Early Detection Prevents Melanoma From Spreading
While there are still many mysteries when it comes to why and how melanoma develops, it is certain that the sooner melanoma is discovered, the lower the chances of it spreading and becoming deadly. Thats why its essential to perform regular skin checks and know the symptoms of melanoma so you can catch it early.
What Causes Subungual Melanoma
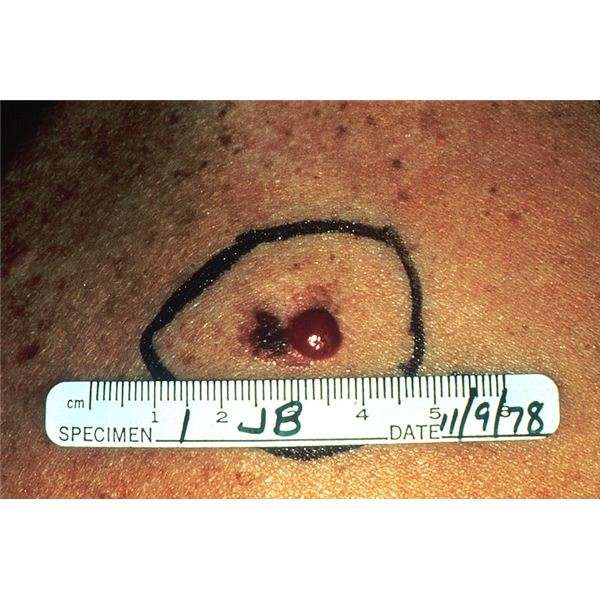
Subungual melanoma is more common in Native American, African American, and Asian individuals. It usually has a brown-black pigment, and a blurred border. When melanoma changes, it means size increase and / or growth speed of the nail or the pigment. When there is no apparent change, we speak of nail dystrophy, which person does not improve despite an adequate treatment. Subungual melanoma extension affects to the pigmentation to the proximal or lateral nail fold , or to the free edge of the nail. The family clinical history of melanoma , as well as dysplastic nevus syndrome, are determining factors in the appearance of the subungual melanoma, since the probability of developing this cancer increases significantly. Professional medical research does not consider the development of this cancer due to prolonged exposure to the sun.
Medical and health professionals have found evidence linking subungual melanoma and trauma. 58% of subungual melanoma of the hand is located in the thumb, and 86% of the subungual melanoma of the foot is located in the first finger, probably because of the larger size of the nail bed , also because they are the more exposed to trauma fingers. The morphology can be very variable, from a longitudinal brown band , to a destruction of the nail articulation, or macular lesions in the nail bed extending from the matrix. Up to 20% of subungual melanoma are amelanotic, making diagnosis especially difficult.
Spread Through The Bloodstream
Cancer cells can go into small blood vessels and then get into the bloodstream. They are called circulating tumour cells .
Researchers are looking at using circulating tumour cells to diagnose cancer instead of a tissue sample . And at whether they can test circulating cancer cells to predict which treatments will work better. They are also looking to detect circulating tumour DNA to help diagnose cancer and monitor treatment.
The circulating blood sweeps the cancer cells along until they get stuck somewhere. Often they get stuck in a very small blood vessel such as a capillary.
Then the cancer cell must move through the wall of the capillary and into the tissue of the organ close by. The cell can multiply to form a new tumour if:
- the conditions are right for it to grow
- it has the nutrients that it needs.
This is quite a complicated process and most cancer cells donât survive it. Of the many thousands of cancer cells that reach the bloodstream, only a few survive to form a secondary cancer.
The white blood cells in our immune system find and kill some cancer cells. Others cancer cells might die because they get battered around by the fast flowing blood.
Cancer cells in the circulation may try to stick to platelets to form clumps to give themselves some protection. Platelets are blood cells that help the blood to clot. This could also help the cancer cells to move into the surrounding tissues.
