Actinic Keratosis Signs And Symptoms
Many people have actinic keratosis , also called solar keratosis, on their skin. It shows that youâve had enough sun to develop skin cancer, and it is considered a precursor of cancer, or a precancerous condition.
Usually AK shows up on the parts of your body that have received the most lifetime sun exposure, like the face, ears, scalp, neck, backs of the hands, forearms, shoulders and lips.
Some of the same treatments used for nonmelanoma skin cancers are used for AK to ensure it does not develop into a cancerous lesion.
Appearance
This abnormality develops slowly. The lesions are usually small, about an eighth of an inch to a quarter of an inch in size. You may see a few at a time. They can disappear and later return.
- AK is a scaly or crusty bump on the skinâs surface and is usually dry and rough. It can be flat. An actinic keratosis is often noticed more by touch than sight.
- It may be the same color as your skin, or it may be light, dark, tan, pink, red or a combination of colors.
- It can itch or produce a prickling or tender sensation.
- These skin abnormalities can become inflamed and be encircled with redness. Rarely, they bleed.
Paranasal Sinus And Nasal Cavity Cancer Is A Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In The Tissues Of The Paranasal Sinuses And Nasal Cavity
Paranasal sinuses
“Paranasal” means near the nose. The para sinuses are hollow, air-filled spaces in the bones around the nose. The sinuses are lined with cells that make mucus, which keeps the inside of the nose from drying out during breathing.
There are several para sinuses named after the bones that surround them:
- The frontal sinuses are in the lower forehead above the nose.
- The maxillary sinuses are in the cheekbones on either side of the nose.
- The ethmoid sinuses are beside the upper nose, between the eyes.
- The sphenoid sinuses are behind the nose, in the center of the skull.
Nasal cavity
The nose opens into the nasal cavity, which is divided into two nasal passages. Air moves through these passages during breathing. The nasal cavity lies above the bone that forms the roof of the mouth and curves down at the back to join the throat. The area just inside the nostrils is called the nasal vestibule. A small area of special cells in the roof of each nasal passage sends signals to the brain to give the sense of smell.
Together the paranasal sinuses and the nasal cavity filter and warm the air, and make it moist before it goes into the lungs. The movement of air through the sinuses and other parts of the respiratory system help make sounds for talking.
Paranasal sinus and nasal cavity cancer is a type of head and neck cancer.
Different Types Of Cells In The Paranasal Sinus And Nasal Cavity May Become Malignant
The most common type of paranasal sinus and nasal cavity cancer is squamous cell carcinoma. This type of cancer forms in the thin, flat cells lining the inside of the paranasal sinuses and the nasal cavity.
Other types of paranasal sinus and nasal cavity cancer include the following:
- Melanomas: Cancer that starts in cells called melanocytes, the cells that give skin its natural color.
- Sarcomas: Cancer that starts in muscle or connective tissue.
- Inverting papillomas: Benign tumors that form inside the nose. A small number of these change into cancer.
- Midline granulomas: Cancer of tissues in the middle part of the face.
Also Check: What Is Metastatic Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Oral Medications For Advanced Bcc
It is rare for skin cancer to reach advanced stages, but when it does, oral medications may help. In addition to chemotherapy, targeted drugs may be used to treat advanced skin cancer. Targeted therapy means that the medication is able to directly target the cancer cells without destroying healthy cells. This can help to reduce side effects from treatment.
Vismodegib and sonidegib are hedgehog pathway inhibitors that work to prevent cancer cells from growing and spreading. The capsules are taken once per day and may be considered after surgery and other treatments. These medications come with several possible side effects and should never be taken during pregnancy since they can affect fetal growth.
Cetuximab is an EGFR inhibitor that can help to stop the spread of cancerous squamous cells. Its possible side effects include skin infections, diarrhea, mouth sores, and loss of appetite.
Causes And Risk Factors
Researchers do not know why certain cells become cancerous. However, they have identified some risk factors for skin cancer.
The most important risk factor for melanoma is exposure to UV rays. These damage the skin cellsâ DNA, which controls how the cells grow, divide, and stay alive.
Most UV rays come from sunlight, but they also come from tanning beds.
Some other risk factors for skin cancer include:
- A lot of moles: A person with more than 100 moles is more likely to develop melanoma.
- Fair skin, light hair, and freckles: The risk of developing melanoma is higher among people with fair skin. Those who burn easily have an increased risk.
- Family history:Around 10% of people with the condition have a family history of it.
