Skin Cancer Symptoms Often Begin With Actinic Keratosis
Lesions are abnormal changes in tissues, such as a break or wound on the skin. Lesions from actinic keratosis are referred to as precancerous because they can turn into malignant tumors. Forty to 60 percent of all SCCs begin as actinic keratosis, and recent evidence suggests the two are genetically linked.
Actinic keratosis is likely to be caused by cumulative exposure to the suns rays. Its characteristics are as follows:
- It occurs most often in sun-sensitive, light-skinned, light- or red-haired individuals with blue or green eyes.
- It develops in areas of the skin frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, scalp, back of the hands, ears, neck, and forearms.
- It is often characterized by a rough or crusty dry skin lesion that is limited to a small areausually between one-eighth and one-quarter-inch.
- They may be gray, pink, red, or the same color as the skin, and may itch or cause a pricking or tender sensation.
Diagnosis of skin cancer symptoms may be as simple as an inspection by a dermatologist, but a biopsy may be necessary to determine if potentially cancerous changes are present.
How Widespread Is Bcc
Basal cell carcinoma is quite common, and the number of reported cases in the U.S. has steadily increased.
- An estimated 3.6 million Americans are diagnosed with BCC each year.
- More than one out of every three new cancers are skin cancers, and the vast majority are BCCs.
- The diagnosis and treatment of nonmelanoma skin cancers, including BCC and squamous cell carcinoma , increased up to 77 percent between 1994 and 2014.
Reviewed by:
Who Gets Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is the most common of all cancers, and basal cell carcinoma is the most prevalent type of skin cancer, striking one out of every eight Americans, including people in their 20s and 30s, women as well as men. It represents about one-third of all newly diagnosed cancers in the United States.
The most common site for basal cell carcinoma is the face, especially the nose or ears, but it can appear on any sun-exposed areas of skin. It is usually painless and slow growing, and rarely spreads to other parts of the body.
Don’t Miss: Basal Cell Carcinoma Late Stages
What Happens If Basal Cell Carcinoma Is Left Untreated
Basal cell carcinoma is a very slow growing type of non-melanoma skin cancer. If left untreated, basal cell carcinomas can become quite large, cause disfigurement, and in rare cases, spread to other parts of the body and cause death.
You may ask, What skin cancer looks like when it starts?
Squamous Cell Carcinoma This nonmelanoma skin cancer may appear as a firm red nodule, a scaly growth that bleeds or develops a crust, or a sore that doesnt heal. It most often occurs on the nose, forehead, ears, lower lip, hands, and other sun-exposed areas of the body.
Donât Miss: How To Tell If Itâs Skin Cancer
Basal Cell Carcinoma Is Common
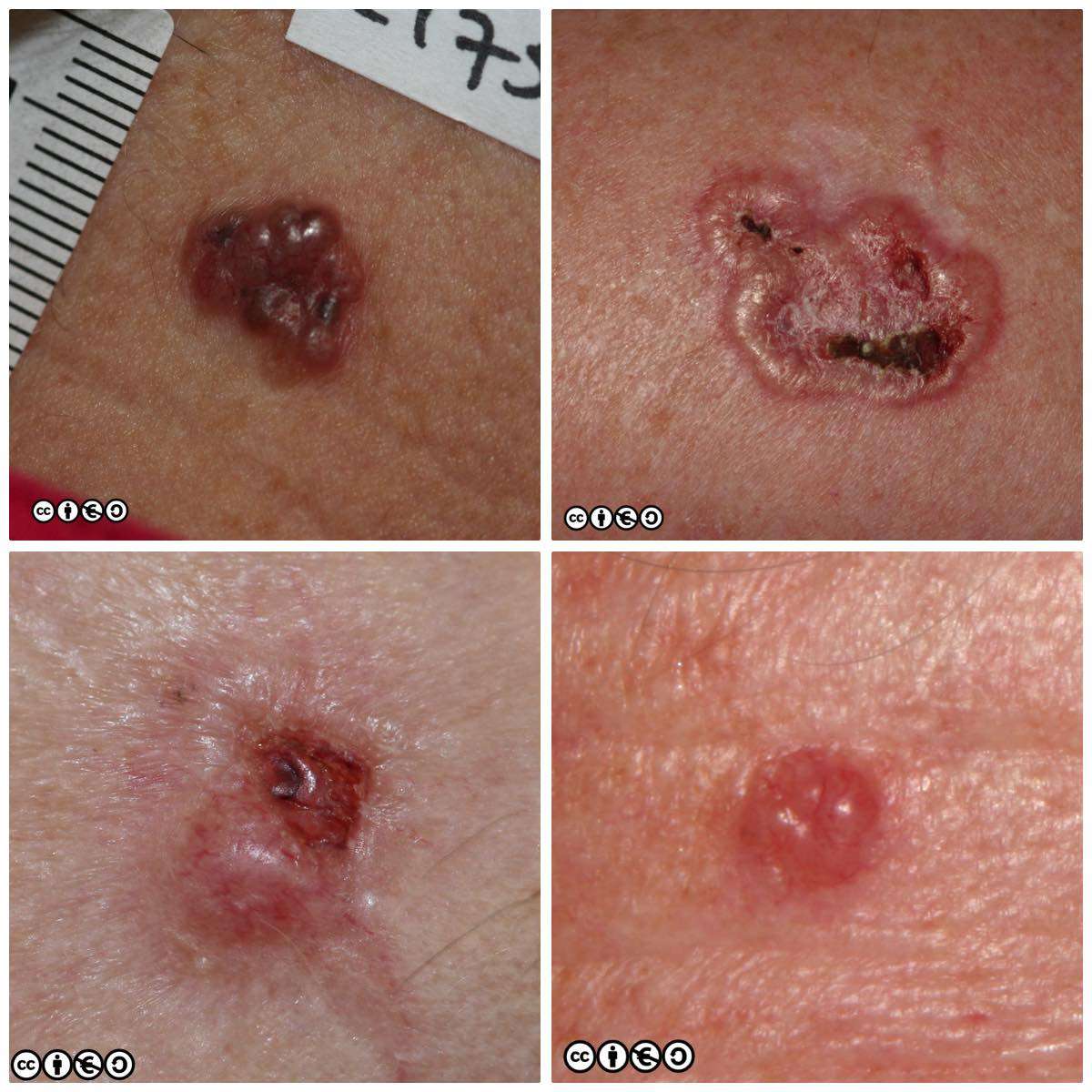
