How Is Melanoma Diagnosed
If you have a mole or other spot that looks suspicious, your doctor may remove it and look at it under the microscope to see if it contains cancer cells. This is called a biopsy.
After your doctor receives the skin biopsy results showing evidence of melanoma cells, the next step is to determine if the melanoma has spread. This is called staging. Once diagnosed, melanoma will be categorized based on several factors, such as how deeply it has spread and its appearance under the microscope. Tumor thickness is the most important characteristic in predicting outcomes.
Melanomas are grouped into the following stages:
- Stage 0 : The melanoma is only in the top layer of skin .
- Stage I: Low-risk primary melanoma with no evidence of spread. This stage is generally curable with surgery.
- Stage II: Features are present that indicate higher risk of recurrence, but there is no evidence of spread.
- Stage III: The melanoma has spread to nearby lymph nodes or nearby skin.
- Stage IV: The melanoma has spread to more distant lymph nodes or skin or has spread to internal organs.
Certain Factors Affect Prognosis And Treatment Options
The prognosis and treatment options depend on the following:
- The thickness of the tumor and where it is in the body.
- How quickly the cancer cells are dividing.
- Whether there was bleeding or ulceration of the tumor.
- How much cancer is in the lymph nodes.
- The number of places cancer has spread to in the body.
- The level of lactate dehydrogenase in the blood.
- Whether the cancer has certain mutations in a gene called BRAF.
- The patients age and general health.
Prognosis For Melanoma On The Nail
Like other forms of melanoma, subungual melanoma can metastasize to other parts of the body if left untreated.3,4 Because it can be difficult to see and is often mistaken for a bruise or other nail problem, this condition often goes undetected. However, checking your nails and showing any changes to your healthcare provider can help reduce your chances of an undetected subungual melanoma.
Don’t Miss: Skin Cancer Perineural Invasion
Physical Emotional And Social Effects Of Cancer
Melanoma and its treatment cause physical symptoms and side effects, as well as emotional, social, and financial effects. Managing all of these effects is called palliative care or supportive care. It is an important part of your care that is included along with treatments intended to slow, stop, or eliminate the cancer.
Palliative care focuses on improving how you feel during treatment by managing symptoms and supporting patients and their families with other, non-medical needs. Any person, regardless of age or type and stage of cancer, may receive this type of care. And it often works best when it is started right after a cancer diagnosis. People who receive palliative care along with treatment for the cancer often have less severe symptoms, better quality of life, and report that they are more satisfied with treatment.
Palliative treatments vary widely and often include medication, nutritional changes, relaxation techniques, emotional and spiritual support, and other therapies. You may also receive palliative treatments similar to those meant to get rid of the cancer, such as chemotherapy, surgery, or radiation therapy.
Learn more about the importance of tracking side effects in another part of this guide. Learn more about palliative care in a separate section of this website.
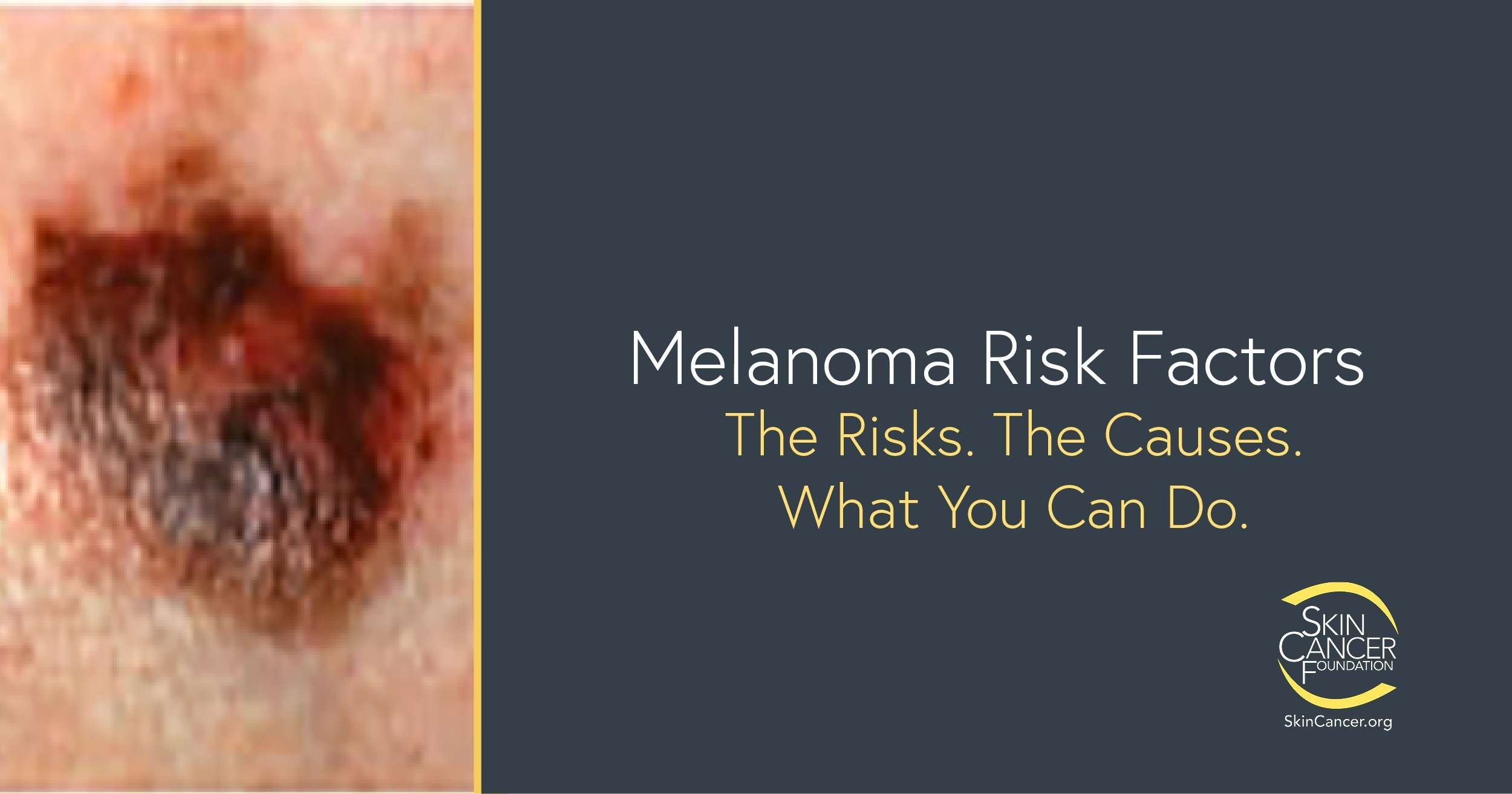
Who Is At Risk