- Personal history: Melanoma is likelier to form in a person who has already had it. People who have had basal cell or squamous cell cancers also have an increased risk of developing melanoma.
The best way to reduce the risk of skin cancer is to limit oneâs exposure to UV rays. A person can do this by using sunscreen, seeking shade, and covering up when outdoors.
People should also avoid tanning beds and sunlamps to reduce their risk of skin cancer.
It can be easy to mistake benign growths for skin cancer.
The following skin conditions have similar symptoms to skin cancer:
Also Check: What Is Pigmented Basal Cell Carcinoma
How Can I Lower My Risk Of Skin Cancer
The single most important thing you can do to lower your risk of skin cancer is to avoid direct sun exposure. Sunlight produces ultraviolet radiation that can directly damage the cells of our skin. People who work outdoors are at the highest risk of developing a skin cancer. The suns rays are the most powerful between 10 am and 2 pm, so you must be particularly careful during those hours. If you must be out during the day, wear clothing that covers as much of your skin as possible, including a wide-brimmed hat to block the sun from your face, scalp, neck, and ears.
The use of a sunscreen can provide protection against UV radiation. When selecting a sunscreen, choose one with a Sun Protection Factor of 15 or more. For people who live in the Southern U.S., a SPF of 30 or greater should be used during summer and when prolonged exposure is anticipated. Sunscreen should be applied before exposure and when the skin is dry. If you will be sweating or swimming, most sunscreens will need to be reapplied. Sunscreen products do not completely block the damaging rays, but they do allow you to be in the sun longer without getting sunburn.
Treatment Of Stage Iii Paranasal Sinus And Nasal Cavity Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
- External radiation therapy and/or internal radiation therapy with or without surgery.
- A clinical trial of combination chemotherapy before surgery or radiation therapy.
- A clinical trial of combination chemotherapy after surgery or other cancer treatment.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Read Also: How Long For Squamous Cell Carcinoma To Spread
What You Can Do
If youve already had a BCC, you have an increased chance of developing another, especially in the same sun-damaged area or nearby.
A BCC can recur even when it has been carefully removed the first time, because some cancer cells may remain undetectable after surgery and others can form roots that extend beyond whats visible. BCCs on the nose, ears and lips are more likely to recur, usually within the first two years after surgery.
Heres what you can do to detect a recurrence and safeguard yourself against further skin damage that can lead to cancer:
Reviewed by:
Looking For Signs Of Skin Cancer
Non melanoma skin cancers tend to develop most often on skin that’s exposed to the sun.
To spot skin cancers early it helps to know how your skin normally looks. That way, you’ll notice any changes more easily.
To look at areas you cant see easily, you could try using a hand held mirror and reflect your skin onto another mirror. Or you could get your partner or a friend to look. This is very important if you’re regularly outside in the sun for work or leisure.
You can take a photo of anything that doesn’t look quite right. If you can it’s a good idea to put a ruler or tape measure next to the abnormal area when you take the photo. This gives you a more accurate idea about its size and can help you tell if it’s changing. You can then show these pictures to your doctor.
Read Also: How Many People Die From Melanoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma Signs And Symptoms
This type of cancer is usually found on sun-exposed areas of the skin like the scalp, forehead, face, nose, neck and back.
Basal cell carcinomas may bleed after a minor injury but then scab and heal. This can happen over and over for months or years with no visible growth, making it easy to mistake them for wounds or sores. They rarely cause pain in their earliest stages.
Appearance
In addition to the bleeding and healing, these are other possible signs of a basal cell cancer:
- A persistent open sore that does not heal and bleeds, crusts or oozes.
- A reddish patch or irritated area that may crust or itch.
- A shiny bump or nodule that is pearly or translucent and often pink, red or white. It can also be tan, black or brown, especially in dark-haired people, and easy to confuse with a mole.
- A pink growth with a slightly elevated, rolled border and a crusted indentation in the center. Tiny blood vessels may appear on the surface as the growth enlarges.
- A scar-like lesion in an area that you have not injured. It may be white, yellow or waxy, often with poorly defined borders. The skin seems shiny and tight sometimes this can be a sign of an aggressive tumor.
