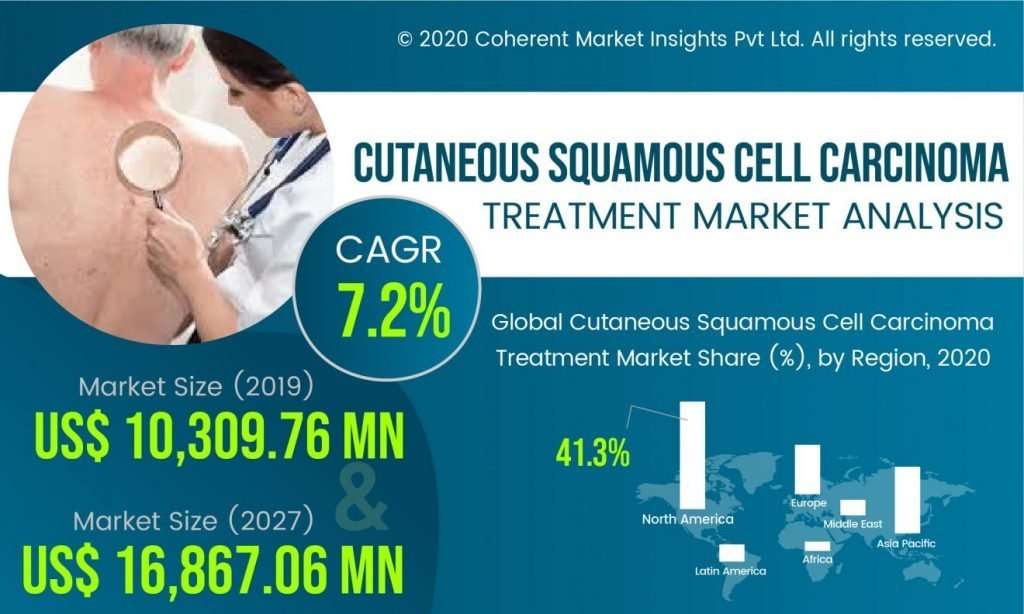
Skin Color And Being Exposed To Sunlight Can Increase The Risk Of Basal Cell Carcinoma And Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin
Anything that increases your chance of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer; not having risk factors doesnt mean that you will not get cancer. Talk with your doctor if you think you may be at risk.
Risk factors for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin include the following:
- Being exposed to natural sunlight or artificial sunlight over long periods of time.
- Having a fair complexion, which includes the following:
- Fair skin that freckles and burns easily, does not tan, or tans poorly.
- Blue, green, or other light-colored eyes.
- Red or blond hair.
Although having a fair complexion is a risk factor for skin cancer, people of all skin colors can get skin cancer.
Older age is the main risk factor for most cancers. The chance of getting cancer increases as you get older.
Treating Advanced Squamous Cell Cancers
Lymph node dissection:Removing regional lymph nodes might be recommended for some squamous cell cancers that are very large or have grown deeply into the skin, as well as if the lymph nodes feel enlarged and/or hard. The removed lymph nodes are looked at under a microscope to see if they contain cancer cells. Sometimes, radiation therapy might be recommended after surgery.
Immunotherapy: For advanced squamous cell cancers that cant be cured with surgery or radiation therapy, one option might be using an immunotherapy drug such as cemiplimab or pembrolizumab . However, these drugs havent been studied in people with weakened immune systems, such as people who take medicines for autoimmune diseases or who have had an organ transplant, so the balance between benefits and risks for these people isnt clear.
Systemic chemotherapy and/or targeted therapy:Chemotherapy and targeted therapy drugs might be other options for patients with squamous cell cancer that has spread to lymph nodes or distant organs. These types of treatment might be combined or used separately.
When Your Cancer Comes Back
Finishing your treatment can come as a huge relief, especially if your doctor tells you youre in remission. Yet your cancer can come back. This is called a recurrence.
See your doctor for regular follow-up visits to catch any recurrence early, when its most treatable. The doctor who treated your cancer will let you know how often to get check-ups. You may see your doctor every 3 months for the first year, and then less often.
Read Also: How Basal Cell Carcinoma Is Treated
What Are The Risk Factors For Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Oral Cavity
The risk factors for Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Oral Cavity include:
- Smoking and chewing of tobacco are strong risk factors for this type of Oral Cavity Cancer
- Radiation therapy in the face or mouth region
- Arsenic exposure
- Coal tar exposure
- Individuals with weak immune system, which could be due to cancer treatment, AIDS, or those on immunosuppressant drugs after receiving an organ transplant
- Caucasians are more vulnerable compared to other dark-skinned individuals
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
Different Types Of Cancer Start In The Skin
Skin cancer may form in basal cells or squamous cells. Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the most common types of skin cancer. They are also called nonmelanoma skin cancer. Actinic keratosis is a skin condition that sometimes becomes squamous cell carcinoma.
Melanoma is less common than basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma. It is more likely to invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body.
This summary is about basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, and actinic keratosis. See the following PDQ summaries for information on melanoma and other kinds of cancer that affect the skin:
Recommended Reading: Can I Die From Skin Cancer
How Do Dermatologists Diagnose Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin
Because this cancer begins on the skin, its possible to find it early when its highly treatable.
