Certain Factors Affect Prognosis And Treatment Options
The prognosis for squamous cell carcinoma of the skin depends mostly on the following:
- Stage of the cancer.
- Whether the patient is immunosuppressed.
- Whether the patient uses tobacco.
- The patient’s general health.
Treatment options for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin depend on the following:
- The type of cancer.
- The stage of the cancer, for squamous cell carcinoma.
- The size of the tumor and what part of the body it affects.
- The patients general health.
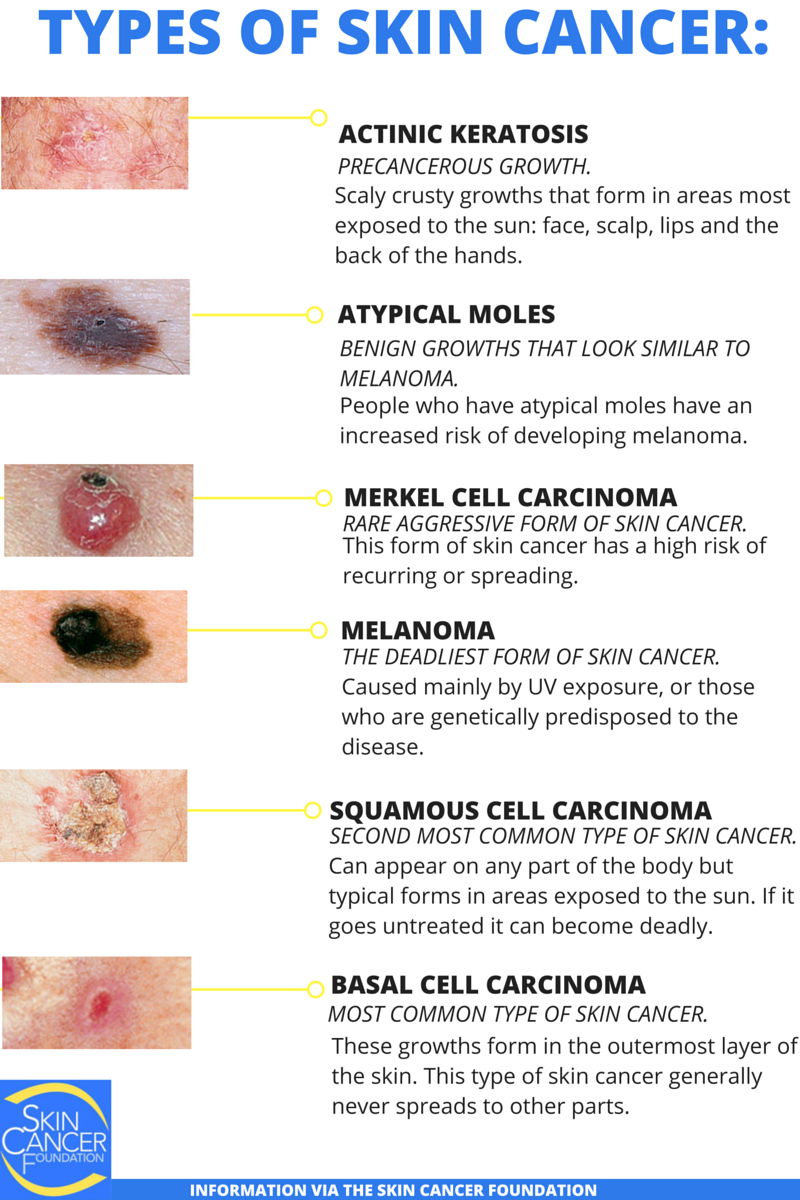
Do You Know The 4 Main Types Of Skin Cancer
As the sun shines in spring and the days lengthen toward summer, tis the season for sunscreen. Using a sunscreen of SPF 15 or higher is one of the best ways to protect yourself against skin cancer, which affects more than 3.3 million people in the U.S. each year.
