How Is Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Of Breast Diagnosed
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of Breast may be diagnosed in the following manner:
- Complete physical examination with comprehensive medical and family history evaluation
- The following information may be sought by the healthcare provider:
- Family history of breast cancer and ovarian cancer
- Family history of BRCA 1 or BRCA 2 mutation
- History of pregnancy
Talk With Others Who Understand
MyBCTeam is the social network for people with breast cancer and their loved ones. On MyBCTeam, more than 53,000 members come together to ask questions, give advice, and share their stories with others who understand life with breast cancer.
Are you living with invasive ductal carcinoma? Share your experiences in the comments below, or start a conversation by posting on MyBCTeam.
Symptoms Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Invasive breast cancer doesn’t always have obvious signs or symptoms that affect your daily life. This is why regular screenings are essential to detect this type of cancer in its early stages.
Common symptoms of invasive ductal carcinoma include:
- Lump in the breast
- Red skin or rash on the breast
- Pain or changes in the appearance of the nipple
Recommended Reading: Ductal Invasive Carcinoma Survival Rate
Part 3histologic Types Of Invasive Breast Carcinoma
Invasive carcinomas are divided into two large categories based on the histology: invasive ductal and invasive lobular. Many of the histologic subtypes, such as tubular carcinoma, mucinous carcinoma, medullary carcinoma, invasive papillary carcinoma, invasive micropapillary carcinoma, and invasive apocrine carcinoma, are considered special variants of invasive ductal carcinoma. As with in situ lesions, the designations invasive ductal and invasive lobular refer to a growth pattern and do not necessarily imply a site of origin. A morphologic study by Wellings and colleagues19 demonstrated that most breast carcinomasboth ductal and lobularoriginate in the terminal duct lobular unit.
Frederick C. Koerner MD, in, 2009
What If A Carcinoma Is Infiltrating Or Invasive
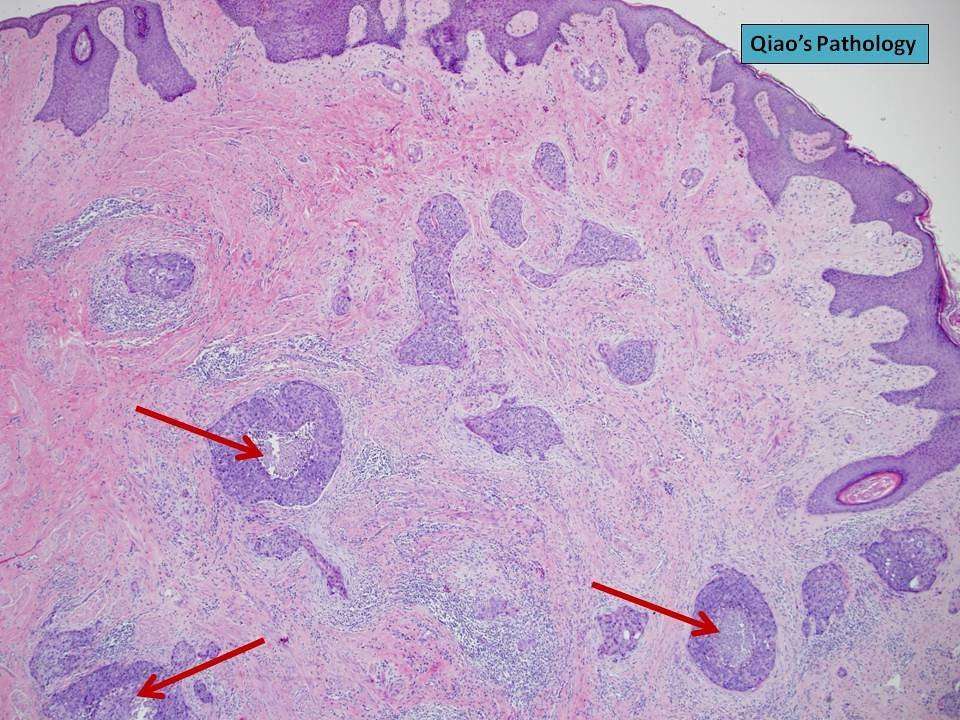
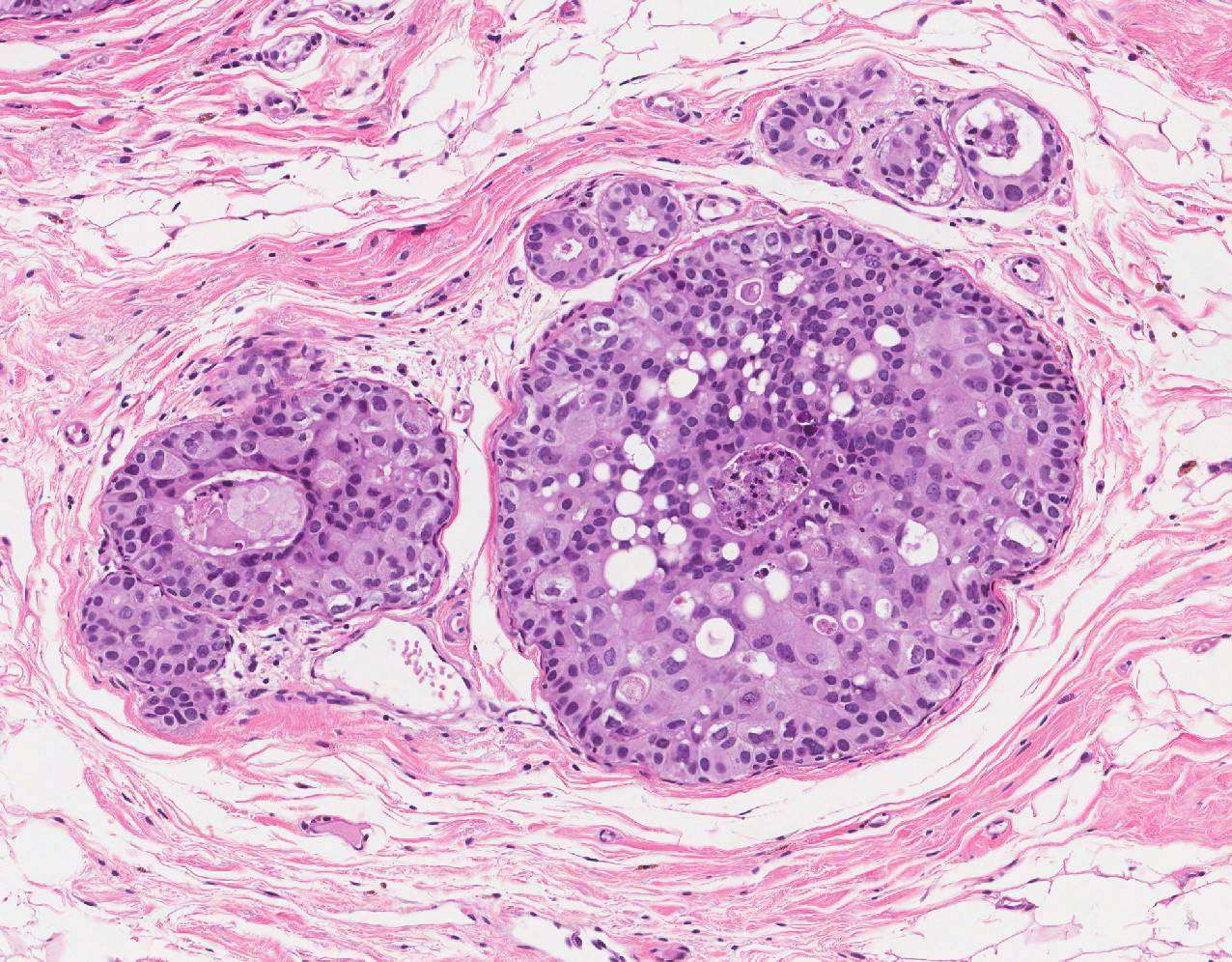
These words are used to mean that the cancer is not a pre-cancer , but is a true cancer.