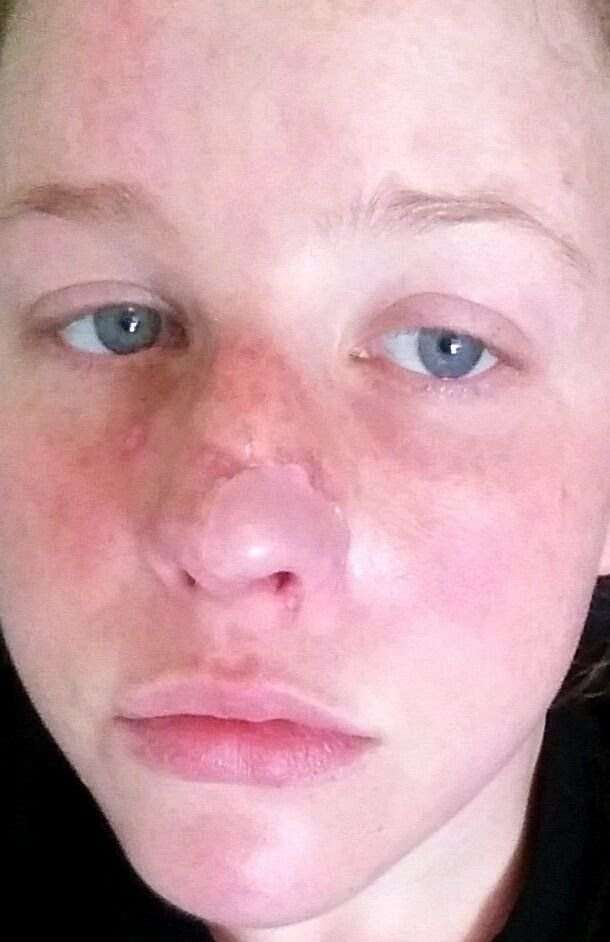
Skin Cancer On The Face: Types And Prevention
Casey Gallagher, MD, is board-certified in dermatology. He is a clinical professor at the University of Colorado in Denver, and co-founder and practicing dermatologist at the Boulder Valley Center for Dermatology in Colorado.
Because it is exposed to the sun more than other parts of the body, the skin on your face is especially vulnerable to skin cancer. And skin cancer on the face can be mistaken for other conditionssuch as age spots, pimples, scarring, acne, styes, and cysts.
Skin cancers that tend to occur more often on the face include actinic keratosis, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. The face is also a common site of melanoma and there are several other lesser-common skin cancers that can affect the face. The risk of getting skin cancers on the face increases with high amounts of sun exposure and other ultraviolet light exposure.
About 75% of non-melanoma skin cancers occur on the head or neck.
Skin cancer occurs when cells in the skin’s layers become damaged in ways that cause them to look and act differently than the normal healthy cells around them and start to grow out of control. UV rays play a major role in damaging cells by causing gene mutations.
You can watch for signs of skin cancer on your face by paying attention to new or odd-looking spots or feeling growths, splotches, or moles.
Don’t Miss: What Does Stage 4 Skin Cancer Look Like
Where Does Bcc Develop
As the above pictures show, this skin cancer tends to develop on skin that has had lots of sun exposure, such as the face or ears. Its also common on the bald scalp and hands. Other common areas for BCC include, the shoulders, back, arms, and legs.
While rare, BCC can also form on parts of the body that get little or no sun exposure, such as the genitals.
Skin Cancer Pictures: What Does Skin Cancer Look Like
Skin cancer images by skin cancer type. Skin cancer can look different than the photos below.
Basal Cell Carcinoma | Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Bowens Disease | Keratoacanthoma | Actinic Keratosis | Melanoma
Skin cancer often presents itself as a change in the skins appearance. This could be the appearance of a new mole or other mark on the skin or a change in an existing mole.
Please remember that you should always seek advice from your doctor if you have any concern about your skin. Skin cancers often look different from skin cancer images found online.
Don’t Miss: How Much Is Skin Cancer Screening
Ask About Your Skin Cancer Treatment Options
Among the most common treatments for facial skin cancer is Mohs surgery. Mohs involves removing the cancer in thin layers. This approach helps preserve surrounding healthy tissue and has a very high cure rate.
Mohs can be a lengthy process, taking several hours or longer, says Dr. Lee. I do everything I can to keep my patients comfortable and inform them of how things are going at each step.
Dr. Lee adds that not everyone with skin cancer on the face will need Mohs surgery. There may be other treatment options that are right for you. Its OK to ask. And if you do have options, ask your doctor to explain the pros and cons of each before you make your decision, she says.
