What Is The Success Rate For Treating Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Unlike basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma tends to be more invasive and is likely to spread if left untreated. As with basal cell carcinoma, Mohs micrographic surgery has the best success rates, at 97 percent. Excision has a 92 percent success rate. For low-risk, small tumors, curettage, and electrodesiccation is successful in 96 percent of cases, but it cannot be used for larger, deeper growths.
Squamous cell carcinoma is generally not considered life-threatening if treated early. However, if left untreated, squamous cell carcinoma can spread and it can then become life-threatening. Reliable statistics are not available, however, because most of these cancers are treated in a dermatologists office.
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Survival Rates
Because basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas are lower-risk skin cancers, theres little information on survival rates based on stage.
Both types of cancer have a very high cure rate. According to the Canadian Cancer Society, the five-year survival rate for basal cell carcinoma is 100 percent. The five-year survival rate for squamous cell carcinoma is 95 percent.
Taking Care In The Sun
- Stay in the shade between the hours of 11am and 3pm.
- Make sure you never burn.
- Avoid the use of sun beds.
- ;Always cover up. Wear light cool clothing of a tight weave, wide-brimmed hats and U.V. protective sunglasses, look for the CE or BS EN 1836:1997 mark these offer the highest protection.
- Take extra care of children as their skin is delicate. Very young babies should be kept out of strong direct sunshine.
- Use a sunscreen of factor 30 and above, according to your skin type, ensure the sunscreen has UVB and UVA protection. Look for the star rating ****or ***** on the label, the price is not important. ;Apply it 15-30 minutes before you go out and re-apply regularly; every 2-3 hours.
- Remember:;Pass on the message to family and friends about protecting themselves from the sun and being aware of changes to moles on their skin.
Telephone numbers for follow up appointments:
- Dermatology 01752 439712
- Plastic Surgery 01752 439937/ 431184
- Oncology 01752 432336
Also Check: How Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Removed From The Nose
Curettage And Electrodesiccation Are Common Approaches To Scc Removal
Curettage and electrodesiccation are surgical procedures used mainly to treat small and thin Squamous Cell Cancers that are less than 1cm across in size. Although it is not commonly used for larger tumors, the method of cutting out tumors with the edge of the healthy skin is an overall standard treatment.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Oral Cavity
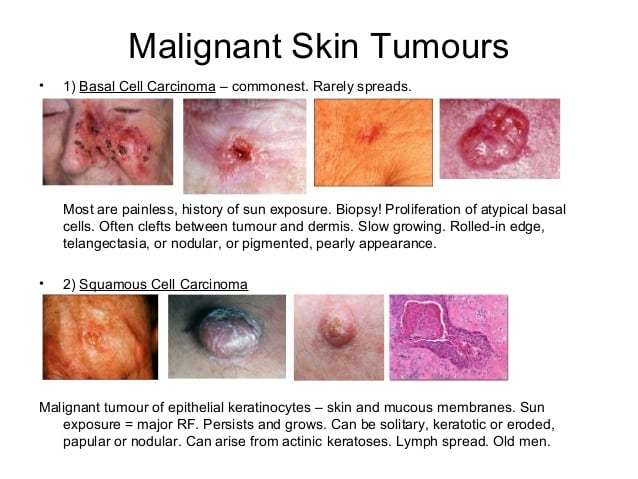
The signs and symptoms of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Oral Cavity include:
- In majority of the cases, the condition is asymptomatic and does not present any signs or symptoms
- Generally, squamous cell carcinomas are slow-growing tumors; though SCC of Oral Cavity is an aggressive form of cancer
- The mouth parts affected may include the cheek, hard and soft palate, gums, etc.
- The skin lesions may appear as crusted ulcer, plaques, and nodules
- It may ulcerate and bleed. Occasionally, after the ulcer heals, it may become ulcerated again
- The size of the lesions range from 1-10 cm; average size is usually less than 3 cm
- Individuals with immunocompromised states have more aggressive tumors
- Due to the presence of the lesion on the oral mucosa, it may be difficult for the individual to consume food and drink. Also, speaking may be difficult and painful
Recommended Reading: How Bad Is Melanoma Skin Cancer
What Are The Signs Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinomas are more typical on sun-exposed skin: the scalp, the backs of the hands, the ears, and the lips. But this form of skin cancer can spread anywhere on your body.
