Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma
Papillary RCC is the second most common form of kidney cancer and makes up about 15% of all cases. Papillary RCC is a non-clear cell renal carcinoma which is different from the more common clear cell type. There are two main types of papillary RCC: type 1 and type 2. Type 1 tumors tend to be slower growing, and type 2 tumors tend to be faster growing and are more likely to spread. Papillary RCC can be The passing of genetic information from parent to child through parental genes.hereditaryor non-hereditary.
Genetic Risk Assessment For Hereditary Renal Cell Carcinoma: Clinical Consensus Statement
Department of Urology, State University of New York (SUNY, Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, New York
Corresponding Authors: Gennady Bratslavsky, MD, Department of Urology, SUNY Upstate Medical University, 750 E. Adams Street, Syracuse, NY 13210 ; Brian Shuch, MD, Department of Urology, University of California, Los Angeles, 300 Stein Plaza Drive, 3rd Floor, Los Angeles, CA 90095 .
Department of Urology, State University of New York (SUNY, Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, New York
Urologic Oncology Branch, Center for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, Maryland
Division of Human Genetics and Translational Medicine, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Abramson Cancer Center, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Abramson Cancer Center, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Division of Hematology/Oncology, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Department of Urology, University of California Los Angeles, Los Angeles, California
Department of Urology, State University of New York (SUNY, Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, New York
Department of Urology, State University of New York (SUNY, Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, New York
Von Hippel Lindau Disease
Patients with this autosomal dominant cancer susceptibility syndrome can present with a wide spectrum of hemangioblastomas of the brain, spine and retina, pancreatic and renal cysts and neuroendocrine tumors, endolympatic sac tumors and pheochromocytomas. Some but not all patients develop clear cell renal cancer presenting as bilateral and sometimes hundreds of lesions within the kidney.
The first patients with this syndrome were described in 1860 and it recognized as a familial by Von Hippel some thirty years later; Lindau recognized that the retinal lesions were part of a larger heritable syndrome that affected the central nervous system., In 1993, the gene responsible for these families and von Hippel-Lindau disease , VHL, was found through the study of multiple case families to be located at 3p2526.
In vHL disease, there is significant variation in phenotype, which had been observed prior to gene identification. Subsequent to the identification of the vHL gene, a strong genotype-phenotype correlation was seen with mutational type predictive of disease. Patients with type 1 mutations have a decreased incidence of pheochromocytoma as compared to those with type 2 mutations . Families with type 2 mutations have either a high or low risk of ccRCC ; type 2C families only develop pheochromocytoma. Type 2A disease is associated with the Black Forest founder mutation originating from southwestern Germany, which is commonly found in the Pennsylvania Dutch population.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
Rare Non Clear Cell Rcc Subtypes
- Collecting duct carcinoma: A very rare and aggressive type of RCC. At initial diagnosis, it is usually metastatic and has spread to other parts of the body. It is more common in younger people.
- Translocation RCC: A rare type of kidney cancer. This cancer can be identified by seeing mutations, or changes, in a gene called TFE3. This type affects children and young adults but can also affect older adults.
- Renal medullary carcinoma : This is a very rare type of kidney cancer. It affects young people who carry the sickle cell trait or have sickle cell disease. These cancers are usually metastaticspread to other parts of the bodyat diagnosis.
- Unclassified RCC: Less than 1% of RCCs are unclassified. They are very rare and do not easily fit into one of the more common subtypes. They tend to be more aggressive.