Its also a good time to practice good skin habits like staying in shade during the hottest part of the day, keeping skin covered with clothing, and checking your skin for irregularities. Which brings up the question: Are you familiar with the 4 main types of skin cancer?
Basal Cell Skin Cancer
BCC is the most common type of skin cancer. About 75 out of every 100;non melanoma skin cancers are BCCs. They develop from basal cells and these are found in the deepest part of the outer layer of the skin .
They develop mostly in areas of skin exposed to the sun, including parts of the face such as the nose, forehead and cheeks. Also, on your back or lower legs.
They are;most often diagnosed in people who are middle aged or older.
Doctors might also call;a basal cell cancer;a rodent ulcer.
There are;a number of different types of BCC.;Each type can look and behave differently. They;include:
- nodular basal cell skin cancer
- superficial basal cell skin cancer
- morphoeic basal cell skin cancer â also known as sclerosing or infiltrating basal cell skin cancer
- pigmented basal cell skin cancer
Nodular basal cell cancer is the most common subtype.
Itâs very rare for basal cell skin cancer to spread to another part of the body to form a;secondary cancer. Itâs possible to have more than one basal cell cancer at any one time and having had one does increase your risk of getting another.
Also Check: How To Know If You Have Melanoma Skin Cancer
You May Like: How Likely Is Skin Cancer
Identifying Skin Cancer: 37 Photos You Need To See
As we head into summer, its time to kick your safe;skin;practices into high gear. All individuals should apply a broad spectrum SPF every day, and watch their local UV forecast for daily updates when outside activities are planned.;
Why? Skin;cancer;is the most common form of;cancer;in the United States. One in five Americans will be diagnosed with the disease in his or her lifetime. There are more new cases of;skin;cancer;every year than breast, prostate, lung and colon cancers;combined,;according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Although family history and your natural;skin;pigmentation play a role in your risk, the number-one thing that causes;skin cancer;is exposure to UV rays.
Erin Gilbert, M.D., Ph.D., a spokesperson for the;Skin;Cancer;Foundation, offered these guidelines to weather.com in 2014: Avoid the sun when its at its peak ; wear sun-protective clothes, such as a hat; always wear a broad-spectrum SPF. Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or after swimming or sweating.
Its a myth that most sun damage occurs in childhood, so theres nothing you can do about it as an adult, Dr. Gilbert said.
Twenty-three percent of sun damage happens before youre 18, but it is cumulative. Its never too late to start protecting yourself, she said. Your melanoma risk doubles if youve had more than five severe sunburns at any age. Dont let a sunburn or a tan deter you from seeing your dermatologist or wearing sun screen the next day.
What Is A Melanocyte
Melanocytes are skin cells found in the upper layer of skin. They produce a pigment known as melanin, which gives skin its color. There are two types of melanin: eumelanin and pheomelanin. When skin is exposed to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or tanning beds, it causes skin damage that triggers the melanocytes to produce more melanin, but only the eumelanin pigment attempts to protect the skin by causing the skin to darken or tan. Melanoma occurs when DNA damage from burning or tanning due to UV radiation triggers changes in the melanocytes, resulting in uncontrolled cellular growth.
About Melanin
Naturally darker-skinned people have more eumelanin and naturally fair-skinned people have more pheomelanin. While eumelanin has the ability to protect the skin from sun damage, pheomelanin does not. Thats why people with darker skin are at lower risk for developing melanoma than fair-skinned people who, due to lack of eumelanin, are more susceptible to sun damage, burning and skin cancer.
Don’t Miss: What Is Melanoma In The Brain
Merkel Cell Carcinoma: A Rare Skin Cancer On The Rise
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare type of skin cancer that affects about 2,000 people in the United States each year.
Though its an uncommon skin cancer, cases of Merkel cell carcinoma have increased rapidly in the last couple of decades.
This type of cancer starts when cells in the skin, called Merkel cells, start to grow out of control.
Merkel cell carcinomas typically grow quickly and can be difficult to treat if they spread.
They can start anywhere on the body, but Merkel cell carcinomas commonly affect areas exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, and arms.