When you see a board-certified dermatologist, your dermatologist will examine your skin carefully.
If your dermatologist finds a spot on your skin that could be any type of skin cancer, your dermatologist will first numb the area and then remove all of it. This can be done during an office visit and is called a skin biopsy. This is a simple procedure, which a dermatologist can quickly, safely, and easily perform.
Having a skin biopsy is the only way to know for sure whether you have skin cancer.
What your dermatologist removes will be examined under a high-powered microscope. Your dermatologist or a doctor who has in-depth experience diagnosing skin growths, such as a dermatopathologist, is best qualified to examine the removed tissue under a microscope.
After examining the removed tissue, the doctor writes a biopsy report. Also called a pathology report, this report explains what was seen under the microscope, including whether any skin cancer cells were seen.
If you have squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, the report will contain the following information when possible:
-
Type of SCC
-
Whether the cancer has any features that make it aggressive
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Prevention
Skin cancer prevention always starts with sun protection. No, you cant undo the damage thats been done to your skin cells. But its never too late to start applying sunscreen and wearing protective gear for your time in the sun. Apply sunscreen every day. Make sunscreen application part of your morning routine. Then youre protecting yourself from the rays throughout the day, even if the only sun exposure you plan to get is through a window.If youre a parent, start instilling good sun protection practices for your kids at an early age. Make sun protection a habit in your home. Just like you teach your kids to grab a jacket if its cold, teach them to grab a hat and apply their sunscreen when theyre in the sun. Yes, we want our kids to be outdoors, but we want them to be safe while theyre out.Unfortunately, squamous cell carcinoma prevention isnt completely in our control. There are other health factors that play a role in the spread of this disease. However, with early detection, sun protection, and a skin care specialist to walk you through treatment, we have a high chance of curing it.
Read Also: How Long For Squamous Cell Carcinoma To Spread
Targeted Therapy Or Immunotherapy For Advanced Basal Cell Cancers
In rare cases where basal cell cancer spreads to other parts of the body or cant be cured with surgery or radiation therapy, a targeted drug such as vismodegib or sonidegib can often shrink or slow its growth.
If these drugs are no longer working , the immunotherapy drug cemiplimab can sometimes be helpful.;
What Are The Different Types Of Skin Cancer
Your skin has multiple layers. The outer, protective layer of the skin is known as the epidermis. The epidermis is made up of squamous cells, basal cells, and melanocytes. These cells are constantly shedding to make way for fresh, new skin cells.
However, when certain genetic changes occur in the DNA of any of these cells, skin cancer can occur. The main types of skin cancer are squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, and malignant melanoma.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Risk Factors Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
What Are The Treatments For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Your doctor will help you to decide on the best type of treatment. Factors in the decision include your overall health and age, the location of the cancer, and how invasive the cancer is.
Treatment options include:
- Scratching off with a curette, an instrument that may end in a ring or a spoon, and then burning with a special electric needle. This method is called electrodessication and curettage.
- Surgical removal:
- Mohs surgery: This is a specialized technique. The doctor first removes the visible cancer and then begins cutting around the edges. The tissues are examined during the surgery until no more cancer cells are found in tissues around the wound. If necessary, a skin graft or flap might be applied to help the wound heal.
- Excisional surgery: The growth and a bit of surrounding skin is removed with a scalpel.
If you have some type of advanced or very invasive SCC, you might find that it returns or metastasizes . There are several medications which have been approved to treat locally advanced cancers that cannot be simply treated or those that have spread to other areas of the body.
Causes Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
SCC is caused by mutations or changes in DNA in the squamous cells in the skin. These mutations cause squamous cells to grow uncontrollably and live longer.
Changes in DNA in squamous cells can be triggered by ultraviolet radiation, such as from exposure to direct sunlight or from a procedure to darken the skin with UV light .
Also Check: What Does Advanced Skin Cancer Look Like
Factors That Could Affect Your Prognosis
Certain aspects of your health or cancer could affect your outlook. For example, people who have a weakened immune system from a disease like HIV or a medication they take tend to have a less positive outlook.
The location of the tumor also matters. Cancers on the face, scalp, fingers, and toes are more likely to spread and return than those on other parts of the body. SCC that starts in an open wound is also more likely to spread.
Larger tumors or ones that have grown deep in the skin have a higher risk of growing or returning. If a cancer does recur after treatment, the prognosis is less positive than it was the first time around.
Ask your doctor if you have any risk factors that can be managed or controlled. You may need more aggressive treatment, or to be monitored more closely for recurrence.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stages
There are certain features that are considered to make the cancer at higher risk for spreading or recurrence, and these may also be used to stage squamous cell carcinomas. These include:
- Greater than 2 mm in thickness
- Invasion into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin
- Invasion into the tiny nerves in the skin
- Location on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip
After the TNM components and risk factors have been established, the cancer is assigned to one of the five squamous cell carcinoma stages, which are labeled 0 to 4. The characteristics and stages of squamous cell cancer are:
Stage 0: Also called carcinoma in situ, cancer discovered in this stage is only present in the epidermis and has not spread deeper to the dermis.
