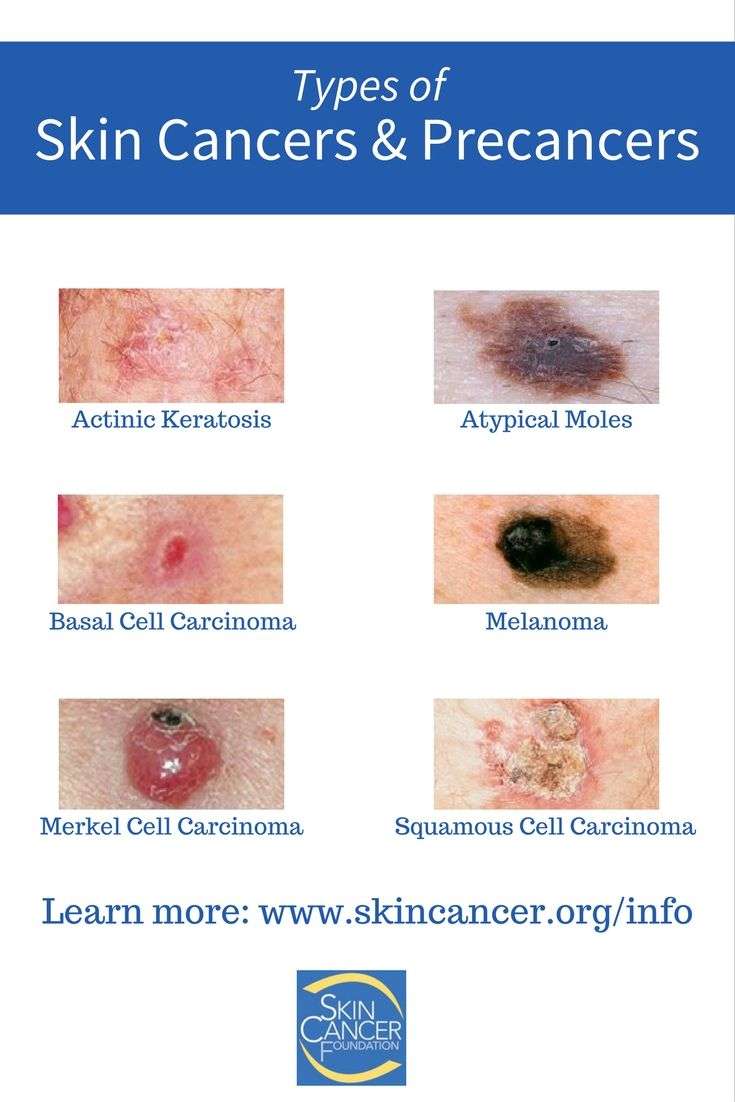
Basal Cell Carcinoma Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin And Actinic Keratosis Often Appear As A Change In The Skin
Not all changes in the skin are a sign of basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, or actinic keratosis. Check with your doctor if you notice any changes in your skin.
Signs of basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin include the following:
- A sore that does not heal.
- Areas of the skin that are:
- Raised, smooth, shiny, and look pearly.
- Firm and look like a scar, and may be white, yellow, or waxy.
- Raised and red or reddish-brown.
- Scaly, bleeding, or crusty.
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin occur most often in areas of the skin exposed to the sun, such as the nose, ears, lower lip, or top of the hands.
Signs of actinic keratosis include the following:
- A rough, red, pink, or brown, scaly patch on the skin that may be flat or raised.
- Cracking or peeling of the lower lip that is not helped by lip balm or petroleum jelly.
Actinic keratosis occurs most commonly on the face or the top of the hands.
Can Skin Cancer On The Scalp Spread To The Brain
Yes. If left untreated, skin cancer on the scalp can spread from your scalp to other areas of your body, including your brain.
This is known as metastatic cancer or, in some areas, stage IV cancer. Spreading to the brain is a relatively common form of metastatic skin cancer, especially with melanoma, which is part of why early treatment is essential.
Recommended Reading: Is Stage 0 Melanoma Considered Cancer
What Are The Three Warning Signs Of Skin Cancer
Our skin cancer clinic in Cairns performs skin checks and can identify any abnormalities that may lead us to diagnose skin cancer.;
Cairns skin experts provide you with effective skin treatments and skin cancer solutions that ease any worries you have about your skin.;
Here are some warning signs that you always need to watch out for and if you identify any of them, consult a skin expert immediately.