Squamous cell carcinomas will have these characteristics:
- A firm, red nodule
- A flat sore with a scaly crust
- A new sore or raised area on an old scar
- A rough, scaly patch on your lip that can become an open sore
- A red sore or rough patch inside your mouth
- A red, raised patch or wart-like sore on or in the anus or on the genitals
How Chipsa Treats Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients
Learn how CHIPSA treats patients with squamous cell carcinoma, the second most common form of skin cancer.;
What is squamous cell carcinoma?;
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common form of skin cancer after basal cell carcinoma. It begins in the thin, flat cells that make up the outermost layer of the skin. Although the cancer is slow growing, if left untreated, it can spread to other parts of the body and become life-threatening.
SCC usually shows up in red, scaly patches, open sores, or warts on the skin. They most often appear in areas that are exposed to the ultraviolet rays, such as the face, hands, and ears. It can also show up in the mouth, anal area, or genitals. As the SCC grows, it may look like a raised bump that crusts or bleeds.
Risk factors for developing SCC include being fair-skinned, having light hair and blue, green, or gray eyes, having had long-term exposure to UV radiation, and having a history of multiple severe sunburns.;
The earlier SCC is detected, the better. Once it has spread to lymph nodes or other organs, the disease becomes much more serious.;
CHIPSAs Squamous Cell Carcinoma Success Stories
CHIPSA has treated several SCC patients, most of whom came in at the late stages when the cancer had already spread.;
Johns SCC Story
So John began to research hospitals outside of the U.S., and thats when he discovered CHIPSA. He was pleased to find a place who was willing to listen to his ideas and be open to other treatment options.
Read Also: How To Tell If Something Is Skin Cancer
Care For Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinomas
We take a multidisciplinary approach to your medical care, which means that the expertise of other specialists can be coordinated easily and effectively, if needed.
Patients who come to our clinic receive a preoperative consultation to assess, coordinate, plan and prepare you for surgery. In most cases this can be done on the phone without scheduling a preoperative visit. All patients have their biopsy slides reviewed by one of our pathologists before receiving a treatment plan. If it’s determined Mohs surgery is your best option, you will be scheduled for the procedure at a later date.
What Happens If Precancers Go Untreated
As the name suggests, precancers are damaged skin cells that arent considered cancerous, but if they are left untreated, these lesions are at high risk to become skin cancer. There are two main types of precancerous skin conditions: actinic keratosis and dysplastic nevi. Actinic keratosis looks like a rough, scaly patch of the skin that is usually red or brown. This condition may develop into squamous cell carcinoma if left untreated.
Nevi are moles, and dysplastic nevi is a term that means a mole is abnormal. Dysplastic nevi may develop into melanoma without proper treatment. While precancerous skin cancers are not malignant on their own, the potential to develop into life-threatening forms of this condition means they need to be evaluated regularly.
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of Skin Cancer Naturally
How Dangerous Is Scc
While the majority of SCCs can be easily and successfully treated, if allowed to grow, these lesions can become disfiguring, dangerous and even deadly. Untreated SCCs can become invasive, grow into deeper layers of skin and spread to other parts of the body.
Did you know?
Americans die each year from squamous cell carcinoma
These Cancers Can Be Treated
Fortunately, basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are usually very responsive to treatment and have a survival rate of more than 95% with early detection and treatment. The American Cancer Society reports that deaths from basal cells and squamous cells are uncommon, with an estimation of 2,000 deaths in the United States a year, but dont become one of the statistics. See a dermatologist regularly for a skin check, and in-between visits, perform self-checks and keep a close eye on your skin for anything suspicious or worrisome. If you do see something, call your doctor for an appointment because the sooner you can get diagnosis and treatment, the better.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Metastasize
How Fast Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
Squamous cell carcinoma rarely metastasizes , and when spreading does occur, it typically happens slowly. Indeed, most squamous cell carcinoma cases are diagnosed before the cancer has progressed beyond the upper layer of skin. There are various types of squamous cell carcinoma and some tend to spread more quickly than others.