If youve been diagnosed with basal cell carcinoma or BCC, you have plenty of company. As the most common type of cancer in the world, doctors diagnose millions of people with BCC every year. In the United States alone, its estimated that about 2 million Americans hear, You have basal cell carcinoma, each year.1
Most people who develop this skin cancer have fair skin that they seldom protected with sunscreen or sun-protective clothing. Before they developed skin cancer, they often noticed signs of sun damage on their skin, such as age spots, patches of discolored skin, and deep wrinkles.
Dermatologist examining patient for signs of skin cancer
You have a greater risk of developing this skin cancer if youve seldom protected your skin from the sun throughout your life or used tanning beds.
Although BCC is most common in people who have fair skin, people of all colors get this skin cancer.
For most people, BCC is not life-threatening. It tends to grow slowly. It seldom spreads to another part of the body. Even so, treatment is important.
When found early, this skin cancer is highly treatable. An early BCC can often be removed during an appointment with your dermatologist.
Given time to grow, this skin cancer can grow deep, injuring nerves, blood vessels, and anything else in its path. As the cancer cells pile up and form a large tumor, the cancer can reach into the bone beneath. This can change the way you look, and for some people the change may be disfiguring.
Don’t Miss: Small Blue Cell Tumor Prognosis
Where Do Skin Cancers Start
Most skin cancers start in the top layer of skin, called the epidermis. There are 3 main types of cells in this layer:
- Squamous cells: These are flat cells in the upper part of the epidermis, which are constantly shed as new ones form. When these cells grow out of control, they can develop into squamous cell skin cancer .
- Basal cells: These cells are in the lower part of the epidermis, called the basal cell layer. These cells constantly divide to form new cells to replace the squamous cells that wear off the skins surface. As these cells move up in the epidermis, they get flatter, eventually becoming squamous cells. Skin cancers that start in the basal cell layer are called basal cell skin cancers or basal cell carcinomas.
- Melanocytes: These cells make the brown pigment called melanin, which gives the skin its tan or brown color. Melanin acts as the bodys natural sunscreen, protecting the deeper layers of the skin from some of the harmful effects of the sun. Melanoma skin cancer starts in these cells.
The epidermis is separated from the deeper layers of skin by the basement membrane. When a skin cancer becomes more advanced, it generally grows through this barrier and into the deeper layers.
What Happens If You Don’t Treat Basal Cell Carcinoma
Mamelak. In this way, the cancer can spread to the muscle and bone, causing further damage that has to be dealt with. If an open sore or ulcer develops, patients can also be at risk for infections and other complications.
How serious is basal cell skin cancer?