Also Check: What Is The Difference Between Skin Cancer And Melanoma
How Skinvision Can Help You
SkinVision enables you to check your skin spots for signs of skin cancer within 30 seconds. Our algorithm is currently at the level of a specialist dermatologist.In skin spots with a potential health risk, SkinVision provides feedback about the preferred next step to take.
SkinVision also enables you to store photos to keep track of changes over time, helping you to monitor your health in the long term.
The efficient and easy-to-use solution is available for iOS and Android and helps to make skin monitoring a simple routine.
Leukemias Lymphomas And Multiple Myeloma
Any type of blood-related cancer may present with itching, but the most common culprits include Hodgkin’s lymphoma, leukemia, and cutaneous T cell lymphoma .
With cutaneous T cell lymphomas, the cancer can cause itching both due to direct skin involvement and due to the secretion of inflammatory substances such as interleukin-31.
Myelodysplastic disorders such as polycythemia vera also commonly present with itching.
With both T cell lymphomas and myeloproliferative disorders, itching of the skin due to the exposure to water may even be present for years before the cancer is diagnosed.
Read Also: Are There Stages Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Risk Factors And Causes Of Skin Cancer
Despite the fact that high melanin content confers better photo protection, significant photo damage in the form of epidermal atypia and atrophy, dermal collagen and elastin damage and pigmentary disorders can cause skin cancer which could be fatal due to delay in detection in skin of color . Skin cancer is skin growth with varying degrees of malignancy . It is not yet very clear why skin cancer incidence has grown so dramatically over the past decades but the reason is likely to be multi factorial which includes increased UV exposure, environmental, hereditary risk factors and improved surveillance and earlier recognition . In addition, genetic polymorphisms also modulate the susceptibility to skin cancer .
Organ transplant receivers especially kidney and HIV patients have an increased frequency of skin cancers . Some treatments, including radiation therapy, phototherapy, psoralen and long-wave ultraviolet radiation can also predispose to skin malignancies . Viral infections such as the human papilloma virus can cause cancer. Patients with familial genetic patterns are vulnerable to particular types of skin cancers . Certain drugs, from common antibiotics to heart medications, can increase the skins sensitivity to sunlight, causing the skin to burn in less time and may increase the incidence of skin cancer .
Tests Or Procedures That Examine The Skin Are Used To Diagnose Basal Cell Carcinoma And Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin
The following procedures may be used:
- Physical exam and health history: An exam of the body to check general signs of health, including checking for signs of disease, such as lumps or anything else that seems unusual. A history of the patients health habits and past illnesses and treatments will also be taken.
- Skin exam: An exam of the skin for bumps or spots that look abnormal in color, size, shape, or texture.
- Skin biopsy: All or part of the abnormal-looking growth is cut from the skin and viewed under a microscope by a pathologist to check for signs of cancer. There are four main types of skin biopsies:
- Shave biopsy: A sterile razor blade is used to shave-off the abnormal-looking growth.
- Punch biopsy: A special instrument called a punch or a trephine is used to remove a circle of tissue from the abnormal-looking growth. Enlarge Punch biopsy. A hollow, circular scalpel is used to cut into a lesion on the skin. The instrument is turned clockwise and counterclockwise to cut down about 4 millimeters to the layer of fatty tissue below the dermis. A small sample of tissue is removed to be checked under a microscope. Skin thickness is different on different parts of the body.
- Incisional biopsy: A scalpel is used to remove part of a growth.
- Excisional biopsy: A scalpel is used to remove the entire growth.
Recommended Reading: What Does Skin Cancer On The Hand Look Like
Medical Treatment For Skin Cancer
Surgical removal is the mainstay of skin cancer treatment for both basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas. For more information, see Surgery.People who cannot undergo surgery may be treated by external radiation therapy. Radiation therapy is the use of a small beam of radiation targeted at the skin lesion. The radiation kills the abnormal cells and destroys the lesion. Radiation therapy can cause irritation or burning of the surrounding normal skin. It can also cause fatigue. These side effects are temporary. In addition, topical chemotherapy creams have been FDA approved for the treatment of certain low-risk nonmelanoma skin cancers. Patients with advanced or many basal cell carcinomas are sometimes prescribed oral pills to block the growth of these cancers. Side effects include muscle spasms, hair loss, taste changes, weight loss and fatigue.
