What Do Actinic Keratoses And Bowens Disease Look Like
Lesions look like rough, red, dry patches of varying sizes. At first they can be hard to see, and are more easily felt, being rough, like sandpaper. They may grow up to a centimetre or two in diameter. Some are skin coloured, others are pink, red or brown. They can become raised, hard and warty, and may even develop a small horny outgrowth. The surrounding skin often looks sun-damaged blotchy, freckled and wrinkled
Treatments For Bowen’s Disease
There are a number of treatment options for Bowen’s disease. Talk to your dermatologist about which treatment is most suitable for you.
The main treatments are:
- cryotherapy liquid nitrogen is sprayed on to the affected skin to freeze it. The procedure may be painful and the skin may remain a bit uncomfortable for a few days. The affected skin will scab over and fall off within a few weeks.
- imiquimod cream or chemotherapy cream this is applied to the affected skin regularly for a few weeks. It may cause your skin to become red and inflamed before it gets better.
- curettage and cautery the affected area of skin is scraped away under local anaesthetic, where the skin is numbed, and heat or electricity is used to stop any bleeding, leaving the area to scab over and heal after a few weeks.
- a light-sensitive cream is applied to the affected skin and a laser is directed on to the skin a few hours later to destroy the abnormal cells. The treatment session lasts about 20 to 45 minutes. You may need more than 1 session.
- surgery the abnormal skin is cut out under local anaesthetic and stitches may be needed afterwards.
In a few cases, your dermatologist may just advise monitoring your skin closely for example, if it’s very slow growing and they feel the side effects of treatment will outweigh the benefits.
What Does Bowens Disease Look Like
Bowens disease is also referred to as squamous cell carcinoma in situ, and can present similar-looking lesions. Patients with the Bowens disease skin disorder often report a reddish scaly patch that continues to grow over an area of skin, resulting in dry, slightly raised sores. It is sometimes mistaken for psoriasis or eczema due to visual similarities. In most cases, the lesions will appear without any other symptoms, but they can result in:
- Itchy skin
- Sores that bleed, pus, or crust over
- Tender areas
Reddish-brown scaly patches are the most common form of what Bowens disease looks like, but it can also present with more darkly pigmented lesions that can develop warts or split open. Most patients only see one patch at a time, but it is possible for Bowens disease to develop across the body.
Similarly to squamous cell carcinoma, Bowens disease is most likely to form on areas of the body that see more sun. Chronic sun exposure is likely a contributor to this disorder but the exact cause is unknown. Patients most frequently see lesions develop on their:
- Head
- Lower legs
Don’t Miss: Prognosis For Skin Cancer
What Is Bowens Disease
Posted on August 5, 2014 in Skin Cancer, Mohs Micrographic Surgery, How to Protect Yourself From the Sun, Skin Tumor, Skin Lesions, Surgery
Bowens Disease, or Squamous Cell Carcinoma in situ, is a skin cancer found in the outermost layer of the skin. It is generally considered a precursor to invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma, and should not be ignored. Bowens disease is not considered an indolent tumor and requires treatment to ensure it does not spread, invade local structures or spread beyond the skin.
What does Bowens Disease look like?
Bowens Disease typically appears as an expanding pink to red patch of skin, that grows slowly over time. Like many skin cancers, Bowens Disease can have irregular borders, scaling and/or crusting. Bowens Disease can develop anywhere on the skin, but is common on chronically sun exposed areas including the lower leg area. Bowens Disease often appears irritated and is often confused with a patch of eczema or ringworm all of these can be red, scaly, or crusted. The difference is Bowens Disease doesnt go away when you treat it with a cortisone or antifungal cream. The cancer will persist, despite these treatments.
Treatment
Irregular patches, marks, or moles on the skin can be signs of skin cancer, and it is always important to act if you notice a change or something new. The American Academy of Dermatology recommends yearly skin checks for all individuals to help detect skin cancers early, before complications arise.
