Preventing Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma prevention is the same as prevention methods for all skin cancers, with the goal of protecting skin from harmful UV rays.
The number one thing people can do is to practice good sun protection and sun avoidance, meaning wear sunscreen and protect the skin from getting sun damage, says Stevenson. Its also important to get skin checks regularly for early detection.
Stevenson says if someone is prone to skin cancers for example, has very fair skin, sunburns as a child, or a history of skin cancer in the family its better to go out in the late afternoon or early morning when the sun isnt as strong, or stay primarily in the shade.
Anyone spending time in the sun, regardless of complexion, should practice sun protective behaviors, including wearing sunscreen.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends a sunscreen with a minimum sun protection factor of 15, and UVA and UVB broad spectrum protection. It also advises people to stay in the shade as much as possible and wear protective clothing including brimmed hats and sunglasses. Stevenson suggests looking for a SPF over 30.
Lebwohl says the SPF number directly correlates with the amount of protection it gives you. He says to divide the amount of time in the sun by the SPF number. For example, if someone is in the sun for 60 minutes, and wearing SPF 30, its as if they were exposed to two minutes of damaging rays rather than the full 60 minutes.
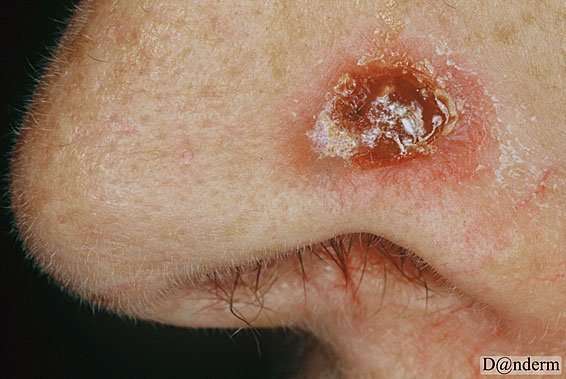
Nodular Ulcerative Basal Cell Carcinoma
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Mohs Micrographically Controlled Excision
This is a type of excision that uses a microscope to remove the lesion layer by layer until no signs of cancer are present. The microscope allows the doctor to pinpoint the cancerous areas of skin to better target removal and save healthy skin. This is a very effective form of removal with a success rate of 99 percent or higher.
Donât Miss: Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Malignant
Recommended Reading: How Common Is Renal Cell Carcinoma
When Should I See My Doctor
If you have had one BCC, you have a 50% chance of developing another one, so it is important to check your skin regularly.
Most people find BCCs by checking their own skin and looking for changes. See a doctor if you find:
- a spot that is different from other spots on your skin
- a spot that has changed size, shape, colour or texture
- a sore that doesnt heal
- a sore that is itchy or bleeds
How Is Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin Diagnosed
Some of the tests that may help in diagnosing Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin include:
- Complete physical examination with detailed medical history evaluation
- Examination by a dermatologist using a dermoscopy, a special device to examine the skin
- Woodâs lamp examination: In this procedure, the healthcare provider examines the skin using ultraviolet light. It is performed to examine the change in skin pigmentation
- Skin or tissue biopsy: A skin or tissue biopsy is performed and sent to a laboratory for a pathological examination, who examines the biopsy under a microscope. After putting together clinical findings, special studies on tissues and with microscope findings, the pathologist arrives at a definitive diagnosis
- Differential diagnosis of other tumors should be ruled out; hence, biopsy is an important diagnostic tool
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
Also Check: How Deadly Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Surgery For Skin Cancer
Small skin cancer lesions may be removed through a variety of techniques, including simple excision , electrodesiccation and curettage , and cryosurgery .
Larger tumors, lesions in high-risk locations, recurrent tumors, and lesions in cosmetically sensitive areas are removed by a technique called Mohs micrographic surgery. For this technique, the surgeon carefully removes tissue, layer by layer, until cancer-free tissue is reached.
Malignant melanoma is treated more aggressively than just surgical removal. To ensure the complete removal of this dangerous malignancy, 1-2;cm of normal-appearing skin surrounding the tumor is also removed. Depending on the thickness of the melanoma, neighboring lymph nodes may also be removed and tested for cancer. The sentinel lymph node biopsy method uses a mildly radioactive substance to identify which lymph nodes are most likely to be affected.