Donât Miss: Basal Skin Cancer Survival Rates
Don’t Miss: Melanoma Stage 3 Life Expectancy
Survival For All Stages Of Melanoma
Generally for people with melanoma in England:
- almost all people will survive their melanoma for 1 year or more after they are diagnosed
- around 90 out of every 100 people will survive their melanoma for 5 years or more after diagnosis
- more than 85 out of every 100 people will survive their melanoma for 10 years or more after they are diagnosed
Cancer survival by stage at diagnosis for England, 2019Office for National Statistics
These figures are for people diagnosed in England between 2013 and 2017.
These statistics are for net survival. Net survival estimates the number of people who survive their cancer rather than calculating the number of people diagnosed with cancer who are still alive. In other words, it is the survival of cancer patients after taking into account that some people would have died from other causes if they had not had cancer.
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- How far has the melanoma spread under my skin?
- Has it spread anywhere else?
- What treatment do you think is best for me?
- Whats the goal of this treatment? Do you think it could cure the cancer?
- Will treatment include surgery? If so, who will do the surgery?
- What will the surgery be like?
- Will I need other types of treatment, too?
- Whats the goal of these treatments?
- What side effects could I have from these treatments?
- What can I do about side effects that I might have?
- Is there a clinical trial that might be right for me?
- What about special vitamins or diets that friends tell me about? How will I know if they are safe?
- How soon do I need to start treatment?
- What should I do to be ready for treatment?
- Is there anything I can do to help the treatment work better?
- Whats the next step?
You May Like: Last Stage Of Cancer Symptoms
Alternative Treatment Options: Radiation Therapy
For Squamous and Basal cell cancer, Mohs surgery is often not the only viable treatment option. The invasive nature of Mohs surgery coupled with the possibility of scarring and the need for antibiotics following the procedure makes some patients uneasy.
If you are searching for a non-invasive alternative, youll want to learn more about Image Guided Superficial Radiotherapy . IG-SRT uses Ultrasound Imaging and Superficial Radiotherapy to treat Basal and Squamous cell cancers with a precise, measured dose of radiation delivered directly under the patients skin surface. It is completely non-invasive and has less of an effect on the patients daily life post-treatment, with no scarring, no need for antibiotics, and no requirement to stop taking certain medications prior to the procedure.
How Fast Melanoma Spreads
Some forms of melanoma can spread quickly, though the exact timeline will depend on your individual health situation. The timeline can be impacted by factors like your age, family history, any underlying medical conditions you may have, as well as what kind of melanoma you have.
During the diagnosis process, your dermatologist will determine what stage your cancer is at. The stage of your melanoma indicates what kind of treatment youll need.
Melanoma can spread quickly and be difficult to treat at later stages, so its important to seek treatment immediately after diagnosis, even if youre only at Stage 0 or Stage 1.
Protect the skin youre in.
Skincare is healthcare
Don’t Miss: Web Md Skin Cancers
How Does The Doctor Know I Have Skin Cancer
Basal and squamous skin cancer may look like:
- Flat, firm, pale or yellow areas that look a lot like a scar
- Raised reddish patches that might itch
- Rough or scaly red patches, which might crust or bleed
- Small, pink or red, shiny, pearly bumps, which might have blue, brown, or black areas
- Pink growths or lumps with raised edges and a lower center
- Open sores that dont heal, or that heal and then come back
- Wart-like growths
How Fast Does Skin Cancer Grow
Skin cancer starts when cells in the skin grow out of control. Some forms of skin cancer tend to grow in a matter of weeks, while others grow over months or longer. While a number of factors determine how fast or slow skin cancer may grow in any one individual, some types of skin cancer are more aggressive than others. In the space below, we look at typical growth rates for some specific types of cancer.