Contact Us
Infiltrative Basal Cell Carcinoma
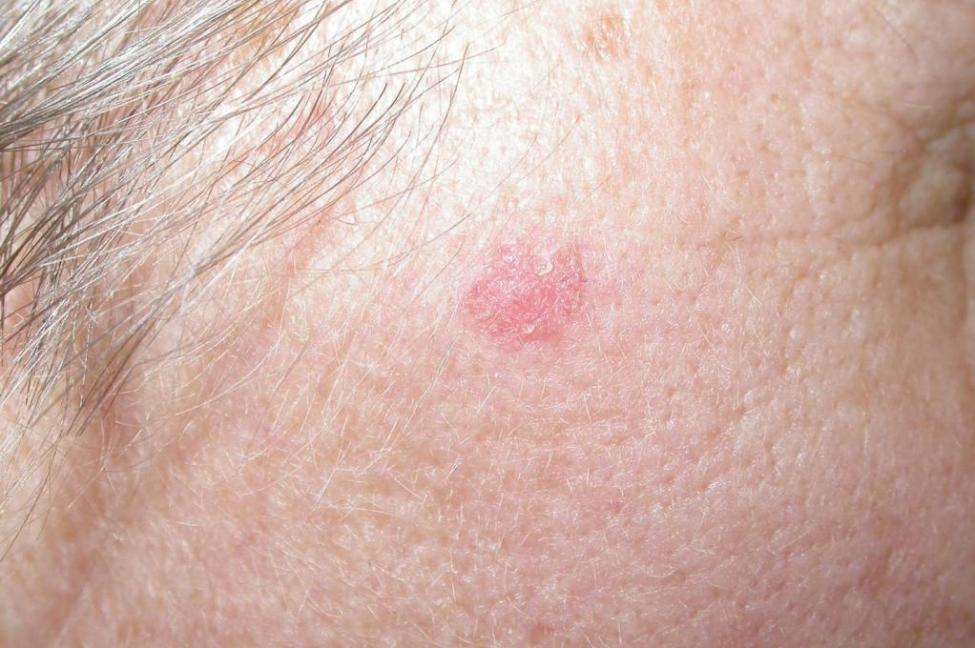
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
DermNet NZ
Infiltrative basal cell carcinoma occurs when a tumor makes its way into the dermis via thin strands between collagen fibers. This aggressive type of skin cancer is harder to diagnose and treat because of its location. Typically, infiltrative basal cell carcinoma appears as scar tissue or thickening of the skin and requires a biopsy to properly diagnose.
To remove this type of basal cell carcinoma, a specific form of surgery, called Mohs, is used. During a Mohs surgery, also called Mohs micrographic surgery, thin layers of skin are removed until there is no cancer tissue left.
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
DermNet NZ
Superficial basal cell carcinoma, also known as in situ basal-cell carcinoma, tends to occur on the shoulders or the upper part of the torso, but it can also be found on the legs and arms. This type of cancer isnt generally invasive because it has a slow rate of growth and is fairly easy to spot and diagnose. It appears reddish or pinkish in color and may crust over or ooze. Superficial basal cell carcinoma accounts for roughly 15%-26% of all basal cell carcinoma cases.
You May Like: What Is Clear Cell Carcinoma
Treatment Options For Bowens Disease
Efficacy comparison and evaluation of different treatment options and treatment studies of Bowens disease are difficult because there is a variety of different protocols and the success of a treatment modality is dependent on several factors .
The choice of treatment should be guided by efficacy, location and size of BD, number of lesions, availability of the therapy, the clinicians expertise, patient factors , cosmetic outcome and the patients preference.
The different treatment options for BD are cryotherapy, curettage with cautery, excision, 5-fluorouracil , radiotherapy, laser, photodynamic therapy , imiquimod and some other therapies that were described in some case reports or small numbers of patients. Up to now none of the treatment options has been unequivocally proven to be superior to any other.
This paper is focused on the newer treatment options for BD: topical diclofenac and imiquimod and photodynamic therapy.
What Is The Outlook
With most treatments for Bowen’s disease, there is probably about a 1 in 10 chance that Bowen’s disease will come back after treatment. Therefore, regular follow-up is needed to look for any signs of recurrence. Further treatment may be needed if this happens.
The outlook for most people with Bowen’s disease is very good. The vast majority of people who have Bowen’s disease that is recognised and treated will not develop a skin cancer.
Also Check: 3b Melanoma
Who Gets Intraepidermal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Risk factors for intraepidermal SCC include:
- Sun exposure: intraepidermal SCC is most often found in sun-damaged individuals.
- Arsenicingestion: intraepidermal SCC is common in populations exposed to arsenic.
- Ionising radiation: intraepidermal SCC was common on unprotected hands of radiologists early in the 20th century.
- Human papillomavirus infection: this is implicated in intraepidermal SCC on fingers and fingernails.
- Immune suppression due to disease or medicines .
Up to 50% of patients with intraepidermal SCC have other keratinocytic skin cancers, mainly basal cell carcinoma.
When A Sore Doesnt Heal
People of all ages experience pimples or sores on their bodies from time to time. Usually these sores clear up in a few days or a week. A sore that doesnt heal or go away is a potentially bigger problem.