Continued
How Is Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin Treated
In general, the treatment of Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin depends upon a variety of factors including:
- The subtype of BCC
- The location of the tumor
- The number of tumors
- The size of the tumor
- Whether the tumor has metastasized
A combination of treatment methods may be used to treat Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin. The type of surgery may include:
- Shave biopsy of skin: This procedure is used for small tumors. There is no requirement of sutures after the surgery
- Excision of tumor: In this procedure, the tumor and surrounding tissue are removed with clear margins. Depending upon the amount of skin removed, surgical sutures may be necessary
- Mohs surgery: In this procedure, the tumor is removed layer by layer precisely, until clear margins are achieved. Each layer removed is examined under a microscope through a âfrozen sectionâ procedure, for the presence of residual tumor
In most cases, a surgical removal of the entire tumor is the preferred treatment option. This can result in a cure.
Other techniques to treat this skin cancer may include:
- Cryotherapy: Here the tumor tissue is destroyed through a freezing technique. Typically liquid nitrogen is used to freeze the tumor
- Topical creams, such as 5-fluorouracil cream and imiquimod cream, are two examples that can be used for topical treatment. These creams may be applied for several weeks, which slowly destroys the tumor
Recommended Reading: Can I Die From Skin Cancer
Basal Cell Carcinoma Signs And Symptoms
This type of cancer is usually found on sun-exposed areas of the skin like the scalp, forehead, face, nose, neck and back.
Basal cell carcinomas may bleed after a minor injury but then scab and heal. This can happen over and over for months or years with no visible growth, making it easy to mistake them for wounds or sores. They rarely cause pain in their earliest stages.
Appearance
In addition to the bleeding and healing, these are other possible signs of a basal cell cancer:
- A persistent open sore that does not heal and bleeds, crusts or oozes.
- A reddish patch or irritated area that may crust or itch.
- A shiny bump or nodule that is pearly or translucent and often pink, red or white. It can also be tan, black or brown, especially in dark-haired people, and easy to confuse with a mole.
- A pink growth with a slightly elevated, rolled border and a crusted indentation in the center. Tiny blood vessels may appear on the surface as the growth enlarges.
- A scar-like lesion in an area that you have not injured. It may be white, yellow or waxy, often with poorly defined borders. The skin seems shiny and tight; sometimes this can be a sign of an aggressive tumor.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Overview
Basal cell carcinoma, also called epithelioma, is the uncontrolled growth of the skin’s basal cells. These are the cells that line the deepest layer of the epidermis, the skin’s outermost layer. This type of cancer rarely spreads to other parts of the body.
It is mainly caused by repeated long-term exposure to sunlight. Light-skinned people who spent a lot of time in the sun as children, or who spend time in tanning booths, are especially susceptible. X-ray treatments for acne and exposure to industrial pollutants such as arsenic and hydrocarbons also increase the risk of developing basal cell carcinoma.
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common skin cancer in the United States, with nearly 3 million cases diagnosed each year.
You May Like: Can Renal Cell Carcinoma Be Benign
What Happens If A Basal Cell Carcinoma Is Not Treated
Posted on September 26, 2015 in Skin Cancer, Mohs Micrographic Surgery, Practice News, Skin Tumor, Basal Cell Carcinoma, malignancy
A basal cell carcinoma is one of the more common forms of skin cancers and, fortunately, one of the most treatable, says Dr. Adam Mamelak, board certified dermatologist and skin cancer specialist in Austin, Texas.
Basal cell carcinoma is most commonly caused by exposure of the skin to ultraviolet light, either from the sun or a tanning bed. Gradually, the effects of exposure damage the DNA, resulting in the development of cancer. The process can take anywhere from weeks to months to several years before it becomes noticeable.
Basal cell carcinomas can look different. They can appear as tiny, pearl shaped bumps. They can also manifest as shiny red or pink patches that feel slightly scaly. They are fragile and can bleed easily. Some appear to be dark against the surrounding skin, while others will break down and create a sore or ulcer on the skin.
If Dr. Mamelak suspects his patients have a basal cell carcinoma, he often does a biopsy on the growth to see if cancer cells are present. Dr. Mamelak also asks his patients a number of questions about their potential risk factors, including how often they are out in the sun, whether or not they use a tanning bed, and what kind of sunblock they use, if any.
What happens if a basal cell carcinoma is not treated?