The Most Common Skin Cancer BCCs arise from abnormal, uncontrolled growth of basal cells. Because BCCs grow slowly, most are curable and cause minimal damage when caught and treated early. Understanding BCC causes, risk factors and warning signs can help you detect them early, when they are easiest to treat and cure.
Don’t Miss: What Does Stage 3 Melanoma Look Like
Basal Cell Carcinoma Symptoms
An irritated patch of skin that wont heal, as was the case with Lebwohls colleague, isnt the only indication of basal cell carcinoma.
Anthony M. Rossi, MD, a dermatologic surgeon at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City who specializes in Mohs micrographic surgery and skin cancer treatment, says one of the most common scenarios is when people say they thought they had a pimple, but it wouldnt heal or go away.
Warning signs for basal cell carcinoma include something thats red, crusted, scaly, not healing, bleeding, or even a new shiny pearl papule says Dr. Rossi.
Basal cell carcinoma can also appear atypically it can be flat with a whitish discoloration or appear as a bump on the skin thats pink or brown, says Rossi. There are multiple subtypes of BCC, which, characteristically, have different degrees of pigmentation and can be broad ranging in appearance.
This type of skin cancer rarely causes pain as it develops. Because it can look like a scab and appear to heal repeatedly without growing, people can go for months or even years thinking the skin abnormality is just a sore or wound. If you notice a spot that won’t heal or constantly bleeds you should see a dermatologist, says Lebwohl.
What Are The Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
A basal cell carcinoma is a stubborn, persistent spot that usually appears on areas that have been exposed to the sun, such as the head, neck, chest, arms and legs. The spot may take one of several forms: an open sore, a reddish irritated patch, a shiny red bump or nodule, a pink growth, or a small scar-like patch. In some people, the condition may resemble psoriasis or eczema. The spot will sometimes bleed, scab and heal up after a week or two, then bleed or become irritated again.
The main warning sign for basal cell carcinoma is that the spot doesn’t go away on its own. Patients often mistake basal cell carcinomas for minor injuries, says Dr. Christensen. They dont realize that an ordinary cut or scratch will heal within a month or so. So if something hasnt healed within a month, it should be examined by a dermatologist.
You May Like: Is Melanoma In Situ Malignant
Melanoma: The Deadliest Skin Cancer
Melanoma is the most serious type of skin cancer, because it tends to spread if its not treated early.
This cancer starts in the melanocytes cells in the epidermis that make pigment.
About 100,350 new melanomas are diagnosed each year.
Risk factors for melanoma include:
- Having fair skin, light eyes, freckles, or red or blond hair
- Having a history of blistering sunburns
- Being exposed to sunlight or tanning beds
- Living closer to the equator or at a higher elevation
- Having a family history of melanoma
- Having many moles or unusual-looking moles
- Having a weakened immune system
Melanoma can develop within a mole that you already have, or it can pop up as a new dark spot on your skin.
This cancer can form anywhere on your body, but it most often affects areas that have had sun exposure, such as the back, legs, arms, and face. Melanomas can also develop on the soles of your feet, palms of your hands, or fingernail beds.
Signs to watch out for include:
- A mole that changes in color, size, or how it feels
- A mole that bleeds
RELATED: The Difference Between Chemical and Mineral Sunscreen
Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Considered Malignant
The vast majority of skin cancers are basal cell carcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas. While malignant, these are unlikely to spread to other parts of the body if treated early. They may be locally disfiguring if not treated early. A small but significant number of skin cancers are malignant melanomas.
Don’t Miss: Stage 2 Cancer Symptoms
Common Skin Cancer Can Signal Increased Risk Of Other Cancers
Frequent skin cancers due to mutations in genes responsible for repairing DNA are linked to a threefold risk of unrelated cancers, according to a Stanford study. The finding could help identify people for more vigilant screening.
Basal cell carcinomas are common. More than 3 million cases a year are diagnosed nationwide.jax10289/Shutterstock.com
People who develop abnormally frequent cases of a skin cancer known as basal cell carcinoma appear to be at significantly increased risk for developing of other cancers, including blood, breast, colon and prostate cancers, according to a preliminary study by researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine.
The increased susceptibility is likely caused by mutations in a panel of proteins responsible for repairing DNA damage, the researchers found.
We discovered that people who develop six or more basal cell carcinomas during a 10-year period are about three times more likely than the general population to develop other, unrelated cancers, said Kavita Sarin, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology. Were hopeful that this finding could be a way to identify people at an increased risk for a life-threatening malignancy before those cancers develop.
Sarin is the senior author of the study, which was published online Aug. 9 in JCI Insight. Medical student Hyunje Cho is the lead author.
