Treating Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Most of squamous cell carcinomas can be cured if they are treated early. Once squamous cell carcinoma has spread beyond the skin, though, less than half of people live five years, even with aggressive treatment.
There are many ways to treat squamous cell carcinoma that has not spread. These include:
- cutting away the cancer and a small amount of healthy tissue around it. If a large area of skin is removed, a skin graft may be necessary.
- scraping away the cancer with a surgical tool. An electric probe is used to kill any cancerous cells left behind.
- freezing cancer cells with liquid nitrogen. This treatment is usually used only for very small tumors or for a patch of skin that looks abnormal but isnât yet cancerous.
- destroying the tumor with radiation.
- shaving away the cancer, one thin layer at a time. Each layer is examined under the microscope as it is removed. This technique helps the doctor preserve as much healthy skin as possible.
- applying drugs directly to the skin or injecting them into the tumor
- using a narrow laser beam to destroy the cancer.
The treatment that is best for you depends on the size and location of the cancer, whether it has returned after previous treatment, your age, and your general health.
Once your treatment is finished, itâs important to have regular follow-up skin exams. Your doctor may want to see you every three months for the first year, for example, and then less often after that.
You May Like: What Type Of Skin Cancer Is Deadly
Carcinoma In Situ Vs Precancerous Cells Vs Dysplasia
There are many terms describing the spectrum of normal cells and invasive cancer cells. One of these is dysplasia. Dysplasia can run the spectrum from mild dysplasia in which the cells are barely abnormal appearing, to carcinoma in situ, which some pathologists describe as severe dysplasia involving the full thickness of the epithelium. The term precancerous cells may also be used to describe cells on this continuum between normal and cancer cells.
These terms are also used in different ways depending on the sample analyzed. For example, cells visualized on a pap smear may show dysplasia , but since the cells are “loose,” nothing can be said about whether carcinoma in situ is present or not. With cervical dysplasia, a biopsy is required before the diagnosis of CIS is made. A biopsy sample provides a view of the cells as they occur in relation to the basement membrane and other cells, and is needed to understand if abnormal cells seen on a pap smear are concerning.
What Are The Risk Factors For Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ Of Anus
The following factors increase the risk of Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ of Anus:
- Infection with human papilloma virus subtypes 16, 18, 31, 33, and 45,
- High-risk sexual behavior sexual promiscuity
- Weakened immune system as a result of HIV infection or AIDS, or due to administration of immunosuppressants
- Smoking
- Lack of proper hygiene
- Longstanding ulcerative lichen planus
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
You May Like: Skin Cancer Prognosis
What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ Of Anus
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ of Anus is a malignant condition affecting the skin or mucosal membranes of the anus. The carcinoma may be present as a well-defined red patch it is frequently solitary or they may be many in numbers
- The lesion may itch, ulcerate, or even bleed. The condition may be diagnosed definitively through a tissue biopsy
- Middle-aged and elderly adults are at risk for the condition. The cause of Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ of Anus is unknown, but it is influenced by factors such as HPV infection, poor immunity, high-risk sexual practices, etc.
- Any combination of radiation therapy and invasive procedures are used to treat Anal Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ. The prognosis depends upon early diagnosis and treatment that is administered
How Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Oral Cavity Be Prevented
A few methods to prevent Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Oral Cavity include:
- Maintain proper oral hygiene
- Avoid chewing tobacco and smoking
- Avoid prolonged and chronic exposure to the sun
Regular medical screening at periodic intervals with blood tests, scans, and physical examinations, are mandatory, due to its high metastasizing potential and possibility of recurrence. Often several years of active vigilance is necessary.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Spread
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stages
There are certain features that are considered to make the cancer at higher risk for spreading or recurrence, and these may also be used to stage squamous cell carcinomas. These include:
- Greater than 2 mm in thickness
- Invasion into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin
- Invasion into the tiny nerves in the skin
- Location on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip
After the TNM components and risk factors have been established, the cancer is assigned to one of the five squamous cell carcinoma stages, which are labeled 0 to 4. The characteristics and stages of squamous cell cancer are:
Stage 0: Also called carcinoma in situ, cancer discovered in this stage is only present in the epidermis and has not spread deeper to the dermis.