How Is Scc Diagnosed And Treated
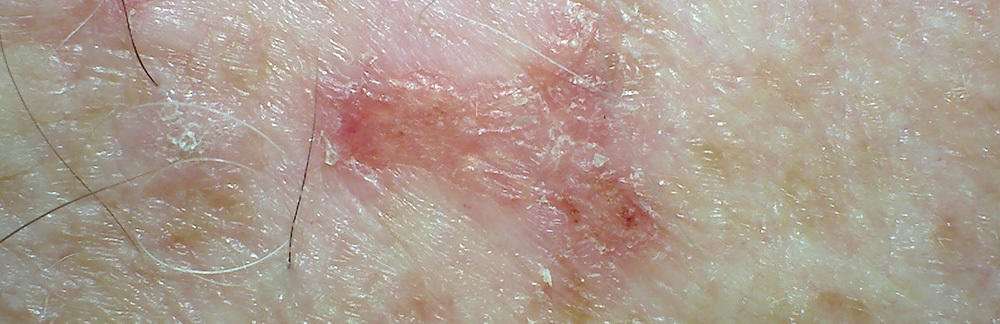
A biopsy may be taken and tested for cancer. Treatment depends on where the SCC is located:
- Cryosurgery is a procedure that uses a chemical, called liquid nitrogen, to freeze and kill a small area of tissue. The tissue dies and later falls off.
- Mohs surgery is used to remove only skin with cancer cells and as little healthy tissue as possible. Thin layers of the tumor are scraped off one at a time until all the cancer cells are removed.
- Surgery is used to remove the cancer.
- Electrodesiccation and curettage is used for skin SCC. The tumor is scraped and then heated with an electric probe to kill the cancer cells.
- Laser therapy uses a narrow beam of light to kill the cancer cells.
- Topical chemotherapy is given as a lotion or cream to put directly on skin cancer to kill cancer cells.
- Radiation uses x-rays or gamma rays to treat cancer. Radiation kills cancer cells and may stop the cancer from spreading. It may be used for hard-to-treat areas, such as the eyelids, tongue, or esophagus.
Also Check: What Does Merkel Cell Skin Cancer Look Like
Chemotherapy For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Superficial Squamous Cell Carcinoma may be able to be treated with topical chemotherapy that is applied to the skin as an ointment or cream. This type of treatment is only for skin cancers that biopsy-proven to affect only the top layer of skin.
5-fluorouracil is approved for the treatment of Superficial Squamous Cell Carcinoma, however, invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma should not be treated topically due to the risk of spread.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Screening
Diagnosis and management of Squamous Cell Carcinoma is best performed via a Full Body Scan. In the first incidence, this process includes
- Digitally Mapping a patient’s entire body for any suspicious skin damage or lesion
- Followed by a detailed Dermoscopic Examination by a trained skin cancer Specialist
- Recording and combining all images and skin metrics into the patient record
Our expert Doctors at Bondi Junction Skin Cancer Clinic will then clearly identify and diagnose any skin cancers. ;Having a digital molemap or a baseline of all your skins sun damage for all family members with
- any suspicious sun damage,
- those with a large number of moles, or
- have been diagnosed with melanoma is recommended.
Any changes can be more easily spotted and understood.
Read Also: Do You Need Chemo For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common form of skin cancer. Its usually found on areas of the body damaged by UV rays from the sun or tanning beds. Sun-exposed skin includes the head, neck, chest, upper back, ears, lips, arms, legs, and hands.
SCC is a fairly slow-growing skin cancer. Unlike other types of skin cancer, it can spread to the tissues, bones, and nearby lymph nodes, where it may become hard to treat. When caught early, its easy to treat.
