What Is The Outlook For Patients With Melanoma
Melanoma in situ is cured by excision because it has no potential to spread around the body.
The risk of spread and ultimate death from invasive melanoma depends on several factors, but the main one is the Breslow thickness of the melanoma at the time it was surgically removed.
Metastases are rare for melanomas < 0.75 mm and the risk for tumours 0.751 mm thick is about 5%. The risk steadily increases with thickness so that melanomas > 4 mm have a risk of metastasis of about 40%.
Examples Of Melanoma In A Sentence
melanoma Alluremelanoma ForbesmelanomaAnchorage Daily NewsmelanomaScientific Americanmelanoma oregonlivemelanoma Milwaukee Journal Sentinelmelanoma Harper’s BAZAARmelanoma USA TODAY
These example sentences are selected automatically from various online news sources to reflect current usage of the word ‘melanoma.’ Views expressed in the examples do not represent the opinion of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback.
How You Might Feel
Finding out you have advanced melanoma can be a shock. Its common to feel uncertain and anxious and not be able to think about anything else.
Treatments are available that can shrink the melanoma or stop it growing. It might be possible to control it for quite a while. You will need to talk very carefully to your own specialist to understand:
- what your diagnosis means
- whats likely to happen
- what treatments are available
- how treatment can help you
Although you have advanced cancer, it might be months or sometimes years before doctors can no longer control the melanoma.
Some people are diagnosed with melanoma when it is too far advanced for treatment to be able to control the cancer. If this happens then your doctor will still be able to do things to help control any symptoms you may have.
There is lots of information and support available to you and your family and friends. Some days you might want lots of information and on others it might be too much for you. It can help to find out more about your cancer and the different treatments you can have. Many people find that knowing more about their situation can make it easier to cope.
Read Also: What Is Clear Cell Carcinoma
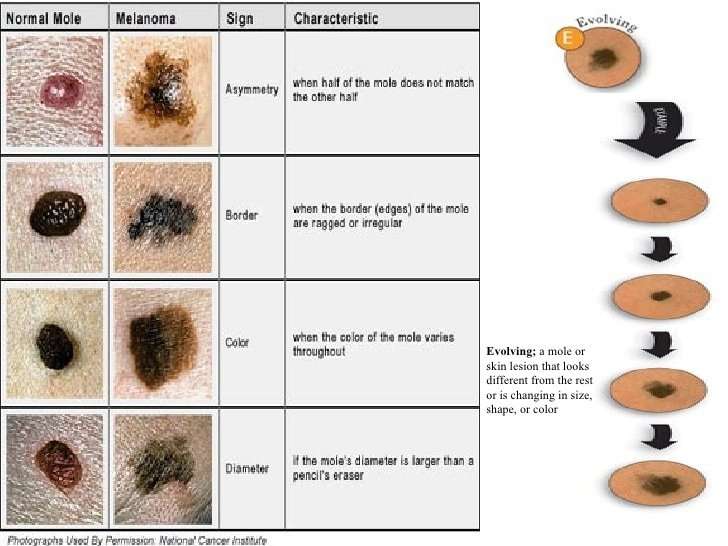
What Are The Signs Of Melanoma
Knowing how to spot melanoma is important because early melanomas are highly treatable. Melanoma can appear as moles, scaly patches, open sores or raised bumps.
Use the American Academy of Dermatology’s “ABCDE” memory device to learn the warning signs that a spot on your skin may be melanoma:
- Asymmetry: One half does not match the other half.
- Border: The edges are not smooth.
- Color: The color is mottled and uneven, with shades of brown, black, gray, red or white.
- Diameter: The spot is greater than the tip of a pencil eraser .
- Evolving: The spot is new or changing in size, shape or color.
Some melanomas don’t fit the ABCDE rule, so tell your doctor about any sores that won’t go away, unusual bumps or rashes or changes in your skin or in any existing moles.
Another tool to recognize melanoma is the ugly duckling sign. If one of your moles looks different from the others, its the ugly duckling and should be seen by a dermatologist.
How Is Melanoma Treated

Your melanoma treatment will depend on the stage of the melanoma and your general health.
Surgery is usually the main treatment for melanoma. The procedure involves cutting out the cancer and some of the normal skin surrounding it. The amount of healthy skin removed will depend on the size and location of the skin cancer. Typically, surgical excision of melanoma can be performed under local anesthesia in the dermatologist’s office. More advanced cases may require other types of treatment in addition to or instead of surgery.