What Is Skin Cancer
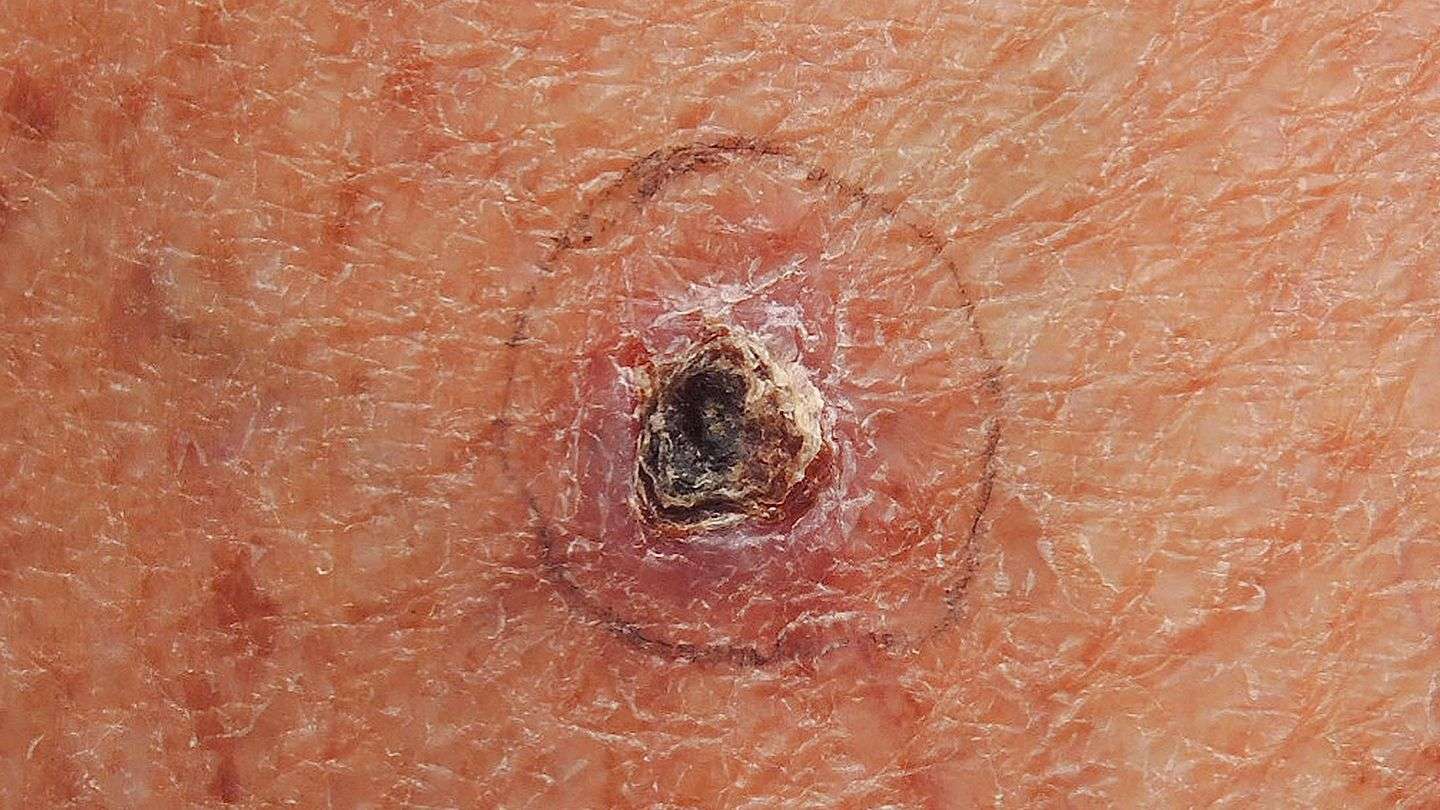
Skin cancer is the uncontrolled growth of cancer cells in the skin. Left untreated, with certain types of skin cancer, these cells can spread to other organs and tissues, such as lymph nodes and bone. Skin cancer is the most common cancer in the United States, affecting 1 in 5 Americans during their lifetimes, according to the Skin Cancer Foundation.
Read Also: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 3 Survival Rate
How Serious Should I Take Basal Cell Cancer Removed From My Nose
I recently had small area removed from my noseâ¦that came back as basal cell cancer from the biopsy. The Dr now wants to go in and work on the area more. My issue is he requires $950 up front for the procedure, because my health insurance has high deductible. Itâs entirely possible that the basal cell was removed with the first procedure. How likely are the risks and my chances that it will cause more problems.