The normal breast is made of tiny tubes that end in a group of sacs . Cancer starts in the cells lining the ducts or lobules, when a normal cell becomes a carcinoma cell. As long as the carcinoma cells are still confined to the breast ducts or lobules, without breaking out and growing into surrounding tissue, it is considered in-situ carcinoma .
Once the carcinoma cells have grown and broken out of the ducts or lobules, it is called invasive or infiltrating carcinoma. In an invasive carcinoma, the tumor cells can spread to other parts of your body.
Don’t Miss: Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome
How Is Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Treated
No two patients are the same. Your doctor will customize your treatment plan based on your test results and medical history. Among other things, your doctor will consider:
- Tumor location
- Aggressiveness of the cancer cells
- Your family history of breast cancer
- Results of tests for a gene mutation that would increase the risk of breast cancer
Most women with DCIS don’t have the breast removed with a mastectomy. Instead, they have a lumpectomy.
Most common is a lumpectomy followed by radiation. The surgeon removes the cancer and a small area of healthy tissue around it. Lymph nodes under the arm donât need to be removed as they are with other types of breast cancer.
After a lumpectomy, radiation cuts the chances that the cancer will come back. If cancer does return, itâs called recurrence.
Some women may opt to have a lumpectomy only. Discuss the risks of not having radiation with your doctor before deciding against it.
You and your doctors may decide that a mastectomy to remove the breast is the best course of treatment if you have any of the following:
- A strong family history of breast cancer
- A gene mutation that makes having breast cancer more likely
- Very large areas of DCIS
- DCIS lesions in multiple areas throughout your breast
- Not being able tolerate radiation therapy
You and your treatment team may also consider the use of hormone therapy if the cancer tests positive for hormone receptors. It can cut the chance of getting another breast cancer.
Show Sources
Grade 3 Breast Cancer Life Expectancy
Breast CancerBreast Cancer SurvivorsCancer Life ExpectancyBreast cancerRisk factorsAtypical cancers
You May Like: How Do You Know If You Have Breast Cancer
Also Check: What Is The Survival Rate Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Tnm System For Breast Cancer
Doctors also group cancers by the letters T, N, or M. Each of those letters tells you something about your cancer.
âTâ stands for tumor, or the lump of cancer found in the breast itself. The higher the number assigned after it, the bigger or wider the mass.
âNâ stands for nodes, as in lymph nodes. These small filters are found throughout the body, and theyâre especially dense in and around the breast. Theyâre meant to catch cancer cells before they travel to other parts of the body. Here, too, a number tells you whether the cancer has spread to lymph nodes near the breast and, if so, how many.
âMâ stands for metastasis. The cancer has spread beyond the breast and lymph nodes.
Age At The Time Of Diagnosis Affects Breast Cancer Survival Rates
It has always been known that curiously, young women have a poorer prognosis than older ones
Indeed, one cohort study examined 4,453 women with breast cancer between 1961 and 1991 who were all treated at the same center.
This study found that both ends of the age spectrum fared less well. So, women under the age of 40 years at diagnosis and those over 80 years had a statistically poorer prognosis.
However, for younger women, this may be due to the fact that they often present with higher-grade tumors that tend to be more aggressive and less likely to be hormone receptor-positive. This means that breast cancer may not respond as well to treatment.
So, it is important to bear in mind other factors discussed in this post, such as stage, grade and hormone receptor status play an important role in prognosis.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stage 3 Survival Rate
What Is The Significance Of The Stage Of The Tumor
The stage of a cancer is a measurement of the extent of the tumor and its spread. The standard staging system for breast cancer uses a system known as TNM, where:
- T stands for the main tumor
- N stands for spread to nearby lymph nodes
- M stands for metastasis
If the stage is based on removal of the cancer with surgery and review by the pathologist, the letter p may appear before the T and N letters.