Sometimes Mohs really is the best option for facial cancer, however. Thats typically the case with skin cancer on the nose or eyelid. The nose and the eyelid are tougher areas to treat for a variety of reasons, says Dr. Lee. It takes finesse to achieve excellent cosmetic results in these areas. Removing a cancer from the eyelid also has a lot of challenges related to how the eyelid functions and feels to the patient after the surgery.
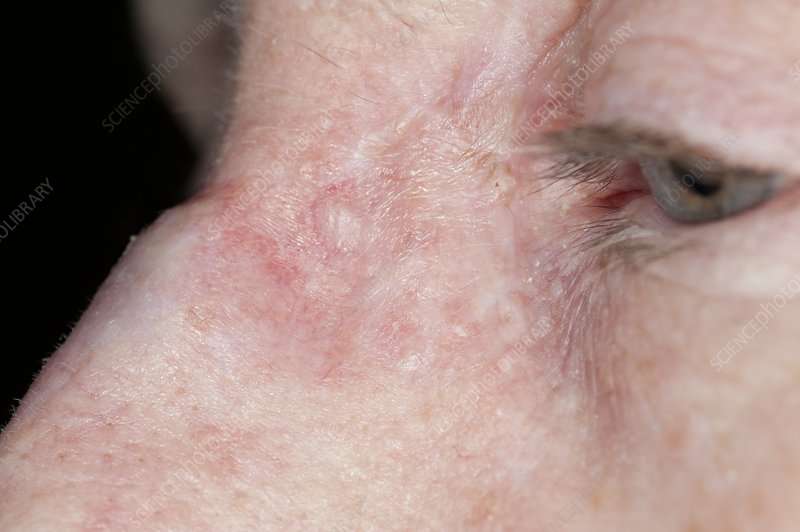
Warning Signs Of Basal Cell Carcinoma That You Could Mistake As Harmless
Warning sign: A pink or reddish growth that dips in the centerCan be mistaken for: A skin injury or acne scar
A pink or reddish growth that dips in the center
The BCC on this patients cheek could be mistaken for a minor skin injury.
Warning sign: A growth or scaly patch of skin on or near the earCan be mistaken for: Scaly, dry skin, minor injury, or scar
A growth or scaly patch of skin on or near the ear
BCC often develops on or near an ear, and this one could be mistaken for a minor skin injury.
Warning sign: A sore that doesn’t heal and may bleed, ooze, or crust overCan be mistaken for: Sore or pimple
A sore that doesn’t heal, or heals and returns
This patient mistook the BCC on his nose for a non-healing pimple.
Warning sign: A scaly, slightly raised patch of irritated skin, which could be red, pink, or another colorCan be mistaken for: Dry, irritated skin, especially if it’s red or pink
A scaly, slightly raised patch of irritated skin
This BCC could be mistaken for a patch of dry, irritated skin.
Warning sign: A round growth that may be pink, red, brown, black, tan, or the same color as your skinCan be mistaken for: A mole, wart, or other harmless growth.
A round growth that may be same color as your skin
Would you recognize this as a skin cancer, or would you dismiss it as a harmless growth on your face?
You May Like: How Do You Get Skin Cancer From The Sun
Seek Comprehensive Care If Your Skin Cancer Is Complicated To Treat
Complicated skin cancer may require the expertise of multiple specialists. Plastic surgeons may get involved when the cosmetic challenges are significant. An ocular surgeon or an oculoplastic specialist may be needed if you have an especially difficult-to-treat skin cancer close to the eye. A head and neck surgeon may join your care team if there is nerve involvement or if the cancer is too extensive for local anesthesia.
The beauty of a comprehensive cancer center like MSK is that the expertise is all here, says Dr. Lee. We have a multidisciplinary program especially for people with complex skin cancer. You can usually see all of your doctors on the same day and in the same location. The dermatology team works with you to coordinate your appointments with your schedule.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Pictures
Basal cell carcinoma usually appears in areas of the skin previously exposed to high levels of UV radiation such as the head, neck, ears and the back of the arms and hands. It is common in exposed skin of outdoor workers or people who have used sun tanning beds in the past.
As the basal cell carcinoma pictures below indicate, this type of skin cancer usually shows as a fleshy coloured bump that does not disappear over time and tends to grow slowly in size, eventually breaking down and ulcerating.
Below are pictures of skin cancer on the neck, face and trunk . These images show common areas where basal cell carcinoma develops, but it can develop anywhere.
Basal cell carcinoma. The skin cancer pictures in this article were licensed from DermNet NZ
Read Also: Can Skin Cancer Look Like Psoriasis