Stage;1 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer is less than 2 centimeters, about 4/5 of an inch across, has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs, and has one or fewer high-risk features.
Stage 2;squamous;cell carcinoma: The cancer is larger than 2 centimeters across, and has not spread to nearby organs or lymph nodes, or a tumor of any size with 2 or more high risk features.
Stage 3;squamous;cell carcinoma: The cancer has spread into facial bones or 1 nearby lymph node, but not to other organs.
Stage 4;squamous;cell carcinoma: The cancer can be any size and has spread to 1 or more lymph nodes which are larger than 3 cm and may have spread to bones or other organs in the body.
Read Also: Are There Stages Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
What Is Squamous Cell Cancer
Squamous cell cancer , also known as squamous cell carcinoma, is a type of skin cancer that typically begins in the squamous cells.
Squamous cells are the thin, flat cells that make up the epidermis, or the outermost layer of the skin.
SCC is caused by changes in the DNA of these cells, which cause them to multiply uncontrollably.
According to the Skin Cancer Foundation, cutaneous SCC is the second most common form of skin cancer. Approximately 700,000 people in the United States are diagnosed with this type of skin cancer each year.
People with SCC often develop scaly, red patches, open sores, or warts on their skin. These abnormal growths can develop anywhere, but theyre most often found in areas that receive the most exposure to ultraviolet radiation, either from sunlight or from tanning beds or lamps.
The condition usually isnt life threatening, but it can become dangerous if it goes untreated. When treatment isnt received promptly, the growths can increase in size and spread to other parts of your body, causing serious complications.
What Is The Outlook For Someone Who Has Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin
When found early, this cancer is highly treatable. Left untreated, however, SCC can spread deep into the skin and travel to other parts of the body, making treatment difficult.
While treatment can remove the cancer, its important to know that this cancer can return. You also have a greater risk of developing another skin cancer.
Thats why self-care becomes so important after treatment for SCC of the skin. Youll find the self-care that dermatologists recommend at, Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: Self-care.
ImagesGetty Images
ReferencesAlam M, Armstrong A, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J Am Acad Dermatol 2018;78:560-78.
Anadolu-Brasie R, Patel AR, et al., Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. In: Nouri K, et al. Skin Cancer. McGraw Hill Medical, China, 2008: 86-114.
Marrazzo G, Zitelli JA, et al. Clinical outcomes in high-risk squamous cell carcinoma patients treated with Mohs micrographic surgery alone. J Am Acad Dermatol 2019;80:633-8.
Que SKT, Zwald FO, et al. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: Management of advanced and high-stage tumors. J Am Acad Dermatol 2018;78:249-61.
Ribero S, Stucci LS, et al. Drug therapy of advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: Is there any evidence? Curr Opin Oncol. 2017;29:129-35.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves cemiplimab-rwlc for metastatic or locally advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. New release issued 9/28/2018. Last accessed 1/13/2020.
Read Also: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Metastasize
What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common form of skin cancer. Its usually found on areas of the body damaged by UV rays from the sun or tanning beds. Sun-exposed skin includes the head, neck, chest, upper back, ears, lips, arms, legs, and hands.
SCC is a fairly slow-growing skin cancer. Unlike other types of skin cancer, it can spread to the tissues, bones, and nearby lymph nodes, where it may become hard to treat. When caught early, its easy to treat.
SCC can show up as:
- A dome-shaped bump that looks like a wart
- A red, scaly patch of skin thats rough and crusty and bleeds easily
- An open sore that doesnt heal completely
- A growth with raised edges and a lower area in the middle that might bleed or itch
How Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Oral Cavity Be Prevented
A few methods to prevent Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Oral Cavity include:
- Maintain proper oral hygiene
- Avoid chewing tobacco and smoking
- Avoid prolonged and chronic exposure to the sun
Regular medical screening at periodic intervals with blood tests, scans, and physical examinations, are mandatory, due to its high metastasizing potential and possibility of recurrence. Often several years of active vigilance is necessary.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know If You Have Basal Cell Carcinoma
What Causes Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Repeated exposure to ultraviolet light, either from the sun or from tanning beds, is the main cause of SCC. Indoor tanning is linked to about 168,000 cases of SCC in the US each year.
People with light skin, light hair , and light eyes have a higher risk of skin cancer in general, as well as SCCs. However, most of the skin cancers that develop in African Americans are SCCs.
Other risk factors include:
- Having an impaired immune system, including:
- Cancers of the blood or bone marrow.
- Chronic infections like HIV.
- Taking immunosuppressive medications, including chemotherapy or some biologic medications.
How Fast Does Oral Cancer Spread
About one half of people with oral cancer will live more than 5 years after they are diagnosed and treated.
If the cancer is found early, before it has spread to other tissues, the cure rate is nearly 90%.
More than half of oral cancers have spread when the cancer is detected.
Most have spread to the throat or neck.17 Oct 2017
You May Like: What Are The Forms Of Skin Cancer