Contact Us
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- Do you know the stage of the cancer?
- If not, how and when will you find out the stage of the cancer?
- Would you explain to me what the stage means in my case?
- What will happen next?
There are many ways to treat skin cancer. The main types of treatment are:
- Surgery
- Immunotherapy
- Chemotherapy
Most basal cell and squamous cell cancers can be cured with surgery or other types of treatments that affect only the spot on the skin.
The treatment plan thats best for you will depend on:
- The stage and grade of the cancer
- The chance that a type of treatment will cure the cancer or help in some way
- Your age and overall health
- Your feelings about the treatment and the side effects that come with it
You May Like: What Is Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Looking Out For Basal Cell Carcinoma
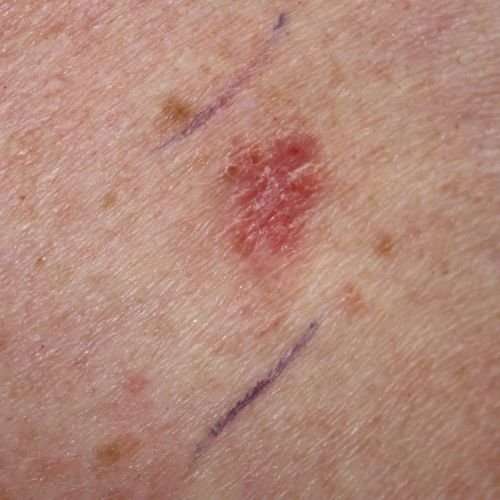
Sometimes basal cell carcinoma is overlooked because it doesnt “look like cancer.” It might appear as a small dome shaped skin growth or a shiny or slightly scaly pink or red patch. It might be skin colored and resemble a scar. It might be a small pink dot on your skin. It could look like a sore.
Regular skin checks are important. When you complete self-skin checks monthly, you notice if new spots or lesions appear. Some of the warning signs of BCC that should be checked by a dermatologist, according to the American Academy of Dermatology, are:
-
An open sore that doesnt heal or that starts to heal and then opens up again.
-
A skin bump that is pearly, waxy, or red and scaly.
-
A scar-like spot without having had an injury.
-
A spot that oozes or crusts.
-
A spot with irregular blood vessels around it.
-
A sore that has a depressed center.
As always, if you have a sore or spot that changes in appearance, color, size or texture, you should contact your dermatologist.
What About Other Treatments That I Hear About
When you have cancer you might hear about other ways to treat the cancer or treat your symptoms. These may not always be standard medical treatments. These treatments may be vitamins, herbs, special diets, and other things. You may wonder about these treatments.
Some of these are known to help, but many have not been tested. Some have been shown not to help. A few have even been found to be harmful. Talk to your doctor about anything youre thinking about using, whether its a vitamin, a diet, or anything else.
Recommended Reading: How Does Immunotherapy Work For Melanoma
Treatment Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
-
Removal of the tumor
Doctors may remove the cancer in the office by scraping and burning it with an electric needle or by cutting it out. Doctors may destroy the cancer by using extreme cold .
Certain chemotherapy drugs may be applied to the skin. Photodynamic therapy , in which chemicals and a laser are applied to the skin, also may be used. Occasionally, radiation therapy is used.
A technique called Mohs microscopically controlled surgery may be required for some basal cell carcinomas that are large or regrow or occur in certain areas, such as around the nose and eyes.
People whose cancer has spread to nearby tissues or spread to other parts of the body and who are not candidates for surgery or radiation therapy may be given the drug vismodegib or sonidegib taken by mouth.
What Are The Risk Factors For Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma are all skin cancers caused by exposure to damaging ultraviolet raysfrom natural and artificial sunlight. Thereâs also a genetic condition called basal cell nevus or Gorlin syndrome, which can cause people to develop hundreds of basal cell skin cancers, but itâs extremely rare, says Dr. Christensen.
People at the highest risk for basal cell carcinoma tend to have fair or light-colored skin, a history of sun exposure and a tendency to sunburn quickly. Fair-skinned people have a 50 percent risk of developing basal skin cancer at some point in their lives, Dr. Christensen says. The cancer is the result of cumulative damage of years spent in the sun, and may take 20 years to manifest.
Although itâs often more common in older people, it can occur in younger adults, too.
