.
Strength training builds your muscles so that you can more easily perform tasks.
The American Cancer Society suggests 150 to 300 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 to 150 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week.
Look at these lists to see how you can incorporate both types of exercise into your daily routine.