People with fair skin and lighter eyes and hair tend to be particularlyvulnerable to skin cancer. Other risk factors include a family history ofmelanoma, more time spent unprotected in the sun, early childhoodsunburns, immunosuppressive disorders, a weakened immune system, and havingmany freckles or moles.
Both men and women are at risk, but there is one troublingtrend: an alarming surge in melanoma rates in young women.This is largely due to tanning from the sun and in tanning salons. Tanning either at beaches or salons is a major risk factor forskin cancers.
Telemedicine Dermatology Services
You May Like: Skin Cancer Mayo
Who Treats Melanoma Skin Cancer
Depending on your options, you may have different types of doctors on your treatment team. These doctors may include:
- A dermatologist: a doctor who treats diseases of the skin
- A surgical oncologist : a doctor who uses surgery to treat cancer
- A medical oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with medicines such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapy
- A radiation oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with radiation therapy
Many other specialists may be involved in your care as well, including physician assistants , nurse practitioners , nurses, psychologists, social workers, rehabilitation specialists, and other health professionals.
Permission To Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text. It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. However, a user would be allowed to write a sentence such as NCIs PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks in the following way: .
The best way to cite this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Adult Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Melanoma Treatment. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated < MM/DD/YYYY> . Available at: . Accessed < MM/DD/YYYY> .
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author, artist, and/or publisher for use in the PDQ summaries only. If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in Visuals Online. Visuals Online is a collection of more than 3,000 scientific images.
Don’t Miss: Well-differentiated
Treating Stage Iv Melanoma
Stage IV melanomas have already spread to distant lymph nodes or other areas of the body. Skin tumors or enlarged lymph nodes causing symptoms can often be removed by surgery or treated with radiation therapy.
Metastases in internal organs are sometimes removed, depending on how many there are, where they are, and how likely they are to cause symptoms. Metastases that cause symptoms but cannot be removed may be treated with radiation, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or chemotherapy.
The treatment of widespread melanomas has changed in recent years as newer forms of immunotherapy and targeted drugs have been shown to be more effective than chemotherapy.
Immunotherapy drugs called checkpoint inhibitors such as pembrolizumab or nivolumab are typically the first drugs tried, especially in people whose cancer cells do not have BRAF gene changes. These drugs can shrink tumors for long periods of time in some people. Ipilimumab , a different type of checkpoint inhibitor, is not typically used by itself as the first treatment, although it might be combined with nivolumab or pembrolizumab. This slightly increase the chances that the tumor will shrink, although itâs also more likely to result in serious side effects, which needs to be considered carefully. People who get any of these drugs need to be watched closely for serious side effects..