Treatments for melanoma:
- Melanoma Surgery: In the early stages, surgery has a high probability of being able to cure your melanoma. Usually performed in an office, a dermatologist numbs the skin with a local anesthetic and removes the melanoma and margins .
- Lymphadenectomy: In cases where melanoma has spread, removal of the lymph nodes near the primary diagnosis site may be required. This can prevent the spread to other areas of your body.
- Metastasectomy: Metastasectomy is used to remove small melanoma bits from organs.
- Targeted cancer therapy: In this treatment option, drugs are used to attack specific cancer cells. This targeted approach goes after cancer cells, leaving healthy cells untouched.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy includes treatments with high-energy rays to attack cancer cells and shrink tumors.
- Immunotherapy: immunotherapy stimulates your own immune system to help fight the cancer.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 3 Survival Rate
What Is A Melanocyte
Melanocytes are skin cells found in the upper layer of skin. They produce a pigment known as melanin, which gives skin its color. There are two types of melanin: eumelanin and pheomelanin. When skin is exposed to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or tanning beds, it causes skin damage that triggers the melanocytes to produce more melanin, but only the eumelanin pigment attempts to protect the skin by causing the skin to darken or tan. Melanoma occurs when DNA damage from burning or tanning due to UV radiation triggers changes in the melanocytes, resulting in uncontrolled cellular growth.
About Melanin
Naturally darker-skinned people have more eumelanin and naturally fair-skinned people have more pheomelanin. While eumelanin has the ability to protect the skin from sun damage, pheomelanin does not. Thats why people with darker skin are at lower risk for developing melanoma than fair-skinned people who, due to lack of eumelanin, are more susceptible to sun damage, burning and skin cancer.
Can Changing My Diet Help Prevent Melanoma
The American Cancer Society advocates eating a plant-based diet over an animal-based diet as part of a healthy plan to avoid all cancers. Growing evidence suggests that plants pack a powerful punch in any fight against cancer because they’re nutritious, cholesterol-free and fiber-rich.
Theres no doubt that a healthy diet can protect your immune system. Having a strong immune system is important to help your body fight disease. Some research has shown that a Mediterranean diet is a healthy choice that may help prevent the development of cancer. Talk to your healthcare provider about the role food plays in lowering your cancer risks.
Some skin and immune-system healthy foods to consider include:
- Daily tea drinking: The polyphenols in tea help strengthen your immune system. Green tea contains more polyphenols than black tea.
- High vegetable consumption: Eating carrots, cruciferous and leafy vegetables is linked to the prevention of cutaneous melanoma.
- Weekly fish intake: Study participants who ate fish weekly seemed to avoid developing the disease when compared to those who did not eat fish weekly.
Also Check: Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rates
Why Is The Patients Contribution So Important For Translational Medicine
Translational medicine involves a more patient-centric approach to medicine than the traditional process. The role of the patient in this research is considered critical: Patients provide the biospecimens from which biomarkers at the molecular and immune level can be identified and are then used to develop diagnostics and drugs targeted at sub-groups of disease. Patients become the real heroes of translational medicine and the true protagonists of all the advances in novel therapeutic interventions.
It is important for the scientific community to remember to inform patients and their families of their critical involvement in translational medicine research and to also share with them all the successes achieved through their contributions.
What Is The Most Likely Prognosis Of Melanoma In Situ
Melanoma originates in the skin cells and is therefore frequently visible unlike other forms of cancer which remain invasive and hidden. Melanoma derives its name from melanin, a darkish brown or black pigment present in the skin, hair and eyes in both people and mammals. Melanin controls the skins tanning response via Melanocytes, the skins pigment cells. To create melanoma, there is usually an external trigger, for instance, commonly persistent sunburn or just continuous quantities of UV light. Ethnically, Caucasian people are at greater risk than those with darker skin tones such as people of African or Hispanic heritage.
Don’t Miss: Small Blue Cell Tumor Prognosis
A Dangerous Skin Cancer
Melanoma is a serious form of skin cancer that begins in cells known as melanocytes. While it is less common than basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma , melanoma is more dangerous because of its ability to spread to other organs more rapidly if it is not treated at an early stage.
Learn more about melanoma types, risk factors, causes, warning signs and treatment.
Melanoma Fact
Only 20-30% of melanomas are found in existing moles.
While 70-80% arise on normal-looking skin.
Melanoma In Situ: Prognosis Recurrence Margins Treatments
The global population is so clued up nowadays on the dangers of excessive exposure to harmful rays of sunshine. Additionally, the environmental lobby has fuelled this with tons of information broadcast in the public domain about the hole in the ozone layer. So, forget tanning parlours and sun beds, so last century, its all about covering up with Factor 50 or fake spray tans to achieve that golden glow and honeyed look. Melanoma is a diagnosis most people associate with the skin but what is the actual meaning of melanoma?
Also Check: Merkel Cancer Prognosis
What Happens At Follow
Follow-up after a melanoma diagnosis is required to:
- detect recurrence early
- diagnose a new primary melanoma at the first possible opportunity. A second invasive melanoma occurs in 510% of melanoma patients and a new melanoma in situ is diagnosed in more than 20% of melanoma patients.
The Australian and New Zealand Guidelines for the Management of Melanoma make the following recommendations for follow-up for patients with invasive melanoma.
- Self-skin examination
- Routine skin checks by patient’s preferred health professional
- Follow-up intervals are preferably six-monthly for five years for patients with stage 1 disease, three-monthly or four-monthly for five years for patients with stage 2 or 3 disease, and yearly after that for all patients.
- Individual patients needs should be considered before an appropriate follow-up is offered
- Provide education and support to help the patient adjust to their illness
The follow-up appointments may be undertaken by the patient’s general practitioner and specialist.
Follow-up appointments may include:
- Check of the scar where the primary melanoma was removed -visual inspection and palpation
- Feel for the regional lymph nodes
- General skin examination
- Full physical examination
- In those with many melanocytic naevi or atypical melanocytic naevi, baseline whole-body imaging and sequential macro and dermoscopy images of melanocytic lesions of concern .
In those with more advanced primary disease, follow-up may include:
Health Literacy To Empower Patients
With the right information, patients can make the best decisions about their care. By partnering with patients, healthcare providers, and hospitals, we hope to provide all patients with the tools and knowledge to understand their pathology report.
For more information about this site, contact us at .
Disclaimer: The articles on MyPathologyReport are intended for general informational purposes only and they do not address individual circumstances. The articles on this site are not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment and should not be relied on to make decisions about your health. Never ignore professional medical advice in seeking treatment because of something you have read on the MyPathologyReport site. MyPathologyReport is independently owned and operated and is not affiliated with any hospital or patient portal. The articles on MyPathologyReport.ca are intended for use within Canada by residents of Canada only.
Copyright © 2020. All rights reserved. Privacy Policy
Our work is generously supported by:
Recommended Reading: Skin Cancer Spreading To Lymph Nodes
What Is The Best Treatment For Melanoma
Treatments for melanoma have a lot to do with the progress it has taken. If caught fairly early, then a routine tumor removal where only local anesthesia is normally enough. When spotted in later times, you will generally have to utilize a much stronger intervention beyond a few moments awake and under the scalpel.
- Nodular Melanoma Symptoms, Diagnosis, Prognosis, Treatment, Pictures
- Best Options and Guidelines for Melanoma Treatments
More invasive removals or even amputations of an entire appendage may do this. Additionally, chemotherapy and radiation drugs are a reliable option, although they are associated with relatively harsh side effects.
Why Do We Have Melanin
You may have noticed that across the planet, human beings come in a wide spectrum of shades. Your shade will vary as a function of genetics. Your nationality and ethnicity will likely dictate the color of your skin. scattered across western europe, scandinavia, and the nordics, you can expect pale skin as with the stereotypical german, dutch, polish, or swedish person.
- Melanoma Under Toenail, Fingernail, on Toe, on Finger: Symptoms, Treatments
- What is Uveal Melanoma: Symptoms, Causes, Prognosis, Staging, Treatments
Skin starts to get a little browner when you enter countries such as native brazilians, mongolians, and egyptians. The darkest skin can be found in those descending from the people of nilotic groups in south sudan or ethiopia. Or members of the dinka and anyuak. mutations can lead to albinism. An albino is a person whose body lacks the normal production of melanin leaving them with very white skin and hair as well as light eyes. multiracial children often inherit a hue in between their parents, but its not always the case.
Don’t Miss: How Long Until Melanoma Spreads
What Have We Achieved With Translational Medicine In Melanoma
Recent progress in melanoma drug development highlights the critical impact that translational medicine plays in advancing the care of melanoma patients.
Prior to 2011, the treatment of melanoma was limited to the usage of dacarbazine, interleukin -2, and interferon -2b for all patients with melanoma thus resulting in a relatively poor response.
A renaissance occurred when, with the usage of translational medicine approaches, it was discovered that many patients with melanoma harbor molecular alterations in the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. As result, any patients with melanoma harboring this mutation could be treated with compounds able to target the mutated pathway. Three directed consequences followed this discovery: 1) pharmaceutical companies vigorously pursued the development of treatment options able to inhibit the MAPK pathway 2) in a very short period, the FDA approved the usage of three successful MAPK pathway inhibitors for the treatment of patients with advanced melanoma harboring mutations in MAPK pathway and 3) thanks to translational medicine, the era of precision medicine, which fosters the usage of a specific drug for specific subsets of patients, just began!
What Is The Melanoma Definition
The definition of melanoma is when those melanocytes, the cells behind melanin that cause pigment, malfunction. healthy cells go through a natural phase of replication and reproduction. The blueprints of their biology dictate when it happens as to properly restore cells. Sometimes, dysfunction occurs where a cell begins to rapidly divide for no known reason. When it happens, tissue functionality is impaired or can be halted. depending on the severity of tumor size, location, and metastasis, different symptoms will manifest.
Read Also: Skin Cancer Metastasis To Lymph Nodes
What Is The Treatment For Melanoma
Following confirmation of the diagnosis, wide local excision is carried out at the site of the primary melanoma. The extent of surgery depends on the thickness of the melanoma and its site. Margins recommended in New Zealand are shown below.
- Melanoma in situ: 5 10 mm
- Melanoma < 1 mm: 10 mm
- Melanoma 12 mm: 10 20 mm
- Melanoma > 2 mm: 20 mm
Clinical Practice Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of melanoma updated in 2017, recommend, where possible:
- Melanoma in situ: 5 mm, and wider margins if appropriate
- Melanoma < 1 mm: 10 mm
- Melanoma 12 mm: 10 20 mm
- Melanoma 24 mm: 10 20 mm
- Melanoma > 4 mm: 20 mm
What Are The Average Margins Removed With Melanoma In Situ
Currently, surgeons will harvest approximately 5mm of unaffected skin around the lesion. This became a documented industry standard in 1992. Evidence is increasingly demonstrating that this amount is conservative but no scientific data exists to suggest a more appropriate alternative.
- Choroidal Melanoma: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
- Melanoma in Mouth , Ear, Nose, Eye, Retinal, Face: Symptoms, Treatment
Despite cutting edge technology pun intended! so bright lighting, something called Woods lighting which is black light invisible to the naked eye and, the enhancement of magnification the clinician cannot take the risk that he has missed a tiny portion of cancerous cells, undetectable with the naked eye. Thus, the debate over accurate and beneficial margins in cases of melanoma in situ continues to rage amongst the medical profession. Most sufferers want the minimal loss of skin for cosmetic reasons but fear the return of cancer more.
Don’t Miss: What Is Stage 2 Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Skin Cancers
Basal cell and squamous cell cancers are by far the most common skin cancers, and actually are more common than any other form of cancer. Because they rarely spread to other parts of the body, basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers are usually less concerning and are treated differently from melanoma. These cancers are discussed in Basal and Squamous Cell Skin Cancer.
