How Serious Is A Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Id had a few skin cancers removed before, all basal cell carcinomas , the most common type. But when I was diagnosed with a squamous cell carcinoma on my scalp, it seemed different, and a little more scary. I asked C. William Hanke, MD, a Mohs surgeon at the Laser and Skin Surgery Center of Indiana and a senior vice president of The Skin Cancer Foundation, what we need to know about this second most common form of skin cancer.
Q: When people talk about nonmelanoma skin cancers, they tend to lump basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas together as the ones that are far less dangerous than melanoma. Should we take SCCs more seriously?
Dr. Hanke: Yes and no. BCCs hardly ever metastasize. Ive seen two cases in my entire career. But when SCCs that havent been treated early get big, then the chance of metastasis becomes real. Its uncommon, but its much more common than in BCC. We see it in our practice. But we dont want to scare people into thinking that just because they have squamous cell, Oh wow, Ive got a chance of metastasis. Remember, the rate is very low. Its just those big ones.
Q: OK, so its rare. But what happens when an SCC does spread?
Q: Whats the usual treatment for SCCs?
Q: How can we detect SCCs as early as possible?
How Does The Doctor Know I Have Skin Cancer
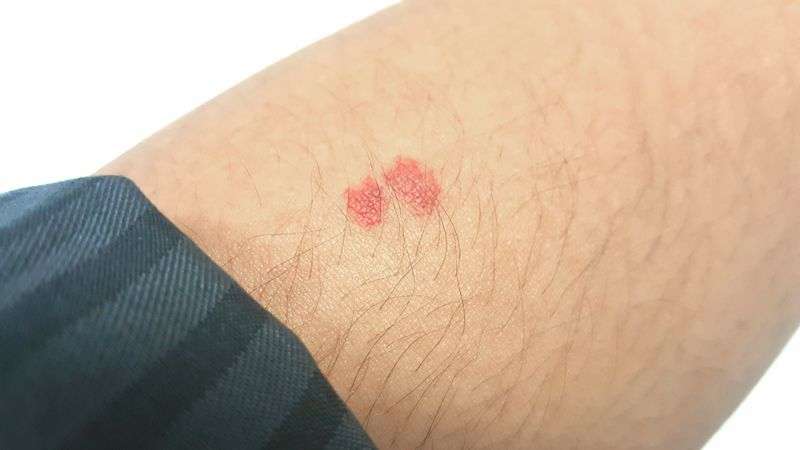
Basal and squamous skin cancer may look like:
- Flat, firm, pale or yellow areas that look a lot like a scar
- Raised reddish patches that might itch
- Rough or scaly red patches, which might crust or bleed
- Small, pink or red, shiny, pearly bumps, which might have blue, brown, or black areas
- Pink growths or lumps with raised edges and a lower center
- Open sores that dont heal, or that heal and then come back
- Wart-like growths
Does Skin Cancer Kill You
Malignant melanoma is a highly aggressive skin cancer that tends to spread to other parts of the body. All other types of skin cancers have the potential to be locally invasive and spread to other parts of the body. Nonmelanoma skin cancers are comparatively less aggressive. Self-examination of the skin for suspicious changes, changes in existing moles, persistent inflammation, ulcers, etc. can help detect skin cancer at its earliest stages. Early detection of skin cancer gives the patient the greatest chance of having successful skin cancer treatment.
Recommended Reading: Is Melanoma Caused By The Sun
Targeted Therapy Or Immunotherapy For Advanced Basal Cell Cancers
In rare cases where basal cell cancer spreads to other parts of the body or cant be cured with surgery or radiation therapy, a targeted drug such as vismodegib or sonidegib can often shrink or slow its growth.
If these drugs are no longer working , the immunotherapy drug cemiplimab can sometimes be helpful.