The T category is based on the size of the tumor and whether or not it has spread to the skin over the breast or to the chest wall under the breast. Higher T numbers mean a larger tumor and/or wider spread to tissues near the breast. Since the entire tumor must be removed to learn the T category, this information is not given for needle biopsies.
The N category indicates whether the cancer has spread to lymph nodes near the breast and, if so, how many lymph nodes are affected. Higher numbers after the N indicate more lymph node involvement by cancer. If no nearby lymph nodes were removed to be checked for cancer spread, the report may list the N category as NX, where the letter X is used to mean that the information is not available .
The M category is usually based on the results of lab and imaging tests, and is not part of the pathology report from breast cancer surgery. In a pathology report, the M category is often left off or listed as MX .
Whats The Most Effective Treatment For Dcis
Surgery is typically the first treatment for DCIS, and it is very effective. There are two types of surgery used for DCIS. The less-invasive option is a lumpectomy, in which a surgeon removes the area of DCIS as well as a little bit of the normal tissue around it, also referred to as a margin. The other option is a mastectomy, which involves removing the entire breast.
Most people with DCIS undergo a lumpectomy, possibly followed by additional treatments. In some cases, a mastectomy is recommended, especially if the DCIS covers a large area or appears in multiple spots throughout the breast. With either of these surgeries, the survival rate is excellent. Our job is to figure out which type of surgery is best for each patient.
Also Check: Melanoma Forearm
What Are The Symptoms Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
In the early stages, invasive ductal carcinoma may not cause any obvious symptoms. Some people may develop certain warning signs, including:
- A new lump in the breast.
- Swelling of the breast.
- Prior radiation to the chest.
- Early start of menstrual periods.
- Late menopause.
- Never being pregnant or having children later in life.
In approximately 5% to 10% of breast cancer cases, invasive ductal carcinoma has been linked to hereditary factors. These include mutations of the breast cancer gene 1 , breast cancer gene 2 and other genes such as PALB2, CHEK2 and ATM.
How Is Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Of Breast Treated
Treatment options available for individuals with Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of Breast are dependent upon the following:
- Type of cancer
- The staging of the cancer
- Whether the cancer cells are sensitive to certain particular hormones, and
- Personal preferences
In general, breast cancer stages range from 0 to IV. 0 may indicate a small and non-invasive cancer, while IV indicates that the cancer has spread to other areas of the body. Briefly, as per US National Cancer Institute , breast cancer is staged as follows:
- Stage 0 : The abnormal cancer cells are confined to their site of origin
- Stage I: The tumor is 2 centimeters in diameter or less, and has not spread outside the breast
- Stage II: The tumor may be up to 5 centimeters in diameter and may have spread to lymph nodes. Another criteria is that the tumor may be larger than 5 centimeters in diameter, but has not spread to surrounding lymph nodes
- Stage III: The tumor may be more than 5 centimeters in diameter and may have spread to several axillary lymph nodes, or to the lymph nodes near the breastbone. The cancer may also have spread to the breast skin/chest wall, causing ulcer-like sores, or a swelling
- Stage IV: The tumor has spread outside the breast and to other organs, such as the bones, liver, lungs, or brain, regardless of its size
If breast cancer is diagnosed, staging helps determine whether it has spread and which treatment options are best for the patient.
Hormone therapy:
- Stage 2A
- Stage 2B
Stage 2A can mean:
Read Also: Skin Cancer Prognosis
Coping With A Diagnosis Of Dcis
Being told you have DCIS can be a difficult and worrying time. Everyone reacts differently to their diagnosis and have their own way of coping.
Although DCIS is an early form of breast cancer with a very good prognosis, people understandably may feel very anxious and frightened by the diagnosis. People can often struggle to come to terms with being offered treatments such as a mastectomy, at the same time as being told their DCIS may never do them any harm.