SCC can show up as:
- A dome-shaped bump that looks like a wart
- A red, scaly patch of skin thats rough and crusty and bleeds easily
- An open sore that doesnt heal completely
- A growth with raised edges and a lower area in the middle that might bleed or itch
What Increases My Risk For Scc
- Age 60 years or older
- Fair skin or light hair
- A history of long-term exposure to the sun or ultraviolet rays from tanning beds
- Exposure to chemicals such as coal tars, arsenic, or radium
- A history of other skin disorders, such as actinic keratosis, radiation dermatitis, or burn scars
- Cigarette or alcohol use
- A human papillomavirus infection
Recommended Reading: What Does Stage 3b Melanoma Mean
Diagnostic Test For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Improving your squamous cell carcinoma prognosis and life expectancy requires receiving an early diagnosis. Your doctor or dermatologist can produce accurate findings with a skin biopsy, which entails removing a small portion of tissue from the suspicious area and then examining the cells under a microscope.
After receiving a skin cancer diagnosis, the most important step is to plan your treatment.
What To Do If You Receive A Skin Cancer Diagnosis
Once a skin biopsy confirms skin cancer, your doctor will recommend a treatment based on the stage of the cancer.
To improve your outlook, its important that you complete your treatment and schedule follow-up appointments as needed. Your doctor may want to see you every few months to make sure the cancer hasnt returned.
Also schedule annual skin exams with a dermatologist. Get into the habit of checking your own skin for abnormal growths, too. This includes your back, scalp, soles of feet, and ears.
You can also ask your doctor about local support groups for those with skin cancer, or search for support programs in your area.
Don’t Miss: What Does Skin Cancer Look Like On Your Head
Are You At Risk
The skin is the largest organ of the body. It is also our bodys first line of defense. There are numerous factors which may increase your risk of skin cancer:
- Genetics: Individuals with fair complexions are at the greatest risk. Your risk is also increased if your parents, children, or siblings have had skin cancer.
- Sun Exposure: Over the course of a lifetime, exposure to the sun can lead to a higher risk of skin cancer. Tanning beds and other false sunlight are no exception.
- Immunosuppression: Immunosuppression therapy following organ transplants, chemotherapy, AIDS, and other treatments can put you at a significant risk for skin cancer.
- Lifespan: Human life expectancy has increased from forty-two years in 1904 to close to eighty years today. As a result, the number of skin cancers being seen around the world is increasing.
Treatment Options: Mohs Surgery
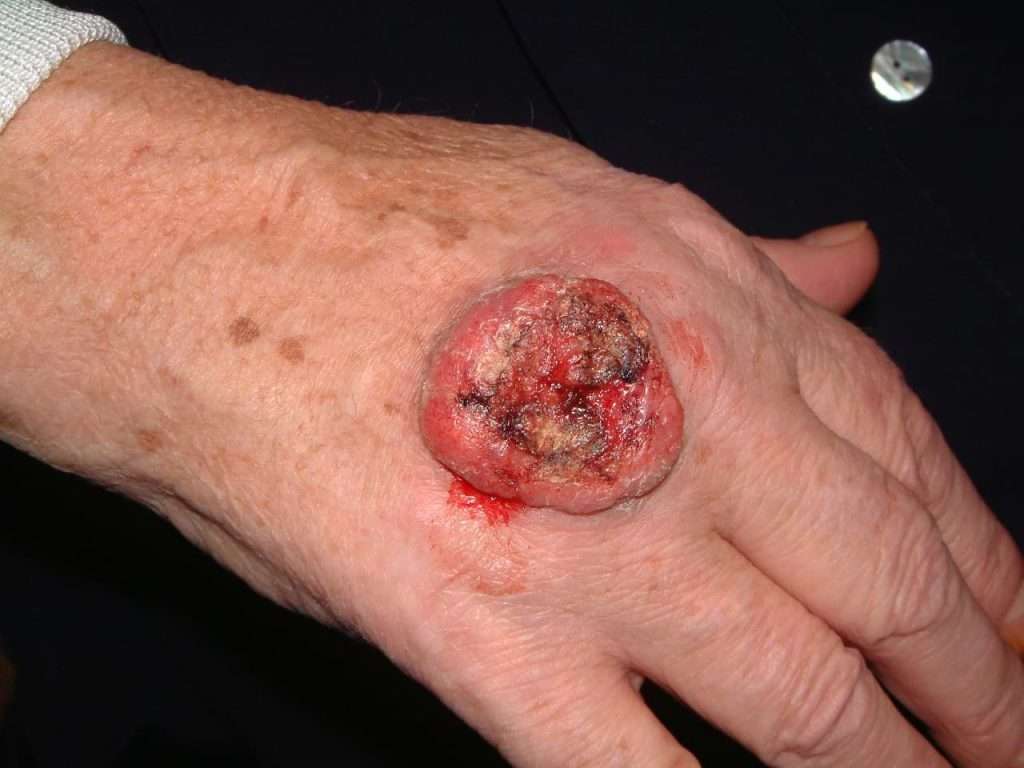
Minor cases of skin cancer can often be treated with a simple excision, but in about half of all cases more significant intervention is needed. In these more significant cases, most dermatologic practices either offer Mohs surgery in-house or refer patients for Mohs surgery to a practice offering the procedure. While Mohs surgery effectively treats non-melanoma skin cancer 95 percent of the time or more, the side effects of Mohs surgery can be significant with bleeding, pain, and healing time being the most common. Theres also a need for reconstructive surgery in about 1 third of cases.