They may look like pink, red, or purple lumps that are firm when you touch them. Sometimes, they can open up as ulcers or sores.
Risk factors include:
Prognosis For Skin Cancer
It is not possible for a doctor to predict the exact course of a disease. However, your doctor may give you the likely outcome of the disease. If detected early, most skin cancers are successfully treated.
Most non-melanoma skin cancers do not pose a serious risk to your health but a cancer diagnosis can be a shock. If you want to talk to someone see your doctor. You can also call Cancer Council 13 11 20.
You May Like: What Is Grade 3 Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Other Types Of Skin Cancer
Unusual types of skin cancer include;Merkel cell tumors.;Merkel cell carcinoma starts when cells in the skin, also called Merkel cells, start to grow uncontrollably. This type of cancer can grow quickly and can be hard to treat if it spreads beyond the skin.
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is another rare skin cancer that begins in the middle layer of skin, known as the dermis. This type of cancer tends to grow slowly and seldom spreads to other parts of the body.
Rarer Types Of Non Melanoma Skin Cancer
There are other less common types of skin cancer. These include:
- Merkel cell carcinoma
- T cell lymphoma of the skin
- Sebaceous gland cancer
These;are all treated differently from basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers. ;
Merkel cell carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma;is very rare. Treatment is with surgery or radiotherapy, or both. This usually works well, but sometimes the cancer can come back in the same place. And sometimes it spreads to nearby lymph nodes.;
Sebaceous gland cancer
Sebaceous gland cancer is another rare type of skin cancer affecting the glands that produce the skin’s natural oils. Treatment is usually surgery for this type of cancer.;
Kaposi’s sarcoma
Kaposis sarcoma;is a rare condition. It’s often associated with HIV but also occurs in people who don’t;have HIV. It’s a cancer that starts;in the cells that form;the lining of lymph nodes and the lining of blood vessels in the skin. Treatment;is;surgery or;radiotherapy, and sometimes;chemotherapy.
T cell lymphoma of the skin;
T cell lymphoma of the skin;can also be called primary cutaneous lymphoma. It’s a type of non Hodgkin lymphoma. There are a number of different types of treatment for this type of cancer. ;
You May Like: How Can You Get Skin Cancer
What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin
Squamous cells are found throughout the human body. These cells line organs, such as the lungs, throat, and thyroid. We also have squamous cells in our skin.
The job of squamous cells is to protect what lies beneath. In our skin, these cells sit near the surface, protecting the tissue beneath.
Anywhere we have squamous cells, we can develop a type of cancer called squamous cell carcinoma .
In the skin, this cancer is usually not life-threatening. It tends to grow slowly, but it can grow deep. When the cancer grows deep, it can injure nerves, blood vessels, and anything else in its path. As the cancer cells pile up, a large tumor can form.
Most people who develop this skin cancer have fair skin that they seldom protected with sunscreen or sun-protective clothing. Before developing this skin cancer, they tend to notice signs of sun damage on their skin, such as age spots, patches of discolored skin, and deep wrinkles.
Anyone can develop squamous cell carcinoma
While anyone can develop this skin cancer, you have a greater risk if you live with a transplanted organ, use tanning beds, or have fair skin that you seldom protected from the sun.
Another sign of sun-damaged skin is having one or more pre-cancerous growths on your skin called actinic keratoses . Some AKs progress, turning into squamous cell carcinoma of the skin.
To find out what this skin cancer can look like and see pictures of it, go to: Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: Signs and symptoms.
ImageGetty Images
Exams And Tests For Skin Cancer
If you think a mole or other skin lesion has turned into skin cancer, your primary care provider will probably refer you to a dermatologist. The dermatologist will examine any moles in question and, in many cases, the entire skin surface. Any lesions that are difficult to identify, or are thought to be skin cancer, may then be checked. Tests for skin cancer may include:
- The doctor may use a handheld device called a dermatoscope to scan the lesion. Another handheld device, MelaFind, scans the lesion then a computer program evaluates images of the lesion to indicate if it’s cancerous.