Stage 1 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer is less than 2 centimeters, about 4/5 of an inch across, has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs, and has one or fewer high-risk features.
Stage 2 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer is larger than 2 centimeters across, and has not spread to nearby organs or lymph nodes, or a tumor of any size with 2 or more high risk features.
Stage 3 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer has spread into facial bones or 1 nearby lymph node, but not to other organs.
Stage 4 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer can be any size and has spread to 1 or more lymph nodes which are larger than 3 cm and may have spread to bones or other organs in the body.
Electronic Skin Surface Brachytherapy
Some skin cancers that do not require very deep radiation may be treated with a new form of radiation therapy applied directly to the skin, called electronic skin surface brachytherapy .
In ESSB, we apply smooth, round disks to the skin these disks are attached to a radiation therapy machine. They are left in place for just a few minutes while the radiation is delivered, allowing the tumor to be treated. The approach spares underlying healthy skin from the effects of the radiation.
Also Check: Whats Cancer Look Like
What Are The Causes Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ Of Penis
- The exact cause of development of Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ of Penis is not completely known in a majority of cases
- In case HPV infection is associated with SCC In Situ of Penis, it is caused by alteration in the DNA by the human papilloma virus that results in uncontrolled cell proliferation
- Other factors that may contribute to the condition include weak immune system, sexual promiscuity, poor hygiene, smoking, etc.
Looking After Your Skin After Treatment
After treatment, you may need follow-up appointments with your dermatologist or GP to see if you need any further treatment.
If you had surgery, you may need to have any stitches removed at your GP surgery a few weeks later.
After treatment:
- see a GP if an existing patch starts to bleed, change in appearance or develops a lump do not wait for your follow-up appointment
- see a GP if you notice any worrying new patches on your skin
- make sure you protect your skin from the sun wear protective clothing and use a sunscreen with a high sun protection factor of at least 30
Page last reviewed: 21 May 2019 Next review due: 21 May 2022
| Other names | Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma , epidermoid carcinoma, squamous cell epithelioma |
|---|---|
| SCC of the skin tends to arise from pre-malignant lesions, actinic keratoses surface is usually scaly and often ulcerates . | |
| 51,900 |
Squamous-cell skin cancer, also known as cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma , is one of the main types of skin cancer along with basal cell cancer, and melanoma. It usually presents as a hard lump with a scaly top but can also form an ulcer. Onset is often over months. Squamous-cell skin cancer is more likely to spread to distant areas than basal cell cancer. When confined to the outermost layer of the skin, a precancerous or in situ form of cSCC is known as Bowenâs disease.