Also Check: Is Stage 3 Melanoma Curable
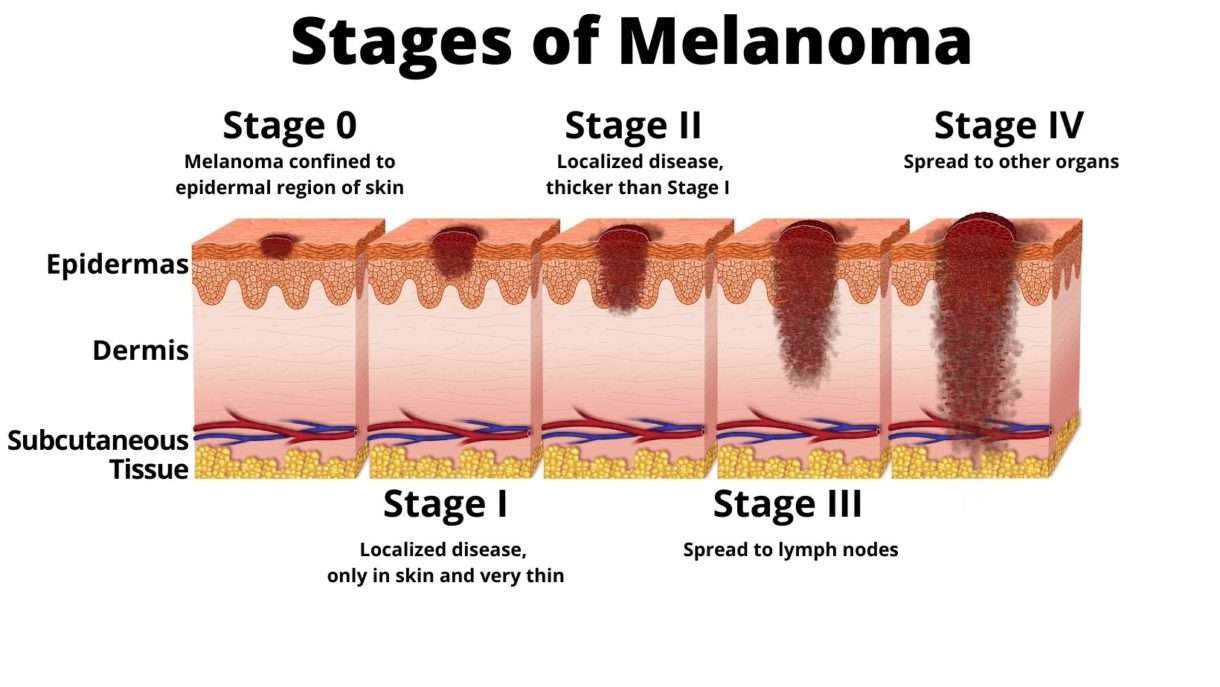
Stages Of Melanoma: Growth Patterns And Stages Of Skin Cancer
Melanocytes, a layer of cells in the skin produce melanin, a brown-black skin pigment that determines skin and hair color and protect against the damaging rays of the sun. These melanocytes spread as the person ages and form clusters.
The controlled proliferation of melanocytes is non-cancerous and cause moles and freckles. At times, however the growth of melanocytes goes out of control and develops into cancerous and life-threatening melanoma. Such uncontrolled growth cause moles with uneven shape, dark color, or mixed color. The causes of such uncontrolled growth is usually excessive sun exposure during childhood, fair skin that burns easily, and certain hereditary conditions
How Cancer Can Spread To Other Areas Of The Body
Cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system . There they can start to grow into new tumours.
Cancers are named according to where they first started developing. For example, bowel cancer that has spread to the liver is called bowel cancer with liver metastases or secondaries. It is not called liver cancer. This is because the cancerous cells in the liver are cancerous bowel cells. They are not liver cells that have become cancerous.
Donât Miss: Metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
Also Check: Lobular Breast Cancer Stage 1
Spread Through The Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system is a network of tubes and glands in the body that filters body fluid and fights infection. It also traps damaged or harmful cells such as cancer cells.
Cancer cells can go into the small lymph vessels close to the primary tumour and travel into nearby lymph glands . In the lymph glands, the cancer cells might die. But some may survive and grow to form tumours in one or more lymph nodes. This is called lymph node spread.
This 2 minute video is about the lymphatic system.
Also Check: Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch
Comparing Metastatic Melanoma Cells In Lymph Versus Blood
Most studies of cancer cell metastasis in people have focused on cells circulating in the blood. Thats because its much easier to collect patient blood samples than it is to collect samples of lymph, the clear fluid that carries immune cells through vessels of the lymphatic system, Dr. Morrison said.