Natural History Of Renal Cell Carcinoma
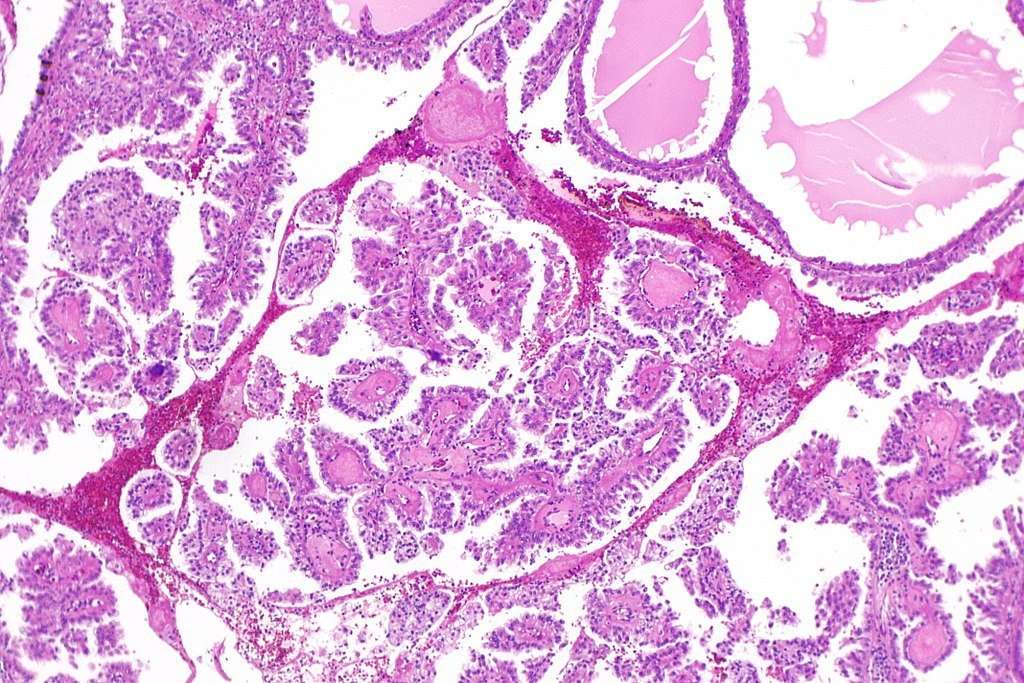
The natural history of each RCC syndrome is distinct and influenced by several factors, including histologic features and underlying genetic alterations. Although it is useful to follow the predominant reported natural history of each syndrome, each affected individual will need to be evaluated and monitored for occasional individual variations. The individual prognosis will depend upon the characteristics of the renal tumor at the time of detection and intervention, and will differ for each syndrome . Prognostic determinants at diagnosis include the stage of the RCC, whether the tumor is confined to the kidney, primary tumor size, Fuhrman nuclear grade, and multifocality.
Read Also: Can Skin Cancer Be Cured With Cream
Pten Hamartoma Tumor Syndrome
PTEN is associated with an increased risk of benign and malignant tumors of the thyroid, breast and endometrium caused by mutations in PTEN. Dermatological manifestations of Cowden syndrome are very common, seen in essentially all patients by their 30s, and include trichilemmomas, papillomatous papules, and acral and plantar keratoses. Clear cell renal cancer has been reported as a observed in patients with Cowden syndrome, with recent estimates suggesting a standardized incidence ratio of 30.6 . One study has shown the loss of the wild type PTEN allele in a renal cancer from a Cowden syndrome patient. A study of sporadic renal cancers and cell lines have shown that mutations in PTEN are present, particularly in late stage and clear cell renal cancers.
Questions To Ask The Health Care Team
If you are concerned about your risk for kidney cancer, talk with your health care team. It can be helpful to bring someone along to your appointments to take notes. Consider asking your health care team;the following questions:
-
What is my risk of developing kidney cancer?
-
What can I do to reduce my risk of cancer?
-
What are my options for cancer screening and prevention?
If you are concerned about your family history and think your family may have HPRC, consider asking the following questions:
-
Does my family history increase my risk of developing kidney cancer?
-
Should I meet with a genetic counselor?
-
Should I consider genetic testing?
Don’t Miss: What Is Melanoma In The Brain
When To Get Medical Advice
See a GP if you have symptoms of kidney cancer.
Although its unlikely you have cancer, its important to get your symptoms checked out.
The GP will ask about your symptoms and may test a sample of your urine to see if it contains blood or an infection.
If necessary, they may refer you to a hospital specialist for further tests to find out what the problem is.
Prevalence And Founder Effects
A novel pathogenic variant was identified in exon 16 of the MET gene in two large hereditary papillary renal carcinoma families in North America. Affected members of the two families shared the same haplotype located within and immediately distal to the MET gene, suggesting a common ancestor . However, HPRC families with identical germlineMET pathogenic variants who do not share a common ancestral haplotype have also been reported.
You May Like: What Are The Types Of Skin Cancer
Family History Of Kidney Cancer
People with a strong family history of renal cell cancer have a higher chance of developing this cancer. This risk is highest for people who have a brother or sister with the cancer. Its not clear whether this is due to shared genes, something that both people were exposed to in the environment, or both.
