Types Of Melanoma Skin Cancer
Melanoma skin cancer can grow into and destroy nearby tissue. It can also spread to other parts of the body. Melanoma skin cancer is also called cutaneous melanoma and malignant melanoma of the skin.
There are 4 main types of melanoma skin cancer superficial spreading, nodular, lentigo maligna and acral lentiginous.
Get Support From All American Hospice
Merkel cell carcinoma is a strange case but no less dangerous despite its oddities. Like all forms of cancer, it should be taken seriously perhaps a bit more than most and treatment should be pursued at the earliest.
Remember, you are the master of your body, and if you notice anything strange that you cannot explain, you should book an appointment with a professional immediately and get yourself checked out. Your safety is what matters most, and this is not something you should take risks with. For a consultation on expert caregiving for Merkel cell carcinoma cases, set up a consultation with All American Hospice today.
Merkel Cell Carcinoma: A Different Type Of Skin Cancer
This post is available in: Spanish
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare form of skin cancer that is being diagnosed in more people. The number of cases of Merkel cell carcinoma diagnosed between 2000 and 2013 increased 95 percent, according to new research published in this months Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
This type of skin cancer is very rare, usually occurring in elderly Caucasians, said Ramon Jimenez, M.D., chief of melanoma and soft tissue sarcoma surgery at Miami Cancer Institute. People who are immune suppressed, such as transplant and HIV patients, are also at risk of Merkel cell carcinoma. And people with lymphoma, or cancers of the lymphatic system, are also more prone to this rare type of skin cancer.
About 1,500 cases of MCC are diagnosed each year in the U.S., and about 70 percent of people diagnosed are older than 70, says the American Cancer Society . It credits better diagnostic tests, people living longer and being exposed to more sun and more people living with weakened immune systems as the most likely reasons for the increase.
While MCC can develop anywhere, the most common area by far, and where about half of the cases appear, is the head and neck area, Dr. Jimenez said. The sun exposed areas of the face, ears, neck and upper extremities are most prone, as well as the scalp in bald men.
Differences Between Merkel Cell Carcinoma and Melanoma
Treatment for Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Also Check: Stage Iii Melanoma Treatment
When Should I See A Doctor
- You should see your doctor if you have any new or changing marks on your skin. Be aware of any lumps, growths, moles, or other abnormal areas on your skin. Watch for new spots or areas that are changing. This can include skin marks that grow larger, bleed, crust, or itch.
- Early diagnosis and treatment is important to prevent the cancer from spreading. Your healthcare provider may recommend you do a skin self-exam once a month or more.
What Are The Risk Factors For Merkel Cell Carcinoma
The known risk factors for Merkel cell carcinoma include:
-
Exposure to UV rays. Like many other types of skin cancer, the risk of Merkel cell carcinoma is higher in people who have been exposed to a lot of UV rays from the sun or from other sources like tanning beds. People who are treated for psoriasis with UV rays may also have a higher risk.
-
Weakened immune system. People with weakened immune systems, such as people who have had an organ transplant, are at increased risk for this cancer.
-
Light-colored skin. People with lighter skin are at higher risk.
-
Older age. People older than 50 are more likely to get this cancer.
-
Being male. Men are more likely to get Merkel cell carcinoma.
Researchers have found that Merkel cell carcinoma almost always shows infection with a virus known as Merkel cell polyomavirus . It is not known how the virus may contribute to the growth of this cancer. Most people are infected with this virus at some point. But very few people develop this cancer.
Don’t Miss: What Does Skin Cancer On Scalp Feel Like
What You Need To Know
Merkel cell carcinoma is rare and dangerous but treatable, especially when found at an early stage. Be watchful for any new or changing lesions on your skin and look out for these warning signs.
If youve been treated for a previous MCC, pay close attention to the site and the surrounding region. Contact your medical team immediately if you see any suspicious changes.
How to spot a Merkel Cell Carcinoma
APPEARANCE Painless shiny or pearly lesions or nodules
SIZE Dimensions vary, but the average size at detection is 1.7 cm, about the diameter of a dime.
COLOR Skin-colored, red, purple or bluish-red
LOCATION Frequently on sun-exposed areas, often on the head and neck, particularly the eyelids.
While rare, Merkel cell carcinomas are often aggressive and can advance rapidly which is why early detection and removal are especially important. Memorial Sloan Kettering oncologist Sandra DAngelo, MD, shares some important warning signs you should never ignore.
Basal Cell Carcinoma: The Most Common Skin Cancer
Basal cell carcinoma, which is also called basal cell skin cancer, is the most common form of skin cancer, accounting for about 80 percent of all cases.
Rates of basal cell carcinoma have been increasing. Experts believe this is due to more sun exposure, longer lives, and better skin cancer detection methods.