Basal cell carcinoma spreads very slowly and very rarely will metastasize, Dr. Christensen says. But if itâs not treated, basal cell carcinoma can continue to grow deeper under the skin and cause significant destruction to surrounding tissues. It can even become fatal. For example, an untreated basal cell carcinoma on the face can grow into the bones and, over time, directly into the brain, Dr. Christensen says.
Also Check: What Does Skin Cancer On Scalp Feel Like
How Serious Is Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Basal cell skin cancer, also called basal cell carcinoma, is usually very curable, but it can cause disfigurement and complications if it’s not treated. In the majority of cases, basal cell carcinoma is very treatable.
It is unusual for basal cell carcinoma to cause death. Approximately 2,000 people in the U.S. die each year from basal and squamous skin cancers. In most cases, people who die from these types of skin cancer tend to be older, immunosuppressed, or have been diagnosed at a very late stage.;
Remember: All Omas Arent Cancer
In cancers, including carcinoma and sarcoma, cells divide uncontrollably, invade nearby tissues and can eventually spread to distant sites.
It is important to know that benign masses may also end in oma, which means tumor, but these cells behave and are treated quite differently, says Dr. Shepard.
For example, cells in benign tumors such as adenomas, fibromas and angiomas will not invade nearby tissues or spread to other sites.
Thus, the tumors dont have the same negative consequences as a carcinoma or sarcoma.
Recommended Reading: What Happens If I Have Skin Cancer
What Are Basal And Squamous Cell Skin Cancers
Basal and squamous cell skin cancers are the most common types of skin cancer. They start in the top layer of skin , and are often related to sun exposure.
Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow out of control. Cells in nearly any part of the body can become cancer cells. To learn more about cancer and how it starts and spreads, see What Is Cancer?
Neglected Basal Cell Carcinomas In The 21st Century
Erika Varga
1Department of Dermatology and Allergology, Albert Szent-Györgyi Clinical Center, University of Szeged, Korányi fasor 6, 6720 Szeged, Hungary
2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Albert Szent-Györgyi Clinical Center, University of Szeged, Kálvária sgt. 57, 6725 Szeged, Hungary
Abstract
Although tumors on the surface of the skin are considered to be easily recognizable, neglected advanced skin neoplasms are encountered even in the 21st century. There can be numerous causes of the delay in the diagnosis: fear of the diagnosis and the treatment, becoming accustomed to a slowly growing tumor, old age, a low social milieu, and an inadequate hygienic culture are among the factors leading some people not to seek medical advice. The treatment of such advanced neoplasms is usually challenging. The therapy of neglected cases demands an individual multidisciplinary approach and teamwork. Basal cell carcinoma , the most common cutaneous tumor, usually develops in the elderly, grows slowly, and has an extremely low metastatic potential; these factors are suggesting that BCCs might well be the ideal candidates for neglected tumors. Five neglected advanced cases of BCC were diagnosed in our dermatological institute between 2000 and 2009. The clinical characteristics and treatment modalities of these neoplasms are discussed, together with the possible causes of the neglect.
1. Introduction
2. Case Reports
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
References
Also Check: What Does Stage 4 Skin Cancer Look Like
How Dermatologists Diagnose Basal Cell Carcinoma
When you see a board-certified dermatologist, your dermatologist will:
-
Examine your skin carefully
-
Ask questions about your health, medications, and symptoms
If your dermatologist finds a spot on your skin that could be any type of skin cancer, your dermatologist will first numb the area and then remove all of it. This can be done during an office visit and is called a skin biopsy. This is a simple procedure, which a dermatologist can quickly, safely, and easily perform.
Having a skin biopsy is the only way to know for sure whether you have any type of skin cancer. After your dermatologist removes the spot, a doctor, such as your dermatologist or a dermatopathologist, will examine it under a high-powered microscope. The doctor is looking for cancer cells.
If the doctor sees cancerous basal cells, the diagnosis is BCC.
After the doctor examines the removed skin under a microscope, the doctor writes a report. Called a biopsy report or a pathology report, this document explains in medical terms what was seen under the microscope.
If the diagnosis is any type of skin cancer, the information in this report will tell your dermatologist the key facts needed to treat the cancer, including:
-
The type of BCC you have
-
How deeply the cancer has grown
Your dermatologist will carefully consider your health and the findings in the report before choosing how to treat the cancer.