Read Also: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
How Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ Of Penis Treated
The treatment options for Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ of Penis may include:
- Surgery: Complete surgical excision can be curative
- Laser ablation: The use of laser to remove solid tumors or lesions
- Radiation therapy: The use of high-energy beams to kill cancer cells
- In some cases, a circumcision may be helpful
- Close monitor and follow-up reviews of the condition
How Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ Of Penis Be Prevented
Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ of Penis may be prevented by following some of these measures:
- Use of condoms, avoiding multiple sexual partners, etc. to avoid sexually-transmitted infections
- Undertake immediate treatment of ulcers in the genital region
- Avoidance of smoking
- Availing vaccinations against the human papilloma virus
- Maintaining personal hygiene
You May Like: Signs Of Stage 4 Cancer
Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ
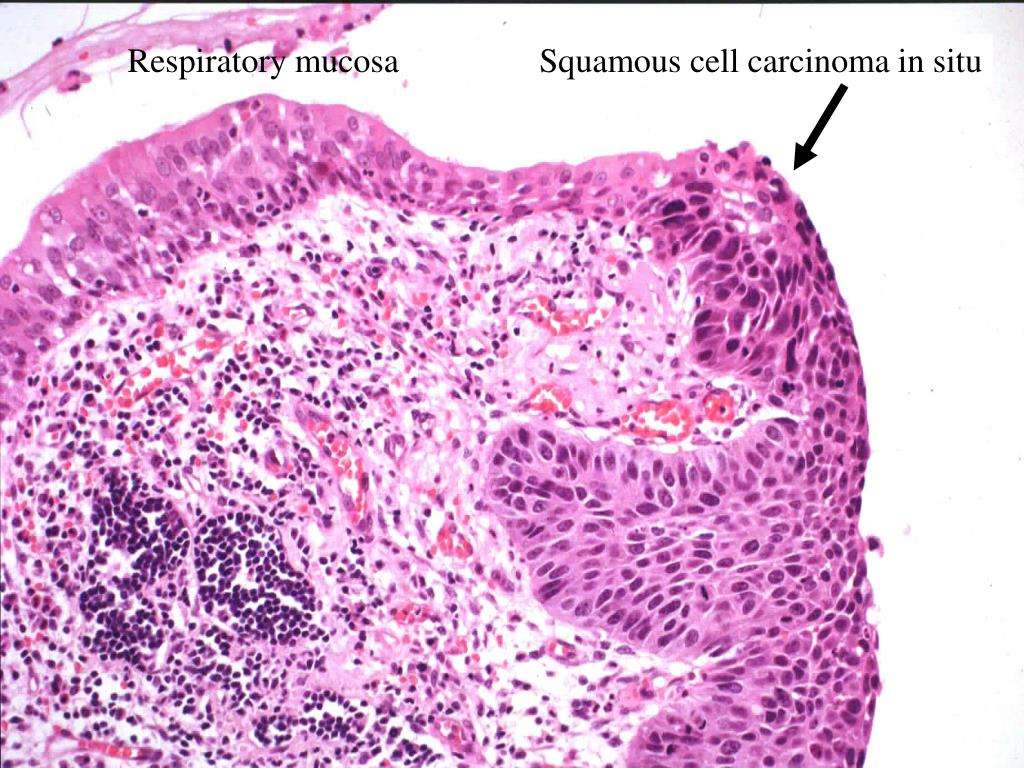
Early forms of squamous cell carcinoma, also known as Bowen disease, are classified as in situ, which means in place in Latin. This simply means that the cancer cells havent yet spread beyond the epidermis. When the carcinoma spreads deeper into the skin, into the lymph nodes or organs, it is considered to be metastasized.
Typically, Bowen disease will first appear as a red, scaly plaque of skin, often larger than 1/2 inch across. It can also sometimes appear as a hard domed bump. Both varieties typically feel rough and crusty and can bleed when scraped. Cancer usually shows up on areas of the skin that are exposed to the sun, such as the face, ears, lips, arms, legs, and tops of hands, but it can also more rarely appear on areas not exposed to the sun including the lower lip and genitals. This cancer usually develops slowly but can spread to the lymph nodes and other organs if left untreated. If caught early though, it is highly treatable.
A doctor will diagnose squamous cell carcinoma with a biopsy. Treatment of the cancer will then vary depending on location, size, severity, how far it has spread and the health of the patient.
Diagnosing Squamous Cell Carcinoma
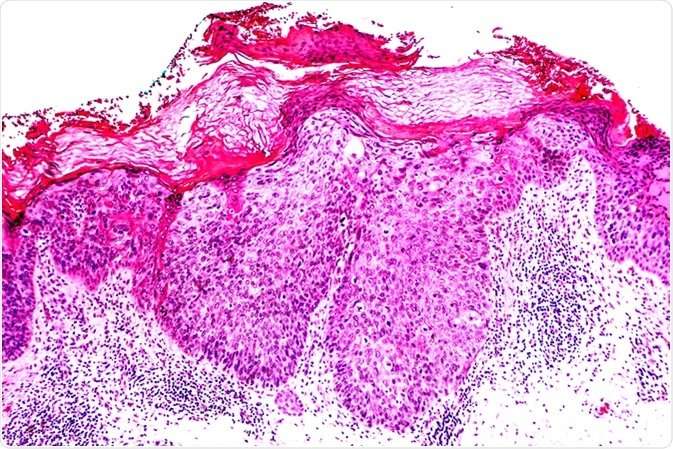
The main way to diagnose squamous cell carcinoma is with a biopsy. This involves having a small piece of tissue removed from the suspicious area and examined in a laboratory.
In the laboratory, a pathologist will examine the tissue under a microscope to determine if it is a skin cancer. He or she will also stage the cancer by the number of abnormal cells, their thickness, and the depth of penetration into the skin. The higher the stage of the tumor, the greater the chance it could spread to other parts of the body.