Dr. Morrisons team found that human melanoma cells injected into lymph nodes in the mice were more likely to form distant tumors than melanoma cells injected into blood.
To study the role of lymph in metastasis, lead investigator Jessalyn Ubellacker, Ph.D., a postdoctoral researcher in Dr. Morrisons lab, figured out how to collect melanoma cells from lymph in mice. This allowed the team to do the first side-by-side comparison of melanoma cells spreading through lymph and through blood in the same animal, Dr. Morrison said.
Next the team found that melanoma cells in lymph experienced less oxidative stress than melanoma cells in blood. That offered a potential explanation for why melanoma cells from lymph nodes were surviving better and better able to form a tumor, Dr. Morrison said.
Further experiments showed that melanoma cells in blood are vulnerable to ferroptosisa form of cell death that occurs when lipids damaged by oxidative stress build up in the outer membrane of a cell. By contrast, melanoma cells from lymph nodes were protected from ferroptosis.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 1 Survival Rate
Where Melanoma Spreads
Studies have shown that melanoma can spread to almost any area of the bodya wider variety of areas than any other cancer. The likelihood that it will spread to each organ is as follows:
- Lymph Nodes: 50% to 75%
- Lungs and area between the lungs: 70% to 87%
- Liver: 54% to 77%
- Gastrointestinal tract: 26% to 58%
- Heart: 40% to 45%
- Adrenal glands: 36% to 54%
- Kidneys: 35% to 48%
- Spleen: 30%
Metastasis in the brain usually occur late in stage IV disease and carry the worst prognosis, with an average survival of only four months.
Skin Exam And Physical
You may have had a complete skin exam during your last dermatology appointment. Dermatologists often perform this exam when a patient has a suspicious spot on their skin that could be skin cancer.
During a complete skin exam, your dermatologist examines you head to toe. This exam includes a look at all of your skin, including the skin on your scalp, face, genitals, and the bottoms of your feet. Your dermatologist will also examine your nails and look inside your mouth.
If you did not have a complete skin exam before being diagnosed with melanoma, youll have one at your next appointment.
During a complete skin exam, your dermatologist may use a device called a dermatoscope
This device provides a closer look at the spots on your skin.
At your next appointment, youll receive a physical. During your physical, your dermatologist will ask how youre feeling and about your health, illnesses, and injuries. Your dermatologist will also want to know what diseases run in your family and the medications you take.
During your physical, your dermatologist will check your lymph nodes to find out if any feel swollen. There are many reasons for swollen lymph nodes. For example, if you have an infection or recently received a vaccination, lymph nodes can feel swollen. When you have melanoma, the swelling might be a sign that the cancer has spread.
If youre unsure what diseases your close blood relatives have had, try to find out
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Prevention Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Because basal cell carcinoma is often caused by sun exposure, people can help prevent this cancer by doing the following:
-
Avoiding the sun: For example, seeking shade, minimizing outdoor activities between 10 AM and 4 PM , and avoiding sunbathing and the use of tanning beds
-
Wearing protective clothing: For example, long-sleeved shirts, pants, and broad-brimmed hats
-
Using sunscreen: At least sun protection factor 30 with UVA and UVB protection used as directed and reapplied every 2 hours and after swimming or sweating but not used to prolong sun exposure
In addition, any skin change that lasts for more than a few weeks should be evaluated by a doctor.
Stop Tumors In Their Tracks
Every melanoma has the potential to become deadly, but the difference between an in situ melanoma and one that has begun to metastasize cannot be overstated. There is a drastic change in the survival rate for the various stages of tumors, highlighting the importance of detecting and treating melanomas before they have a chance to progress. Its impossible to predict exactly how fast a melanoma will move from stage to stage, so you should be taking action as soon as possible.
To be sure youre spotting any potential skin cancers early, The Skin Cancer Foundation recommends monthly skin checks, and scheduling an annual total body skin exam with a dermatologist. These skin exams can help you take note of any new or changing lesions that have the potential to be cancerous, and have them biopsied and taken care of before they can escalate.