- A sample of skin will be taken so that the suspicious area of skin can be examined under a microscope.
- A biopsy is;done in the dermatologist’s office.
If a biopsy shows that you have malignant melanoma, you may undergo further testing to determine the extent of spread of the disease, if any. This may involve blood tests, a chest X-ray, and other tests as needed. This is only needed if the melanoma is of a certain size.
Continued
Read Also: Does Melanoma Metastasize To The Brain
Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
DermNet NZ
Squamous cell carcinoma in situ, also known as Bowens disease, is a precancerous condition that appears as a red or brownish patch or plaque on the skin that grows slowly over time. The patches are often found on the legs and lower parts of the body, as well as the head and neck. In rare cases, it has been found on the hands and feet, in the genital area, and in the area around the anus.
Bowens disease is uncommon: only 15 out of every 100,000 people will develop this condition every year. The condition typically affects the Caucasian population, but women are more likely to develop Bowens disease than men. The majority of cases are in adults over 60. As with other skin cancers, Bowens disease can develop after long-term exposure to the sun. It can also develop following radiotherapy treatment. Other causes include immune suppression, skin injury, inflammatory skin conditions, and a human papillomavirus infection.
Bowens disease is generally treatable and doesnt develop into squamous cell carcinoma. Up to 16% of cases develop into cancer.
Tumors Of The Skin Glands
Most glandular tissue tumors in dogs are benign . Malignant glandular tumors include sebaceous follicle carcinomas, sweat gland carcinomas, and eccrine carcinomas. Sometimes benign tumors are often recognized visually, but its still best to get rid of any questionable mass and submit the tissue for biopsy. Most malignant glandular tumors are often treated with surgery alone. However, if the tumors are incompletely excised, radiotherapy is suggested to stop recurrence. Dogs with malignant tumors should even be screened for any evidence of spread of disease via chest X-rays and regional lymph gland aspirates.
Also Check: What Does Skin Cancer Of The Vulva Look Like
Cancer May Spread From Where It Began To Other Parts Of The Body
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if skin cancer spreads to the lung, the cancer cells in the lung are actually skin cancer cells. The disease is metastatic skin cancer, not lung cancer.
Recommended Reading: Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Slow Growing
Melanoma Requires Expert Care Know Your Options
Melanoma is a cancer that forms in melanocytes, the skin cells that produce a brown pigment known as melanin. These are the cells that darken when exposed to the sun, a protective response to shield the deeper layers of the skin from the harmful effects of UV rays. But, unlike other forms of skin cancer, melanoma may develop in parts of the body not normally exposed to sunlight, such as the groin or bottoms of the feet. It may also form in the eye.
Melanoma is a complex disease, so it is important to work with experienced cancer doctors;who are trained and up to date on todays technologies and treatments. At Cancer Treatment Centers of America® , our oncologists have experience with the growing array of precision cancer treatments;for the disease, including immunotherapy;and targeted therapy. Your CTCA® care team will explain your options and design an individualized plan based on your specific needs. We also offer evidence-informed supportive care services;to help you manage treatment-related side effects.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Feel When You Have Skin Cancer
Infiltrative Basal Cell Carcinoma
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
DermNet NZ
Infiltrative basal cell carcinoma occurs when a tumor makes its way into the dermis via thin strands between collagen fibers. This aggressive type of skin cancer is harder to diagnose and treat because of its location. Typically, infiltrative basal cell carcinoma appears as scar tissue or thickening of the skin and requires a biopsy to properly diagnose.
To remove this type of basal cell carcinoma, a specific form of surgery, called Mohs, is used. During a Mohs surgery, also called Mohs micrographic surgery, thin layers of skin are removed until there is no cancer tissue left.