What Are The Types Of Skin Cancer
The main types of skin cancers are
Basal cell carcinoma usually occurs in sun-exposed areas of the body, such as the face, lips or neck. Basal cell carcinoma may present as
- A pearly or waxy bump
- A flat, flesh or brownish scar-like lesion
- An ulcer that bleeds and has crusting
- An ulcer heals and recurs quickly
Squamous cell carcinoma usually arises in sun-exposed areas of the body, such as the face, ears, hands or legs. People with darker skin tones may develop squamous cell carcinoma on areas that are not exposed to the sun. Squamous cell carcinoma presents as
- A firm, red nodule
Melanoma can develop anywhere on the body. It may arise from an existing mole that becomes cancerous or from normal skin cells. Melanoma tends to occur on the face or the trunk in men. In women, it tends to occur on the legs. Melanoma can occur on areas not exposed to the sun. Melanoma can affect people of all skin tones but it is more common in people who have lighter skin tones. Melanoma presents as
- A large brownish spot with darker speckles
- A mole that changes in color, size or feel or bleeds
- A large brownish patch or spot
- A small lesion with an irregular border with areas that appear red, pink, white, blue or blue-black
- Pain, itching or burning of the lesions
Rare types of skin cancers
Other rare types of skin cancer that may occur are
Also Check: Does Skin Cancer Make You Lose Hair
Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Basal cell cancer can occur anywhere on the body, but it typically develops on areas regularly exposed to the sun. This type of cancer may appear on your face, neck, or other body parts in the form of:
-
Flat patches of spots, or lesions, which may be red, purple, or brown in color
-
Slightly raised, brown or reddish lesions
-
Fully raised, bumpy lesions with a red or brown color
If you think you may be experiencing any of the symptoms of different skin cancers described above, you should call a doctor to discuss your symptoms. You may find that you simply have a large, non-cancerous mole, and can have your concerns put to rest by a professional. On the other hand, your doctor may be able to diagnose your condition and recommend treatment sooner rather than later. Either way, it is best to be on the side of caution and speak with your doctor about what youve noticed.
Surgical Procedures For Basal & Squamous Cell Skin Cancers
Basal or squamous cell skin cancers may need to be removed with procedures such as electrodessication and curettage, surgical excision, or Mohs surgery, with possible reconstruction of the skin and surrounding tissue.
Squamous cell cancer can be aggressive, and our surgeons may need to remove more tissue. They may also recommend additional treatments for advanced squamous cell cancer, such as medications or radiation therapyenergy beams that penetrate the skin, killing cancer cells in the body.
Basal cell cancer is less likely to become aggressive, but if it does, our doctors may use surgery and other therapies to treat it.
You May Like: What Are The Risk Factors Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma Treatment Options
No matter how treatable cancer is, facing it can still feel overwhelming. You may wonder whether treatment will leave a scar, or if your cancer can come back. Mercy understands your concerns. Well make sure you feel comfortable and confident before beginning any treatment.
Your treatment strategy will depend on several factors. These include the size and location of your basal cell carcinoma. Your doctor may recommend you have one or more types of treatment, including:
- Medication, especially topical creams or ointments
- Cryotherapy
- Surgery to remove the cancer from your skin. Your surgeon will preserve as much healthy skin as possible.
- Radiation therapy
Your relationship with Mercy wont end when your treatments end. Well continue to watch your skin closely, so you can take your mind off cancerand turn it back to the people and activities you love.
Screening For Skin Cancer
Again, the best way to screen for skin cancer is knowing your own skin. If you are familiar with the freckles, moles, and other blemishes on your body, you are more likely to notice quickly if something seems unusual.
To help spot potentially dangerous abnormalities, doctors recommend doing regular self-exams of your skin at home. Ideally, these self-exams should happen once a month, and should involve an examination of all parts of your body. Use a hand-held mirror and ask friends or family for help so as to check your back, scalp, and other hard-to-see areas of skin. If you or someone else notices a change on your skin, set up a doctors appointment to get a professional opinion.