Do Basal Cell Carcinoma And Melanoma Look Different
The first sign of basal cell carcinoma is usually a small white or flesh-colored skin bump that grows slowly and may bleed. On the other hand, the first sign of melanoma is often a noticeable change in a mole, such as:
- Asymmetry. The shape of one half of the mole does not mirror the other half.
- An irregular border. The edges of the mole may be ragged, notched or blurred, with the pigment appearing to spread into the surrounding skin.
- Uneven coloring. The mole may display shades of black, brown, tan, white, gray, red, pink or blue.
- An increase in diameter. There is a change in size, usually an increase. Melanomas can be tiny, but most are larger than the size of a pea .
- Evolution. The mole has changed over the past few weeks or months.
A skin biopsy is the only way to diagnose basal cell carcinoma or melanoma. A physician can remove a small portion of suspicious tissue, then send it to a lab to be analyzed under a microscope for evidence of cancer. Therefore, it is important to promptly discuss any unusual skin changes with a physician.
If you have been diagnosed with basal cell carcinoma or melanoma, a skin cancer specialist at Moffitt Cancer Center can offer a second opinion after reviewing your lab work, biopsies and images. Or, if you have a suspicious skin lesion, you can have it checked at Moffitt with or without a referral. To request an appointment, call or submit a new patient registration form online.
Don’t Miss: Basal Cell Carcinoma Etiology
How Is Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin Treated
In general, the treatment of Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin depends upon a variety of factors including:
- The location of the tumor
- The number of tumors
- The size of the tumor
- Any health considerations of the patient
A number of treatment methods may be used to treat Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin. The treatment types may include:
Topical medications can be used to treat Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma. This is because the thinness of the tumor permits permeation of the active ingredient to the full depth of the carcinoma. The two most frequently used active ingredients are imiquimod and 5-Flurouracil.
- Imiquimod is an immune system signal which calls for the migration of T-cells into the area of the tumor, which actively kill the cancer cells
- 5-Flurouracil is a metabolic agent which toxically kills the more basal cell carcinoma cells. The surrounding normal skin does not absorb the medication and hence is safe from the toxicity
Both these topical applications take at least a few weeks to treat a typically sized lesion, longer for larger lesions. The actions will lead to redness, irritation, sometimes crusting and possibly secondary infection
One advantage of these creams is that it is sometimes possible to treat the Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma without affecting the underlying skin at all, so after healing, little to no scarring is detectable.
Other techniques to treat this skin cancer may include:
Melanoma Skin Cancer Mole
What Are The Symptoms Of Basal Cell Cancer Of The Head And Neck
Basal cell cancers usually present as an abnormal growth on the skin. The growth may have the appearance of a wart, crusty spot, reddish patch, mole, nodule or bump, or a sore that does not heal. It may or may not bleed and can sometimes be painful. These are usually slow-growing tumors that begin as small spots on sun-exposed areas of the face. Because they can have such a range of appearances, any new persistent skin lesion should be evaluated.
Johns Hopkins Head and Neck Cancer Surgery Specialists
Our head and neck surgeons and speech language pathologists take a proactive approach to cancer treatment. Meet the Johns Hopkins specialists who will work closely with you during your journey.
Don’t Miss: Survival Rate Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Who Gets Basal Cell Carcinoma
Risk factors for BCC include:
- Age and sex: BCCs are particularly prevalent in elderly males. However, they also affect females and younger adults
- Repeated prior episodes of sunburn
- Fair skin, blue eyes and blond or red hairnote BCC can also affect darker skin types
- Previous cutaneous injury, thermal burn, disease
- Inherited syndromes: BCC is a particular problem for families with basal cell naevus syndrome , Bazex-Dupré-Christol syndrome, Rombo syndrome, Oley syndrome and xeroderma pigmentosum
- Other risk factors include ionising radiation, exposure to arsenic, and immune suppression due to disease or medicines
What Is Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is a cancer that grows on parts of your skin that get a lot of sun. It’s natural to feel worried when your doctor tells you that you have it, but keep in mind that it’s the least risky type of skin cancer. As long as you catch it early, you can be cured.
This cancer is unlikely to spread from your skin to other parts of your body, but it can move nearby into bone or other tissue under your skin. Several treatments can keep that from happening and get rid of the cancer.
The tumors start off as small shiny bumps, usually on your nose or other parts of your face. But you can get them on any part of your body, including your trunk, legs, and arms. If you’ve got fair skin, you’re more likely to get this skin cancer.
Basal cell carcinoma usually grows very slowly and often doesn’t show up for many years after intense or long-term exposure to the sun. You can get it at a younger age if you’re exposed to a lot of sun or use tanning beds.
Read Also: Stage 2 Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate