Signs And Symptoms Of Kidney Cancer
Though renal and transitional cancer types affect the kidney in slightly different ways, the signs and symptoms are largely the same. In addition, kidney cancer often doesnât show any obvious signs, especially in the early stages. Plus, many possible kidney cancer symptoms, like blood in the urine, can also result from less serious illnesses, like a bladder infection or kidney stones.
But itâs a good idea to talk to your doctor if you notice:
- Blood in your pee
- Lower back or belly pain with no clear cause
- A fever that doesnât go away and has no obvious cause
- Youâre more tired than normal
- You arenât as hungry or donât eat as much
- Youâve lost weight without trying
- A lump on your lower back, side, or belly
Because kidney cancer sometimes has no early symptoms, the first sign might not show up until after the cancer has spread.
It can go almost anywhere in your body, and symptoms depend on the location. It might show up as a skin lesion. Or, if it spreads to a lung, you might cough up blood. If it reaches your brain, you might have balance or vision problems, among other symptoms in your nervous system.
Regular checkups can help catch early warning signs so that you and your doctor can create a treatment plan.
Urology Care Foundation: âKidney Cancer?â
American Cancer Society: âKidney Cancer,â âKidney Cancer Signs and Symptoms,â âWhat Is Kidney Cancer?â
Cleveland Clinic: âKidney Cancer Overview.â
Dna Mismatch Repair Proteins
DNA mismatch repair proteins are a group of proteins that physiologically stimulate G2 cell cycle checkpoint arrest and apoptosis. Failure of MMR proteins to detect induced DNA damage results in the survival of mutating cells. MMR protein levels have been found to be higher in nonmelanoma skin cancers than in normal skin, and there is also some evidence of MMR dysregulation.
What Happens If Basal Cell Carcinoma Is Left Untreated
Basal cell carcinoma is a very slow growing type of non-melanoma skin cancer. If left untreated, basal cell carcinomas can become quite large, cause disfigurement, and in rare cases, spread to other parts of the body and cause death.
You may ask, What skin cancer looks like when it starts?
Squamous Cell Carcinoma This nonmelanoma skin cancer may appear as a firm red nodule, a scaly growth that bleeds or develops a crust, or a sore that doesnt heal. It most often occurs on the nose, forehead, ears, lower lip, hands, and other sun-exposed areas of the body.
Don’t Miss: What Cancer Looks Like On Skin
Identifying The Types Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Did you know that skin cancer is the most frequently diagnosed cancer in the US and globally? Of the various kinds of skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma is the most common, with up to 4.3 million new cases discovered annually in America. The good news? In the early stages, most types of basal cell carcinoma have a high cure rate and cause very little damage.
This month, were exploring the types of basal cell carcinoma, including the causes, symptoms, and prognosis for recovery.
The Risks The Causes What You Can Do
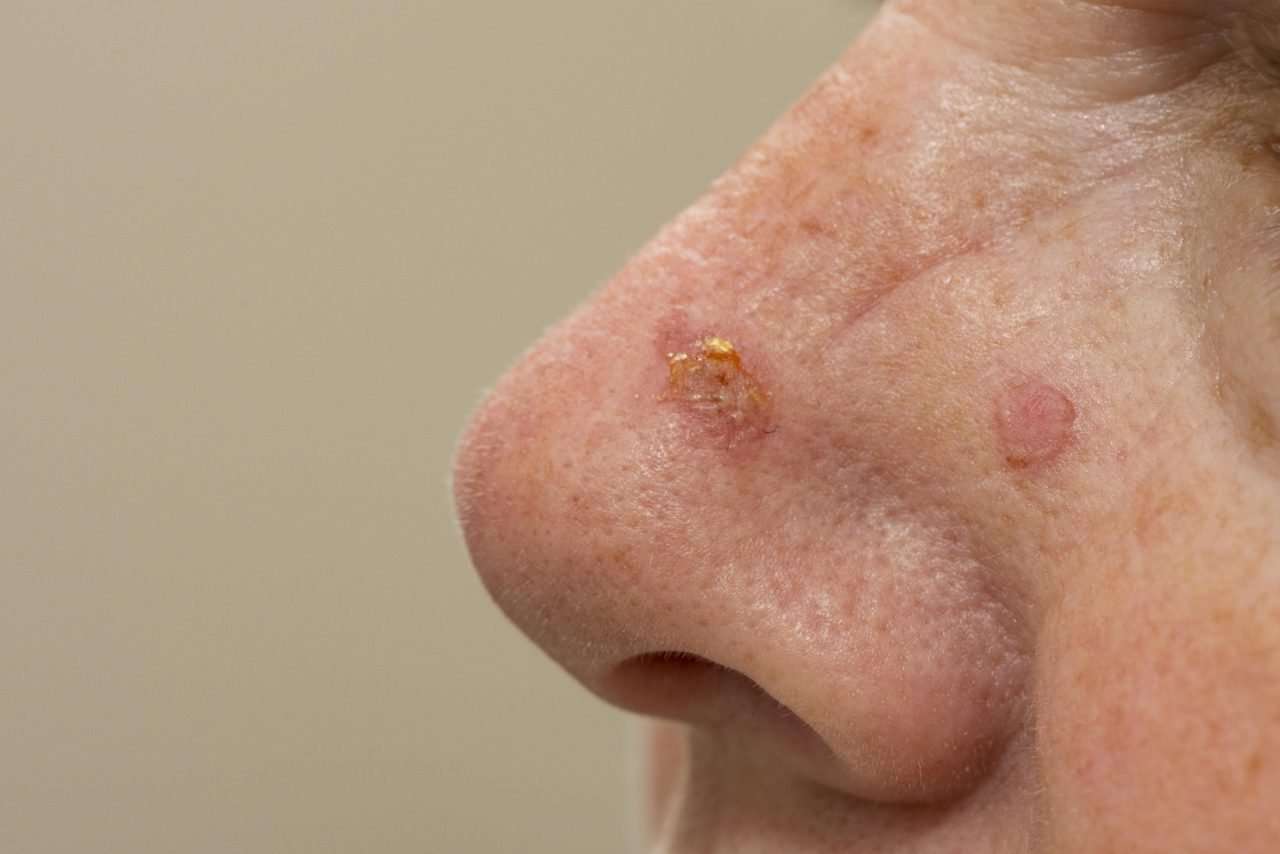
Basal cell carcinoma is caused by damage and subsequent DNA changes to the basal cells in the outermost layer of skin. Exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun and indoor tanning is the major cause of BCCs and most skin cancers.
Understanding what causes BCC and the factors that increase your risk of getting it can help you prevent the disease or detect it in its earliest stages, when its easiest to treat.
These factors increase your BCC risk:
Read Also: What Are The Risk Factors Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stages
There are certain features that are considered to make the cancer at higher risk for spreading or recurrence, and these may also be used to stage squamous cell carcinomas. These include:
- Greater than 2 mm in thickness
- Invasion into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin
- Invasion into the tiny nerves in the skin
- Location on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip
After the TNM components and risk factors have been established, the cancer is assigned to one of the five squamous cell carcinoma stages, which are labeled 0 to 4. The characteristics and stages of squamous cell cancer are:
Stage 0: Also called carcinoma in situ, cancer discovered in this stage is only present in the epidermis and has not spread deeper to the dermis.
Stage;1 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer is less than 2 centimeters, about 4/5 of an inch across, has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs, and has one or fewer high-risk features.
Stage 2;squamous;cell carcinoma: The cancer is larger than 2 centimeters across, and has not spread to nearby organs or lymph nodes, or a tumor of any size with 2 or more high risk features.
Stage 3;squamous;cell carcinoma: The cancer has spread into facial bones or 1 nearby lymph node, but not to other organs.
Stage 4;squamous;cell carcinoma: The cancer can be any size and has spread to 1 or more lymph nodes which are larger than 3 cm and may have spread to bones or other organs in the body.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Stages
There are certain features that are considered to make the cancer at higher risk for spreading or recurrence, and these may also be used to stage basal cell carcinomas. These include:
- Greater than 2 mm in thickness
- Invasion into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin
- Invasion into the tiny nerves in the skin
- Location on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip
After the TNM components and risk factors have been established, the cancer is given a stage. For basal cell carcinoma staging, the factors are grouped and labeled 0 to 4. The characteristics and stages of basal cell carcinoma are:
Stage 0: Also called carcinoma in situ, cancer discovered in this stage is only present in the epidermis and has not spread deeper to the dermis.
Stage 1 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer is less than 2 centimeters, about 4/5 of an inch across, has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs, and has one or fewer high-risk features.
Stage 2;basal cell carcinoma: The cancer is larger than 2 centimeters across, and has not spread to nearby organs or lymph nodes, or a tumor of any size with 2 or more high-risk features.
Stage;3 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer has spread into facial bones or 1 nearby lymph node, but not to other organs.
Stage 4 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer can be any size and has spread to 1 or more lymph nodes which are larger than 3 cm and may have spread to bones;or other organs in the body.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Skin Cancer From Radiation Treatments
Mohs Micrographically Controlled Excision
Mohs micrographically controlled surgery involves examining carefully marked excised tissue under the microscope, layer by layer, to ensure complete excision.
- Very high cure rates achieved by trained Mohs surgeons
- Used in high-risk areas of the face around eyes, lips and nose
- Suitable for ill-defined, morphoeic, infiltrative and recurrent subtypes
- Large defects are repaired by flap or skin graft
Carcinoma Treatment And Therapy Options
Treatment for carcinoma varies depending on the type, location and extent of the disease, but may include:
Surgery: Depending on the type of cancer, carcinoma may be treated with the surgical removal of cancerous tissue, as well as some surrounding tissue. Minimally invasive surgical treatment methods may help to reduce healing time and reduce the risk of infection after surgery.
Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy may be used in combination with surgery and/or chemotherapy. Advanced radiation therapies use image guidance before and during treatment on target tumors, and are designed to help spare healthy tissues and surrounding organs.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy treats carcinoma with drugs designed to destroy cancer cells, either throughout the whole body, or in a specific area. In some cases, chemotherapy may be used in combination with other treatments, such as radiation therapy or surgery.
Expert
Don’t Miss: Should I Be Worried About Basal Cell Carcinoma
What Are The Signs Of Bcc
BCC usually forms on skin that has been exposed to the sun. Tumors on the head, ears, nose, and neck are common. Most tumors are not painful. The following are common signs of a BCC:
- Shiny, waxy, pale or pink bumps or growths that may have blood vessels on the surface
- Red, scaly patches
- Open sores that may bleed and do not heal
How Serious Is My Cancer
If you have skin cancer, the doctor will want to find out how far it has spread. This is called staging.
Basal and squamous cell skin cancers don’t spread as often as some other types of cancer, so the exact stage might not be too important. Still, your doctor might want to find out the stage of your cancer to help decide what type of treatment is best for you.
The stage describes the growth or spread of the cancer through the skin. It also tells if the cancer has spread to other parts of your body that are close by or farther away.
Your cancer can be stage 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4. The lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. A higher number, like stage 4, means a more serious cancer that has spread beyond the skin. Be sure to ask the doctor about the cancer stage and what it means for you.
Other things can also help you and your doctor decide how to treat your cancer, such as:
- Where the cancer is on your body
- How fast the cancer has been growing
- If the cancer is causing symptoms, such as being painful or itchy