Skin cancer prevents your skin from healing. A patch of skin that doesnt heal in regular time may be a sign of squamous cell carcinoma. These spots typically bleed easily if bumped or rubbed.
Also Check: Melanoma Bone Cancer Life Expectancy
Skin: Condition: Infomation Radiotherapy And Laser
Radiotherapy and laserare other therapies occasionally used for the treatment of Bowens disease, although radiotherapy is not used for patches on the lower leg.
A particular problem with Bowens disease is that it is frequently found on the lower leg where the skin is often tight and sometimes quite fragile, especially in older patients. Healing there is slow. Many factors, therefore, play a part in selecting the right treatment:
- The size and thickness of the patch
- The number of patches
- The presence of swelling of the legs
- The general state of the skin on the legs
- The patients preference
If the affected area is judged to be thin and not likely to cause problems, your dermatologist may simply suggest that it is kept under observation in a clinic, or in some cases by yourself or by your GP.
Signs Of Bowens Disease
The signs of Bowens disease include:
- Flat, scaly, red and slightly raised patches appear and persist for months to years.
- A single patch or a number of patches may be present.
- The edges of each patch are irregular, but distinct from the surrounding skin.
- Each patch grows very slowly.
- Bowens is asymptomatic and therefore is easily overlooked.
- Bowens can affect any part of the body, but commonly occurs on the lower leg.
- Only rarely are the patches sore or irritated.
You May Like: What Is The Prognosis For Skin Cancer
When To Get Medical Advice
See a GP if you have a persistent red, scaly patch of skin and do not know the cause.
It’s important to get a proper diagnosis, as Bowen’s disease can look like other conditions, such as psoriasis or eczema.
If necessary, your GP will refer you to a skin specialist to determine what the problem is.
If your GP is not sure about the cause, they may need to remove a small sample of skin so it can be looked at more closely .
Complementary And Alternative Medicine And Lifestyle Changes
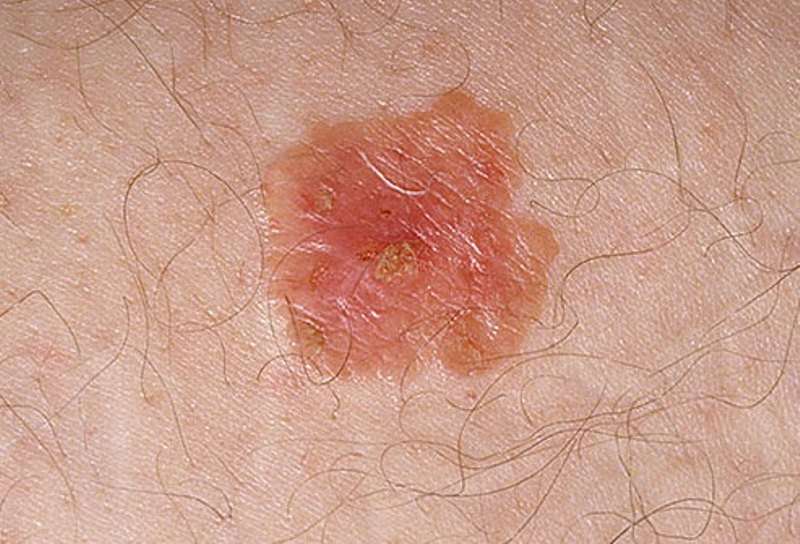
There are no home remedies that have been proven effective in the treatment of Bowen’s disease. There also are no complementary or alternative therapies that have been proven to be effective.
There are a few steps people can take to prevent more patches of Bowen’s disease from appearing.
These include:
- Protecting the skin with clothing
- Wearing a hat that covers the scalp, face, neck, and ears
- Staying in the shade when the sun is at its strongest between 10 a.m. and 3 p.m.
- Using a sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or more
- Applying sunscreen at least 15 minutes before going in the sun
- Reapplying sunscreen regularly, especially when swimming
Also Check: Well Differentiated Carcinoma
What Does Skin Cancer Look Like
Skin cancer can happen to anyone, at any age, on any part of the body. And because skin cancers appear in many shapes and sizes, they can be challenging to identify. Getting to know your own skin and understanding what to look for can help you detect cancer early when its easiest to cure.
Thats why you should examine your skin once a month. If you see something NEW, CHANGING OR UNUSUAL even if it looks nothing like what you see in photos do not wait! Get it checked by a dermatologist right away. Finding and treating skin cancer early can save your life.