Itâs important to carefully consider the possible benefits and side effects of any recommended treatment before starting it.
Treating Stage 4 Melanoma
If melanoma comes back or spreads to other organs it’s called stage 4 melanoma.
In the past, cure from stage 4 melanoma was very rare but new treatments, such as immunotherapy and targeted treatments, show encouraging results.
Treatment for stage 4 melanoma is given in the hope that it can slow the cancer’s growth, reduce symptoms, and extend life expectancy.
You may be offered surgery to remove other melanomas that have grown away from the original site. You may also be able to have other treatments to help with your symptoms, such as radiotherapy and medicine.
If you have advanced melanoma, you may decide not to have treatment if it’s unlikely to significantly extend your life expectancy, or if you do not have symptoms that cause pain or discomfort.
It’s entirely your decision and your treatment team will respect it. If you decide not to receive treatment, pain relief and nursing care will be made available when you need it. This is called palliative care.
Read Also: What Does Cancer Look Like Outside The Body
What Is Recurrent Melanoma
Recurrent melanoma refers to a recurrence of tumor at the site of removal of a previous tumor, such as in, around, or under the surgical scar. It may also refer to the appearance of metastatic melanoma in other body sites such as skin, lymph nodes, brain, or liver after the initial tumor has already been treated. Recurrence is most likely to occur within the first five years, but new tumors felt to be recurrences may show up decades later. Sometimes it is difficult to distinguish recurrences from new primary tumors.
The Stage Of Melanoma Depends On The Thickness Of The Tumor Whether Cancer Has Spread To Lymph Nodes Or Other Parts Of The Body And Other Factors
To find out the stage of melanoma, the tumor is completely removed and nearby lymph nodes are checked for signs of cancer. The stage of the cancer is used to determine which treatment is best. Check with your doctor to find out which stage of cancer you have.
The stage of melanoma depends on the following:
- The thickness of the tumor. The thickness of the tumor is measured from the surface of the skin to the deepest part of the tumor.
- Whether there are:
- Satellite tumors: Small groups of tumor cells that have spread within 2 centimeters of the primary tumor.
- Microsatellite tumors: Small groups of tumor cells that have spread to an area right beside or below the primary tumor.
- In-transit metastases: Tumors that have spread to lymph vessels in the skin more than 2 centimeters away from the primary tumor, but not to the lymph nodes.
Read Also: Is Stage 3 Melanoma Curable
What Is Skin Cancer And Melanoma
Skin cancer is a disease that occurs when your skin cells grow abnormally, usually from too much exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun.
This uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells forms a tumour in the skin. Tumours are either benign , or malignant .
Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer: each year, more than 13,000 Australians are diagnosed with a melanoma and almost 980,000 new cases of non-melanoma skin cancers are treated. Skin cancer is mostly preventable, and there are effective treatment options available.
Skin cancers are named according to the cells in which they form. There are 3 main types:
- Basal cell carcinoma begins in the lower segment of cells of the epidermis your outer layer of skin. These tend to grow slowly, and rarely spread to other parts of the body.
- Squamous cell carcinoma grows from the flat cells found in the top layer of your epidermis. SCC can grow quickly on the skin over several weeks or months. Bowens disease is an early form of SCC that hasnt grown beyond the top layer of skin.
- Melanoma grows from cells called melanocytes cells that give your skin its colour. Melanoma is the rarest type of skin cancer but is considered the most serious because it can spread quickly throughout the body.
BCC and SCC are also called non-melanoma skin cancers. BCC represents more than 2 in 3 non-melanoma skin cancers, and around 1 in 3 are SCC. There are other types of non-melanoma skin cancers, but they are rare.
Recurrence In Nearby Lymph Nodes
If nearby lymph nodes werenât all removed during the initial treatment, the melanoma might come back in these lymph nodes. Lymph node recurrence is treated by lymph node dissection if it can be done, sometimes followed by adjuvant treatments such as radiation therapy and/or immunotherapy or targeted therapy . If surgery is not an option, radiation therapy or systemic treatment can be used.
Read Also: Lobular Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Prognosis And Survival For Non
If you have non-melanoma skin cancer, you may have questions about your prognosis. A prognosis is the doctors best estimate of how cancer will affect someone and how it will respond to treatment. Prognosis and survival depend on many factors. Only a doctor familiar with your medical history, the type, size and grade of the cancer, the treatments chosen and the response to treatment can put all of this information together with survival statistics to arrive at a prognosis.
A prognostic factor is an aspect of the cancer or a characteristic of the person that the doctor will consider when making a prognosis. Prognostic factors help doctors predict a prognosis and plan treatment and follow-up.
Doctors use many of the following prognostic factors to classify basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma into risk groups. The risk groups help the doctor estimate the risk that the cancer will come back . Doctors also use the risk groups to help plan the best treatment.
Prognosis and survival for most non-melanoma skin cancers is excellent. The following are prognostic factors for non-melanoma skin cancer.
Treating Stage 3 Melanoma
If the melanoma has spread to nearby lymph nodes , further surgery may be needed to remove them.
Stage 3 melanoma may be diagnosed by a sentinel node biopsy, or you or a member of your treatment team may have felt a lump in your lymph nodes.
The diagnosis of melanoma is usually confirmed using a needle biopsy .
Removing the affected lymph nodes is done under general anaesthetic.
The procedure, called a lymph node dissection, can disrupt the lymphatic system, leading to a build-up of fluids in your limbs. This is known as lymphoedema.
Cancer Research UK has more information about surgery to remove lymph nodes.
Read Also: Prognosis For Skin Cancer
Treatment By Stage Of Melanoma
Different treatments may be recommended for each stage of melanoma. General descriptions by stage are below. Your doctor will recommend a specific treatment plan for you based on the stage and other factors. Detailed descriptions of each type of treatment are provided earlier on this page. Clinical trials may also be a treatment option for each stage.
Stage 0 melanoma
Stage 0 melanoma is almost always treated with surgery alone, usually a wide excision.
Stage I melanoma
Stage I melanoma is usually treated with surgical removal of the tumor and some of the healthy tissue around it. The doctor may recommend lymph node mapping, and some lymph nodes may be removed.
Stage II melanoma
The standard treatment for stage II melanoma is surgery to remove the tumor and some of the healthy tissue around it. While this surgery is being done, lymph node mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy may also be done. In some people with stage II melanoma, treatment with interferon may be recommended after surgery to lower the chances of the cancer coming back. Treatment in a clinical trial for stage II melanoma may also be an option. Ask your doctor about what clinical trials may be available for you.
Stage III melanoma that can be removed with surgery
Advanced melanoma
-
The persons age and overall health
-
The locations and number of metastases
-
How fast the disease is spreading
-
The presence of specific genetic mutations in the tumor
-
The patients preferences
Treating brain metastases
Who Is At Risk For Melanoma
Those most at risk for developing melanoma include people with
- Family history of the disease
- High amounts of sun exposure or to indoor tanning
- A previous diagnosis of melanoma
- A suppressed immune system, due to illness, such as HIV infection, or a kidney, heart or liver transplant
- Fair skin that tends to burn
- Atypical moles , which are large moles that have irregular color and shape
The risk of developing melanoma also increases with age. Anyindividual who is older than 50 or 60 years of age shouldschedule regular appointments with his/her dermatologist.However, about half of people with melanoma are diagnosedwhen they are younger than 50.
Though a person of any race or ethnicity can develop melanoma,the rate of the disease is 20 times higher in white peoplethan black people. However, because the disease’s early warningsigns are often missed, it is diagnosed in the advanced stagesapproximately three times more often in African-Americansthan in Caucasians.
Read Also: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate Stage 4
Treatment Of Stage I Melanoma
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage I melanoma may include the following:
- Surgery to remove the tumor and some of the normaltissue around it. Sometimes lymph node mapping and removal of lymph nodes is also done.
- A clinical trial of new ways to find cancercells in the lymph nodes.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
How Is Melanoma Treated
Your melanoma treatment will depend on the stage of the melanoma and your general health.
Surgery is usually the main treatment for melanoma. The procedure involves cutting out the cancer and some of the normal skin surrounding it. The amount of healthy skin removed will depend on the size and location of the skin cancer. Typically, surgical excision of melanoma can be performed under local anesthesia in the dermatologist’s office. More advanced cases may require other types of treatment in addition to or instead of surgery.
Treatments for melanoma:
- Melanoma Surgery: In the early stages, surgery has a high probability of being able to cure your melanoma. Usually performed in an office, a dermatologist numbs the skin with a local anesthetic and removes the melanoma and margins .
- Lymphadenectomy: In cases where melanoma has spread, removal of the lymph nodes near the primary diagnosis site may be required. This can prevent the spread to other areas of your body.
- Metastasectomy: Metastasectomy is used to remove small melanoma bits from organs.
- Targeted cancer therapy: In this treatment option, drugs are used to attack specific cancer cells. This targeted approach goes after cancer cells, leaving healthy cells untouched.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy includes treatments with high-energy rays to attack cancer cells and shrink tumors.
- Immunotherapy: immunotherapy stimulates your own immune system to help fight the cancer.
Recommended Reading: Skin Cancer Spreading To Lymph Nodes