Read Also: What Is The Best Treatment For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Tests That May Be Done
The doctor will ask you questions about when the spot on your skin first showed up and if it has changed in size or the way it looks or feels. The rest of your skin will be checked. During the exam your doctor will check the size, shape, color and texture of any skin changes. If signs are pointing to skin cancer, more tests will be done.
Skin biopsy
In a biopsy, the doctor takes out a small piece of tissue to check it for cancer cells. A biopsy is the only way to tell for sure if you have skin cancer and what kind it is.
There are many types of skin biopsies. Ask your doctor what kind you will need. Each type has pros and cons. The choice of which type to use depends on your own case.
In rare cases basal and squamous cell skin cancer can spread to the nearby lymph nodes Ask your doctor if your lymph nodes will be tested.
Basal and squamous cell cancers don’t often spread to other parts of the body. But if your doctor thinks your skin cancer might spread, you might need imaging tests, such as MRI or CT scans.
Preparing For Your Appointment
If you have any concerns about the health of your skin, it is important to share them with your doctor. After making an appointment, there are steps you can take to prepare yourself and make the most of your time with your doctor.
Here are some things to consider and be prepared to discuss before visiting the clinic or hospital:
-
What symptoms are you experiencing ?
-
When did you first notice your symptoms?
-
Have there been any major changes or stressors in your life recently?
-
What medications and/or vitamins are you taking?
-
What questions do you have for your doctor?
Also Check: Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Slow Growing
Causes Of Skin Cancer
Both types of skin cancer occur when mutations develop in the DNA of your skin cells. These mutations cause skin cells to grow uncontrollably and form a mass of cancer cells.
Basal cell skin cancer is caused by ultraviolet rays from the sun or tanning beds. UV rays can damage the DNA inside your skin cells, causing the unusual cell growth. Squamous cell skin cancer is also caused by UV exposure.
Squamous cell skin cancer can also develop after long-term exposure to cancer-causing chemicals. It can develop within a burn scar or ulcer, and may also be caused by some types of human papillomavirus .
The cause of melanoma is unclear. Most moles dont turn into melanomas, and researchers arent sure why some do. Like basal and squamous cell skin cancers, melanoma can be caused by UV rays. But melanomas can develop in parts of your body that arent typically exposed to sunlight.
Your recommended treatment plan will depend on different factors, like the size, location, type, and stage of your skin cancer. After considering these factors, your healthcare team may recommend one or more of the following treatments:
How Dermatologists Diagnose Basal Cell Carcinoma
When you see a board-certified dermatologist, your dermatologist will:
-
Examine your skin carefully
-
Ask questions about your health, medications, and symptoms
If your dermatologist finds a spot on your skin that could be any type of skin cancer, your dermatologist will first numb the area and then remove all of it. This can be done during an office visit and is called a skin biopsy. This is a simple procedure, which a dermatologist can quickly, safely, and easily perform.
Having a skin biopsy is the only way to know for sure whether you have any type of skin cancer. After your dermatologist removes the spot, a doctor, such as your dermatologist or a dermatopathologist, will examine it under a high-powered microscope. The doctor is looking for cancer cells.
If the doctor sees cancerous basal cells, the diagnosis is BCC.
After the doctor examines the removed skin under a microscope, the doctor writes a report. Called a biopsy report or a pathology report, this document explains in medical terms what was seen under the microscope.
If the diagnosis is any type of skin cancer, the information in this report will tell your dermatologist the key facts needed to treat the cancer, including:
-
The type of BCC you have
-
How deeply the cancer has grown
Your dermatologist will carefully consider your health and the findings in the report before choosing how to treat the cancer.
Also Check: What Is Precancerous Skin Cancer
What Is The Cause
The basal cell carcinoma usually happens on the neck and the head as it is most common on those areas which are commonly exposed to the sun. But the underlying cause is a mutation in the basal cells, and it causes them to multiply faster and continue to grow instead of dying and falling off. The risk factors which contribute to this condition include radiation, chronic sun exposure, family or personal history of a skin cancer, fair skin, a regimen of immune-suppressing medication, and exposure to arsenic.