- If the cancer is in a place that was already treated with radiation
- If you have a weakened immune system
Read Also: Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Cure Itself
What Are The Complications/side Effects Of The Treatments For Basal Cell Carcinoma
Most of the complications related to BCC treatments other than the hedgehog inhibitors are cosmetic, such as scarring or redness.
People who use sonidegib or vismodegib should make sure to use effective birth control to avoid pregnancy due to the risk of birth defects. In addition, sonidegib has other potential risks, including problems with nerves and muscles.
Different Kinds Of Skin Cancer
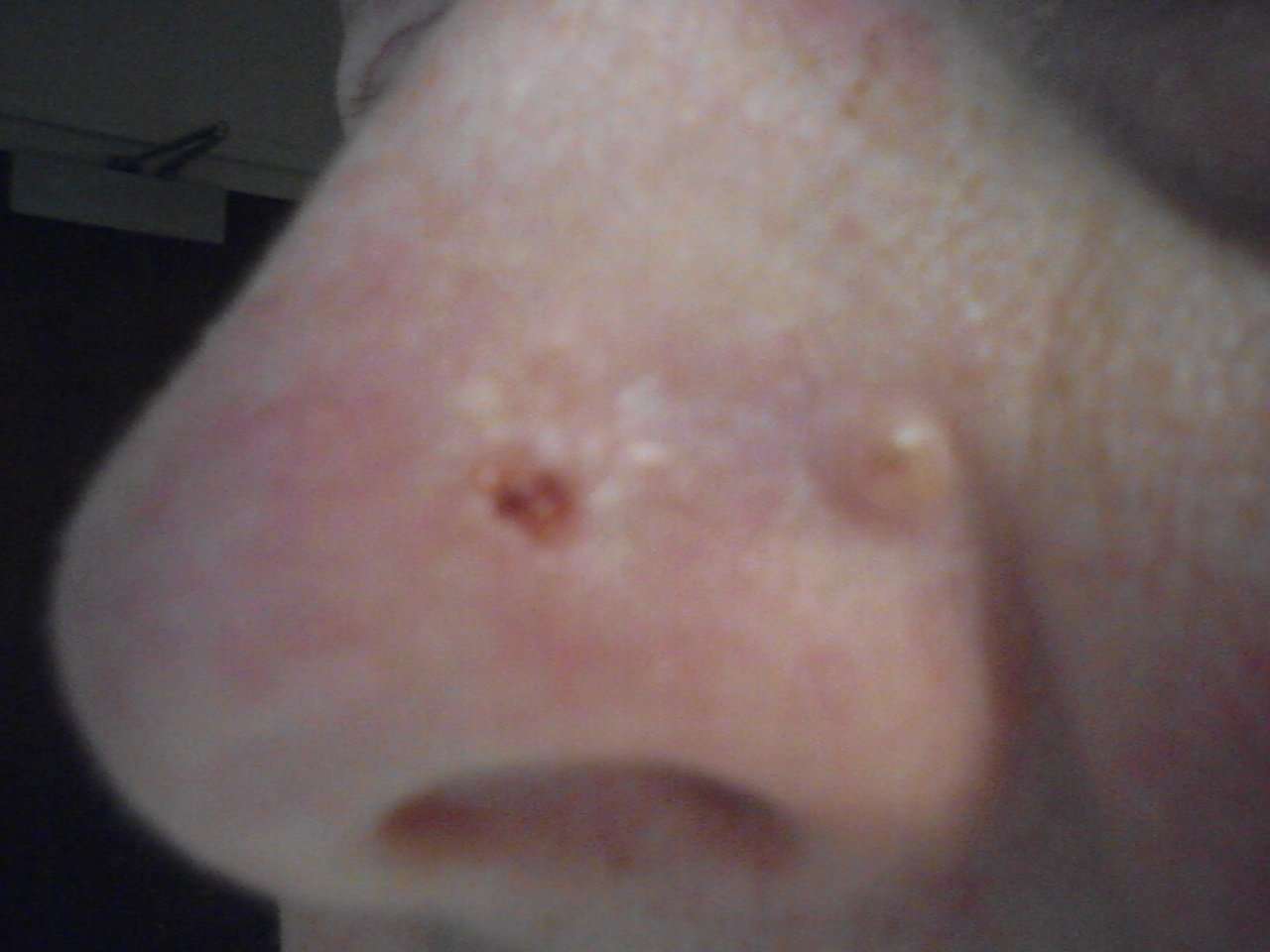
There are many types of skin cancer. Some are very rare. Your doctor can tell you more about the type you have.
The two most common kinds of skin cancers are:
- Basal cell cancer, which starts in the lowest layer of the skin
- Squamous cell cancer, which starts in the top layer of the skin
Another kind of skin cancer is called melanoma. These cancers start from the color-making cells of the skin . You can read about melanoma in If You Have Melanoma Skin Cancer.
Also Check: Can You Have Basal Cell Carcinoma For Years
Warning Signs Of Basal Cell Carcinoma That You Could Mistake As Harmless
Warning sign: A pink or reddish growth that dips in the centerCan be mistaken for: A skin injury or acne scar
A pink or reddish growth that dips in the center
The BCC on this patients cheek could be mistaken for a minor skin injury.
Warning sign: A growth or scaly patch of skin on or near the earCan be mistaken for: Scaly, dry skin, minor injury, or scar
A growth or scaly patch of skin on or near the ear
BCC often develops on or near an ear, and this one could be mistaken for a minor skin injury.
Warning sign: A sore that doesn’t heal and may bleed, ooze, or crust overCan be mistaken for: Sore or pimple
A sore that doesn’t heal, or heals and returns
This patient mistook the BCC on his nose for a non-healing pimple.
Warning sign: A scaly, slightly raised patch of irritated skin, which could be red, pink, or another colorCan be mistaken for: Dry, irritated skin, especially if it’s red or pink
A scaly, slightly raised patch of irritated skin
This BCC could be mistaken for a patch of dry, irritated skin.
Warning sign: A round growth that may be pink, red, brown, black, tan, or the same color as your skinCan be mistaken for: A mole, wart, or other harmless growth.
A round growth that may be same color as your skin
Would you recognize this as a skin cancer, or would you dismiss it as a harmless growth on your face?
What Is The Best Treatment For Basal Cell Carcinoma
When basal cell carcinoma is detected early, patients have many treatment options. The best treatment for basal cell carcinoma depends on several factors:
- the patients characteristics
- the subtype of basal cell carcinoma
- the area in which it is detected
If you have a spot that wont heal, or any spot that seems suspicious, dont wait to call your dermatologist. The earlier a spot is diagnosed, the easier it is to treat and the better your chances are for a full recovery. Give us a call to schedule your appointment so we can see what youre dealing with and get you started on the right treatment right away.