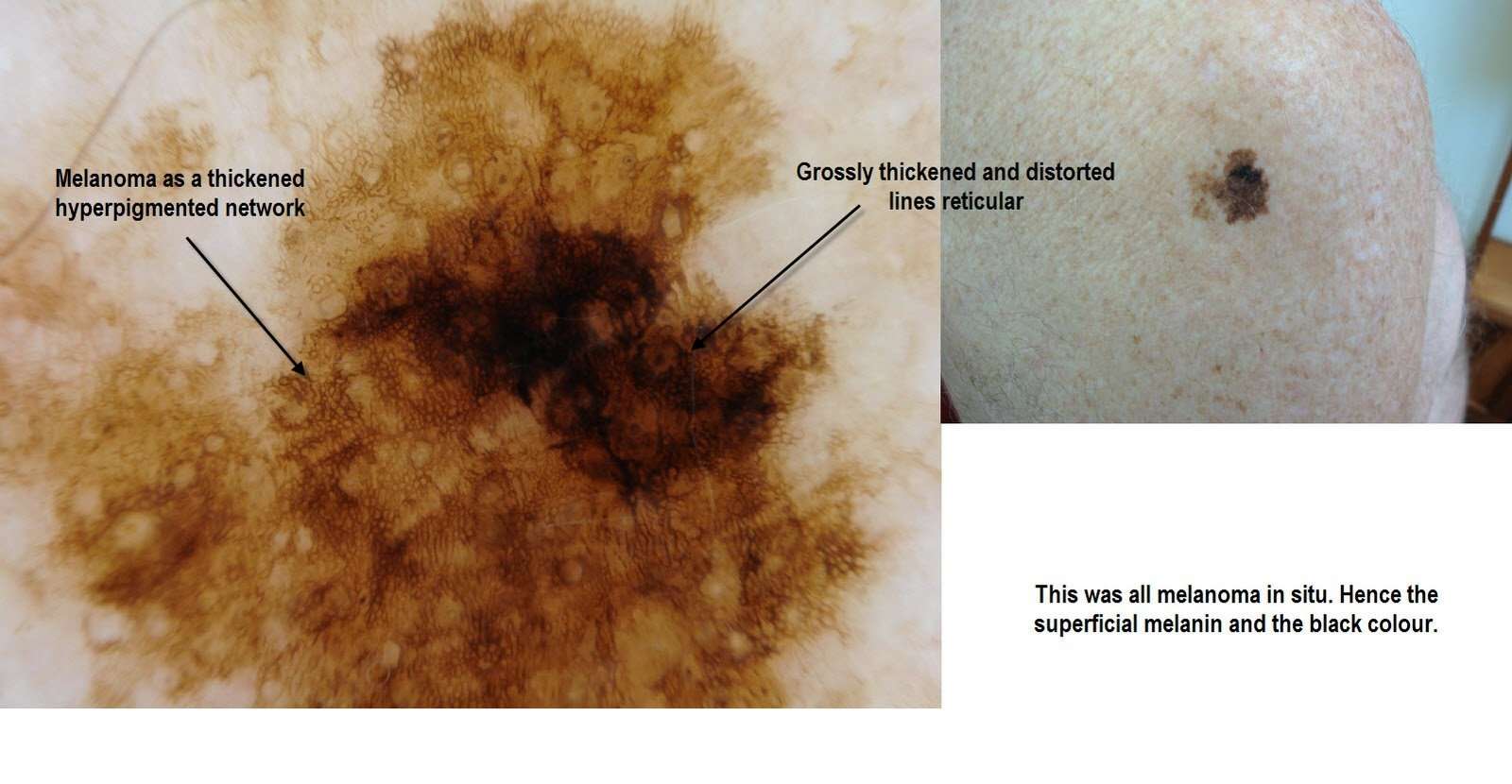
Differential Diagnosis Of Melanoma
When pigmentation is absent, spindle morphology melanoma may be difficult to distinguish from other spindled cell tumours including leiomyosarcoma, spindled cell squamous cell carcinoma, atypical fibroxanthoma and dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. In these cases special stains are helpful in distinguishing melanocyte origin of tumour cells.
Amelanotic epithelioid tumours may be confused with anaplastic carcinoma, Langerhan cell histiocytosis and anaplastic lymphoma.
Read Also: Is Carcinoma Curable
When Should I Call My Doctor
You should have a skin examination by a doctor if you have any of the following:
- A personal history of skin cancer or atypical moles .
- A family history of skin cancer.
- A history of intense sun exposure as a young person and painful or blistering sunburns.
- New or numerous large moles.
- A mole that changes in size, color or shape.
- Any mole that itches, bleeds or is tender.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Receiving a diagnosis of melanoma can be scary. Watch your skin and moles for any changes and seeing your doctor regularly for skin examinations, especially if youre fair-skinned, will give you the best chances for catching melanoma early when its most treatable.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 06/21/2021.
References