Skin Cancer Image Gallery
Below is a selection of photos that give you a general idea about what skin cancers can look like. Remember that skin cancers can look quite different from one person to another due to skin tone, size and type of skin cancer and location on the body. Skin cancer can be tricky in other ways, too. For example, melanoma is a type of skin cancer that is often pigmented tan, brown, black, even blue. But amelanotic melanoma lacks pigment and appears as a skin-tone or pink lesion.
To sum it up, while photos can be helpful, getting your skin examined by a dermatologist is the most vital step in identifying and treating skin cancer.
What Does Scc In Situ Look Like
You may discover SCC on one or more of your dogs light-skinned areas.
The appearance of SCC can be red, irritated, ulcerated or crusted over. When the abnormality is just a small red area, the cancer does not grow very fast and it has not invaded the skin.
If a lump or ulcer has developed on that patch, your pets cancer may have progressed to invasaive squamous cell cancer.
Your pet could have one of many other skin conditions. Actinic keratosis presents as a rough, scaly patch. These can turn into squamous cell skin cancer. Basset Hounds commonly get cutaneous squamous cell carinomas .
Your pet could have basal cell carcinoma. Basal cells and basal cell tumors act pretty much the same as SCC. You could also mistake mast cell tumors for other lesions.
Your dogs mucous membranes should be pink. If the cheeks and gums are blue or purple, check your dogs footpad color. Make a veterinary appointment if the footpads have also turned a bluish color.
Your pet may simply have follicular cysts.
A cutaneous horn, on the other hand, would actually appear like a horn. Youll need to take your pet to your veterinarian whenever you find skin problems on your pet.
Recommended Reading: Skin Cancer Spread To Lymph Nodes
What Are The Symptoms Of Bowen’s Disease
Bowens disease usually looks like a patch of red, scaly skin that grows slowly over time. Sometimes the patch may be raised and look sore, or it can look like a wart or a dark brown patch in the genital area. The patch is often itchy.
There arent usually any other symptoms. Bowens disease is often mistaken for psoriasis, eczema or a fungal infection.
Creams Applied To The Skin
Certain creams may be used in the treatment of Bowen’s disease. These can help to kill and get rid of the abnormal cells in some cases. Such creams include 5-fluorouracil . 5-FU cream may need to be applied once or twice a day for around three to four weeks and sometimes for longer. The cream is easy to apply yourself. The problem is that it can be quite an irritant to the skin. Your skin may become red and may actually look worse when you are using the treatment
Treatment may need to be repeated at a later date if the patch of Bowen’s disease comes back. 5-FU treatment may be particularly useful in large patches of Bowen’s disease or in areas where skin healing may be poor, such as your shin . It may also sometimes be used in people who have a number of different patches of Bowen’s disease.
Other treatments may be given before treatment with 5-FU cream. This is so that the cream may be absorbed more easily by your skin. These include a process called iontophoresis where an electrical current drives the cream into your tissues, or laser treatment of your skin.
Imiquimod cream is also sometimes used to treat Bowen’s disease.
Also Check: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
DermNet NZ
Squamous cell carcinoma in situ, also known as Bowens disease, is a precancerous condition that appears as a red or brownish patch or plaque on the skin that grows slowly over time. The patches are often found on the legs and lower parts of the body, as well as the head and neck. In rare cases, it has been found on the hands and feet, in the genital area, and in the area around the anus.
Bowens disease is uncommon: only 15 out of every 100,000 people will develop this condition every year. The condition typically affects the Caucasian population, but women are more likely to develop Bowens disease than men. The majority of cases are in adults over 60. As with other skin cancers, Bowens disease can develop after long-term exposure to the sun. It can also develop following radiotherapy treatment. Other causes include immune suppression, skin injury, inflammatory skin conditions, and a human papillomavirus infection.
Bowens disease is generally treatable and doesnt develop into squamous cell carcinoma. Up to 16% of cases develop into cancer.
Causes Of Bowen’s Disease
Bowen’s disease usually affects older people in their 60s and 70s.
The exact cause is unclear, but it’s been closely linked with:
- long-term exposure to the sun or use of sunbeds especially in people with fair skin
- having a weak immune system for example, it’s more common in people taking medicine to suppress their immune system after an organ transplant, or those with AIDS
- previously having radiotherapy treatment
- the human papillomavirus a common virus that often affects the genital area and can cause genital warts
Bowen’s disease does not run in families and it’s not infectious.
You May Like: Cell Cancer Symptoms
When Should I See My Doctor
If you notice a new or changing mole, freckle or spot, you should see your doctor. They will examine you and, if necessary, they will refer you to a dermatologist .
See your doctor if the patch starts to bleed, looks different or develops a lump, or if you discover any new patches on your skin.