Some people are reluctant to say theyre anxious about a diagnosis of DCIS because they worry others will see it as less important than other types of breast cancer. Because of this they might feel less able to ask for support. But there are people who can support you so dont be afraid to ask for help if you need it. By letting other people know how you feel, particularly your family and friends, they can be more supportive.
Some people find it helpful to discuss their feelings and concerns with their breast care nurse or specialist. If youd like to talk through your feelings and concerns in more depth over a period of time, a counsellor or psychologist may be more appropriate. Your breast care nurse, specialist or GP can arrange this.
Find out more about coping emotionally with breast cancer.
If you want to talk you can also call our Helpline on 0808 800 6000.
Common Breast Cancer Types
After skin cancer, breast cancer is the most common type of cancer diagnosed in women. About 284,200 cases will be diagnosed in 2021, according to the American Cancer Society . Men also may develop breast cancer, though its much more rare.
Breast cancer is classified into different types based on how the cells look under a microscope. Most breast cancers are carcinomas, a type of cancer that begins in the linings of most organs.
Don’t Miss: Melanoma Bone Cancer Symptoms
How Does Staging Relate To Types Of Breast Cancer
In addition to cancer stage, doctors will determine the tumor grade and subtype.
Tumors are graded on a scale of 1 to 3, based on how abnormal the cells appear compared to normal cells. The higher the grade, the more aggressive the cancer, meaning that it tends to be growing quickly.
The subtype is important because treatment and outlook will vary depending on which subtype of breast cancer that you have. Subtypes include:
These are different types of invasive ductal carcinoma that can be identified under the microscope.
- Tubular, mucinous, and cribriform carcinomas are âspecial typesâ of well-differentiated cancers that often have a better prognosis than the more common type of invasive ductal carcinoma .
- Micropapillary carcinoma is a type of invasive breast carcinoma that often has a worse prognosis.
If your doctor knows that your tumor is made up of one of these special types of breast cancer, he or she may recommend different treatment.
Since some tumors are made up of more than one type, the entire tumor must be removed in order to know what types your tumor contains. A needle biopsy doesnt give enough information to guide treatment.
Treatment For Invasive Breast Cancer
As with all types of breast cancer, the treatments youre offered will depend on the features of invasive breast cancer seen under the microscope. This includes the size, grade, hormone receptor status and HER2 status.
Treatment aims to remove the cancer and reduce the risk of it coming back or spreading to other parts of the body.
Recommended Reading: Survival Rate Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Cancer Cure And All Clear
Many people who have cancer want to know if theyre cured. You may hear words like cure and all clear in the media.
Cured means theres no chance of the breast cancer coming back. However, its not possible to be sure that breast cancer will never come back. Treatment for breast cancer will be successful for most people, and the risk of recurrence gets less as time goes on. Recurrence, unfortunately, can happen even many years after treatment, so no one can say with certainty that youre definitely cured.
All clear, or in remission which is another term you may have heard used, means theres no obvious sign of cancer at the moment.
If your breast cancer has spread to other parts of your body this will affect your prognosis. Secondary breast cancer can be treated, sometimes for many years, but not cured. Find out more about secondary breast cancer.
In order to be as clear as possible, your treatment team is more likely to talk about your chances of survival over a period of time or the possibility of remaining free of breast cancer in the future.
What Is The Prognosis For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Your doctor will discuss what you can expect based on the characteristics of the invasive ductal carcinoma and the effectiveness of your treatment.
Specialty centers such as Johns Hopkins Medicines Breast Health Services can offer integrated teams of breast cancer specialists who have skill and experience in surgery, breast reconstruction, chemotherapy, biologic targeted therapy, radiation therapy and other hormonal therapies.
Medical science is making great strides forward in treating breast cancer, allowing our surgeries to be less invasive and improving surgical outcomes and overall quality of life, Wright says.
Breast Health Services
Johns Hopkins breast health services include preventive and noncancerous surgical treatment, risk assessment, diagnostic screenings and treatment for breast cancer.
You May Like: Melanoma 3b