Read Also: How Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Start
How Aggressive Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is not often considered to be life threatening. This form of skin cancer that affects the squamous cells tends to create slow-growing tumors. Although squamous cell carcinoma is more likely to invade deeper layers of the skin and spread to other parts of the body than basal cell carcinoma, this is still uncommon.
Only about 5 to 10 percent of squamous cell carcinoma tumors are considered to be aggressive.
There Is Some Good News
There is some good news! According to the American Cancer Society, basal cell carcinomas rarely metastasize to lymph nodes, organs, or other areas of the body. This doesn’t mean, however, that they should be left untreated. Basal cell carcinoma can spread and do a lot of damage in the area where they form and can become quite disfiguring if they are left to grow.
Recommended Reading: How Common Is Renal Cell Carcinoma
Answer: Squamous Cell Carcinoma Growth
While it is said that most skin cancers grow slowly, the true answer is “it depends”. It depends on location of the skin cancer, your general health, the health of your skin and the cause of the skin cancer. Most squamous cell carcinomas arise in skin damaged by ultra violet light and, often, grow slowly. However, if the UV damage is severe or if the SCC arose from a burn or infection site, the cancer can grow rapidly and spread to other organs. Additionally, SCC, which grows contiguously will sometimes send “seeds” beyond the tissue containing the “roots”. These factors all have to be considered in determining how to deal with SCC. The best advice I can give you is to not delay and have this evaluated by a fellowship-trained Mohs surgeon. I hope I have answered your question. Best.;;;;;;;;; jlr
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Recurrence
Squamous Cell Carcinomas on the scalp and nose are especially troublesome, with higher rates of recurrence and with these recurrences typically taking place within the first two to three years following surgery.
Should a cancer recur, your Doctor might recommend a different type of treatment. Some methods, such as Mohs micrographic surgery, may be highly effective for recurrences.
Read Also: What Are The Chances Of Skin Cancer
What Is Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is a serious but common skin condition that causes skin cells to replicate in irregular ways or damages the structure of the cells themselves. While there are many different causes of skin cancer, exposure to the suns ultraviolet rays is the most common underlying cause of all forms of skin cancer. When damaged skin cells multiply, they form tumors. These growths can be either benign or malignant. Benign tumors are typically considered noncancerous or precancerous. Malignant tumors are more likely to impact surrounding cells or metastasize, which means they may spread to other parts of the body.
There are many different types of skin precancers and cancers. Skin precancers include actinic keratosis and dysplastic nevi . The four most common skin cancers are basal cell carcinomas, squamous cell carcinomas, melanoma skin cancers, and merkel cell skin cancers. Most skin cancers are either basal or squamous cell carcinomas. While melanomas and merkel cell skin cancers make up a small percentage of cases, they cause the greatest number of skin cancer-related deaths each year as these types are more likely to metastasize.
Signs of skin cancer can be more easily remembered by the mnemonic ABCDEF.; This was developed initially for melanoma detection, but it can be applied to most skin cancers:
A asymmetry the shape isnt uniform throughout
D diameter is the spot greater than the size of a pencil eraser?; Is the diameter growing?