Squamous cell carcinoma on sun-exposed areas of skin usually does not spread. However, squamous cell carcinoma of the lip, vulva, and penis are more likely to spread. Contact your doctor about any sore in these areas that does not go away after several weeks.
Also Check: What Does Stage 3 Melanoma Look Like
Treatment Of Squamous Cell Vulvar Cancer
The stage of a vulvar cancer is the most important factor in choosing treatment. Other factors that affect this decision include the exact location of the cancer on the vulva, the type of vulvar cancer, your age, your preferences, and your overall health.
Because vulvar cancer is rare, it’s hard to study it well. Most experts agree that treatment in a clinical trial should be considered. This way women can get the best treatment available now and may also get the treatments that are thought to be even better.
Causes Of Bowen’s Disease
Bowen’s disease usually affects older people in their 60s and 70s.
The exact cause is unclear, but it’s been closely linked with:
- long-term exposure to the sun or use of sunbeds especially in people with fair skin
- having a weak immune system for example, it’s more common in people taking medicine to suppress their immune system after an organ transplant, or those with AIDS
- previously having radiotherapy treatment
- the human papillomavirus a common virus that often affects the genital area and can cause genital warts
Bowen’s disease does not run in families and it’s not infectious.
Also Check: How Fast Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
Treatment Of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ With Curettage Followed By Topical Imiquimod 5% Cream
- Dermatologic Surgery
You’ve saved your first item
You can find your saved items on your dashboard, in the “saved” tab.
You’ve recommended your first item
Your recommendations help us improve our content suggestions for you and other PracticeUpdate members.
You’ve subscribed to your first topic alert
What does that mean?
Treatments For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The following are treatment options for squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. Your healthcare team will suggest treatments based on the . They will work with you to develop a treatment plan.
SCC is most often treated with local therapy. This means that only the cancer on the skin and the area around it are treated.
But if SCC has spread to other parts of the body, systemic therapy may be used. Systemic therapy travels through the bloodstream to reach and destroy cancer cells all over the body.
You May Like: Well Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Prognosis
Bowens Disease Or Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ
Squamous cell carcinoma in situ is the earliest recognizable form of squamous cell skin cancer This condition is also referred to as stage 0 squamous cell carcinoma, on the scale from 0 to IV. There are typically no visible symptoms. When symptoms are present, a scaly condition may be present, and the skin may seem to catch on clothing. The presence of abnormal cells may be detected by a pathologist. Although the cancerous cells have not yet invaded the deeper layers of the skin and the condition is not considered a serious condition, treatment at this early stage is generally recommended to help prevent this condition from developing into squamous cell carcinoma. In some cases, monitoring may be prescribed.
Donât Miss: What Happens If I Have Melanoma
How Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ Of Penis Diagnosed
Some of the tests that may help in diagnosing Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ of Penis include:
- Complete physical examination with detailed medical history evaluation
- Examination by a dermatologist using a dermoscopy, a special device to examine the skin
- Skin or tissue biopsy: A skin or tissue biopsy is performed and sent to a laboratory for a pathological examination, who examines the biopsy under a microscope. After putting together clinical findings, special studies on tissues and with microscope findings, the pathologist arrives at a definitive diagnosis. A biopsy is performed to rule out other similar conditions too
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
Read Also: Prognosis For Skin Cancer
What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common form of skin cancer. Its usually found on areas of the body damaged by UV rays from the sun or tanning beds. Sun-exposed skin includes the head, neck, chest, upper back, ears, lips, arms, legs, and hands.
SCC is a fairly slow-growing skin cancer. Unlike other types of skin cancer, it can spread to the tissues, bones, and nearby lymph nodes, where it may become hard to treat. When caught early, its easy to treat.