In advanced cases of melanoma, immune therapies, vaccines, or chemotherapy may be used. These treatments are typically offered as clinical trials. Clinical trials are studies of new therapies to see if they can be tolerated and work better than existing therapies.
What Happens If Precancers Go Untreated
As the name suggests, precancers are damaged skin cells that arent considered cancerous, but if they are left untreated, these lesions are at high risk to become skin cancer. There are two main types of precancerous skin conditions: actinic keratosis and dysplastic nevi. Actinic keratosis looks like a rough, scaly patch of the skin that is usually red or brown. This condition may develop into squamous cell carcinoma if left untreated.
Nevi are moles, and dysplastic nevi is a term that means a mole is abnormal. Dysplastic nevi may develop into melanoma without proper treatment. While precancerous skin cancers are not malignant on their own, the potential to develop into life-threatening forms of this condition means they need to be evaluated regularly.
Don’t Miss: How Serious Is Skin Cancer
How To Check Your Skin
- Make sure you check your entire body, as skin cancers can sometimes occur on parts of the body that are not exposed to the sun, such as the soles of the feet, between fingers and toes and under nails.
- Undress completely and make sure you have good light.
- Use a mirror to check hard to see spots, like your back and scalp, or get a family member, partner or friend to check for you.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Pictures
Squamous cell carcinoma;also appears in areas most exposed to the sun and, as indicated in the pictures below, often presents itself as a scab or sore that doesnt heal, a volcano-like growth with a rim and crater in the middle or simply as a crusty patch of skin that is a bit inflamed and red and doesnt go away over time.
Any lesion that bleeds or itches and doesnt heal within a few weeks may be a concern even if it doesnt look like these Squamous cell carcinoma images.
Also Check: How Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Start
What Are Basal And Squamous Cell Skin Cancers
Basal and squamous cell skin cancers are the most common types of skin cancer. They start in the top layer of skin , and are often related to sun exposure.
Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow out of control. Cells in nearly any part of the body can become cancer cells. To learn more about cancer and how it starts and spreads, see What Is Cancer?
The Ugly Duckling Sign New Growths Moles Spots Or Lesions
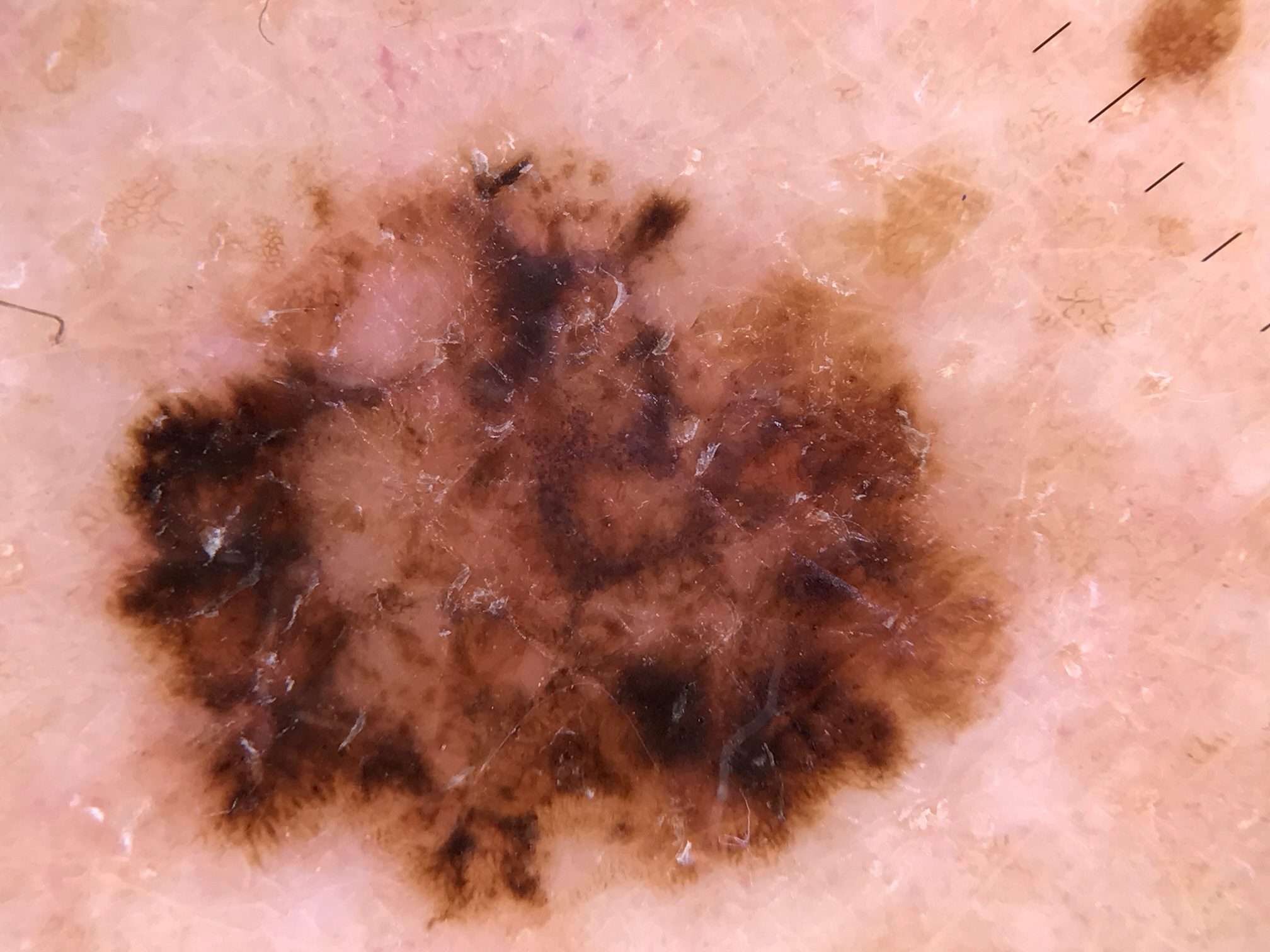
The most significant sign is a;,;mole;or any;new growth on the skin;that looks different from the other spots on your skin. . With the uniqueness of each person comes the uniqueness of our skin and its moles and marks. But if a mole or mark stands out from the other lesions on your skin you should pay closer attention.