Trust your instincts and dont take no for an answer, Leland says. Insist that a doctor biopsy anything you believe is suspicious.
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate Stage 1
Symptoms Of Melanoma Spread
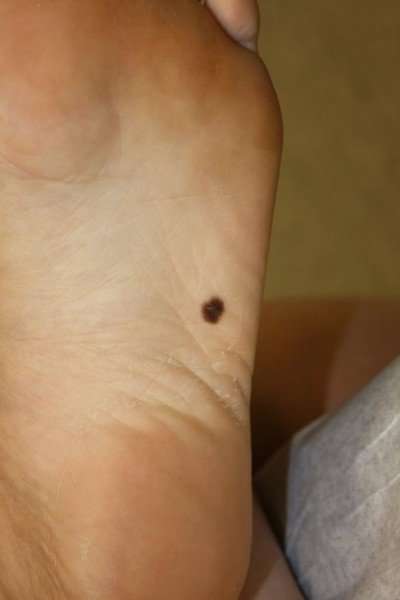
A mole developing the following characteristics at a fast pace, within days or weeks could show melanoma:
- Asymmetry, or both sides of the hole looking different
- Border or moles with blurry or jagged edges
- Color, or moles darkening, loosing color, or spotting multiple colors such as blue, red, white, pink, purple or gray
- Diameter, or a mole larger than 1/4 inch in diameter
- Elevation, or a mole raised above the skin and with a rough surface.
The bleeding or itching of such moles reinforces the possibility of melanoma. Apart from moles, speedy development of a scaly or crusted growth on the skin could also show spread of melanoma.
What Are The Stages Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is classified into the following stages, which are partly based on how far the cancer has spread throughout the body:
- Stage 0 Squamous cell carcinoma develops in the squamous cells, which are located in the epidermis . During Stage 0, the cancer hasnt spread beyond the epidermis.
- Stage 1 When squamous cell carcinoma progresses to Stage 1, it means that the cancer has spread deeper into the skin, but not into any lymph nodes or healthy tissues.
- Stage 2 A Stage 2 classification means that, in addition to progressing deeper into the skin, the cancer also displays at least one high-risk feature. This might include metastasizing to the lower skin layers or the nerves. However, at this stage, the cancer still hasnt spread to lymph nodes or healthy tissues.
- Stage 3 Once squamous cell carcinoma reaches Stage 3, the cancer has spread into lymph nodes but not any other tissues or organs.
- Stage 4 This is the final stage of squamous cell carcinoma, where the cancer has spread to at least one distant organ, whether that be the brain, the lungs or a separate area of skin.
If you think you might have squamous cell carcinoma, its important to seek prompt medical attention to minimize the risk of cancer spread. The specialists in Moffitt Cancer Centers Cutaneous Oncology Program can provide you with the comprehensive diagnostic and treatment services you need. Call or complete our new patient registration form online to request an appointment.
- BROWSE
You May Like: Lobular Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Mistaken For A Bruise
Many people first mistake subungual melanoma as a bruise.3,4 However, unlike a bruise, the streaks from subungual melanoma do not heal or grow out with the nail over time.4 It can also be confused with normal pigmentation of the nail bed or a fungal infection.2 While you can have a streak or bruising under the nail that isnt melanoma, you should ask a dermatologist to check your nails if you notice any changes.
Treatment Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
-
Removal of the tumor
Doctors may remove the cancer in the office by scraping and burning it with an electric needle or by cutting it out. Doctors may destroy the cancer by using extreme cold .
Certain chemotherapy drugs may be applied to the skin. Photodynamic therapy , in which chemicals and a laser are applied to the skin, also may be used. Occasionally, radiation therapy is used.
A technique called Mohs microscopically controlled surgery may be required for some basal cell carcinomas that are large or regrow or occur in certain areas, such as around the nose and eyes.
People whose cancer has spread to nearby tissues or spread to other parts of the body and who are not candidates for surgery or radiation therapy may be given the drug vismodegib or sonidegib taken by mouth.
Don’t Miss: Body Cancer Symptoms