SCC can show up as:
- A dome-shaped bump that looks like a wart
- A red, scaly patch of skin thats rough and crusty and bleeds easily
- An open sore that doesnt heal completely
- A growth with raised edges and a lower area in the middle that might bleed or itch
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treatment
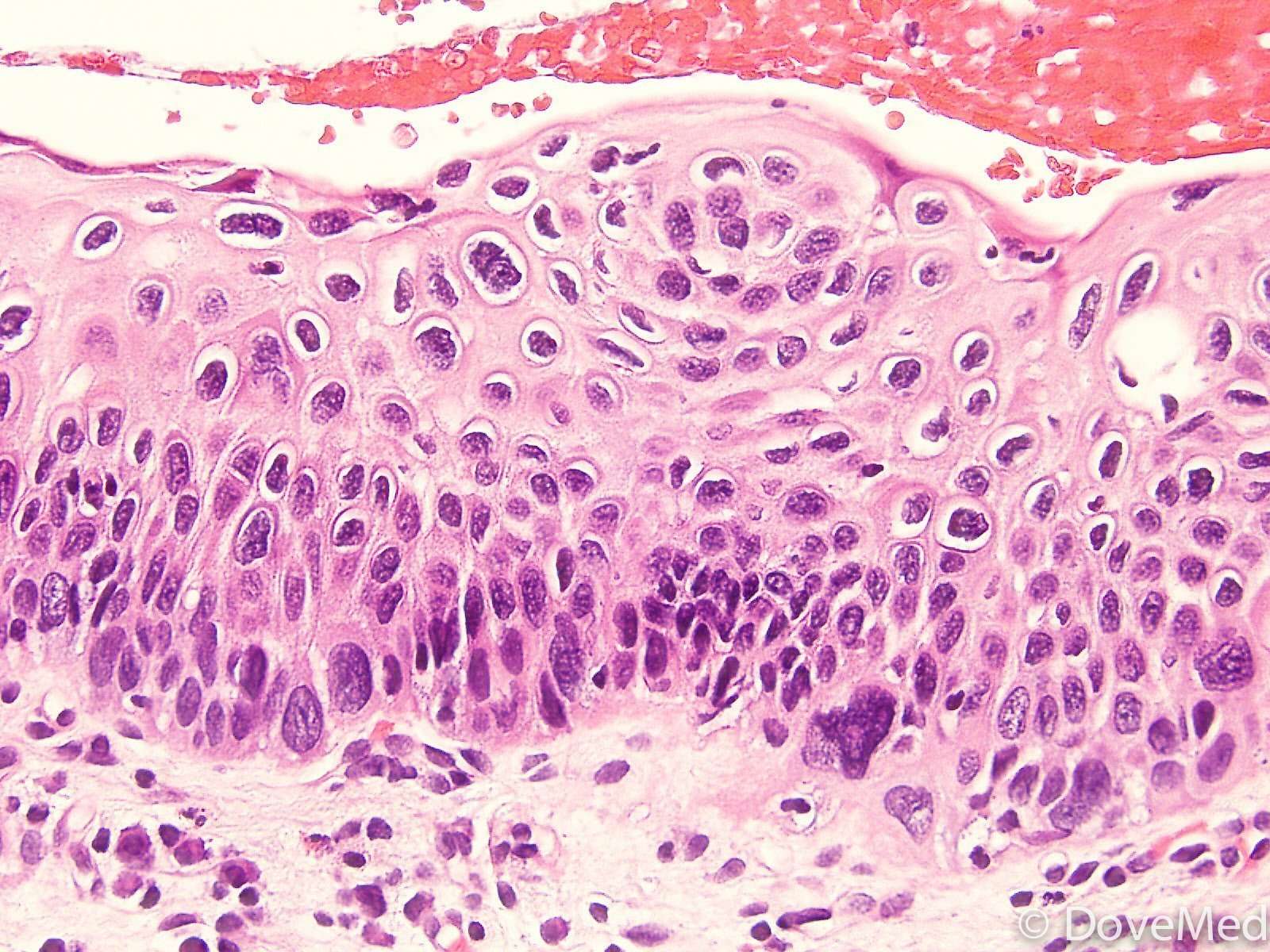
Squamous cell carcinomas detected at an early stage and removed promptly are almost always curable and cause minimal damage. However, left untreated, they may grow to the point of being very difficult to treat.
A small percentage may even metastasize to distant tissues and organs. Your doctor can help you determine if a particular SCC is at increased risk for metastasis and may need treatment beyond simple excision.
Fortunately, there are several effective ways to treat squamous cell carcinoma. The choice of treatment is based on the type, size, location, and depth of penetration of the tumor, as well as the patients age and general health. Squamous cell carcinoma treatment can almost always be performed on an outpatient basis.
Also Check: What Is Stage 2 Squamous Cell Carcinoma