You May Like: What Is The Treatment For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Also Check: How To Identify Skin Cancer
How Is Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck Diagnosed
Diagnosis is made by clinical exam and a biopsy. Squamous cell cancers are staged by size and extent of growth. Squamous cell cancers can metastasize to nearby lymph nodes or other organs, and can invade both small and large nerves and local structures.
Biopsy can help determine if the squamous cell cancer is a low-risk tumor or a high-risk tumor that requires more aggressive treatment. Low-risk tumors are less than 10 millimeters in size, less than or equal to 5 millimeters deep and do not involve structures beyond the surrounding fat. High-risk tumors in the head and neck are those that involve the central face, nose and eye area, as well as those tumors that are greater than or equal to 10 millimeters on the cheeks, scalp and neck, tumors that are more than 5 millimeters thick or involve adjacent structures, tumors that invade nerves, tumors that are recurrent or arising from previously radiated tissue, and tumors arising in patients who are immunosuppressed.
How The Government Of Canada Protects You
The Public Health Agency of Canada monitors cancer in Canada. PHAC identifies trends and risk factors for cancer, develops programs to reduce cancer risks, and researches to evaluate risks from the environment and human behaviours. Health Canada also promotes public awareness about sun safety and the harmful effects of UV rays.
Recommended Reading: What Does Skin Cancer Look Like On Your Skin
Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
SCC is generally faster growing than basal cell cancers. About 20 out of every 100;skin cancers are SCCs. They begin in cells called keratinocytes, which are found in the epidermis.
Most SCCs develop on areas of skin exposed to the sun. These areas include parts of the head, neck, and on the back of your hands and forearms. They can also develop on scars, areas of skin that have been burnt in the past, or that have been ulcerated for a long time.
SCCs don’t;often spread. If they do, it’s;most often to the deeper layers of the skin. They;can spread to nearby;lymph nodes;and other parts of the body, but this is unusual.
Diagnosis Of Skin Cancer
It is important to check your skin regularly and check with your doctor if you notice any changes.
In the majority of cases, your GP will examine you, paying attention to any spots that may look suspicious. Your GP may perform a biopsy . In some cases your GP may refer you to a specialist, such as a dermatologist, if necessary.