Request An Appointment At Moffitt Cancer Center
Please call for support from a Moffitt representative. New Patients and Healthcare Professionals can submit an online form by selecting the appropriate buttonbelow. Existing patients can call . for a current list of insurances accepted at Moffitt.
NEW PATIENTS To request a new patient appointment, please fill out the online form or call 1-888-663-3488.
REFERRING PHYSICIANS Providers and medical staff can refer patients by submitting our online referral form.
Moffit now offers Virtual Visits for patients. If you are eligible for a virtual appointment, our scheduling team will discuss this option further with you.
Moffitt Cancer Center is committed to the health and safety of our patients and their families. For more information on how were protecting our new and existing patients, visit our COVID-19 Info Hub
Recommended Reading: How Fast Does Subungual Melanoma Grow
Inherited Conditions That Increase The Risk Of Kidney Cancer
Von;Hippel-Lindau syndrome
This is an inherited cancer syndrome. The Von;Hippel-Lindau gene runs through affected families.
People who carry the gene have an increased risk of developing several quite rare cancers in the brain, spine, pancreas, eyes and inner ear.;
Tuberous sclerosis
This is another condition caused by a faulty gene. People with tuberous sclerosis have an increased risk of kidney cysts and kidney cancer.
It can cause skin, brain and heart problems, as well as kidney disease.
Birt-Hogg-Dubé;syndrome
This inherited condition causes many non cancerous tumours to develop in the hair follicles of the skin. These usually develop on the face, neck and trunk. People who carry this gene have an increased risk of kidney cancer.
Looking For More Of An Introduction

If you would like more of an introduction, explore these related items. Please note that these links will take you to other sections on Cancer.Net:
-
ASCO Answers Fact Sheet:Read a 1-page fact sheet that offers an introduction to kidney cancer. This free fact sheet is available as a PDF, so it is easy to print.
Recommended Reading: How Common Is Renal Cell Carcinoma
Citation Doi And Article Data
Citation:DOI:Dr Yuranga WeerakkodyRevisions:see full revision historySystems:
- Familial renal cell cancer syndromes
- Familial renal cell carcinoma syndromes
- Hereditary renal cell cancer syndromes
- Hereditary renal cell carcinoma syndromes
Despite the vast majority of renal cancers being sporadic, there are a number of hereditary renal cancer syndromes:
Body Weight And Height
Being overweight or very overweight increases the risk of getting kidney cancer. This causes 24 out of every 100 kidney cancers . So around;a quarter of kidney cancers.
Overweight means that your body mass index is between 25 and 39.9 and obese means that your BMI is 30 or higher. Your BMI is worked out by using your height and weight.;
Being overweight causes changes in hormones in the body, particularly for women. It could be this change in the bodys hormone balance that increases the risk of kidney cancer.
Read Also: What Are The 4 Types Of Melanoma
Kidney Cancer Inherited Risk
Factors that increase risk
Factors that decrease risk
- Quitting cigarette smoking.;Many cases of kidney cancer are believed to be caused by cigarette smoking. Quitting smoking can reduce a person’s risk of kidney cancer greatly, and the risk continues to decrease each year a person has been smoke-free.
- Maintaining a healthy weight.;Obesity and high blood pressure are risk factors for kidney cancer. Eating a healthy diet that is high in fruits and vegetables and exercising can help lower a person’s blood pressure and weight, which reduces the overall chance of developing kidney cancer.
- Avoid chemical exposures.;Studies have shown that cadmium and organic solvents may increase a person’s risk for developing kidney cancer. Avoiding these substances may reduce a person’s overall risk. If a person works around hazardous chemicals, it is important to practice safety procedures to avoid accidental exposures.
Inherited kidney cancer clues
About 5-8 percent of cases of renal cell carcinoma, which is a type of kidney cancer, are due to an inherited gene change. Some clues of an inherited kidney cancer pattern are:
What Other Clinical Manifestations May Help Me To Diagnose Renal Cell Carcinoma
The majority of renal tumors are now discovered incidentally during an imaging procedure, and patients are asymptomatic. The classic presentation that included the triad of hematuria, flank pain and a palpable mass are seldom seen currently.
Past medical history and smoking history are important, as well as a work and environmental exposure history. Patients with suspected RCC should be examined carefully to document any evidence of metastatic or advanced disease. This includes a careful system review focusing on the skeletal, genitourinary and systemic systems.
In young patients with RCC, a family history is relevant, and any manifestations of the various inherited RCC syndromes should be determined.