This type of cancer begins in the skins basal cells, which are found in the outermost layer, the epidermis. They usually develop on areas that are exposed to the sun, like the face, head, and neck.
Basal cell carcinomas may look like:
- A flesh-colored, round growth
- A pinkish patch of skin
- A bleeding or scabbing sore that heals and then comes back
They typically grow slowly and dont spread to other areas of the body. But, if these cancers arent treated, they can expand deeper and penetrate into nerves and bones.
Though its rare, basal cell carcinoma can be life-threatening. Experts believe that about 2,000 people in the United States die each year from basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma.
Some risk factors that increase your chances of having a basal cell carcinoma include:
- Being exposed to the sun or indoor tanning
- Having a history of skin cancer
- Being over age 50
- Having chronic infections, skin inflammation, or a weakened immune system
- Being exposed to industrial compounds, radiation, coal tar, or arsenic
- Having an inherited disorder, such as nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome or xeroderma pigmentosum
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 1 Survival Rate
Where Does Mcc Occur On The Body
MCC primarily occurs on highly sun-exposed skin such as the head/neck and arms , but it can occur anywhere on the body, including sun-protected areas such as the buttock or the scalp under hair.
Solid circles depict MCC tumors that arose on the skin . Open circles indicate MCCs that presented in lymph nodes without an associated primary lesionprimary lesionThe abnormal tissue that appeared first. The majority of Merkel cell carcinoma primary lesions occur in sun-exposed areas. In some cases of MCC the patient has no primary lesion and instead has a nodal presentation . In these cases the primary lesion likely was destroyed by the immune system. . Recent data suggest that patients who present without a primary lesionlesionAn area of abnormal tissue that may be either benign or malignant. originally did have a lesion on the skin, but that their immune system eliminated the tumor. Elimination of the primary lesion is associated with less risk for patients that already have the same stagestagePhysicians determine the stage of cancer by performing physical exams and tests. Stages describe the extent of cancer within the body, especially whether the disease has spread from the primary site to other parts of the body. at presentation .
Survival: Whats The Outlook For People With Merkel Cell Carcinoma
According to the American Cancer Society, the five-year survival rate for people with localized MCC , is 78 percent .
For regional MCC , the five-year survival rate falls to 51 percent. If MCC has spread to distant organs, the survival rate is 17 percent.
Overall, about one third of MCC patients succumb to the disease.
While survival rates can give you an idea of how long people live based on what stage their cancer was at diagnosis, they cant tell you how long you will live. Other factors, such as your age and overall health, as well as how well the cancer responds to treatment, also play a significant role in your prognosis.
Moreover, current survival statistics are based on outcomes of people diagnosed with MCC between 2008 and 2014. Thanks to new and better treatments, people now being diagnosed with MCC may have a much better outlook.
Read Also: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
How Are Mcc Tumors Measured
Merkel cellMerkel cellMerkel cells are found in the lower part of the epidermis. Although the exact function of Merkel cells is unknown, they are thought to be touch receptors. Also known as neuroendocrine cells, they have machinery similar to nerve cells and to hormone-secreting cells. carcinomas are measured by their largest dimension, in centimeters. Among 5722 cases, the average Merkel cell carcinomaMerkel cell carcinomaA skin cancer composed of cells that look microscopically similar to normal Merkel cells present in the skin. MCC was first described in 1972 and only in the 1990s was the CK20 antibody developed to make it easily identifiable by pathologists. Many doctors and patients are not aware of this cancer because of its recent description and relative rarity . About 40% of patients treated for MCC will experience a recurrence, making it far more aggressive than most other types of skin cancer, including melanoma. was 1.7 cm in diameter . Larger MCC tumors are associated with moderately higher risk of recurrence and spread to lymph nodes, but even a very small MCC tumor still has at least a 15% chance of already having spread to nearby lymph nodes.1
What Is The Treatment For Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Diagnosis of Merkel cell carcinoma can be made by conducting a physical examination on the patient. They may also conduct skin biopsy, imaging tests like X-ray and CT scan, and certain blood tests to confirm the diagnosis of Merkel cell carcinoma .
The treatment of Merkel cell carcinoma is done using anti-cancer drugs and radiation therapy. If required, doctors can also consider surgical treatment of Merkel cell carcinoma, to remove the cancerous tumor along with some areas of the skin surrounding the tumor. If the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes in the region affected by skin tumor, treatment of Merkel cell carcinoma can also include surgical removal of the relevant lymph nodes. Other options of treatment for Merkel cell carcinoma also include chemotherapy if the Merkel cell carcinoma has spread to the lymph nodes or other organs in their body, or if it has relapsed despite treatment.
Read Also: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Stages Of Skin Cancer
If you receive a skin cancer diagnosis, the next step is to identify its stage.