Don’t Miss: How To Remove Skin Cancer
Basic Information About Skin Cancer
Cancer is a disease in which cells in the body grow out of control. When cancer starts in the skin, it is called skin cancer.
Skin cancer is the most common cancer in the United States. Some people are at higher risk of skin cancer than others, but anyone can get it. The most preventable cause of skin cancer is overexposure to ultraviolet light, either from the sun or from artificial sources like tanning beds.
Most skin cancers are caused by too much exposure to ultraviolet rays. To lower your risk of getting skin cancer, you can protect your skin from UV rays from the sun and from artificial sources like tanning beds and sunlamps.While enjoying the benefits of being outdoors, people can decrease skin cancer risk by using sun protection. Protect yourself by staying in the shade, wearing protective clothing, and applying and re-applying a broad spectrum sunscreen with a sun protection factor of 15 or higher.Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website.
Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck Treatment
Surgery is the preferred management method for the majority of squamous cell skin cancers. Low-risk, early stage, small squamous cell cancers can be removed by Mohs surgery, which is a technique that spares normal tissue through repeated intraoperative margin testing, removing only the cancer and leaving adjacent normal tissue. Excision, curettage and desiccation, and cryosurgery can also be used to remove the cancer while sparing normal tissue. Radiation alone is an alternative for low-risk tumors when surgery is not desirable because of cosmetic concerns or medical reasons.
Large tumors and tumors with nerve or lymph node involvement are not suitable for Mohs surgery and require removal of at least 5-millimeter margins of normal tissue around the cancer and neck dissection for involved lymph nodes. Larger tumors require reconstruction, which can be done at the time of surgery if margin status is clear. Reconstruction should be staged when margins status is not clear.
Patients with high-risk tumors should meet with a radiation therapist to discuss postoperative radiation. Chemotherapy may be added to radiation for extensive lymph node involvement or positive margins that cannot be cleared with additional surgery. In patients with high-risk tumors who are not surgical candidates, systemic treatment with both radiation and chemotherapy is used. Such cases require multidisciplinary care by a team of surgeons, radiation oncologists and medical oncologists.
You May Like: How Likely Is Skin Cancer
Skin Cancer Types: Basal Cell Carcinoma Overview
All content solely developed by the American Academy of Dermatology
The American Academy of Dermatology gratefully acknowledges the support from Sanofi Genzyme and Regeneron.