What Are The Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Typically, basal cell carcinoma will begin asa new growth on the surface of the skin. These growths can vary greatlydepending on the individual. In some cases, the condition can create shiny redbumps. In others, open sores or red patches may form. In rare instances, thesegrowths can become itchy or start to bleed.
Another thing to consider when looking forwarning signs of BCC is that it occurs on the parts of the body that get themost sun. Usually, the face and head are prime targets, as are arms and legs.
Overall, if you notice any of these things onsun-exposed skin, it could be a sign of basal cell carcinoma:
- Sores that wont heal
- Shiny bumps
- Reddish or irritated area of theskin
- Scar-like tissue
- A small, pink growth with acrusted section in the middle
Also Check: What To Do To Prevent Skin Cancer
What Can I Do To Help Prevent Another Bcc
- Follow up with your healthcare provider as directed. You may need to see your healthcare provider every few months. Ask how often you need to be checked.
- Do a body check 1 time each month. Look for new growths or sores. Check for changes in the size, shape, or color of your moles and freckles. Look for sores that do not heal. Use a mirror to check places that are hard to see. Ask family members or friends to help.
- Protect your skin from UV light. Avoid the sun between 10 am and 4 pm, when the rays are strongest. If you are outside, apply sunscreen with a sun protection factor of 30 or more every 2 hours. Do this even on cloudy days. Wear pants and long sleeves to cover your body. Hats with a wide brim can protect your face, head, and neck. Wear sunglasses that block 99% of UV rays. Avoid tanning beds.
How Serious Is My Cancer
If you have skin cancer, the doctor will want to find out how far it has spread. This is called staging.
Basal and squamous cell skin cancers don’t spread as often as some other types of cancer, so the exact stage might not be too important. Still, your doctor might want to find out the stage of your cancer to help decide what type of treatment is best for you.
The stage describes the growth or spread of the cancer through the skin. It also tells if the cancer has spread to other parts of your body that are close by or farther away.
Your cancer can be stage 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4. The lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. A higher number, like stage 4, means a more serious cancer that has spread beyond the skin. Be sure to ask the doctor about the cancer stage and what it means for you.
Other things can also help you and your doctor decide how to treat your cancer, such as:
- Where the cancer is on your body
- How fast the cancer has been growing
- If the cancer is causing symptoms, such as being painful or itchy
- If the cancer is in a place that was already treated with radiation
- If you have a weakened immune system
Recommended Reading: Is Melanoma The Same As Skin Cancer
Key Points About Skin Cancer In Children
-
Skin cancer is rare in children.
-
Skin cancer is more common in people with light skin, light-colored eyes, and blond or red hair.
-
Follow the ABCDE rule to tell the difference between a normal mole and melanoma.
-
Biopsy is used to diagnose skin cancer.
-
Skin cancer can be treated with surgery, medicine, and radiation.
Staying out of the sun is the best way to prevent skin cancer.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Diagnosis
Basal cell carcinoma usually occurs on the skin with lots of sun exposure, like the face and neck. But it can occur anywhere on the body.
Your primary care doctor or a dermatologist can check your skin during routine medical visits. They can check areas that are hard for you to see, like your scalp and back.
Between medical exams, you should regularly check your own skin. When youre familiar with the look and feel of your skin, you can identify new or suspicious changes.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Be Cured
In the vast majority of cases, basal cell skin cancer can be cured. The survival rates are excellent however, the exact statistics remain unknown. Unlike other cancers, basal and squamous cell skin cancers are not tracked by cancer registries, so the statistics are not available.
In some cases, basal skin cancer can recur. The risk of recurrence appears to be linked to the type of treatment used to treat the cancer.
Research has indicated that the recurrence risk is:
- Just above 10% after surgical excision
- Slightly less than 8% after electrodesiccation and curettage
- Approximately 7.5% after cryotherapy
- Less than 1% after Mohs micrographic surgery
Treatment options vary depending on the subtype, staging, and location of the basal skin cancer.