Also Check: Does Melanoma Metastasize To The Brain
How Is Bcc Treated
Treatment depends on your cancer, the area affected, and any other health conditions you may have:
- Surgery is the most common treatment. Your healthcare provider will remove the tumor. He or she may look at the tissue pieces with a microscope to make sure all of the cancer cells are removed. He or she may use an electric needle to burn off cancer cells or freeze the tumor with a chemical.
- Skin medicines may be used to help remove the cancer. This includes medicines that kill the cancer cells directly or help your immune system to attack the cancer cells.
- Radiation may be used to kill the cancer cell if you cannot have surgery, are older, or have a large tumor.
Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Cause Complications
The most common complication of basal cell carcinoma is recurrence. BCCs commonly recur, even after successful treatment. In some cases, BCC may reappear in the same place. It can also be disfiguring, especially if not treated promptly.
A diagnosis of BCC increases the chance of developing other types of skin cancer. This includes melanoma, which can metastasize and is the most life-threatening form of skin cancer.
Rare, aggressive forms of BCC can invade the body beyond the skin. It can destroy bone, nerves, and muscles. In rare cases it can metastasize to other parts of the body, including key organs, and become life-threatening.
Don’t Miss: Can Renal Cell Carcinoma Be Benign
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- Do you know the stage of the cancer?
- If not, how and when will you find out the stage of the cancer?
- Would you explain to me what the stage means in my case?
- What will happen next?
There are many ways to treat skin cancer. The main types of treatment are:
- Surgery
- Immunotherapy
- Chemotherapy
Most basal cell and squamous cell cancers can be cured with surgery or other types of treatments that affect only the spot on the skin.
The treatment plan thats best for you will depend on:
- The stage and grade of the cancer
- The chance that a type of treatment will cure the cancer or help in some way
- Your age and overall health
- Your feelings about the treatment and the side effects that come with it
What Causes Basal Cell Carcinoma
BCC develops from exposure to damaging ultraviolet sunlight and tanning beds. This cancer starts in the basal cell layer of the skin and grows very slowly. It develops mainly on the areas exposed to the sun, such as the:
- Head and face
Risk factors for basal cell carcinoma include:
- Exposure to UV radiation
- Long-term skin inflammation or injury
- Treatment for psoriasis using psoralens and ultraviolet light treatments
- History of skin cancer
Recommended Reading: How Often Does Basal Cell Carcinoma Spread
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that can show up on the skin in many ways. Also known as BCC, this skin cancer tends to grow slowly and can be mistaken for a harmless pimple, scar, or sore.
Common signs and symptoms of basal cell carcinoma
This skin cancer often develops on the head or neck and looks like a shiny, raised, and round growth.
To help you spot BCC before it grows deep into your skin, dermatologists share these 7 warning signs that could be easily missed.
If you find any of the following signs on your skin, see a board-certified dermatologist.
Of Basal Cell Carcinoma

Basal cell carcinoma: The most common type of skin cancer, which commonly presents as a sore that seems to get better and then recurs and may start to bleed. Basal cell carcinoma often occurs on the face and neck, where the skin is exposed to sunlight. These tumors are locally invasive and tend to burrow in but not metastasize to distant locations.
©1996-2021 MedicineNet, Inc. All rights reserved. Terms of Use.
MedicineNet does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. See additional information.
Health Categories
Read Also: How Do You Spell Melanoma Cancer
More Pictures Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
While the above pictures show you some common ways that BCC can appear on the skin, this skin cancer can show up in other ways, as the following pictures illustrate.
Scaly patch with a spot of normal-looking skin in the center
On the trunk, BCC may look like a scaly patch with a spot of normal-looking skin in the center and a slightly raised border, as shown here.
Basal cell carcinoma can be lighter in some areas and darker in others
While BCC tends to be one color, it can be lighter in some areas and darker in others, as shown here.
Basal cell carcinoma can be brown in color
Most BCCs are red or pink; however, this skin cancer can be brown, as shown here.
Basal cell carcinoma can look like a group of shiny bumps
BCC can look like a group of small, shiny bumps that feel smooth to the touch.
Basal cell carcinoma can look like a wart or a sore
The BCC on this patients lower eyelid looks like a wart* in one area and a sore** in another area.
If you see a spot or growth on your skin that looks like any of the above or one that is growing or changing in any way, see a board-certified dermatologist.