Also Check: Is Melanoma The Same As Skin Cancer
What Are The Screening Options For Hprc
There are no specific screening guidelines for families suspected of having HPRC. Individuals in these families are encouraged to talk with their doctor about screening options for kidney cancer, including:
-
Computed tomography scan. A CT scan takes pictures of the inside of the body using x-rays taken from different angles. A computer combines these pictures into a detailed, 3-dimensional image that shows any abnormalities or tumors. A CT scan can be used to measure the tumors size. Sometimes, a special dye called a contrast medium is given before the scan to provide better detail on the image. This dye can be injected into a patients vein or given as a pill or liquid to swallow.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging . An MRI uses magnetic fields, not x-rays, to produce detailed images of the body. MRI can be used to measure the tumors size. A special dye called a contrast medium is given before the scan to create a clearer picture. This dye can be injected into a patients vein or given as a pill or liquid to swallow.
-
Ultrasound. An ultrasound uses sound waves to create a picture of the internal organs. However, an ultrasound may miss small lesions and is not a recommended screening strategy. As HPRC tumors may not have brisk enhancement, leading to confusion of cystic vs solid composition, an ultrasound ;may be useful as an additional test to confirm a lesion is solid.
Learn more about what to expect when having common tests, procedures, and scans.
Prognosis For Renal Cell Carcinoma
Five-year survival rates range from about 81% for the American Joint Commission on Cancer stage grouping I to 8% for stage grouping IV . Prognosis is poor for patients with metastatic or recurrent renal cell carcinoma because treatments are usually ineffective for cure, although they may be useful for palliation.
Dont Miss: What Is The Deadliest Type Of Skin Cancer
Don’t Miss: Can Melanoma Be Treated Successfully
Risk Factors For Kidney Cancer
A risk factor is anything that increases your chance of getting a disease such as cancer. Different cancers have different risk factors. Some risk factors, like smoking, can be changed. Others, like your age or family history, cant be changed.
But having a risk factor, or even several risk factors, does not mean that you will get the disease. And some people who get the disease may have few or no known risk factors. Even if a person with kidney cancer has a risk factor, it is often very hard to know how much that risk factor contributed to the cancer.
Scientists have found several risk factors that could make you more likely to develop kidney cancer.
What Are The Estimated Cancer Risks Associated With Hprc

The specific risk for type 1 papillary renal cell cancer in families with HPRC is extremely high, with some estimates showing the lifetime risk is nearly 100%. If kidney cancer is diagnosed, talk with your doctor about treatment options. Currently, surgery is the primary method of treating a localized tumor in people with HPRC when a tumor reaches greater than 3 cm in size. A drug called foretinib has shown evidence of being effective in a small study of patients with localized or metastatic HPRC but is not currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Other drugs in this area are also being studied in clinical trials for non-hereditary papillary kidney cancer.
You May Like: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Treatments For Renal Cell Carcinoma
There are five kinds of standard treatments for RCC. One or more may be used to treat your cancer.
Hereditary Leiomyomatosis And Renal Cell Carcinoma
NORD gratefully acknowledges Eamonn R. Maher, MD, FRCP, Department of Medical Genetics, University of Cambridge, UK for assistance in the preparation of this report.
Synonyms of Hereditary Leiomyomatosis and Renal Cell Carcinoma
- HLRCC
General Discussion
Summary
Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma, also known as HLRCC, is a rare genetic disorder characterized by smooth muscle growths on the skin and uterus and an increased risk of developing kidney cancer. Skin growths may appear as appear as small, firm bumps or tiny lumps and are not cancerous . Uterine leiomyomas, also known as uterine fibroids, may be numerous and are also benign, but can cause symptoms such as heavy menstrual periods or pelvic pressure or pain. Affected individuals are at an increased risk of developing kidney cancer, particularly a form known as type II papillary renal cell carcinoma. Kidney cancer associated with HLRCC is cancerous and can be aggressive and spread to other areas of the body. HLRCC is caused by mutations in the fumarate hydratase gene and is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern.
Introduction
Signs & Symptoms
In extremely rare cases, some affected women have developed uterine leiomyosarcomas, a malignant tumor that arises from the smooth muscle lining the walls of the uterus .
Causes
In rare cases, mutations in the FH gene have resulted in the development of other forms of tumor known as pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma which may be malignant.
Affected Populations
Recommended Reading: What Is The Deadliest Type Of Skin Cancer