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
DermNet NZ
Superficial basal cell carcinoma, also known as in situ basal-cell carcinoma, tends to occur on the shoulders or the upper part of the torso, but it can also be found on the legs and arms.;This type of cancer isnt generally invasive because it has a slow rate of growth and is fairly easy to spot and diagnose. It appears reddish or pinkish in color and may crust over or ooze. Superficial basal cell carcinoma accounts for roughly 15%-26% of all basal cell carcinoma cases.
From The Harvard Health Letter May 2006
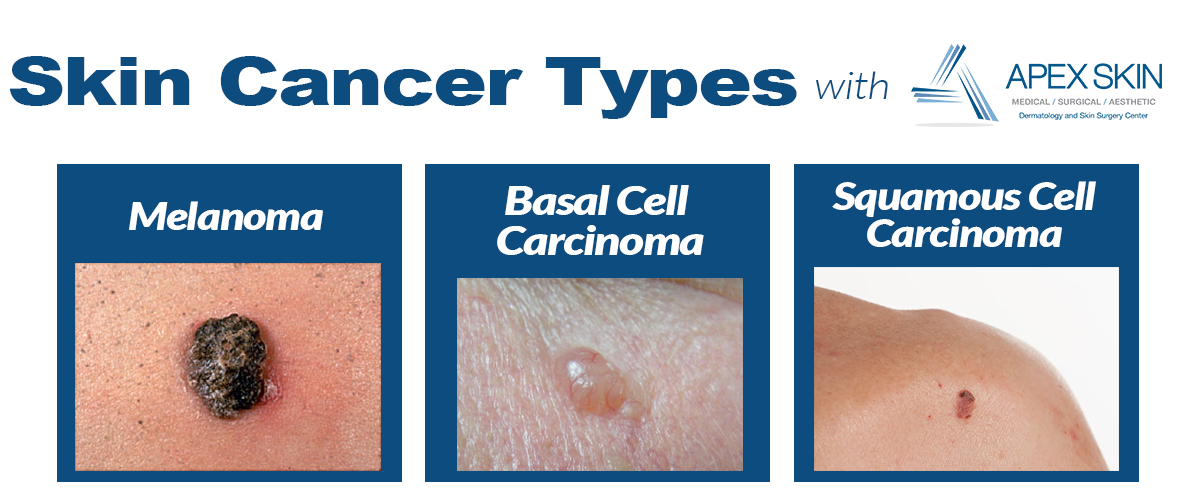
Summers the season for fun in the sunbut also for skin cancer. Of the three main types of skin cancer, melanoma is most deadly, and basal cell, most common. Squamous cell cancer falls in between. Its three times as common as melanoma . Though not as common as basal cell , squamous cell is more serious because it is likely to spread . Treated early, the cure rate is over 90%, but metastases occur in 1%5% of cases. After it has metastasized, its very difficult to treat.
You May Like: How To Know You Have Skin Cancer
What Is Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is a disease that begins in the cells of the skin. The area of skin with the cancer is often called a lesion. There are several types of skin cancer . Melanoma is the most serious. But there are others that are known as nonmelanoma skin cancer. These include:
-
Basal cell carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are by far the most common.
What Causes Non
Overexposure to ultraviolet light is the main cause of non-melanoma skin cancer. UV light comes from the sun, as well as from artificial tanning sunbeds and sunlamps.
Other risk factors that can increase your chances of developing non-melanoma skin cancer include:
- a previous non-melanoma skin cancer
- a family history of skin cancer
- pale skin that burns easily
- a large number of moles or freckles
- taking medicine that suppresses your immune system
- a co-existing medical condition that suppresses your immune system
Recommended Reading: What Is Triple Negative Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Who Is At Risk
Much like with BCC, the more time you spend in the sun, the more at risk you are for developing SCC. About 90% of nonmelanoma skin cancers are caused by sun exposure, and people who have tanned indoors have a 67% higher risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma.
Your risk for SCC is higher if you:
- Have a history of skin cancer
- Have a history of unprotected exposure to the sun or tanning beds
- Have a weakened immune system due to a chronic condition or medication
- Are over age 50
- Have a history of chronic skin infections, precancerous skin growths or human papillomavirus