Basal cell carcinoma
What is basal cell carcinoma?The most common type of skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma can show up on the skin in many ways.
Is it contagious? No;
Rarer Types Of Non Melanoma Skin Cancer
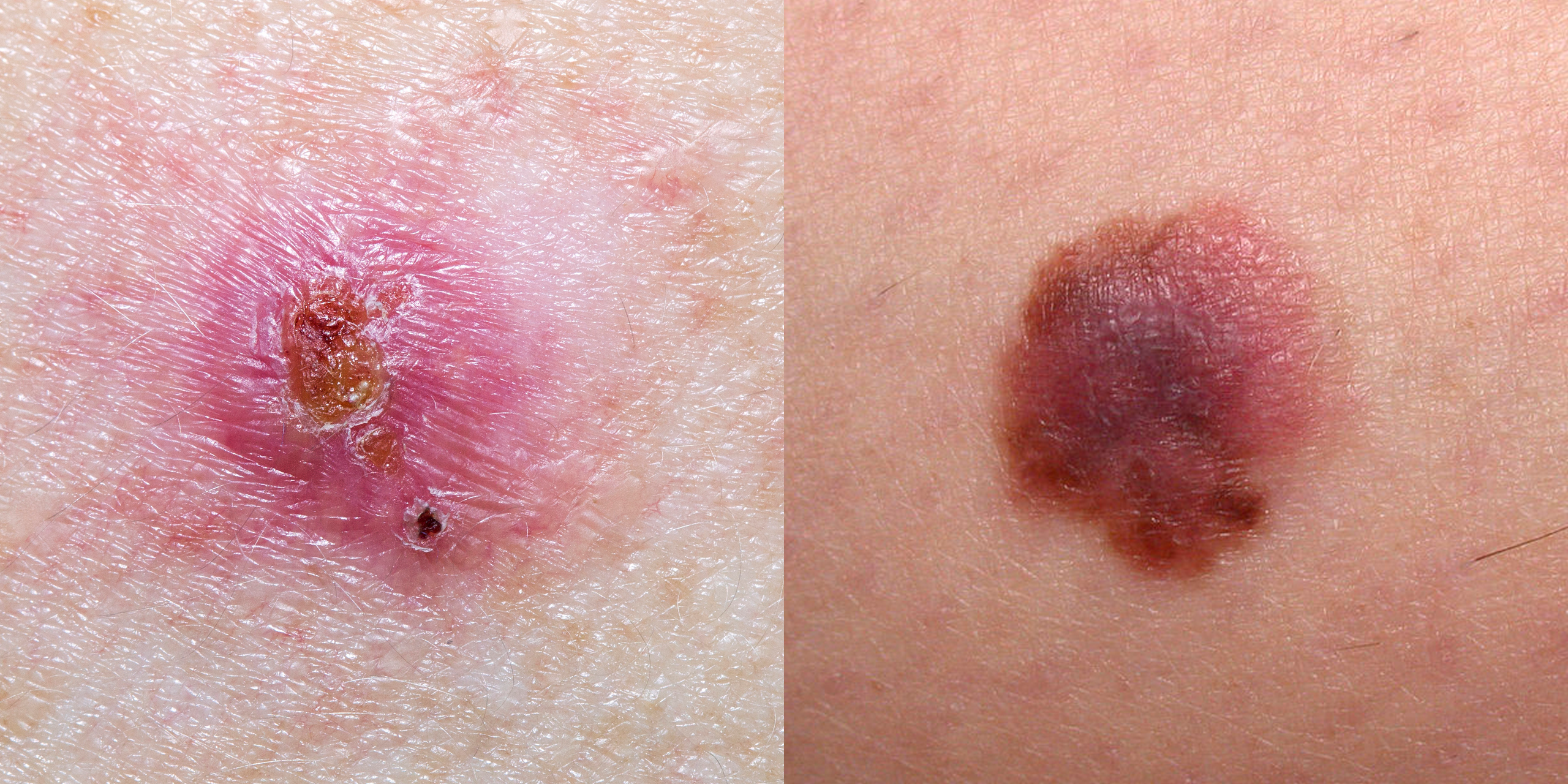
There are other less common types of skin cancer. These include:
- Merkel cell carcinoma
- T cell lymphoma of the skin
- Sebaceous gland cancer
These;are all treated differently from basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers. ;
Merkel cell carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma;is very rare. Treatment is with surgery or radiotherapy, or both. This usually works well, but sometimes the cancer can come back in the same place. And sometimes it spreads to nearby lymph nodes.;
Sebaceous gland cancer
Sebaceous gland cancer is another rare type of skin cancer affecting the glands that produce the skin’s natural oils. Treatment is usually surgery for this type of cancer.;
Kaposi’s sarcoma
Kaposis sarcoma;is a rare condition. It’s often associated with HIV but also occurs in people who don’t;have HIV. It’s a cancer that starts;in the cells that form;the lining of lymph nodes and the lining of blood vessels in the skin. Treatment;is;surgery or;radiotherapy, and sometimes;chemotherapy.
T cell lymphoma of the skin;
T cell lymphoma of the skin;can also be called primary cutaneous lymphoma. It’s a type of non Hodgkin lymphoma. There are a number of different types of treatment for this type of cancer. ;
You May Like: How To Know You Have Skin Cancer
Where Do Skin Cancers Start
Most skin cancers start in the top layer of skin, called the epidermis. There are 3 main types of cells in this layer:
- Squamous cells: These are flat cells in the upper part of the epidermis, which are constantly shed as new ones form. When these cells grow out of control, they can develop into squamous cell skin cancer .
- Basal cells: These cells are in the lower part of the epidermis, called the basal cell layer. These cells constantly divide to form new cells to replace the squamous cells that wear off the skins surface. As these cells move up in the epidermis, they get flatter, eventually becoming squamous cells. Skin cancers that start in the basal cell layer are called basal cell skin cancers or basal cell carcinomas.
- Melanocytes: These cells make the brown pigment called melanin, which gives the skin its tan or brown color. Melanin acts as the bodys natural sunscreen, protecting the deeper layers of the skin from some of the harmful effects of the sun. Melanoma skin cancer starts in these cells.
The epidermis is separated from the deeper layers of skin by the basement membrane. When a skin cancer becomes more advanced, it generally grows through this barrier and into the deeper layers.