Staging is how doctors determine whether the cancer has spread to other parts of your body. Staging is common with melanoma and Merkel cell carcinoma, because these cancers are more likely to spread.
Typically, basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas dont involve staging. These skin cancers are easily treated and dont usually spread. However, your doctor may recommend staging for larger lesions.
Staging is based on the size of the growth and whether it has high-risk features. High-risk features include:
- larger than 2 millimeters thick
- spreads into the lower levels of the skin
- spreads into the space around a nerve
- appears on the lips or ears
- appears abnormal under a microscope
Heres a general breakdown of skin cancer stages:
- Stage 0. The cancer hasnt spread to surrounding areas of the skin.
- Stage 1. The cancer is 2 centimeters across or less, with no high-risk features.
- Stage 2. The cancer is more than 2 cm across and has a least two high-risk features.
- Stage 3. The cancer has spread to the bones in the face or nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage 4. The cancer has spread to the lymph nodes or internal organs.
What It Looks Like
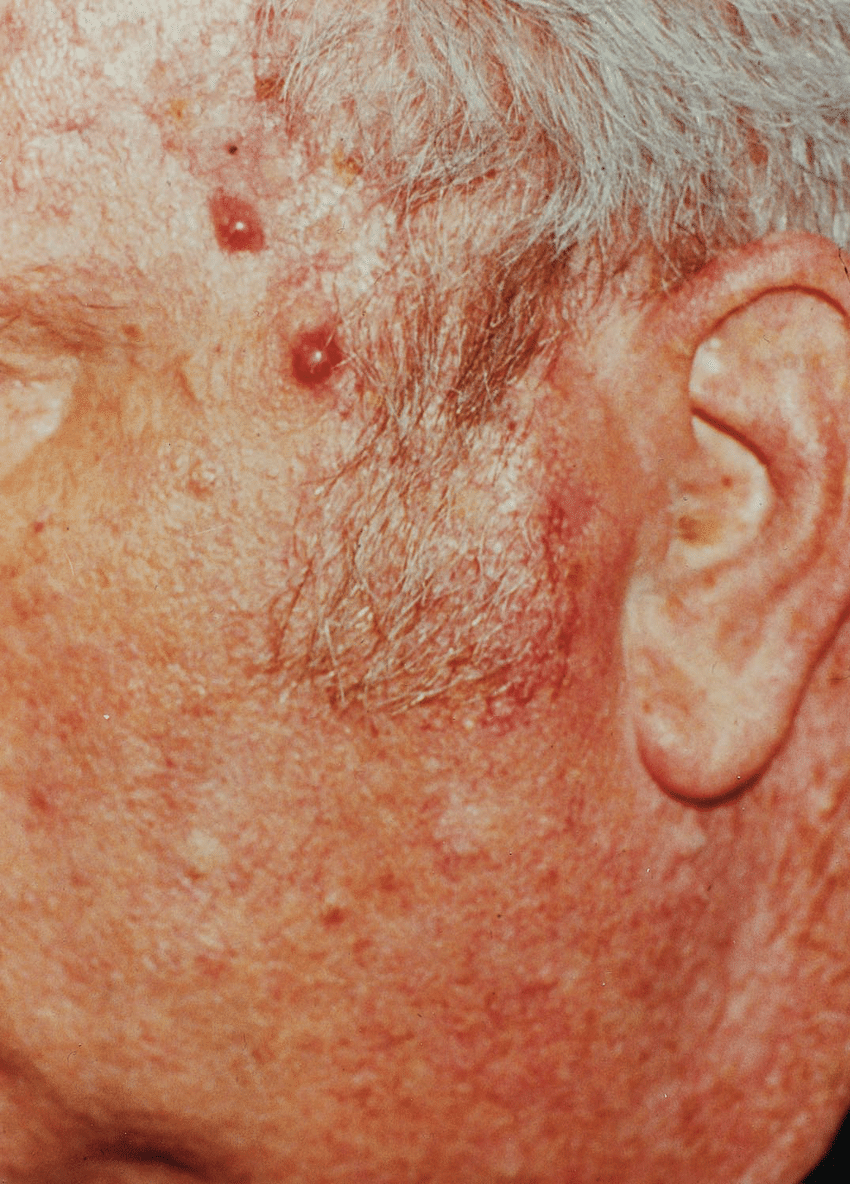
Squamous cell cancer involves the runaway growth of keratinocytes, cells in the outermost layer of skin, which produce the protein keratin. Squamous means scaly in 60%80% of cases, the lesions emerge on or near scaly patches called actinic keratoses that develop from sun-damaged skin.
To continue reading this article, you must log in.
- Research health conditions
- Prepare for a doctors visit or test
- Find the best treatments and procedures for you
- Explore options for better nutrition and exercise
Don’t Miss: Stage 3 Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
Appearance Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
MCC usually develops on sun-exposed skin as a painless, firm bump that can be red-purple or skin-colored. Patients frequently point out a new MCC to their doctor because a bump is growing rapidly and/or does not look like anything the patient has ever had before. Most MCCs are diagnosed when a skin biopsybiopsyThe removal of cells or tissue in order to determine the presence, characteristics, or extent of a disease by a pathologist usually using microscopic analysis. is performed to rule out another sun-induced skin cancercancerA term used to describe diseases in which abnormal cells continually divide without normal regulation. Cancerous cells may invade surrounding tissues and may spread to other regions of the body via blood and the lymphatic system. or to remove a presumed cyst. In the vast majority of cases, both the doctor and the patient are surprised by the diagnosis of MCC. For more examples of MCC tumors beyond those presented on this page, visit the Clinical Photos page.
Staging Merkel Cell Carcinoma
At the time of diagnosis, your medical team will stage your cancer, meaning they will assess how far it has progressed. The stage is based on many factors, including the size of the tumor and the extent of disease in the lymph nodes and elsewhere in the body.
The earliest stage Merkel cell cancers are called stage 0 , and then range from stages 1 through 4. Generally, the lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. Some stages are also subdivided by letter an earlier letter means a lower stage.
The stage of your MCC at diagnosis determines the chance for later spread, as well as your treatment plan.
RELATED: 10 Sun-Care Products That Dermatologists Use
Don’t Miss: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
History Of The Procedure
Freidrich Sigmund Merkel, a German histopathologist, first described the Merkel cell in 1875. He fixed and stained the skin of geese and ducks and demonstrated touch cells in the snouts of pigs. These clear-staining cells at the dermoepidermal junction were near myelinated nerve fibers. Merkel postulated that these cells acted as mechanoreceptors in all animals.
Cyril Toker first described Merkel cell carcinoma in 1972. On the basis of the histologic characteristics of the tumor, he named it trabecular cell carcinoma of the skin.
Subsequent studies involving immunohistochemistry and electron microscopy revealed that these tumors originate from the Merkel cell.
S Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
To help you spot MCC, the following pictures show you diverse ways that it can appear on the skin.
A red or pink spot
Looking much like an insect bite, testing revealed that the reddish spot on this patients shin was actually Merkel cell carcinoma.
Reddish, slightly raised spot that looks like a sore
The reddish, scaly, and slightly raised spot on this patients wrist is Merkel cell carcinoma, which could easily have been mistaken for a sore.
Quickly growing spot on your skin that sometimes bleeds
Any spot on your skin that is growing, bleeding, or changing in any way could be a skin cancer.
Quickly growing, firm, dome-shaped growth
This 87-year-old man was concerned about this quickly growing, dome-shaped mass on this lower eyelid, which testing showed was a Merkel cell carcinoma.
A stye or cyst
This aggressive skin cancer can look like a rapidly growing stye or cyst. Unlike a stye or cyst, Merkel cell carcinoma often feels painless.
A growing sore
Sometimes, this aggressive skin cancer looks like a sore, so its important to see a dermatologist if you notice a new spot on your skin that is growing rapidly. Skin cancer can also look like a sore that heals and returns.
Any fast-growing spot or mass
While Merkel cell carcinoma often looks like a dome-shaped growth or slightly raised and scaly patch, it can appear on the skin in diverse ways, as did the Merkel cell carcinoma on this mans head.
Red, pink, or purple spot thats growing
You May Like: What Stage Is Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Who Is Likely To Have Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Anyone can develop MCC. You are at higher risk of developing this type of cancer if you:
- Have lighter-colored skin
- Have a weakened immune system
- Use tanning beds or ultraviolet light therapy for psoriasis
- Have another type of cancer, especially another type of skin cancer
The incidence of MCC in the US is about 0.6 per 100,000 people per year. This is up about 4X since 1986. However, it must be noted that diagnosis has improved, the population is getting older, and immunosuppressant medications are rising. It is estimated that about 700 people with MCC die per year. The rate of death is about one in three. Melanoma, also a dangerous cancer, is said to kill about one in nine people per year.
Merkel Cell Carcinoma Is A Very Rare Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In The Skin
Merkel cells are found in the top layer of the skin. These cells are very close to the nerve endings that receive the sensation of touch. Merkel cell carcinoma, also called neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin or trabecular cancer, is a very rare type of skin cancer that forms when Merkel cells grow out of control. Merkel cell carcinoma starts most often in areas of skin exposed to the sun, especially the head and neck, as well as the arms, legs, and trunk.
Merkel cell carcinoma tends to grow quickly and to metastasize at an early stage. It usually spreads first to nearby lymph nodes and then may spread to lymph nodes or skin in distant parts of the body, lungs, brain, bones, or other organs.
Merkel cell carcinoma is the second most common cause of skin cancer death after melanoma.
Don’t Miss: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer